Chapter 11 BIOCHEM
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
monosaccharides
simplest saccharides composed of three carbons
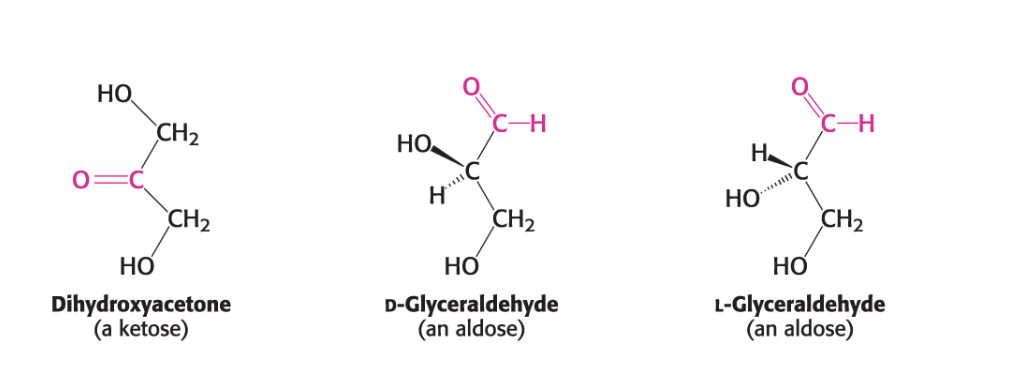
What is the name?
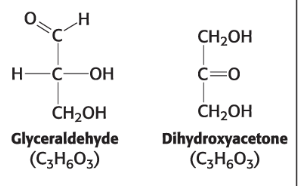
Dihydroxyacetone (a ketose)
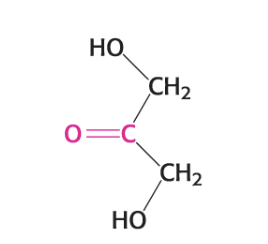
What is the name?
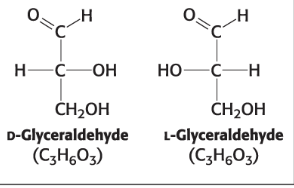
D-Glyceraldehyde (an aldose) (C3H6O3)
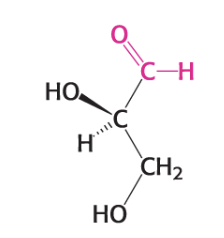
What is the name?
L-Glyceraldehyde (an aldose) (C3H6O3)
isomers
have the same molecular formula but different compounds
constitutional isomers
differ in the order of attachment of atoms
enantiomers
superimposable mirror images
stereoisomers
atoms are connected in the same order but differ in spatial arrangement
disasteroisomers
isomers that are not mirror images
epimers
differ at one of several symmetric carbon atoms
anomers
isomers that differ at a new asymmetric carbon atoms formed on ring closure
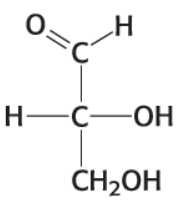
What is this compound?
glyceraldehyde (C3H6O3)
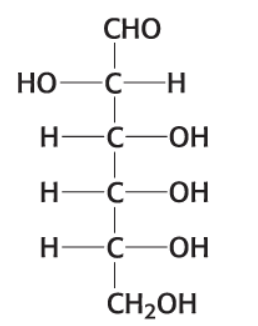
What is this compound?
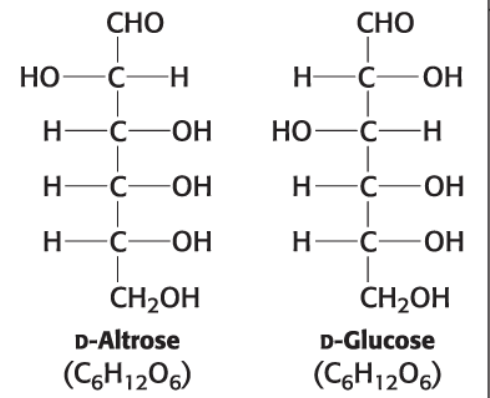
D-Altrose (C6H12O6)
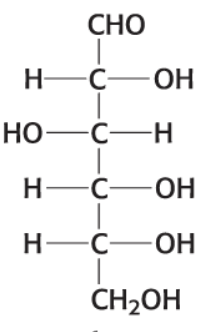
What is this compound?
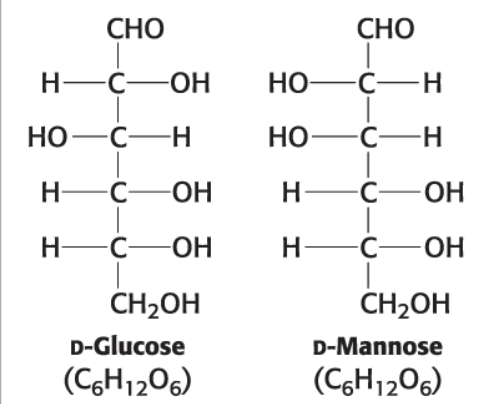
D-Glucose (C6H12O6)
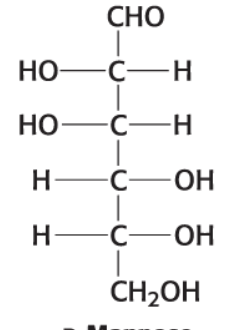
What is this compound?
