IV : Gram Positive Cocci
1/410
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
411 Terms
Sheep blood agar.
When processing throat swabs for a group A Streptococcus culture, the medium of choice is:
Rejected as unacceptable.
A 21 year old patient presents with pharyngitis. A throat swab is collected and submitted for anaerobic culture. This specimen should be:
LIM broth
A vaginal/rectal swab is collected from a pregnant patient to screen for group B Streptococcus colonization. What is the best medium to use for specimen inoculation?
incubated at 56c.
To quality control the autoclave, a vial of Bacillus stearothermophilus is autoclaved and should then be:
Bacterial suspension was not diluted to the proper concentration.
In a quality control procedure on a new batch of Mueller-Hinton plates using a stock culture of staphylococcus aureus, all the disk zone sizes are too small. The most likely reason for this is that the:
Novobiocin susceptibility
A urine Gram stain shows gram-positive cocci in clusters. Th organism tested catalase positive. To speciate this organism from the culture, the technician should perform a coagulase test and a/an:
Abiotrophia defectiva
The Gram stain from a blood culture shows gam-positive cocci in chains. No growth occurs on blood agar plates incubated both aerobically and anaerobically. Additional testing should be done to detect the presence of:
Bile solubility
Viridans streptococci can be differentiated from Streptococcus pneumoniae by:
Coagulase
A reliable test for distinguishing Staphylococcus aureus from other staphylococci is:
Streptococcus pneumoniae
The optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride) disk is used for the identification of:
Group D Streptococcus
A gamma-hemolytic Streptococcus that blackens bile esculin agar but does not grow in 6.5% NaCl broth is most likely:
Catalse production and coagulase test.
Gram stain examiination from a blood culture bottle shows dark blue, spherical organisms in clusters. Growth on sheep blood agar shows small, round, pale yellow colonies. Further tests should include:
Bile esculin, PYR, acitracin, and hippurate.
Gram-positive cocci in chains are seen on a Gram stain from a blood culture. The organisms grows as a beta-hemolytic colony. Further tests that could be performed include:
in the genera Granulicatella and Abiotrophia
"Nutritionally deficient" streptococci are:
Group B streptococci
The organism most commonly associated with neonatal purulent meningitis is:
Streptococcus pyogenes
An important cause of acute exudative pharyngitis is:
Acute glomerulonephritis
Children who have infections with beta-hemolytic streptococci can develop:
Group A
A beta-hemolytic streptococci that is bacitracin-sensitive and CAMP-negative is:
Group B
A beta-hemolytic Streptococcus that is bacitracin-resistant CAMP positive is:
Latex antigen typing.
Group B, beta-hemolytic streptococci may be distinguished from other hemolytic streptococci by which of the following procedures?
Enterococci often show more antibiotic resistance than group D streptococci.
It is important to differentiate between Enterococcus and group D streptococci because:
Bile solubility
Streptococcus pneumoniae can be differentiated best from the viridans group of streptococci by:
Relatively resistant to penicillin.
Characteristically, enterococci are:
Hydrolysis os sodium hippurate
Which of the following would best differentiate Streptococcus agalactiae from Streptococcus pyogenes?
the most critical distinction between Staphylococcus aureus and other Staphylococcus is:
Coagulase production.
Streptococcus pyogenes.
Which of the following organisms is, to date, considered universally susceptible to penicillin?
Latex antigen typing.
A beta-hemolytic gram-positive coccus was isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid of a 2 day old infant with signs of meningitis. The isolate grew on sheep blood agar under aerobic conditions and was resistant to a bacitracin disc. Which of the following should be performed for the identification of the organism?
2-6 hours.
How many hours after eating contaminated food do initial symptoms of staphylococcal food poisoning typically occur?
There has been a break in proper skin preparation before drawing blood for culture
During the past month, Staphylococcus epidermidis has been isolated from blood cultures at 2-3 times the rate from the previous year. The most logical explanation for the increase in these isolates is that:
Furazolidone (100 ug/disk) susceptibility.
A yellow colony from a wound culture tested catalase-positive and coagulase-negative. The organism stained as gram-positive cocci in clusters. Which of the following tests would differentiate between a coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and Micrococcus?
CAMP test and S agalactiae
An isolate of unknown beta-hemolytic Streptococcus is streaked perpendicular to a streak of beta-lysin producing Staphylococcus aureus. After incubation a zone of arrowhead hemolysis is noted at the interface of the 2 streaks. What is the name of the test and the presumptive identification of the unknown Streptococcus?
Enterococcus faecalis
Which of the following may be used as a positive quality control organism for the bile esculin test?
