BSCI201 Exam 2 terms (integumentary system, skeletal system, joints/articulations)
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
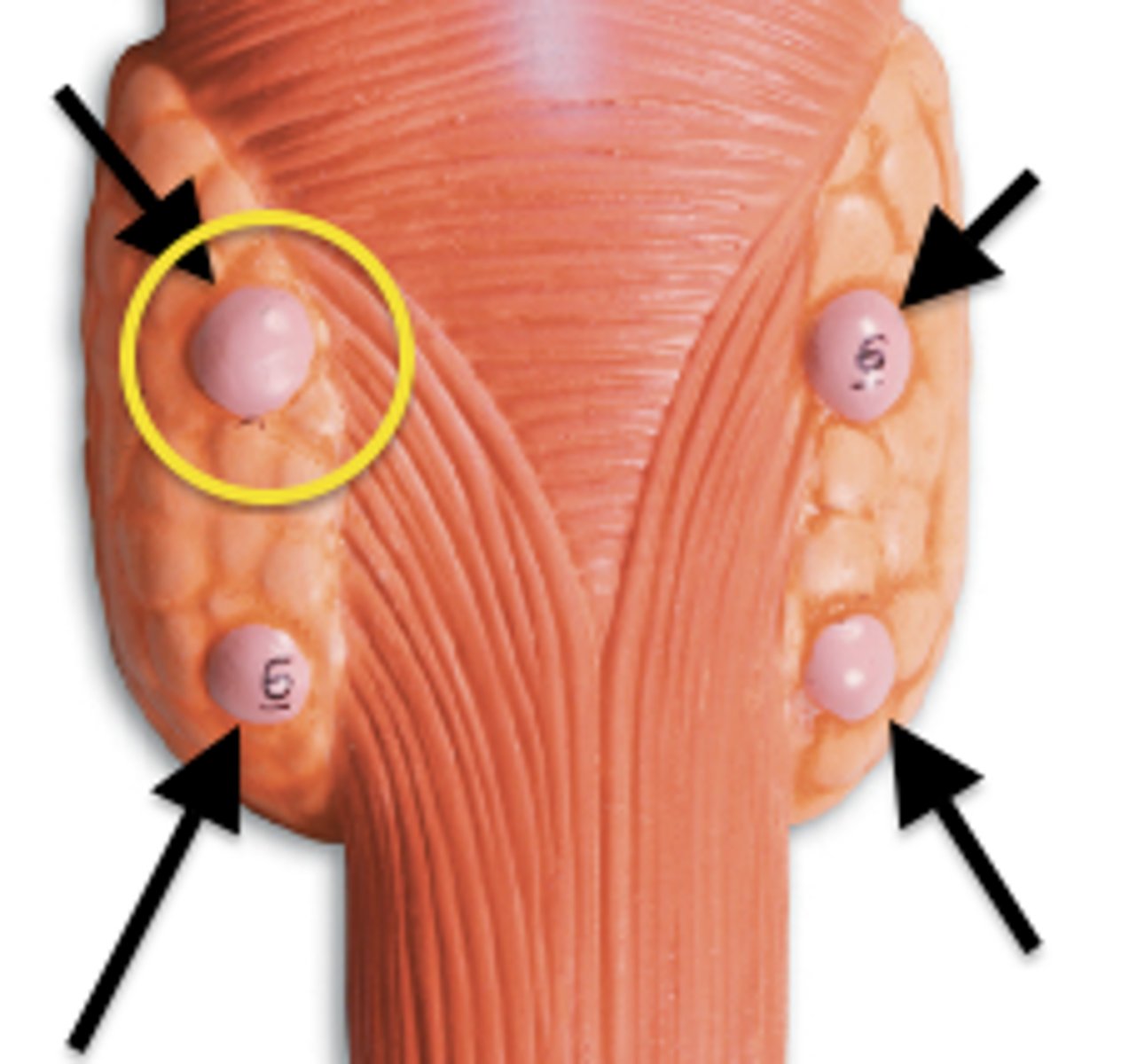
Broadly, explain the divisions of the integumentary system.
1) Skin = cutaneous membrane
- Largest organ of body w/ SA ~1.2-2.2m^2
- Weights 9-11 pounds, ~7% body weight
- Thickness ~0.5mm in thin skin, 4.0 mm in thick (includes epidermis+dermis)
2) Skin Appendages
- Sweat (sudoriferous) glands
- Oil (sebaceous) glands
- Hair + follicles
- Nails
Stratum Corneum
-Dead keratinized cells with hard protein envelope. Cells contain keratin and surrounded by glycolipids; cornification
-20 to 30 layers of flat dead cells
-replaced every 3-4 weeks
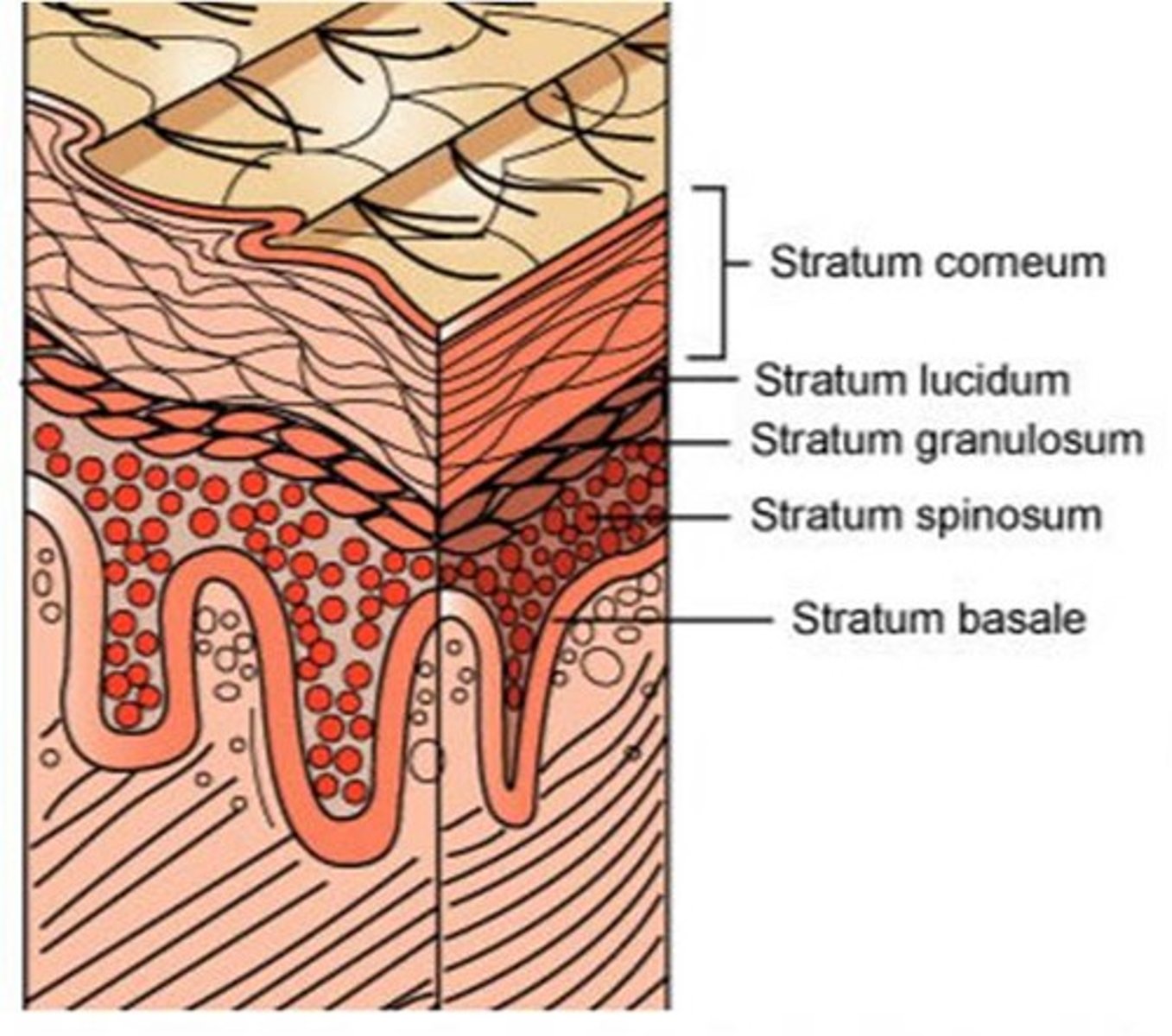
Stratum Lucidum
-Dead cells containing dispersed keratohyalin; transparent layer, thick skin only (palms, soles)
Stratum Granulosum, 2 types of granules
-Keratohyalin and a hard protein envelope form; lamellar bodies release lipids and cells die
(Deteriorating organelles, flattened cells)
-3 to 5 layers
-Lamellated granules: contain glycolipids to make skin water proof
-Keratinohyaline granules: contain keratin (tough, insoluble) to make skin tough and abrasive resistant.