D-Mannose (C6H12O6)
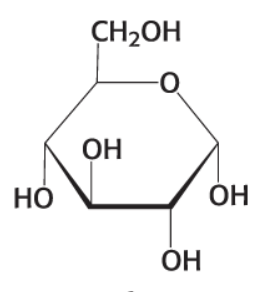
What is this compound?
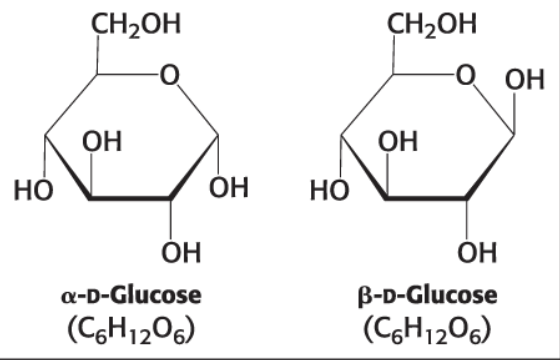
a-D-Glucose (C6H12O6)
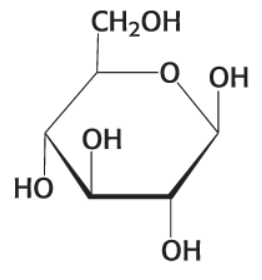
What is this compound?
B-D Glucose (C6H12O6)
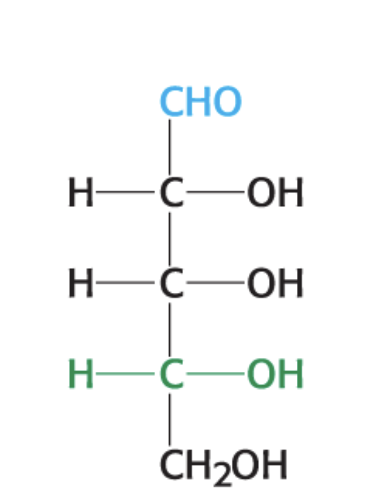
What is this compound?
D-Ribose
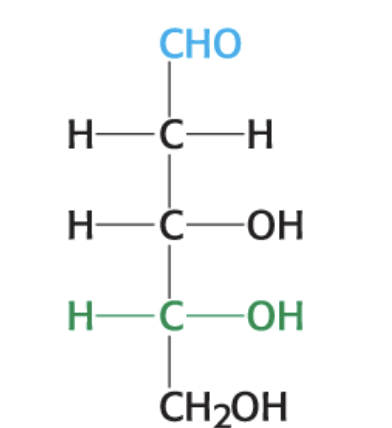
What is this compound?
D-Deoxyribose
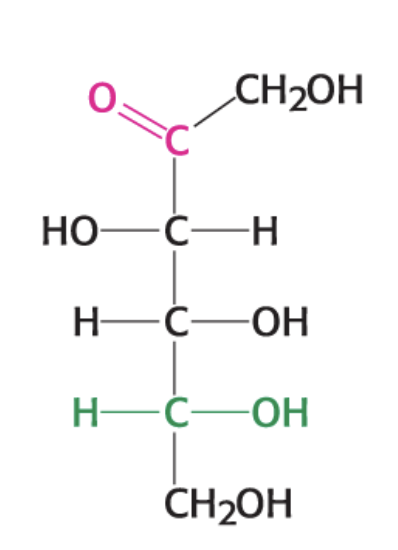
What is this compound?
D-Fructose
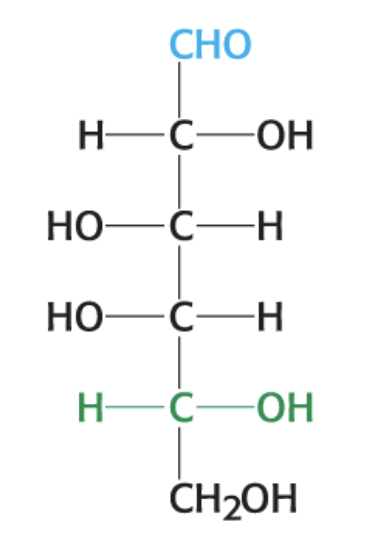
What is this compound?
D-Galactose
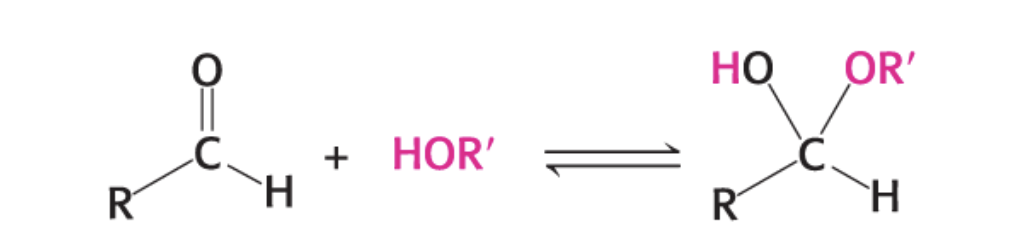
What is happening in this diagram?