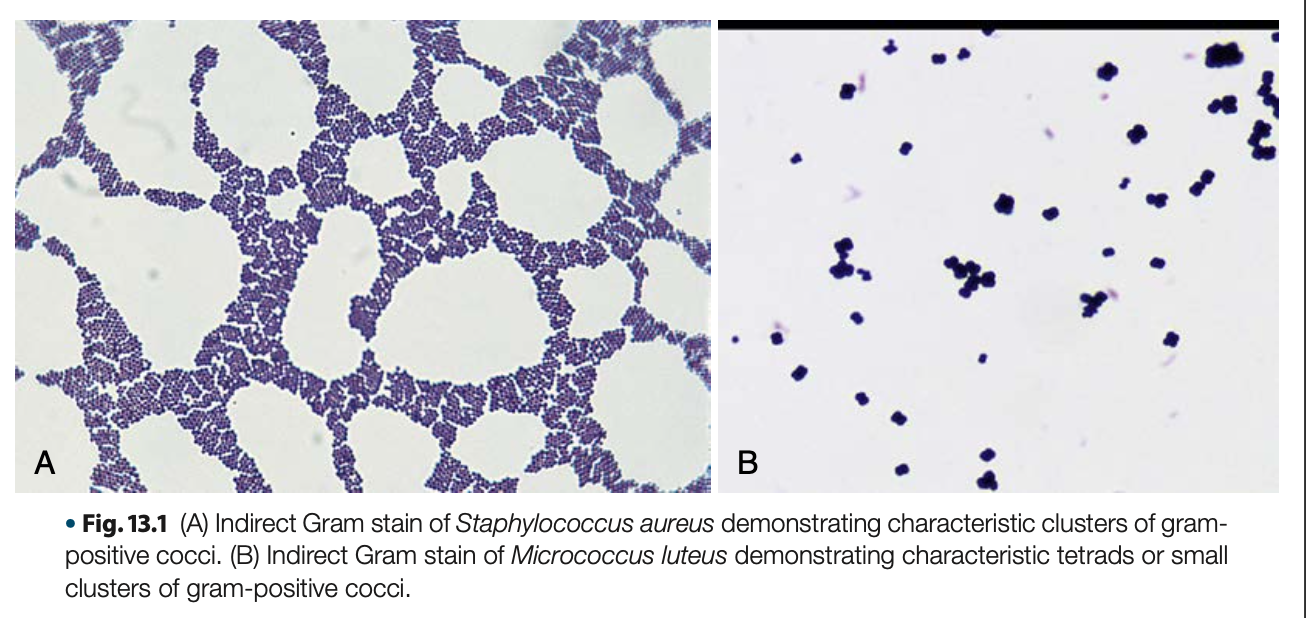
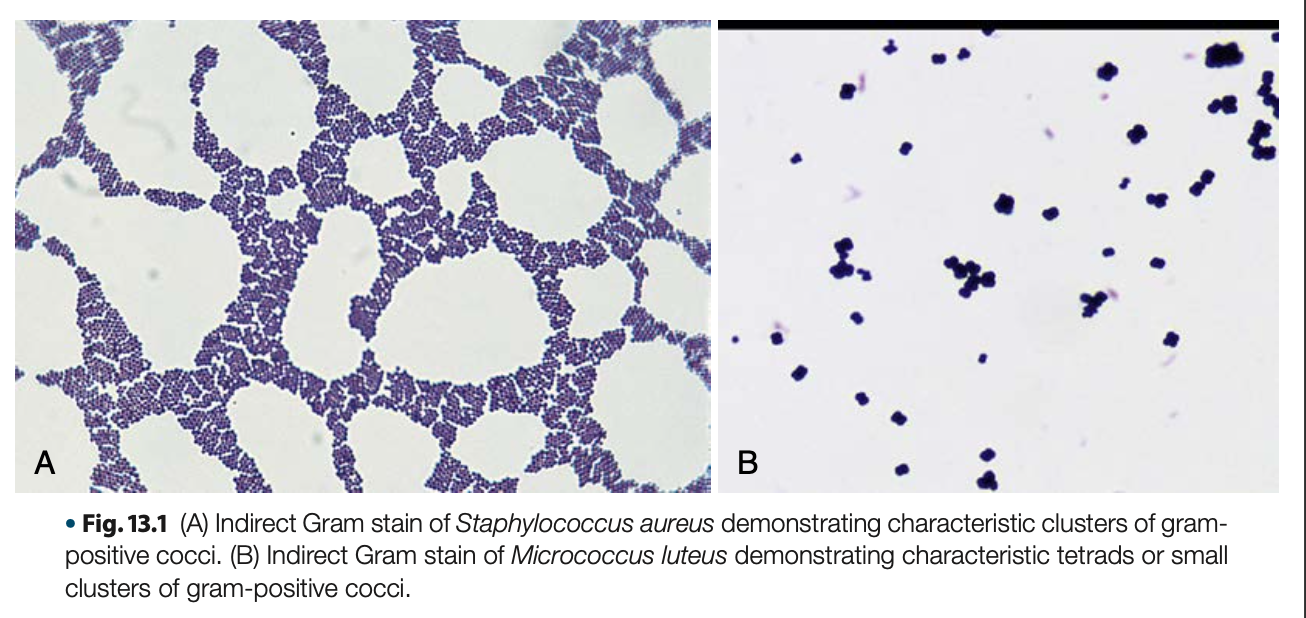
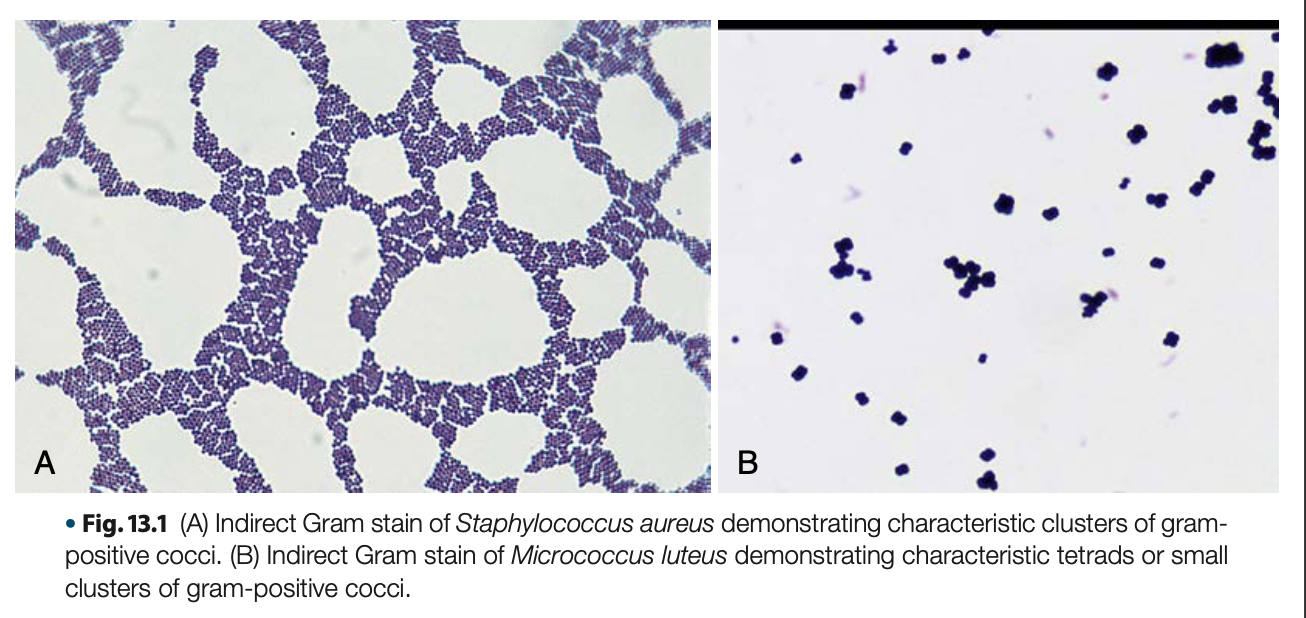
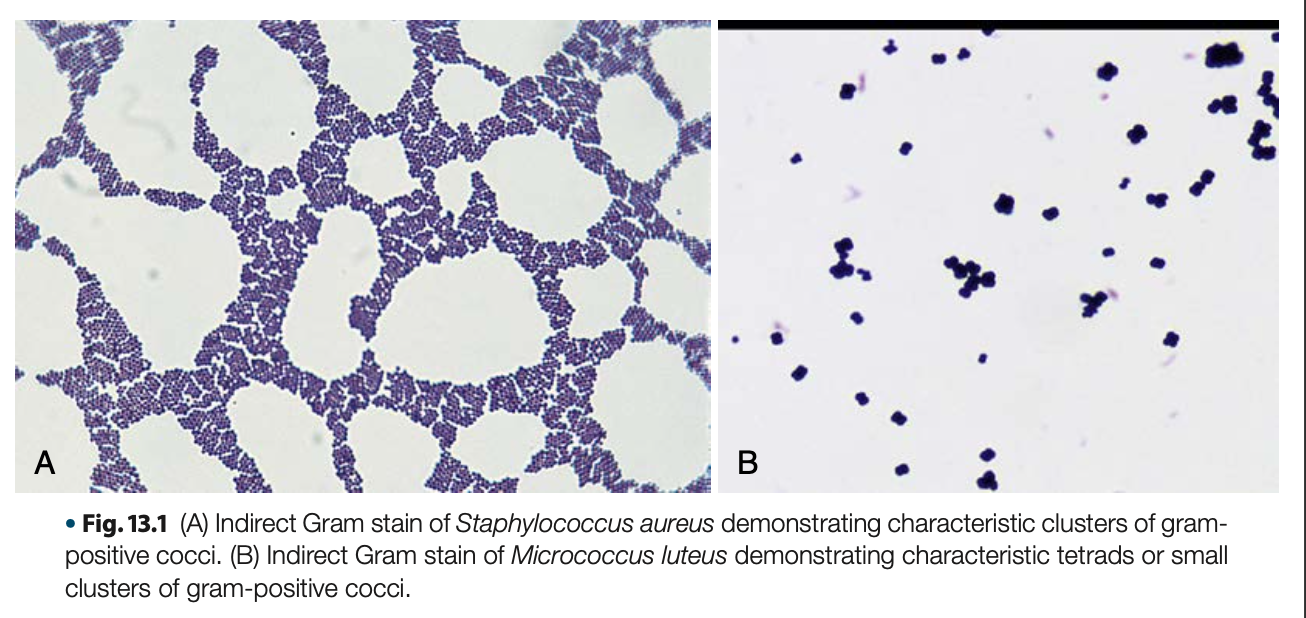
gram + cocci in grapelike clusters, non-motile
General morphology of Staphylococci
Micrococcacea (obsolete)
Staphylococci belongs to the family
Staphylococcus saccharolyticus
Staphylococci is Facultative anaerobes EXCEPT
Catalase
A biochemical test used to separate Staphylococci (+) and Micrococci (+) from Streptococci (-)e
rigorous bubbling / effervescence
+RESULT of Catalase
3% H2O2
+of Catalase uses
F
Do not use colonies from blood agar plate (BAP) as it gives a false positive result
Catalase of Staphylococci (t/f)
Do not use colonies from blood agar plate (BAP) as it gives a false negative result
7.5 - 10% NaCl
Staphylococci is able to grow in
0.04 units of Bacitracin
Staphylococci is resistant to
Beta-hemolytic