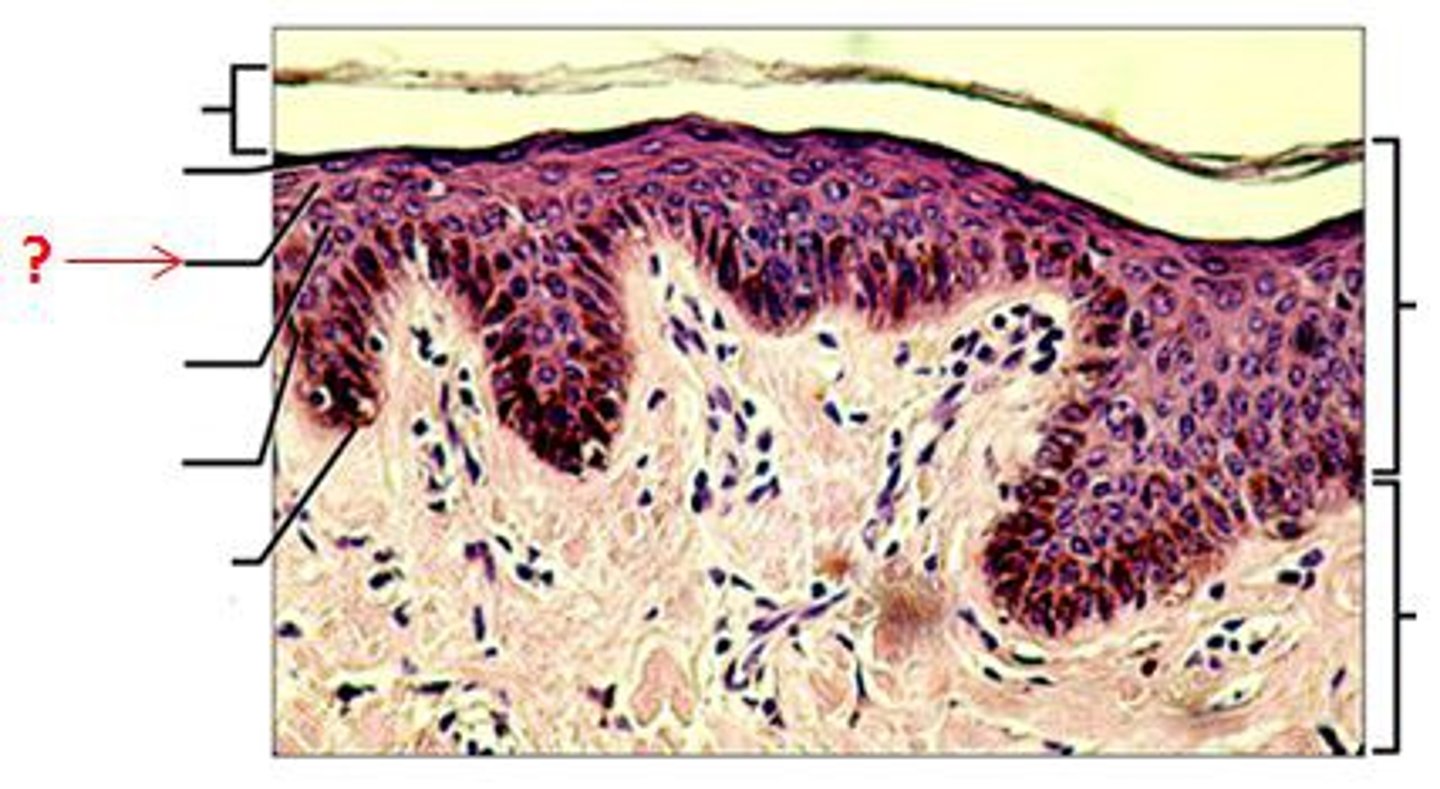
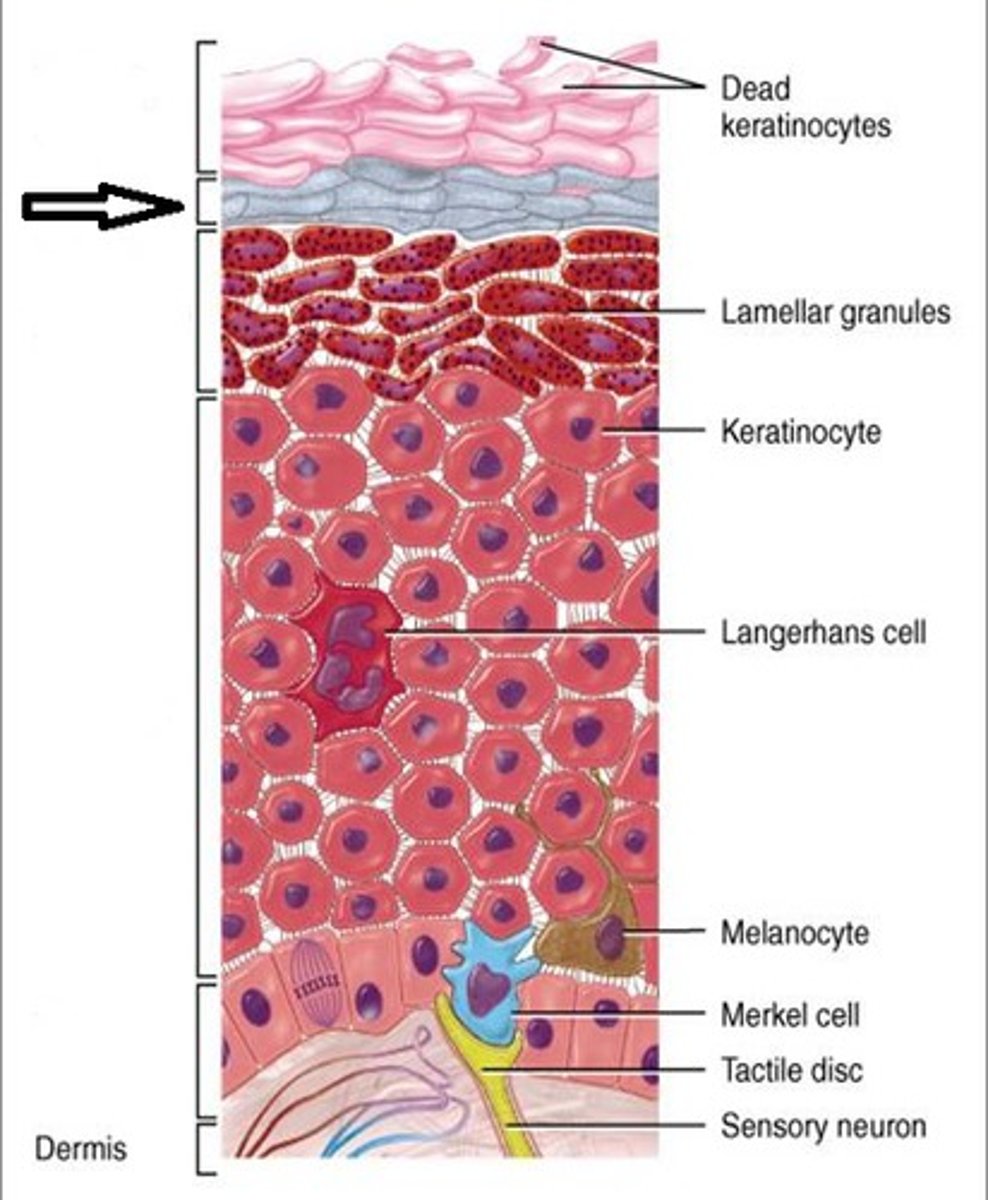
Stratum Spinosum
-Cells have thick bundles of intermediate filaments made of pre-keratin and lipids; lamellar bodies accumulate.