aldehyde & alcohol forms hemiacetal
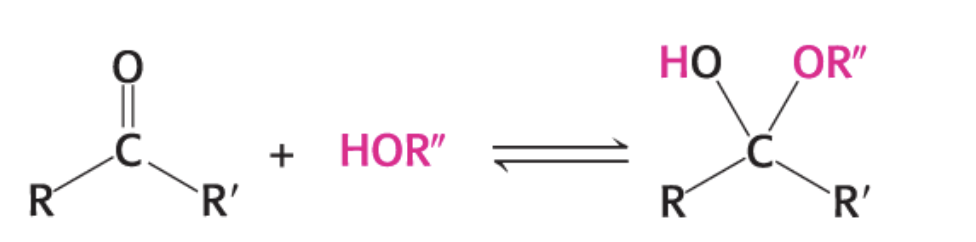
What is happening in this diagram?
ketone & alcohol forms hemiketal
the chemical basis for ring formation is the reaction of ______ or _____
aldehyde & alcohol form hemiacetal or ketone & alcohol form hemiketal
what is glucose’s resulting intramolecular hemiacetal consist of?
six carbon ring pyranose
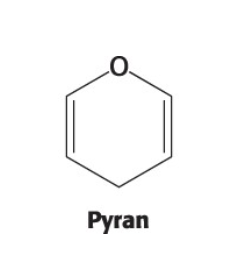
whats is ketose’s fructose intramolecular hemiketal named?
furanose b/c it looks like furan
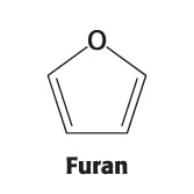
how is pyranose formed ?
with the D-Glucose (open chain form)
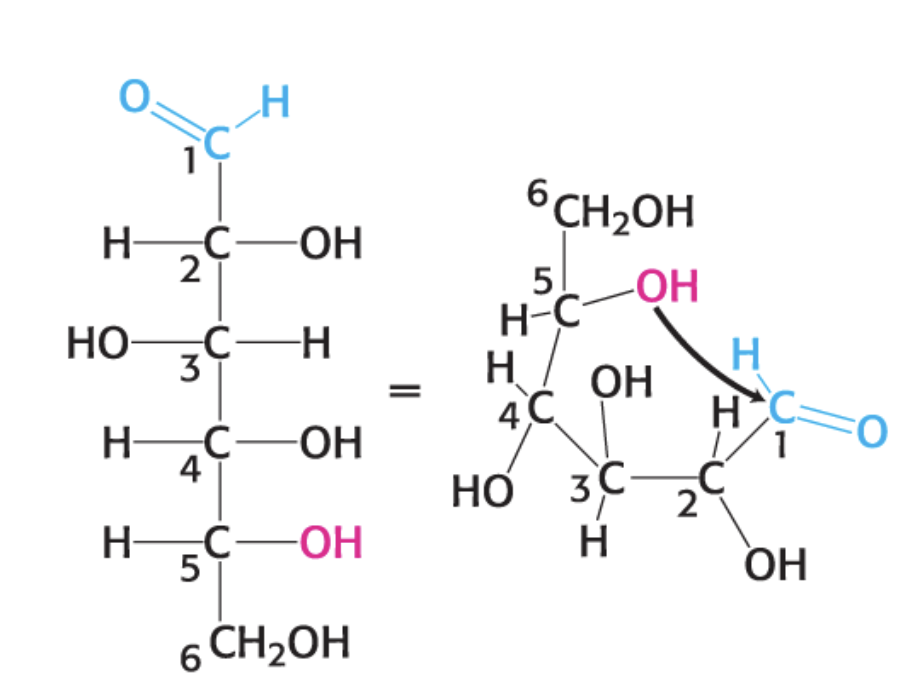
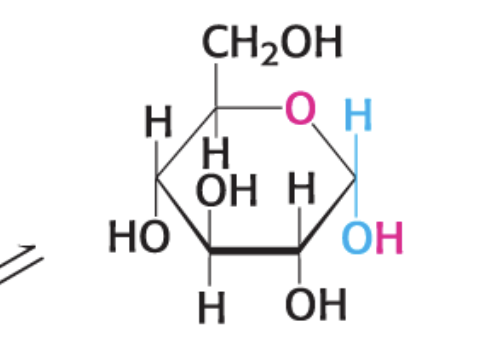
what is this compound?
a-D Glucopyranose
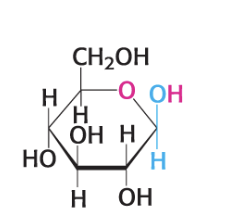
what is this compound?
B-D glucopyranose
how is furanose made?
D-Fructose
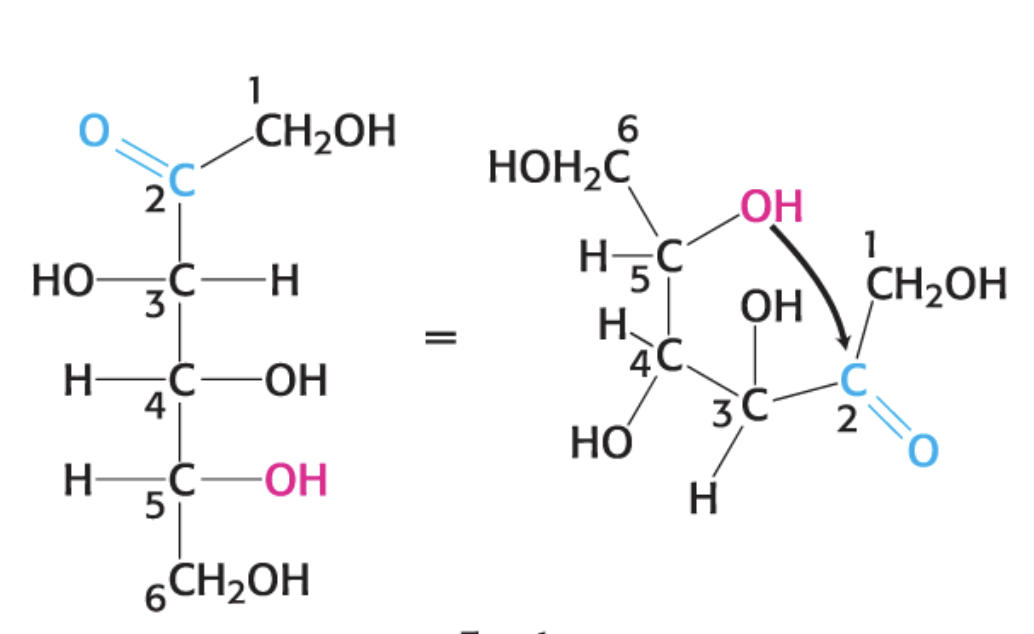
what is this compund?