Staphylococci
_ on BAP
T
Staphylococcus aureus is known as the most virulent spx (t/f)
gold
Staphylococcus aureus
Aureus means
anterior nares & nasopharynx
Staphylococcus aureus
Normal flora of the
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative anaerobe
Staphylococcus aureus is a facultative aerobe (t/f)
PCR
Staphylococcus aureus
what will enable detection from the nasal swab
Uniform turbidity
GROWTH/ COLONY MORPHOLOGY of Staphylococcus aureus
on broth
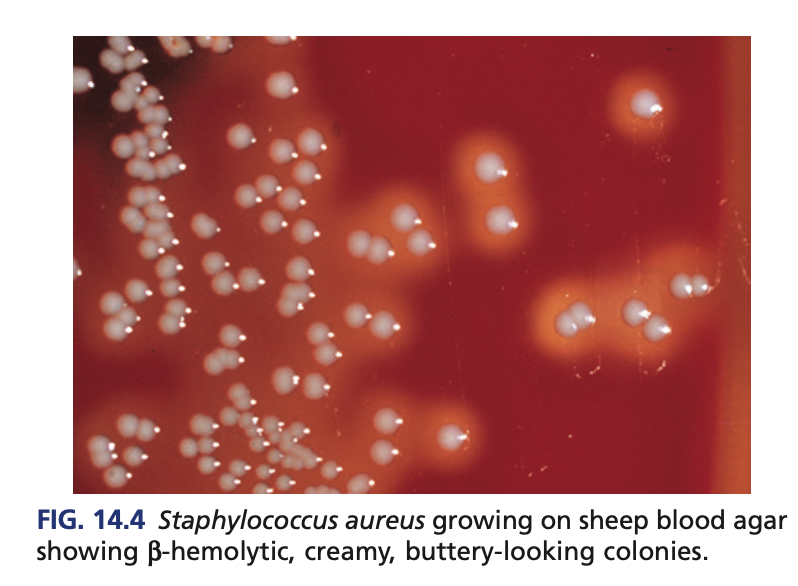
creamy, white with pinhead
GROWTH/ COLONY MORPHOLOGY of Staphylococcus aureus
Growth in BAP as
smooth circular and opaque colonies with oil-like butyrous appearance
GROWTH/ COLONY MORPHOLOGY of Staphylococcus aureus
On plates, they produce
Jet black colonies
GROWTH/ COLONY MORPHOLOGY of Staphylococcus aureus
on tellurite agar/ Vogel Johnson medium
Coagulase Test
Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test
DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
Latex Agglutination Test for Protein A
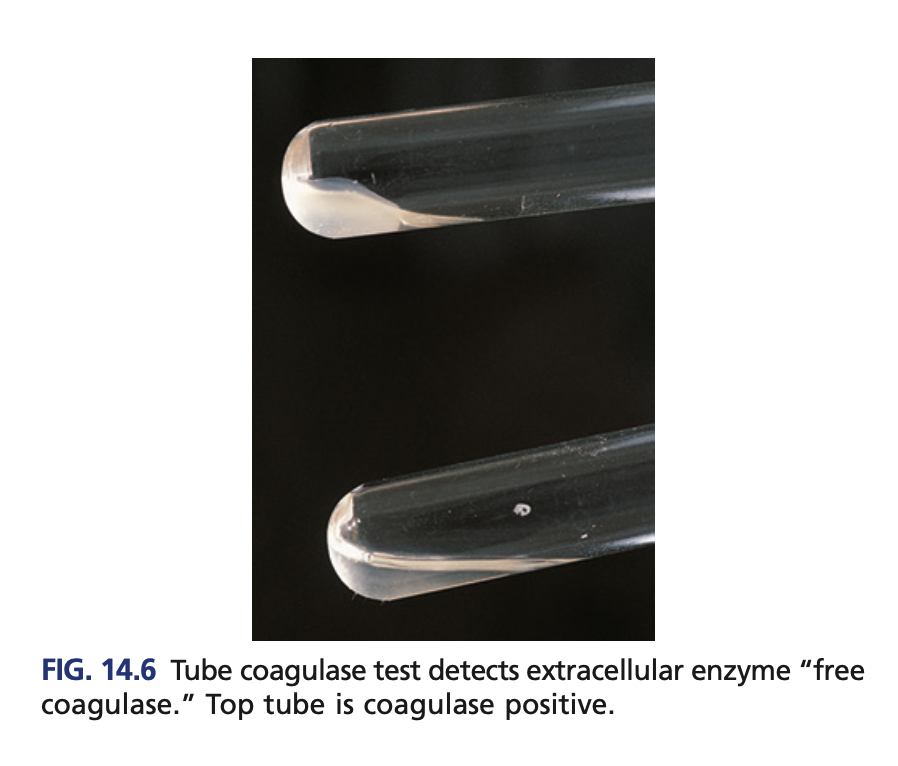
Test for Identification of Staphylococcus aureus
Coagulase Test
DEFINITIVE TEST for S. aureus; test to differentiate from other Staphylococcus
Slide coagulase (screening)
Tube coagulase (confirmatory)
2 types of coagulase test
Slide coagulase (screening)
detects cell bounded coagulase/ clumping factor
Rabbit plasma (obtained using EDTA)
Reagent of Slide coagulase (screening)
clumping
+result of Slide coagulase (screening)
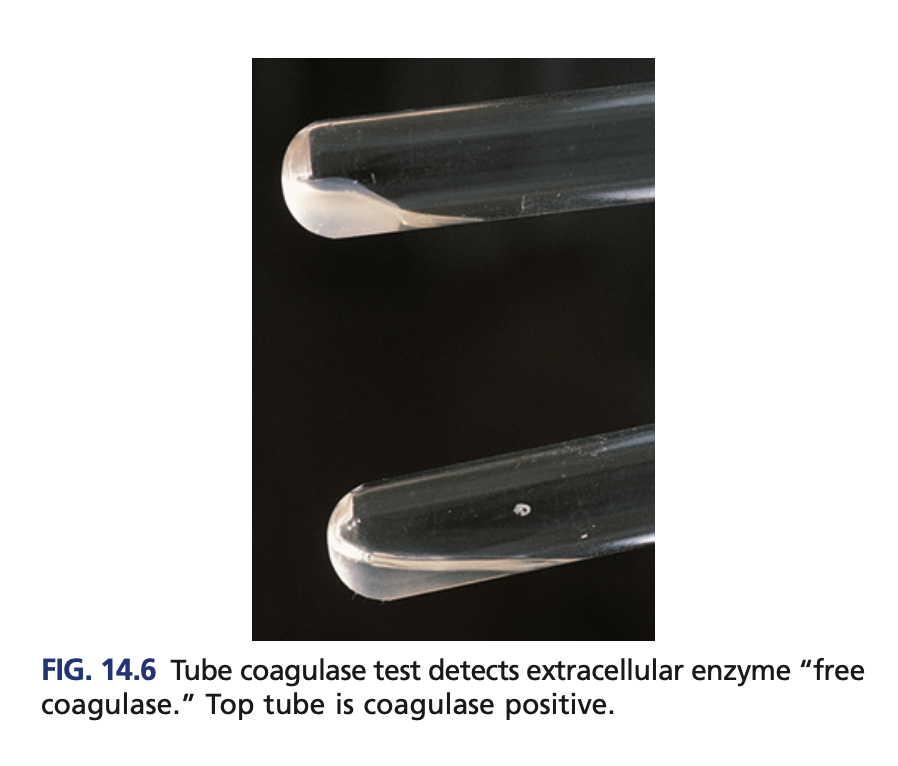
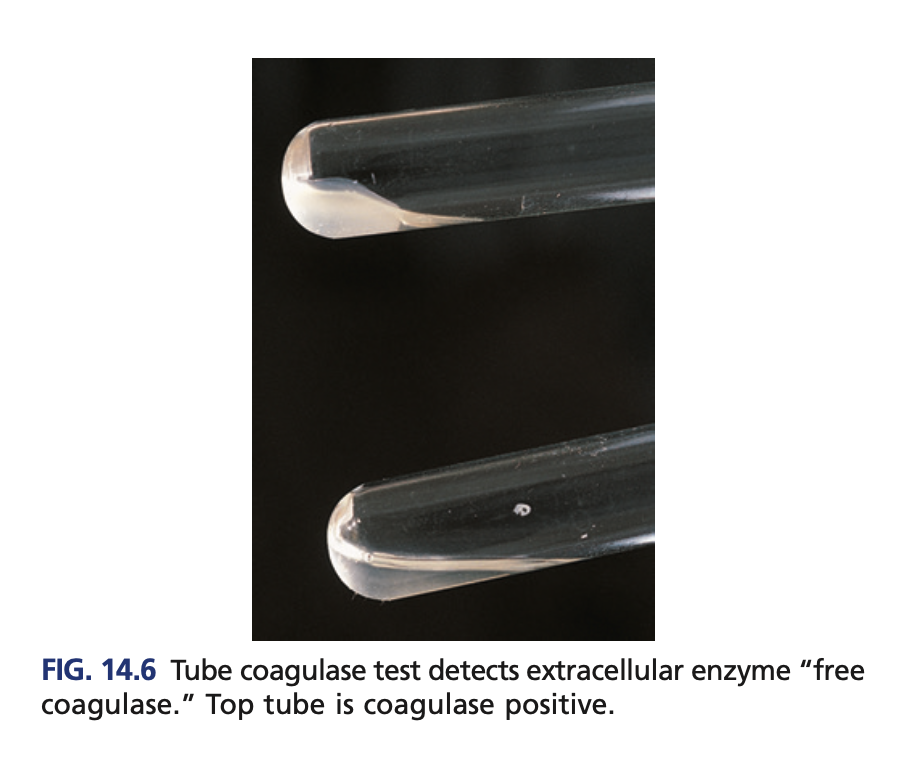
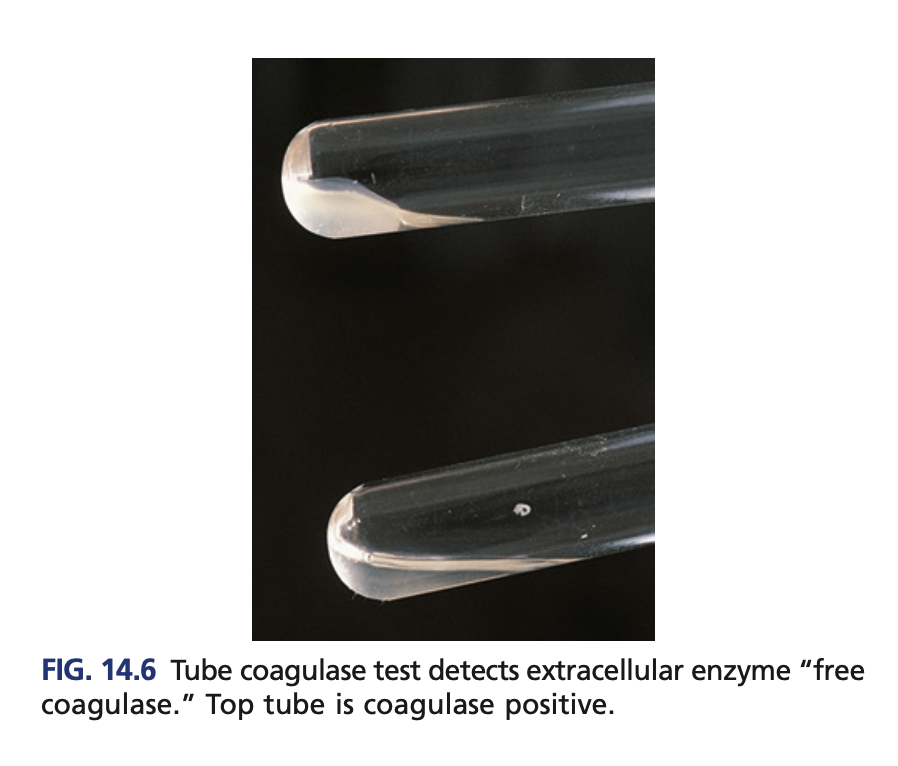
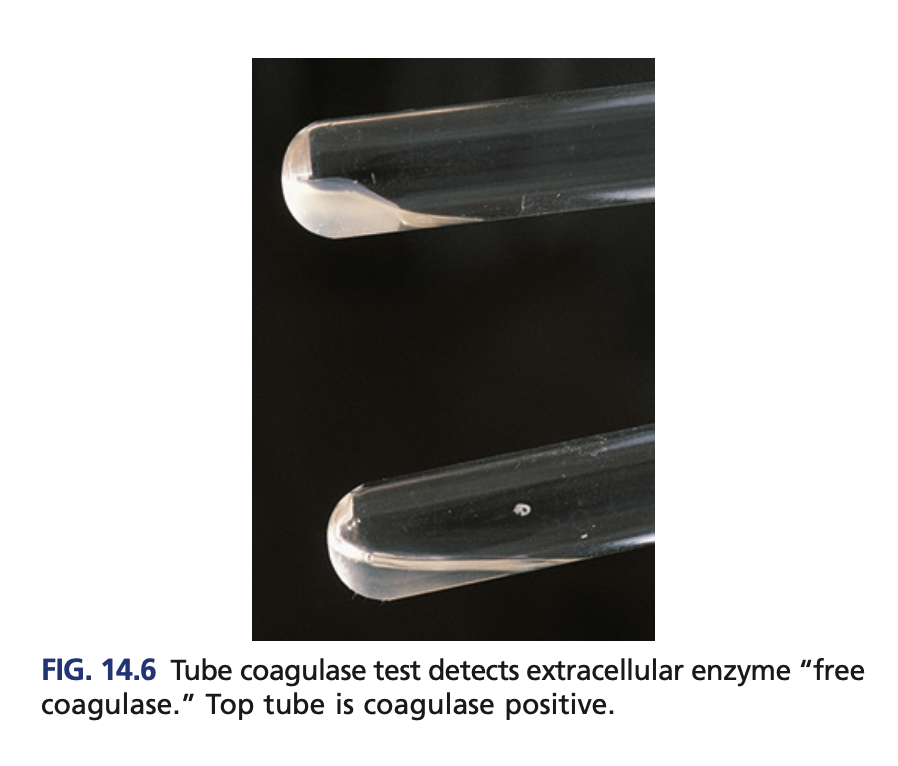
Tube coagulase (confirmatory)
Detects the free coagulase
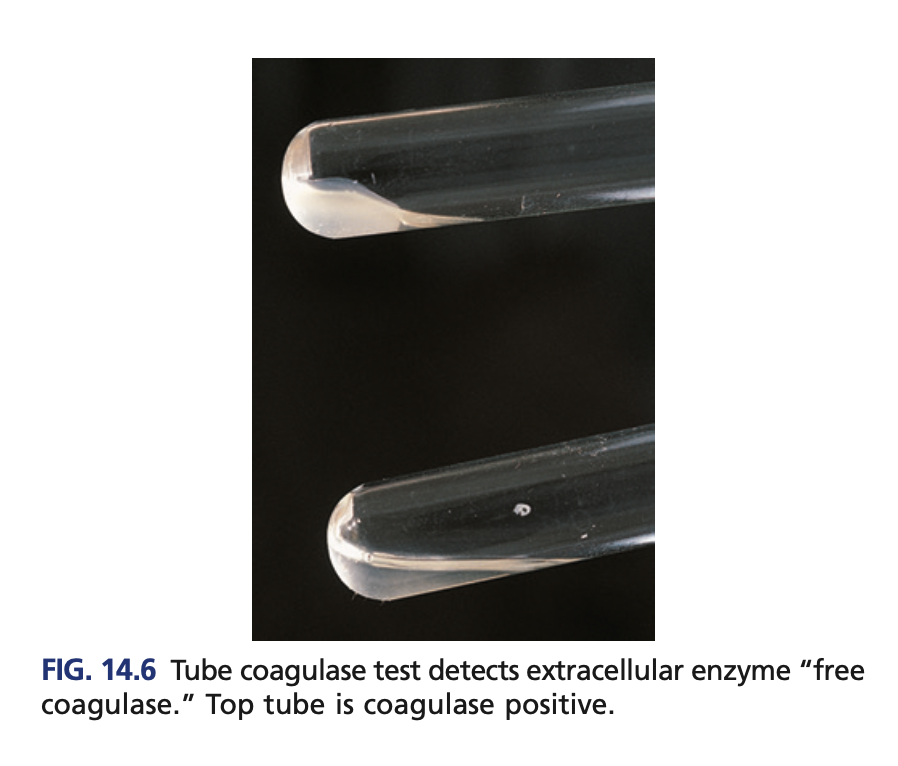
Rabbit plasma
Reagent of Tube coagulase (confirmatory)