-Several layers
-Connected by desmosomes
-Contain tonofilaments to resist tension placed on skin
-Contain dendritic cells
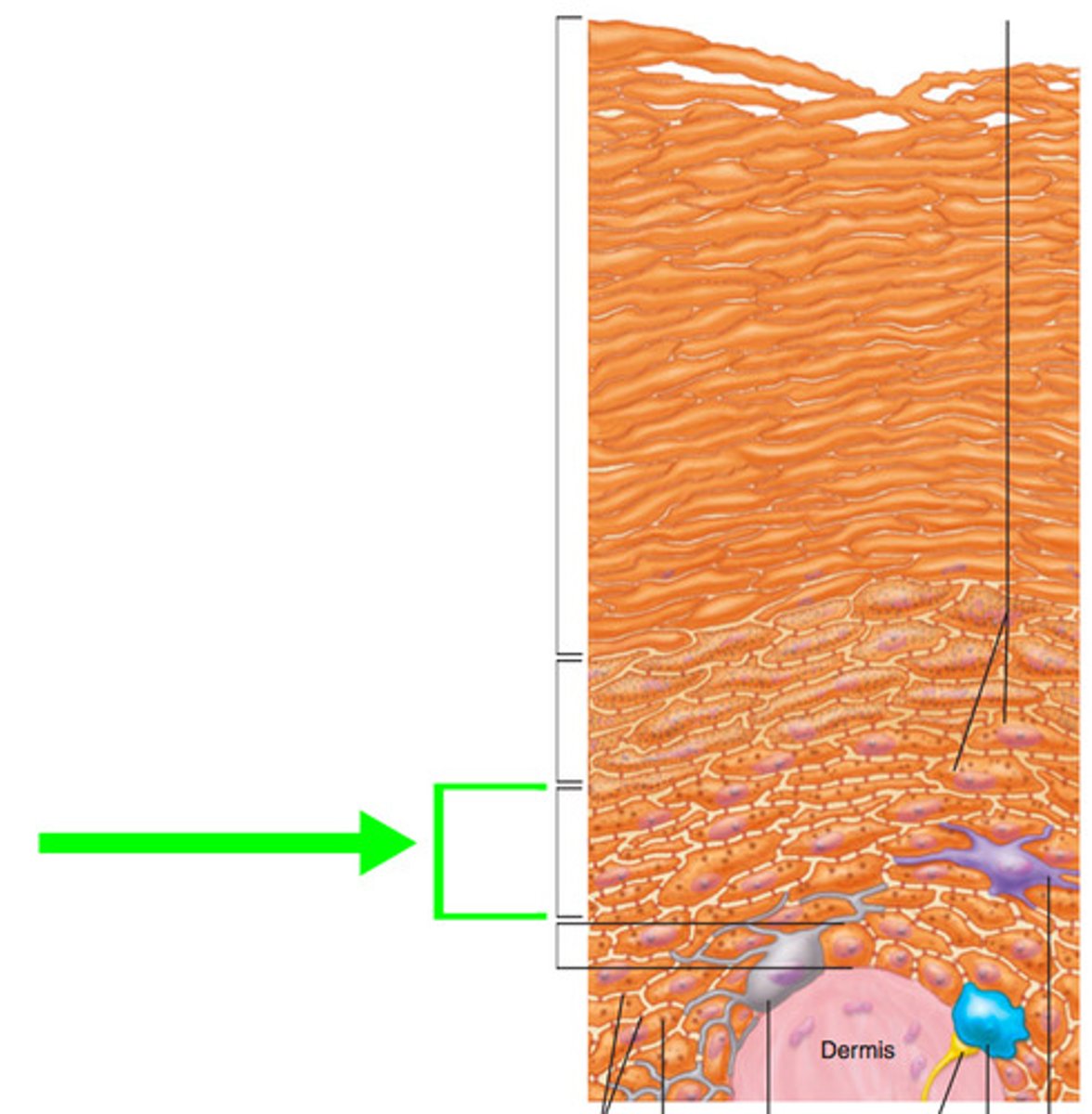
Stratum Basale
-Cells divide by mitosis to form cells of superficial strata
-Deepest stratum
What cells are present in stratum basale?
-Keratinocytes (mitotically active)
-Melanocytes (ex. in sun more melanin produced to protect body from sun; tanning)
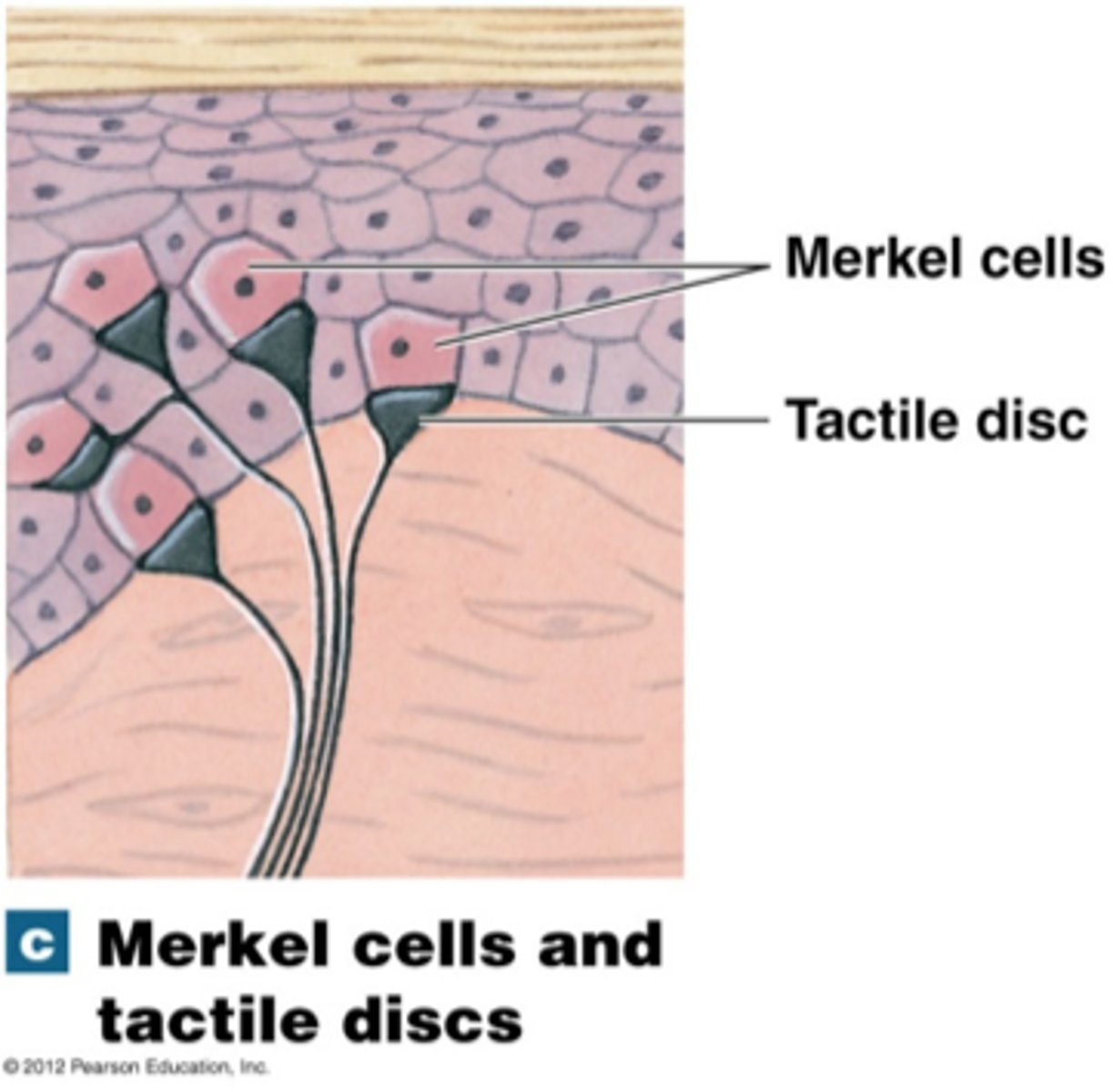
-Merkel cells (epidermal-dermal junction w/ free nerve endings form merkel discs; touch receptors)
Why are albinos more susceptible to developing skin cancer?
-They lack melanin which is crucial to protecting skin from UV radiation. This makes them more vulnerable to skin cancer and UV radiation
Layers in the Dermis?
1. papillary layer
2. reticular layer
Papillary Layer composition/characteristics?
-Composed of areolar connective tissue
-Has peg-like projections; dermal papillae (houses blood capillaries + nerve endings + meissner's corpuscles)
Reticular Layer composition/characteristics?
-80% of dermis
-Composed of dense irregular connective tissue
-Houses pacian corpuscles (deep pressure touch receptors)
-Contains tension/cleavage lines; areas w/ less collagen bundles (parallel: good, across incisions: no bueno)
How do stretch marks form? (Striae)
-Scarring of the skin when the skin stretches rapidly
-This causes the collagen and elastin in the skin to rupture, and as the skin heals, stretch marks appear
What are Merkel Discs?
Large, myelinated fibers that adapt slowly
Location: finger tips, superficial skin
Senses: pressure, deep static touch (shapes, edges), position sense
What are Meissner's corpuscles?