a-D-Fructofuranose
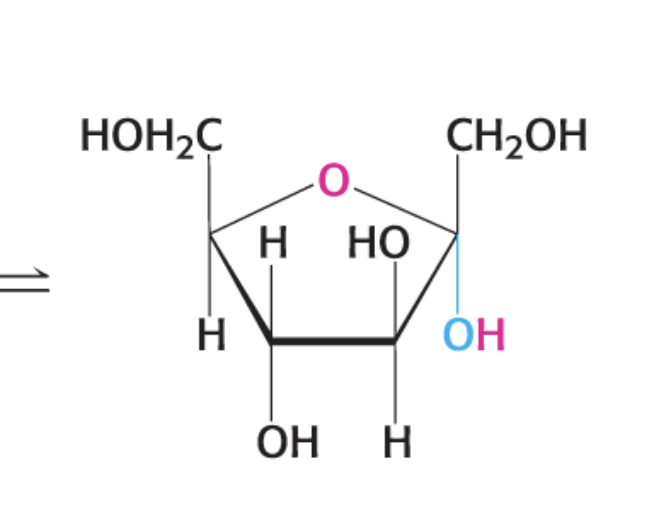
α-form
hydroxyl at C-1 is below the plane of the ring
β-form
hydroxyk at C-1 is above the plane of the ring
furanose form of fructose
α and β form refers to orientation of the hydroxyl at C-2
pyranose form
fructose forms this and a furanose form seen in fructose derivatives
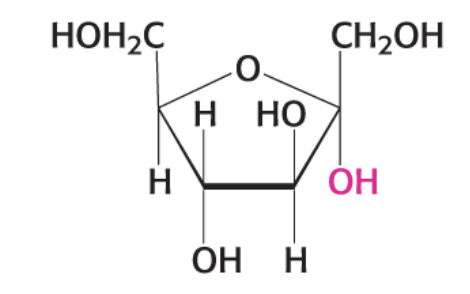
what compound is this?
α- D Fructofuranose
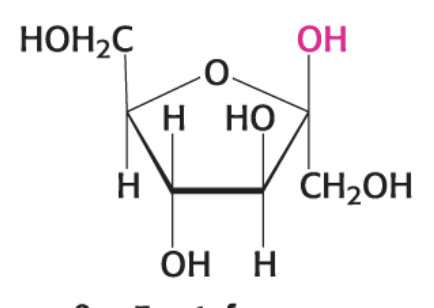
what compound is this?
β-D Fructofuranose
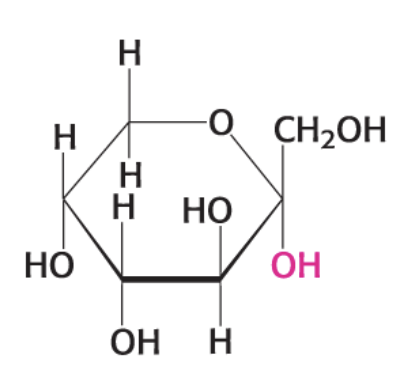
what compound is this?
α- D Fructopyranose
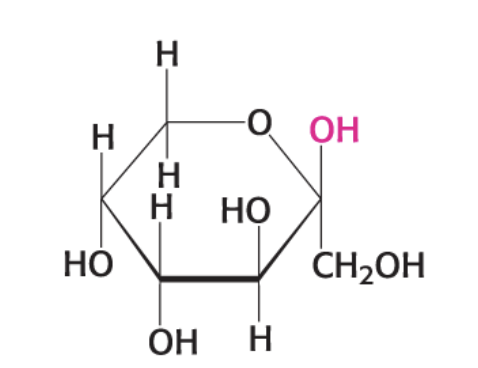
what compound is this?
β-D Fructopyranose
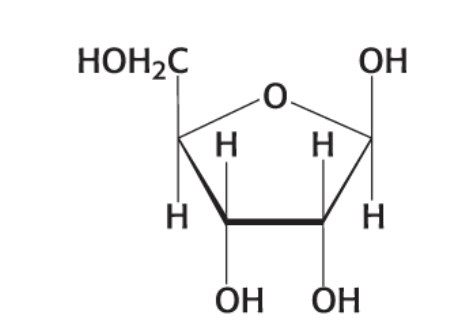
What compound is this?