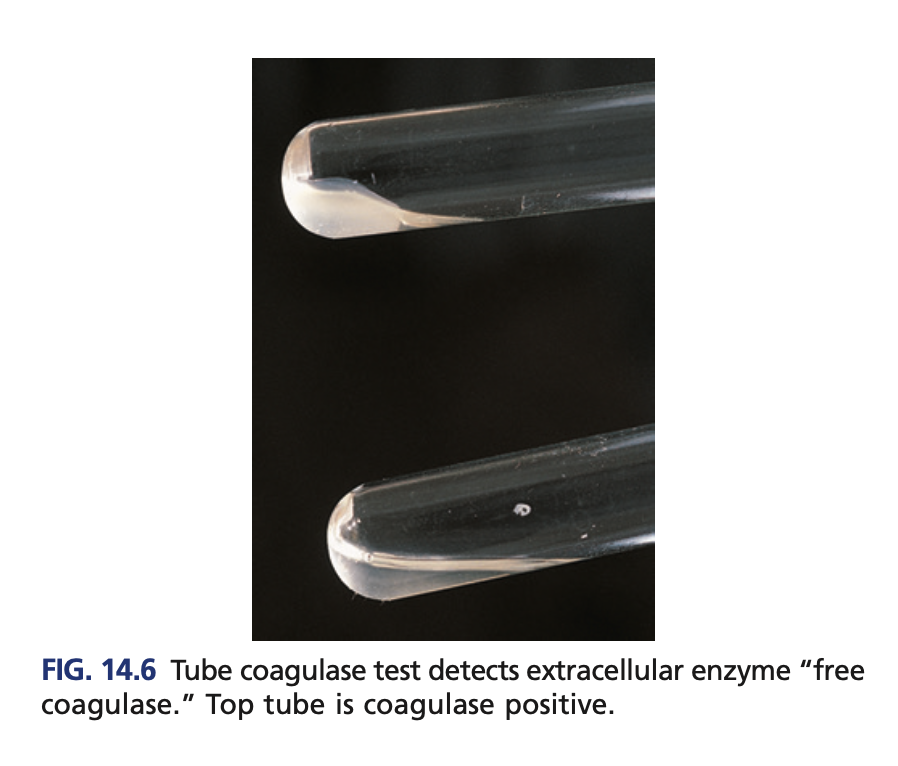
clot
+result of Tube coagulase (confirmatory)
selective medium
Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test is known to be a _ medium
MSA (1% Mannitol)
media of Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test
7.5% NaCl
inhibitor of Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test
Phenol Red
pH indicator of of Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test
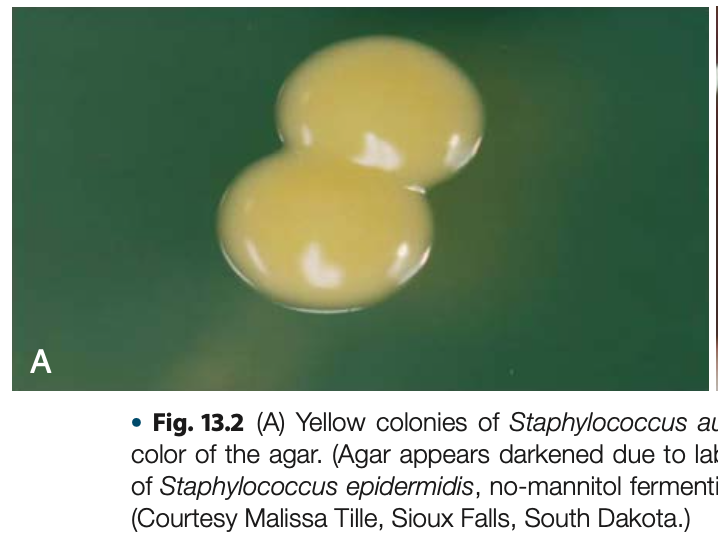
yellow colonies
+result of of Mannitol Salt Agar Test / Mannitol Salt Fermentation Test
DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
detects deoxyribonuclease
DNA + Methyl Green
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
= clear zone around the colonies
DNA + 0.1 % Toluidine Blue
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
= pink zone around the colonies
cells are dead