-nerve fibers in the papillary layer of the dermis for light touch
-Light touch receptors
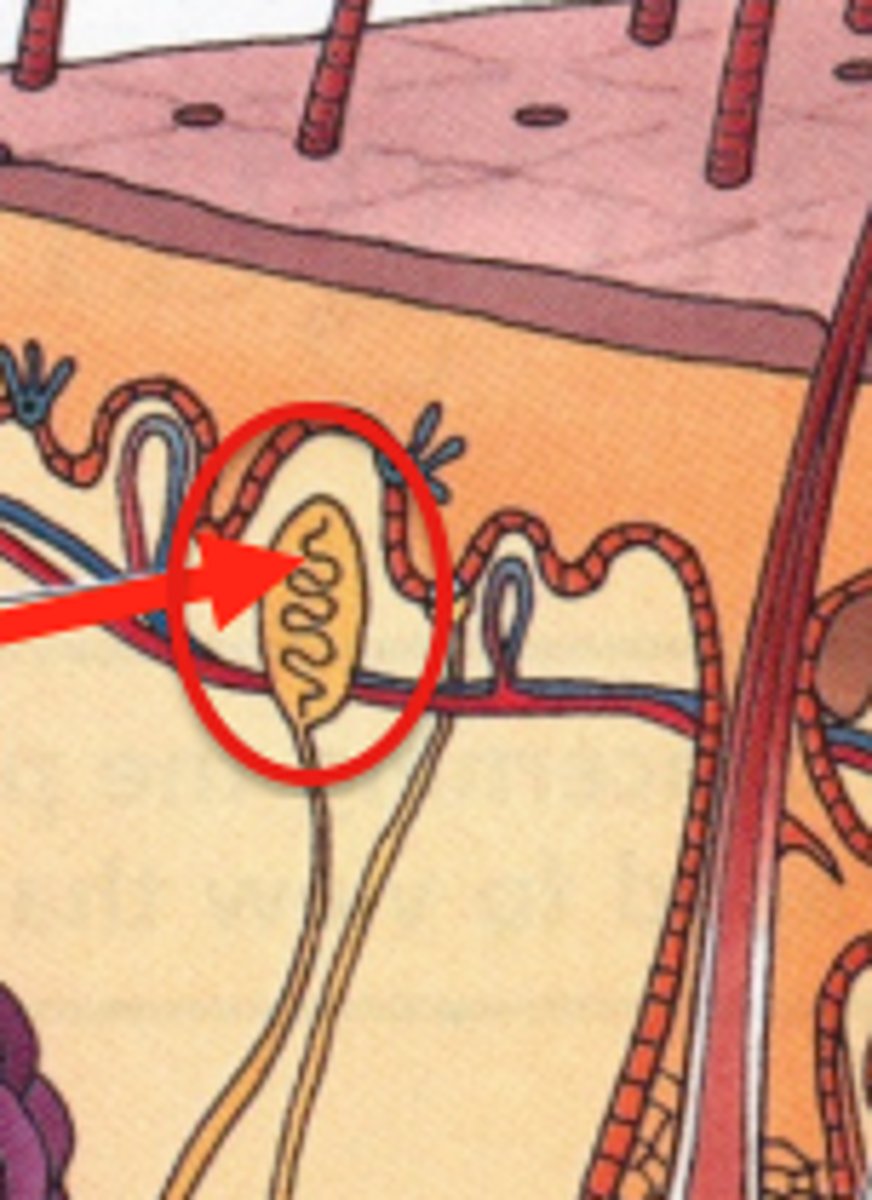
What are Pacinian Corpuscles?
-nerve fibers in the reticular layer of the dermis for vibration and deep pressure
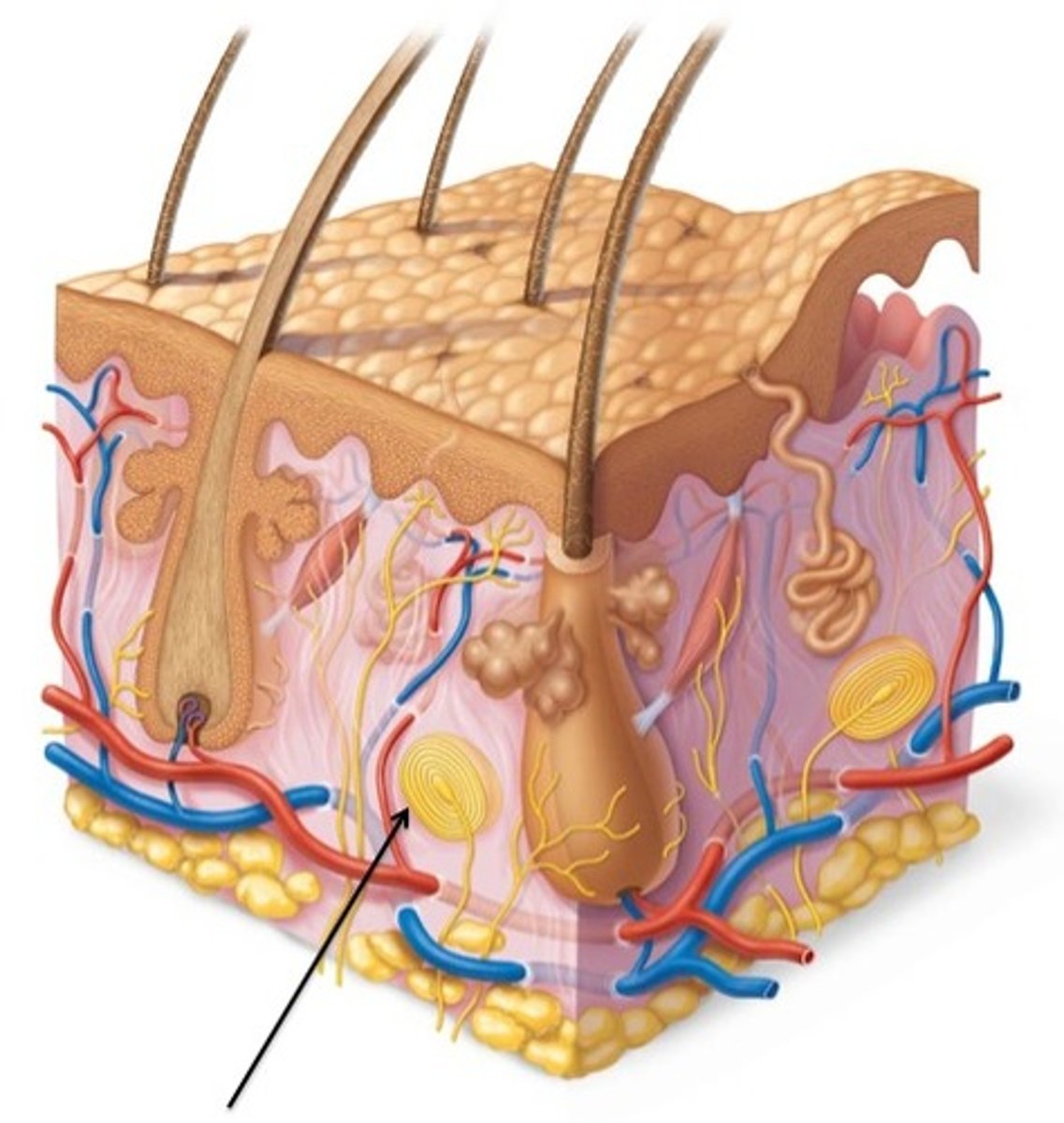
What is the root hair plexus
-sensory nerves that surround the base of each hair follicle; stimulated when hairs bend
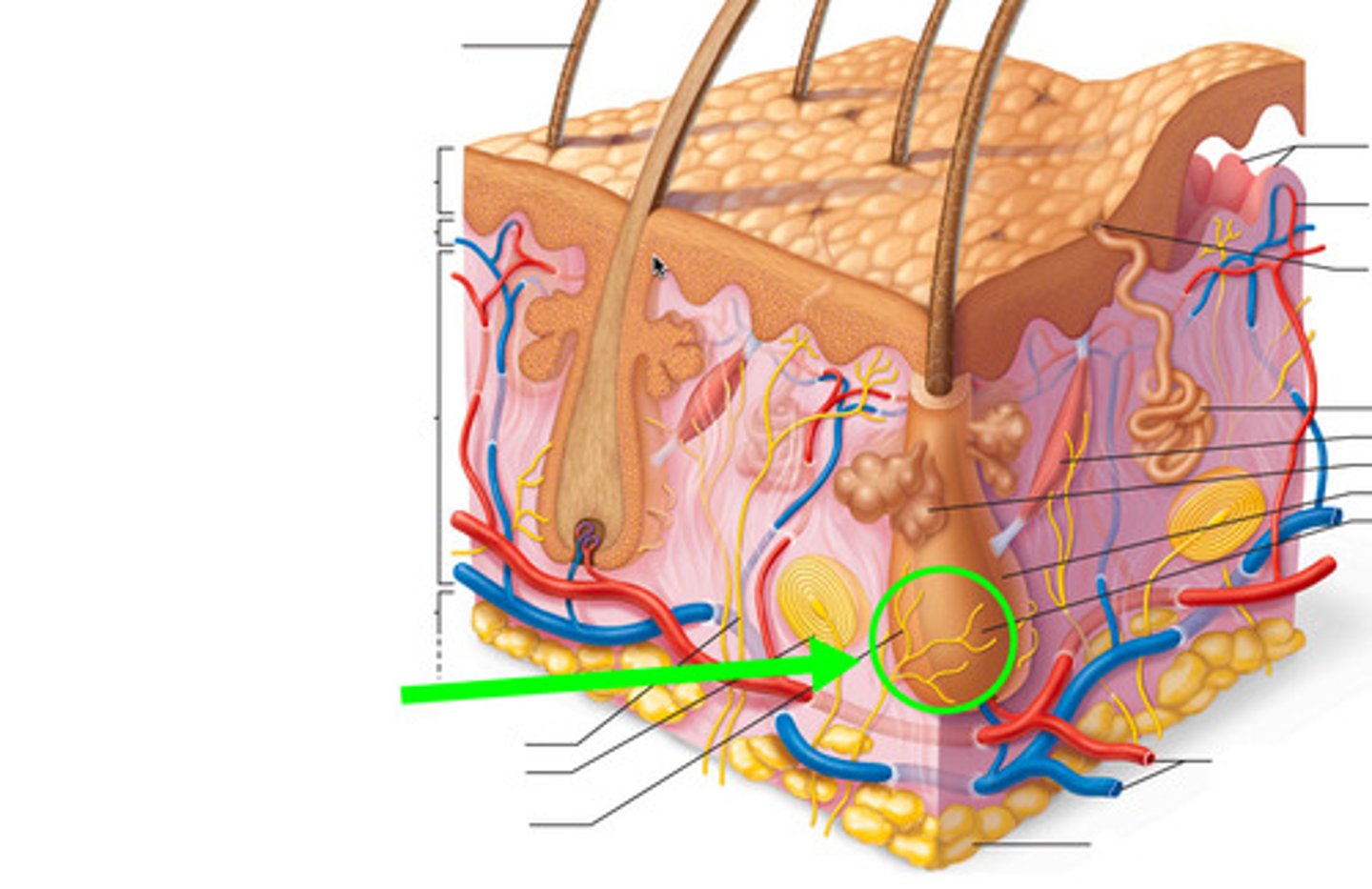
Accessory structures of skin derive from ________ but reside in ______ for what reason?