β-D-Ribose
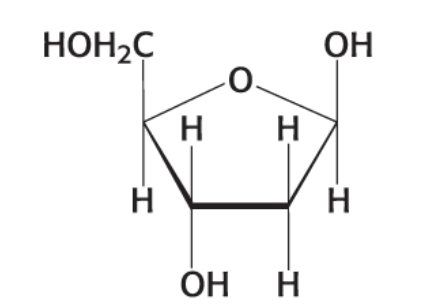
What compound is this?
β-2-Deoxy-D-ribose
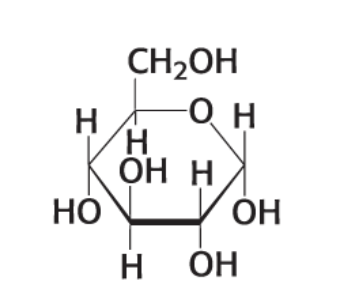
what compound is this?
α-D Glucose
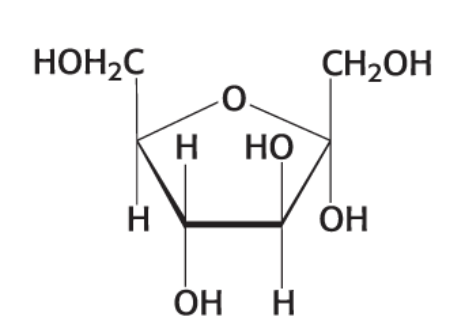
what compound is this?
α-D Fructose
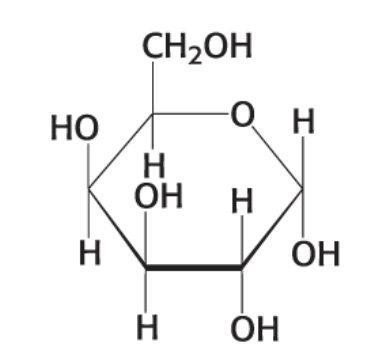
what compound is this?
α-D Galactose
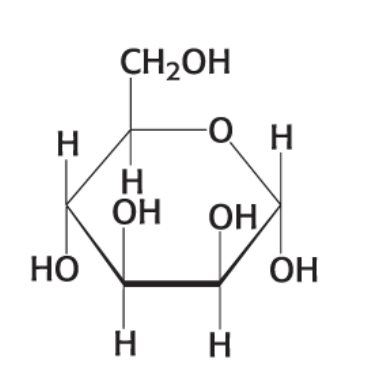
what compound is this?
α-D Mannose
what are the two different types of conformation of pyranose rings?
boat & chair
in pyranose chair form the carbon substituent rings have 2 orientations
axial & equatorial
β-D-Glucopyranose
chair conformation b/c axial positions have H reducing steric hindrance
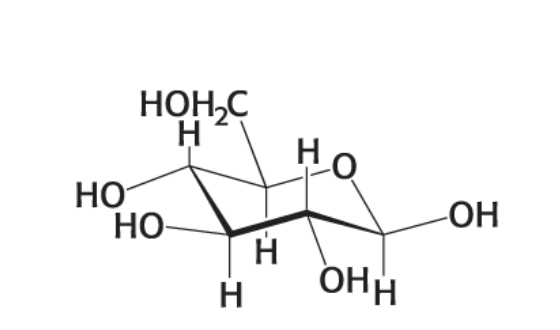
What form and what name is this compound?
chair form of B-D-Glucose
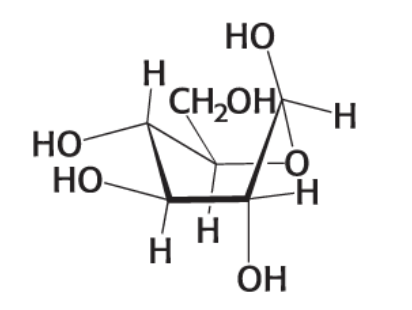
what form and name of this compound?
boat form of B-D-Glucose
furanose rings
like pyranose not planar and usually on the envelope form
ribose component of biomolecules which conformations are observed the most?
C-2 is out of the plane on the same side as C-5 (C-2 endo) or C-3 is out of the plane on the same side as C-5 (C-3-endo)
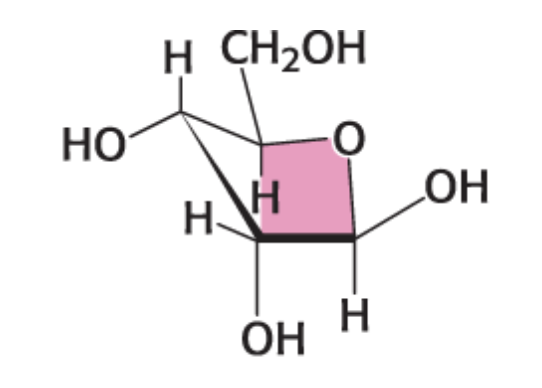
what envelope conformation and compound is this?
C-3-endo β-D-Ribose
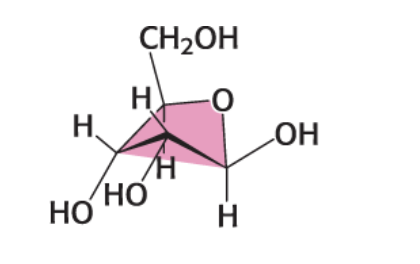
what envelope conformation and compound is this?