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
DNA + 0.1 % Toluidine Blue + pink zone =
cells are alive
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
DNA + 0.1 % Toluidine Blue - blue zone =
clearing of agar around the colonies
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
HCl PRECIPITATION METHOD + result
S - Serratia marcescens
M - Moraxella catarrhalis
A - Aeromonas
S - Streptococcus pyogenes
H - Helicobacter pylori
V - Vibrio cholerae
S - Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
S - Staphylococcus aureus
Dye Method of DNAse / Thermonuclease Test
Bacteria which are DNAse test (+)
Latex Agglutination Test for Protein A
Antigen detection
S. aureus with Protein A
has inert particles to which antibody (Fc fragment) binds
Latex Agglutination Test for Protein A
detects specific bacterial antigens
S. pneumoniae
N. meningitidis
H. influenzae
N. gonorrhoeae
Latex Agglutination Test for Protein A detects specific bacterial antigens such as
Lipase
Hyaluronidase / T Factor / Duran-Raynal Factor
Beta-lactamase
Staphylokinase / Fibrinolysin
Coagulase
DNAse / Thermonuclease
Beta-hemolysin
Protein A
Gelatinase
VIRULENCE FACTOR of S. aureus
Enzymes:
Lipase
a fat splitting enzyme, associated with SKIN INFECTIONS such as boils, carbuncles, and furuncles
Hyaluronidase / T Factor / Duran-Raynal Factor
a spreading factor that enhances invasion to tissue (joints = arthritis)
Hyaluronidase / T Factor / Duran-Raynal Factor
causes hydrolysis of hyaluronic acid
Beta-lactamase
makes S. aureus resistant to penicillin
Beta-lactamase
hydrolysis of penicillin
Staphylokinase / Fibrinolysin
dissolves fibrin clot and may enable the infection to spread once the clot is dissolved
Coagulase
causes bacteria to agglutinate in plasma;
Coagulase
converts fibrinogen to fibrin;
Coagulase
may coat neutrophils with fibrin formed to protect organisms from phagocytosis
DNAse / Thermonuclease
causes degradation of DNA
DNAse / Thermonuclease
decreases the viscosity of exudate giving organisms more mobility
Beta-hemolysin
causes destruction of RBC;
Beta-hemolysin
responsible for beta-hemolysis of S. aureus; ANEMIA
hemolysin
lyse RBC
Protein A
prevents phagocytosis;
Protein A
has the ability to bind Fc portion on IgG;
Protein A
found on the CELL WALL
Gelatinase
Gelatin-→amino acid
liquefy
Gelatinase
At ref temp: (+) gel will
solidify
Gelatinase
At ref temp: (-) gel will
Enterotoxins
Exfoliatin A & B / Epidermolytic Toxin A and B
Panton-Valentin Leukocidin
Toxins of S. aeureus
Enterotoxins
a group of seven heat-stable proteins (A, B, C, C2, D, E, F).
Enterotoxin A and B
Most staphylococcal-related food poisonings are associated with Enterotoxin -.