-Derive from stratum basale
-Reside in dermis
-This is to ensure nutrient uptake for accessory structures
Types of sweat (sudoriferous) glands
eccrine and apocrine
Eccrine Glands
-3 million in body, all over
-abundant in palms, soles, forehead
-Secrete sweat for thermoregulation
-Merocrine mode of secretion
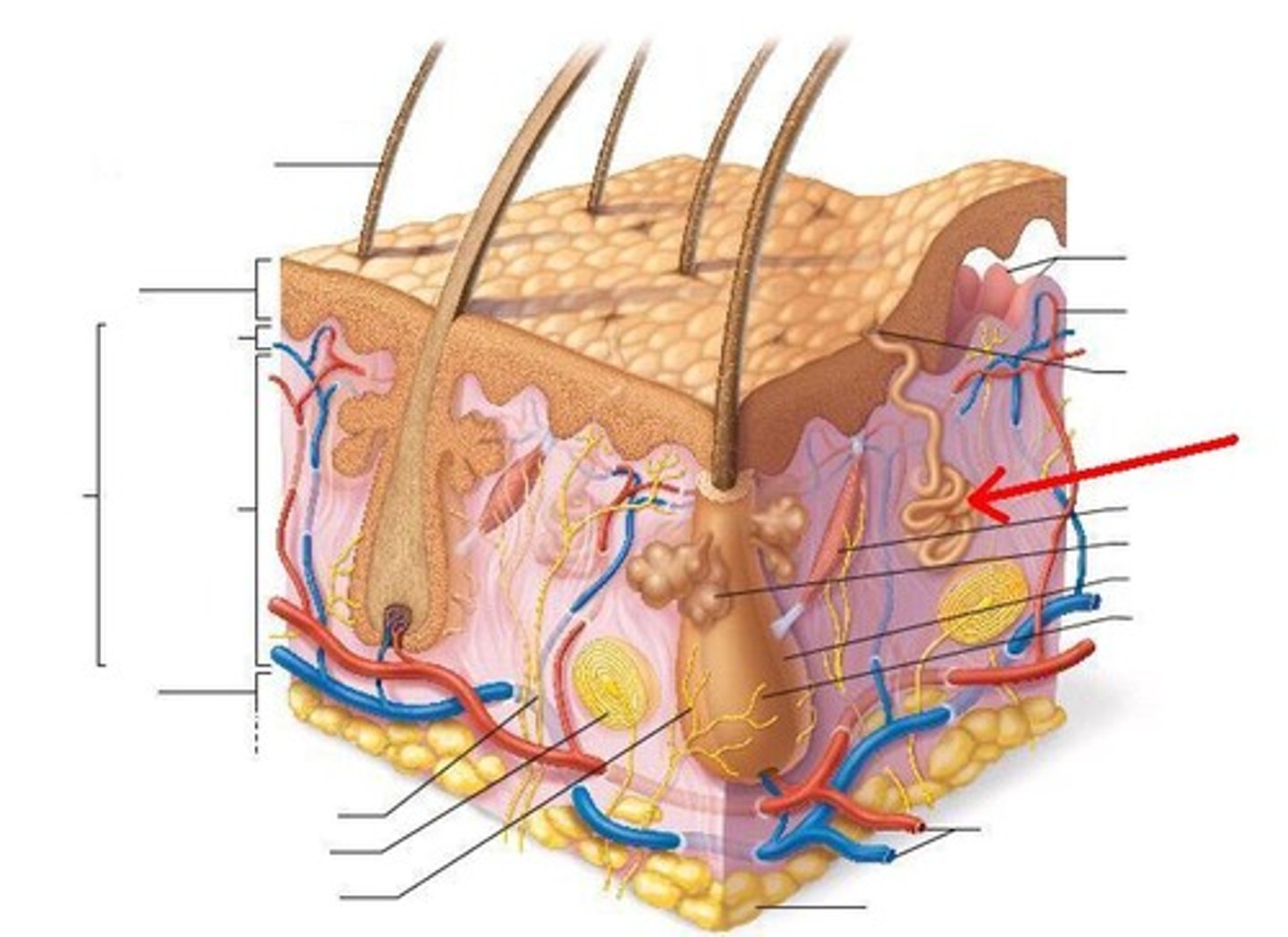
Appocrine Glands
-Larger glands than eccrine
-2000 in genital and axillary areas
-Active after puberty, stimulated by sex steroid hormones
-Secretes yellow fluid on hair follicles via merocrine mode
-Associated w/ body odor; odoriferous glands
Composition/Characteristics of sweat
-Hypotonic filtrate of blood
-99% water composition
-Contains antibodies, vitamin C, salt, metabolic waste, dermicidin (antimicrobial protein)
-pH 4-6
Acid Mantle
-Combination of sweat's acidic pH and dermicidin on skin to retard microbial growth
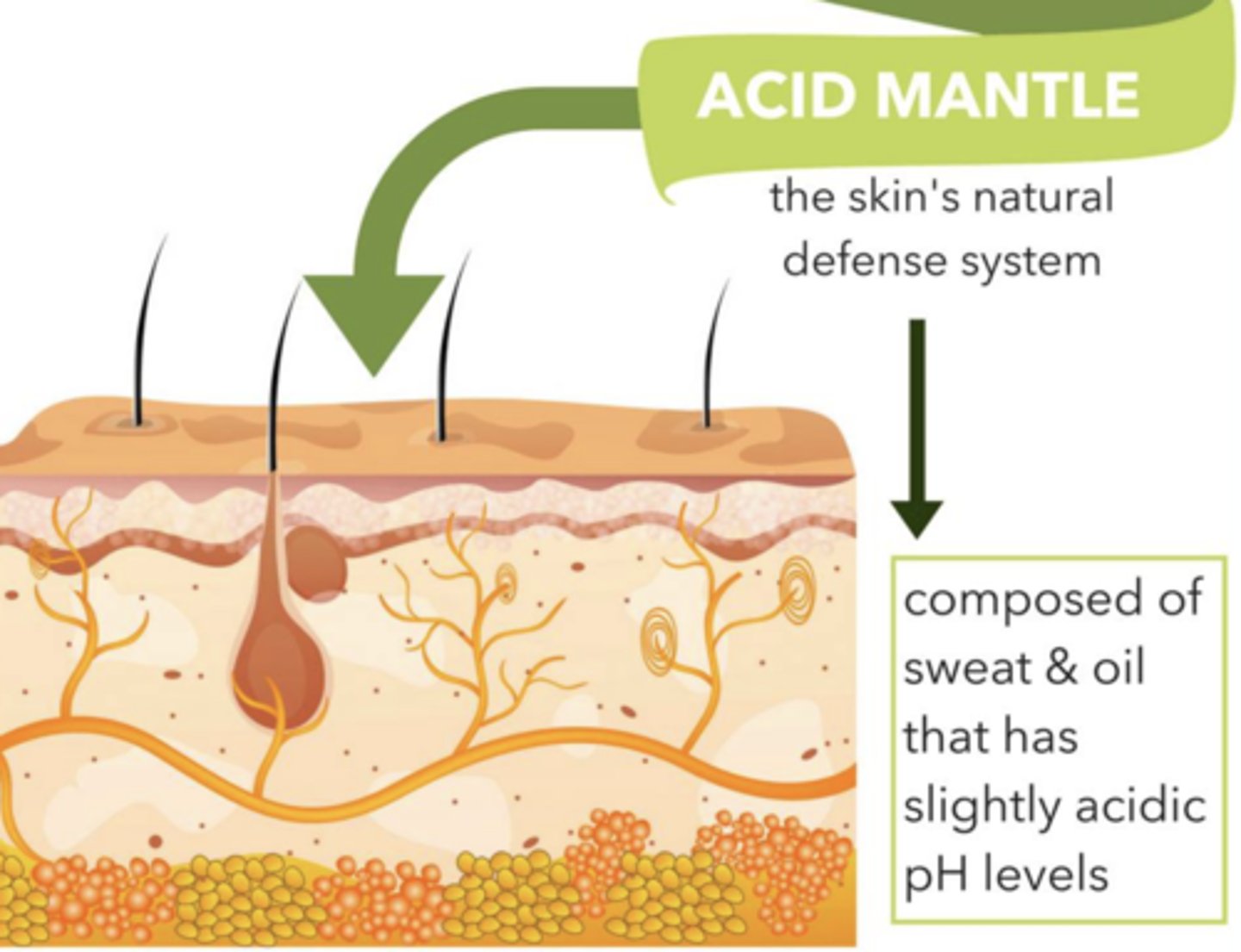
Specialized sweat glands (appocrine)
-ceruminous glands (earwax; prevents foreignity in ear)
-mammary glands (breast milk; secretes to feed the young)
Oil (sebaceous) glands
-Produce oil (sebum)
-Lubricant for skin
-Prevents brittle hair
-Kills bacteria
-Most have ducts that empty into hair follicles; others open directly onto skin surface
-Glands are activated at puberty
-absent in palms and soles
-Holocrine secretion
Whiteheads
-accumulated sebum blocks sebaceous gland ducts
blackheads
-popped whiteheads that oxidize and darken
Acne
-Inflammation of sebaceous glands by bacteria
What is the function of hair?