C-2-endo B-D-Ribose
a solution of glucose contains
1/3 a anomer 2/3 B anomer 1% open chain
two anomeric forms of glucse are in ….
equilibrium and the free open-chain form reacts with oxidizing agents
suagrs that react with oxidizing agents are called
reducing sugars
sugars that react without oxidizing agents are called
nonreducing sugars
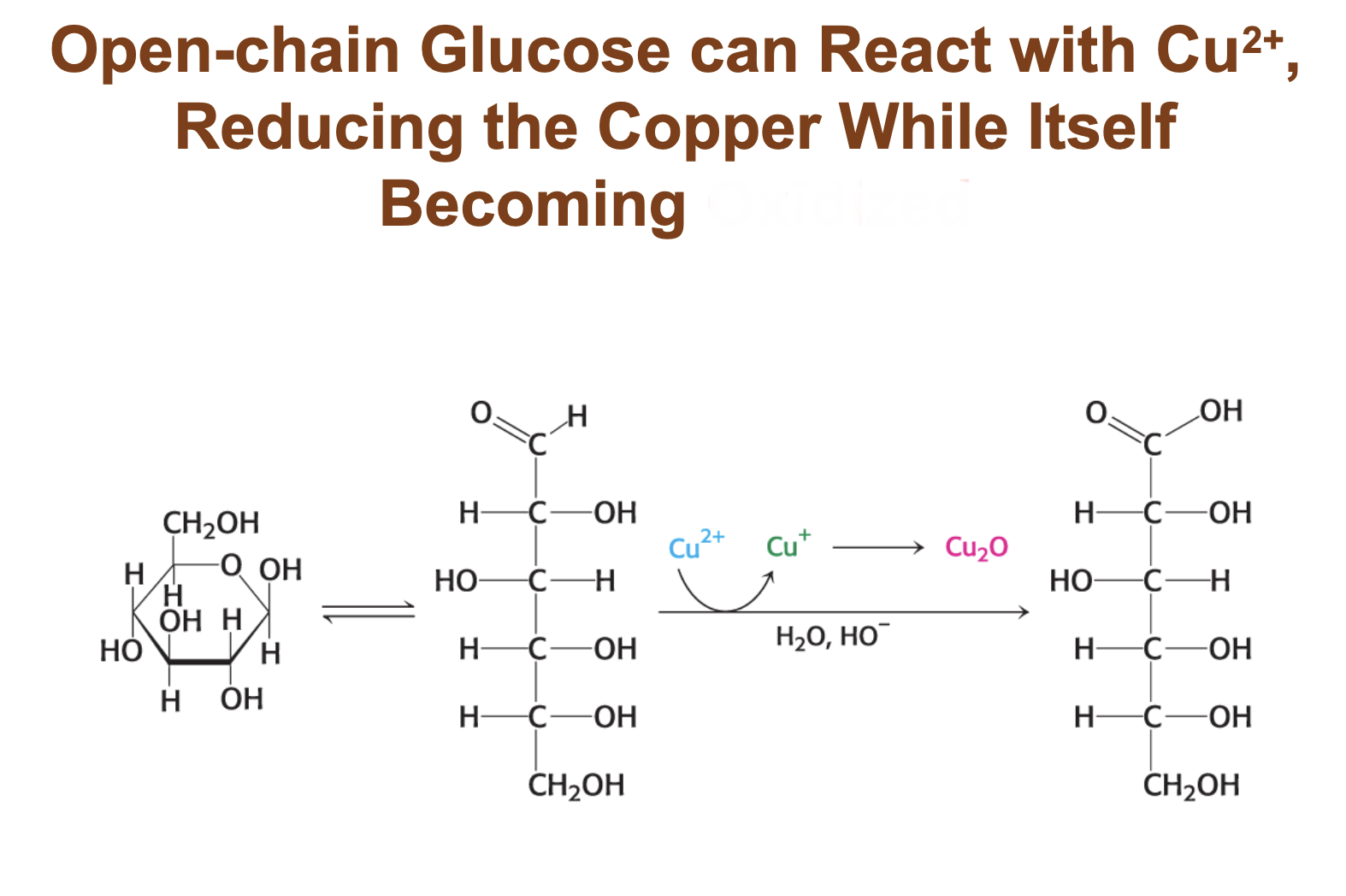
Open-chain glucose can react with Cu+ reducing the copper while itself becoming
oxidized
glucose is a reducing sugar, therefore can react with amino acids like
Lys or Arg residues in proteins
what is an example of glucose reacting with an amino acid?
glucose and hemoglobin forming glycosylated hemoglobin A1c
what allows one to monitor the long term-control of blood glucose levels in diabetics?
the amount of hemoglobin A1c in the blood
Reactions between ___ & ____ often impair protein function
carbohydrates & proteins
advanced glycation end products (AGES) have…
been implicated in a number of pathological conditions
monosaccharides are joined to _____ & ___ through _____ bonds
alcohols & amines glycosidic
what is formed from an O-glycosidic bond
anomeric carbon atom & oxygen atom
what is formed through an N-glycosidic bond?
anomeric carbon & amine
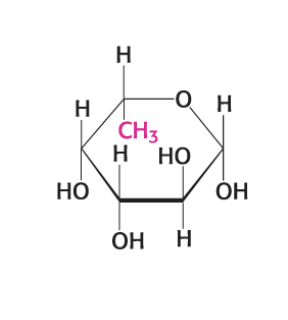
what compound is this?
B-L frucose
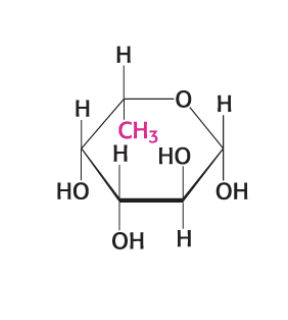
what compound is this?
GalNAc
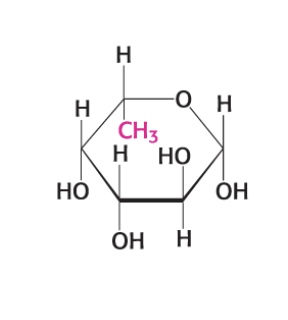
what compound is this?
GlcNAc
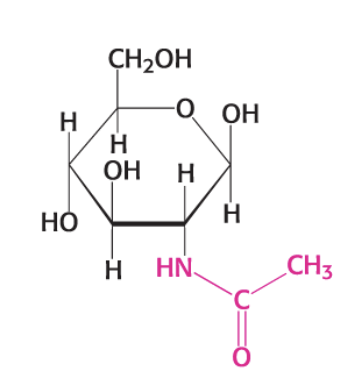
what compound is this?
Sialic acid (Sia)
phosphorylation
modification of carbohydrates
makes the sugars anionic and prevents from leaving the cell
facilitates the metaolism of sugars
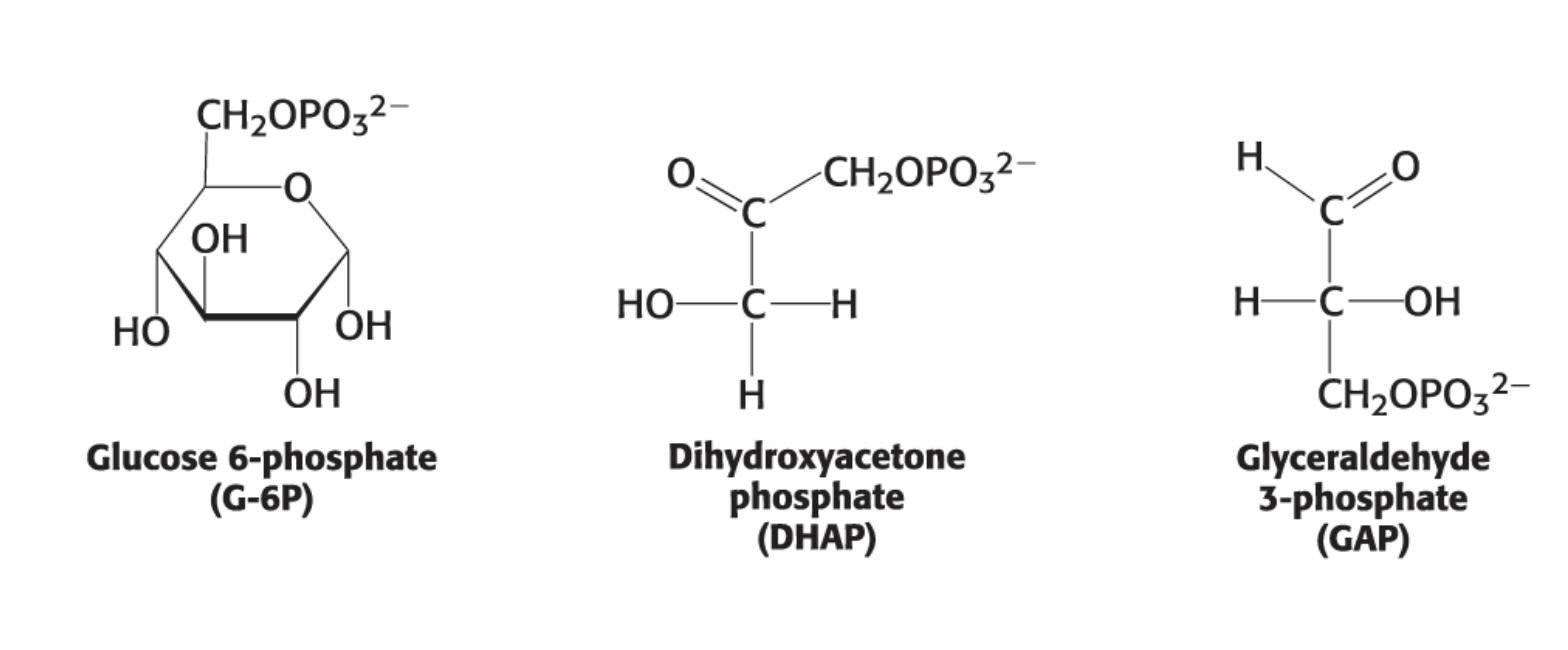
oligosaccharides
two or more monosaccharides are linked by O-glycosidic bonds
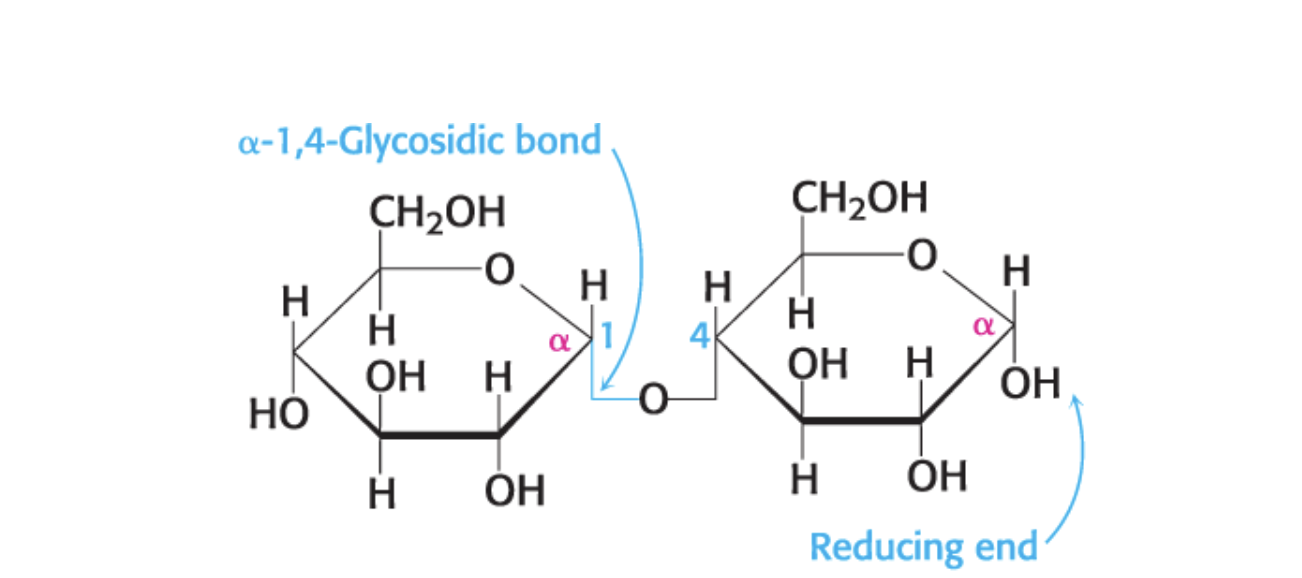
what is sucrose cleaved by?
invertase
where is sucorse obtained from?
sugar cane
what is the linkage for glucose and fructose?
a for glucose b for fructose
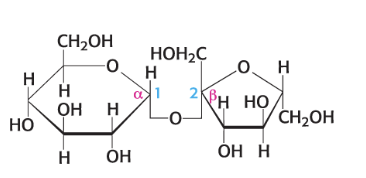
lactose
consists of galactose linked to a glucose by a β-1,4 linkage
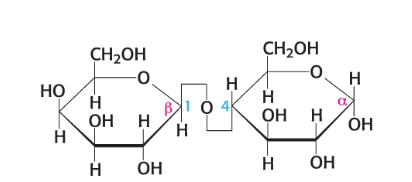
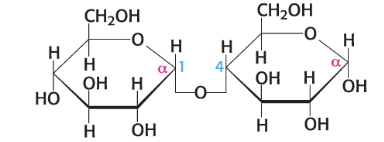
maltose
degradation of large oligosaccharides made up of 2 glucose molecules linked by a 1,4 linkage
hydrolyzed by maltase
what is this compound name?
sucrose
what is this compound name?
lactose
what is this compound name?
Maltose
polysaccharide glycogen
glucose storage in animals
glucose units in glycogen are linked by
a-1,4-glycosidic bonds w/ branches formed by α-1.6 glycosidic bonds for every 12 glucose units
in plants glucose is stored as
starch: amylose and amylopectin
amylose
linear polymer of glucose units linked by a 1,4 glycosidic bonds