Protection and thermoregulation
What is alopecia?
Loss of hair as WBC attack matrix cells in follicles, causing shrinkage and slowed hair production
What is hirsutism?
Excess androgens (male sex hormone; testosterone) stimulate hair follicles to grow thick hair and produce sebum
What is the composition of nails?
-Mainly non-living; tightly packed, hard, keratinized epidermal cells
-Grows 1/8 inch per month
What is the function of nails?
-protects digit ends, grasps and manipulates, scratches
Three types of skin cancer
basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, melanoma
Basal cell carcinoma
-Most common (80%), and least malignant.
-Slow growth, and involves the proliferation of keratinocytes in stratum basale
Squamos cell carcinoma
-Involves cells from stratum spinosum
-Grows rapidly and metastasizes to lymph nodes Results from sun exposure
-Second most common
Melanoma
-Least common (1-2%) and most malignant
-Most aggressive, highly metastatic, and resistant to chemo
-Involves melanocyte proliferation (moles and freckles), growing quickly over weeks to months, anywhere on the body
Types of burns?
first degree, second degree, third degree
First degree burns
-Confined to epidermis
-Includes redness, swelling, pain
-Heals without medical intervention (Ex: sunburn)
Second degree burns
-Damage to entire epidermis and papillary layer of dermis
-Includes blisters (fluid collected @ epidermal-dermal junction), swelling, redness, pain
-Heals in 3-4 weeks if infection is prevented
Third degree burns
-Damage to entire skin; epidermis + dermis + all nerve endings
-Burn site isnt painful, is subject to infection and fluid loss
-Medical interventions include grafting, protein and ion replacement for healing
Head and neck accounts for what percentage of the body
9%
Upper limbs account for what percentage of the body
18%
Trunk accounts for what percentage of the body
36%
Perineum accounts for what percentage of the body
1%