cellulose
homopolymer of glucose units by a B-1,4-glycosidic bond
The β linkage yields a straight chain capable of interacting with other cellulose molecules via
H-bonds to form strong fibrils
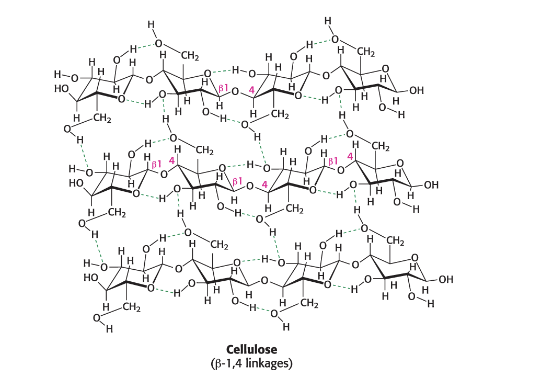
the a linkages of starch and glycogen form
compact hollow cylinders suitable for accessible storage
insoluble and soluble fiber are an ___ ___ ____
important part of the diet
mammals cannot digest _____ and ____ the rate at which digestion products pass through the large ____
cellulose & increasing, intestine
soluble fibers such as _______ ____ also aid in digestion
polygalacturonic acid (pectin)
human milk oligosaccharides protect ___ ____ ___
newborns from infection
more than 150 different _____ have been identified in human milk
oligosaccharides
these carbohydrates are ___ ____ by the infant but they ___
not digested; play an important protective role against bacterial infection
milk oligosaccharides
prevent streptococcus bacteria from VJJ cause pneumonia blood poisoning or meningitis
carbohydrates can be linked to form
glycoproteins
glycoproteins
mainly protein by weight
proteoglycans
attached to a polysaccharide called a glycosaminoglycan; mainly carbohydrate by weight
mucins or mucoproteins
attached to the carbohydrate by N-acetylgalactosamine; act as lubricants
carbohydrates can be linked to proteins through _______ or ___ or ____
asparagine (N-linked) or serine or threonine (o-linked)