Legs account for what percentage of the body
36%
3 types of skin grafts?
Autograft, allograft, xenograft
Autograft
Skin graft from another part of the body
Allograft
Skin graft from donor, used as temp. grafts (usually)
Xenograft
Obtained from animal, usually pig. Used as temp. grafts
Why do wrinkles form?
-collagen and elastin fibers break down, and skin cells divide more slowly. This causes your skin to lose elasticity and become thinner and drier, resulting in wrinkles
-Skin thins and gets drier through age, therefore, it is less resilient,
What does the sun do to cause wrinkles of skin?
UV rays break down collagen and elastic fibers, removing firmness and damages surface of epithelial cells
What does botox do?
Extends collagen production + elastin to upkeep skins structure/elasticity. Reducing muscle contractions
Articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that covers ends of bones in synovial joints
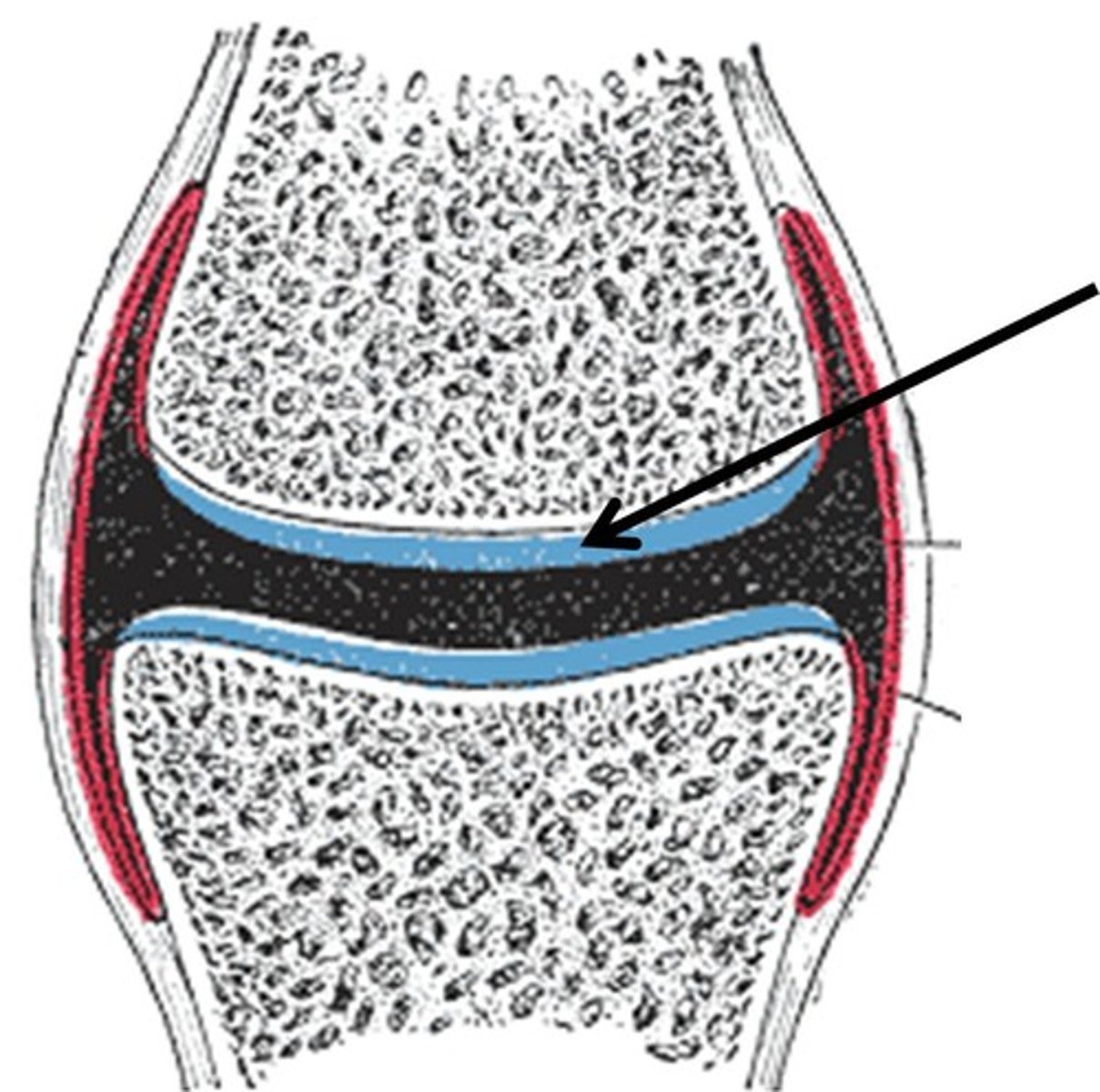
epiphyseal line
remnant of the epiphyseal plate, seen in adult bones
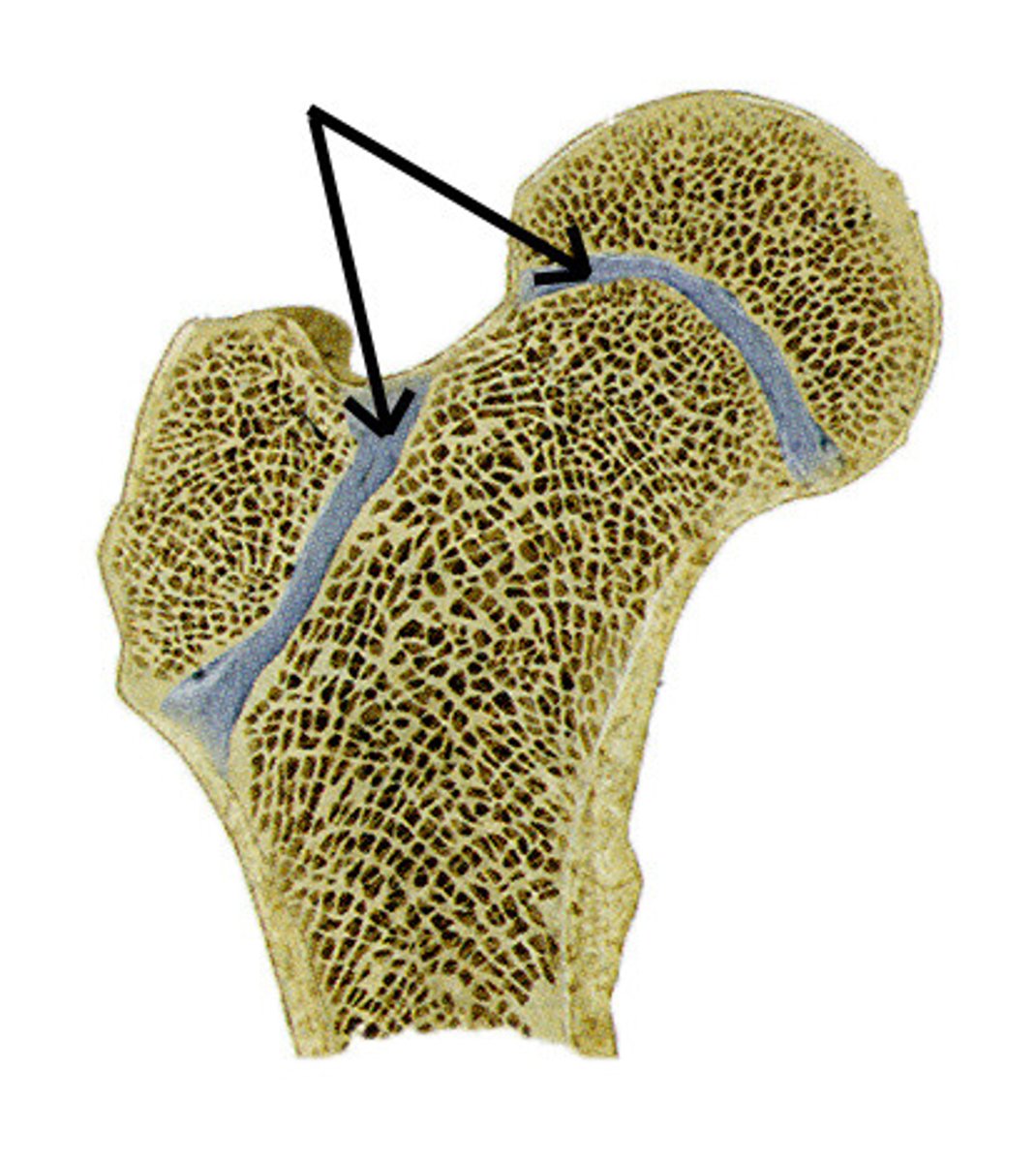
Ephiphyseal plate (growth plate)
forms between two ossification centers
band of hyaline cartilage
fuse together and growth stops when adult
Which bones are typically flat?
Membrane bones (face, skull, clavicle, shoulder girdle)
Composition of spongy bone?
Trabeculae; honeycomb, needle-like structure
Bone structure does what?
Twisting force held in an ostean; resistance against tensional stress is achieved by the woven structure arrangement of collagen fibers
Epiphyses
-Expanded ends of long bones
-Exterior is compact bone, and the interior is spongy bone
-Joint surface is covered with articular (hyaline) cartilage
-Epiphyseal line separates the diaphysis from the epiphyses
Diaphysis
Shaft of long bone; surrounds medullary cavity
Membranes of a bone?
Endosteum and periosteum
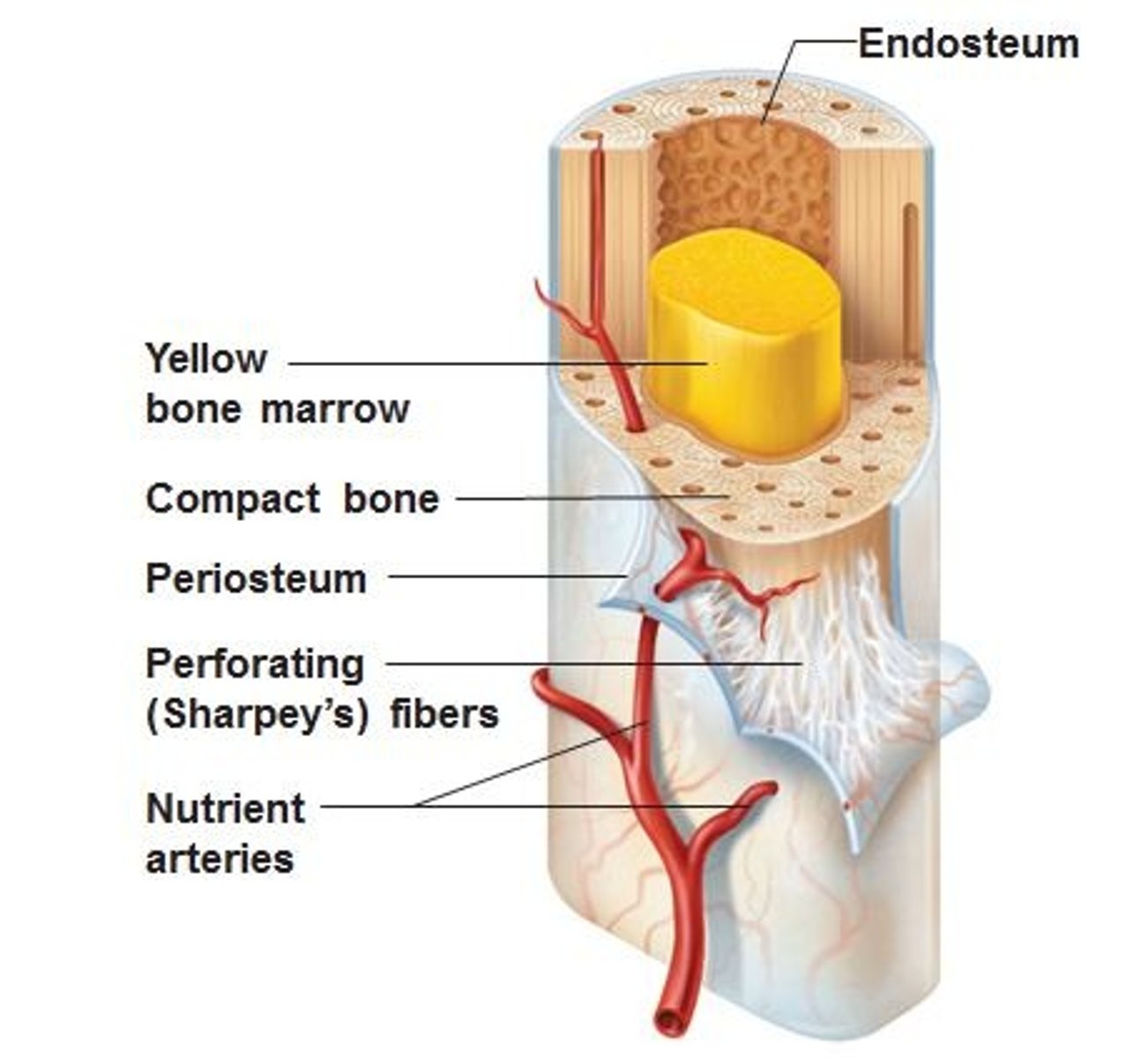
Endosteum
-Covers internal surface of bone, such as canals.
-Has osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Periosteum
-Double layered, outer fibrous and inner osteogenic layer
-Attached to bone by perforating fibers (sharpey's fibers)
Name the four bone cells:
osteogenic cells --> Osteoblasts --> osteocyte, and osteoclast
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells: add to existing tissue
Osteogenic cells
Gives rise to osteoblasts
Osteocyte
Mature osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
bone resorbing cells; destroys bone tissue that is old or damaged
Why does our body break down bone?
To rebuild from scratch about every decade, regulating Ca+ and phosphorus levels as well as repair any damage to the skeleton.
Composition of compact bone
-Osteons, arranged cllagen fibers in adjacent lamellae running in opposite directions to resist twisting force.
-Haversian canal; central canal; core of osteon holding bv and nerves
-Perforating canal: connect bv and nerves between periosteum and central canal
-Lacunae; shallow cavities housing osteocytes
-Canaliculi; canals connecting lacunae to central canal, allowing for substance transfer
Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of...
Development of bony structure from embryonic skeleton
Intramembranous ossification
-Prenatal ossification
-Develops from fibrous CT, results in membrane bones
-ossification center in fibrous CT membrane; centrally isolated mesenchymal cells cluster and differentiate into osteoblasts
-Woven bone to periosteum forms; osteiod accumulates between bv to form random network of trabeculae
Endochondral ossification
-Prenatal ossification
-derived from hyaline cartilage, produced by chondroblasts; called echondral or cartilage bones (all bones except cranial and clavicles)
-After ossification, hyaline cartilage persists in two areas: articular cartilage and epiphyseal plates
Longitudinal growth
-Post natal ossification
-increase in length; new hyaline cartilage added to epiphyseal faces and bone tissue to diaphysial faces)
Bone growth, active zones
1) Growth zone: chondroblasts in mitosis proliferate (hyperplasia); cartilage secretion
2) Hypertrophic zone: chondrocytes increase in size
3) Calcification zone: calcium phosphate salt crystals (hydroxyapatites) in zone calcify matrix and cut off nutrients to chondrocytes
4) Ossification zone: obsteoblasts invade matrix and secrete new osteoid
5) Resorption zone: slight center of new bone resorption to lengthen medullary cavity
Appositional growth
-Increase in diameter/thickness
-osteoblasts in osteogenic layer of periosteum secrete new tissue to external bone surface
-Osteoclasts in endosteum slightly reabsorb tissue in internal surface
Hormonal control in post natal bone growth
-GH promoting effect on long bones in indirect
-Hepatocytes are stimulated to produce IGF's, which stimulate chondroblast proliferation --> hyaline cartilage
-SSH synergize w/ GH's to increase IGF --> growth spurt
-SSH antagonize GH actions @ end of adolescence
-SSH stimulates epiphyseal plate ossification; plate closure; height determined
How does gigantism occur?
-Growth Hormone dysfunction
-Hypersecretion of GH
How does acromegaly occur?
-Growth Hormone dysfunction
-Excess GH release in adults after plate closure
-Excessive appositional bone growth
How does dwarfism occur?
-Hyposecretion of GH
or
-Absence of GH receptors on hepatocytes (no IGFs)
or
-Enzymatic defects in IGF biosynthesis by hepatocytes; IGF deficiency
What is bone remodeling?
-constant process of bone degenerating and rebuilding
-to maintain calcium homeostasis and allow for bone repair
Bone undergoes formation on which surface?
Periosteal surface
Bone undergoes resorption on which surface?
Endosteal surface
Adult bone density characteristics
-Constant
-Rate of formation = rate or resorption
Osteoporosis
-When resorption rate outpaces rate of formation
What are the causes of osteoporosis?
-Low Ca2+ diet
-Lack of physical activity
-genetics
-gender
-ethnicity
-AGING
Factors of osteoporosis
-Hormonal control + Mechanical stress (wolffs law)
-Hypercalcemic conditions; calcitonin released (sends Ca to blood)
-Hypocalcemic conditions; parathyroid hormone releases (Ca to blood)
-Vitamin D stimulates Ca2+ absorption from small intestine; not enough --> ca to blood)
Types of bone fractures
C.C.D.I.S.G
Comminuted: bone fracture
-Many fragments
Compression: bone fracture
-bone is crushed
Depressed: bone fracture
-Bone pressed inward
Impacted: bone fracture
-broken bone ends are forced into each other
Spiral: bone fracture
-ragged break due to twisting forces
Greenstick
-bone breaks incompletely
Healing stage of bone fractures
1) Hematoma formation
2) Fibrocartilaginous callus formation, new BV come in
3) Bony callus formation (spongy bone)
4) Bone remodeling
Parathyroid hormone
-84 AA peptide
-Released by chief cells w/ CaSR in parathyroid glands
Chief cells
-Cells responsible for secretion of substances in the parathyroid gland
What are the major stimulants for PTH?
-Hypocalcemia
-Hyperphosphatemia
-PTH will then bind to PTH receptor to cause dissociation of Gs(alpha)
thyroid gland
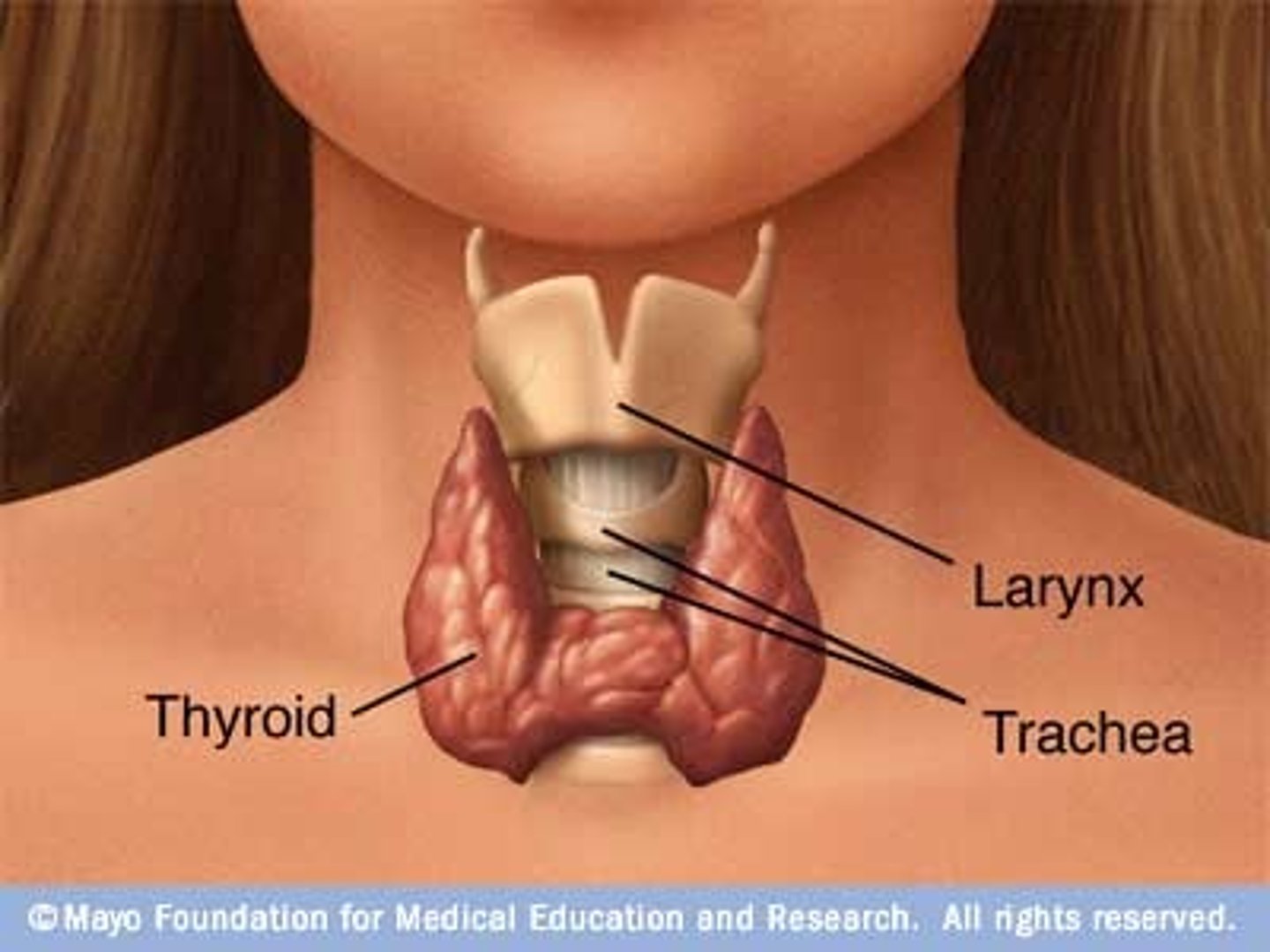
parathyroid glands