biochem chapter 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
107 Terms
Which of the following is the most abundant element in the human body?
1. nitrogen
2. carbon
3. oxygen
4. phosphorus
5. none of the above
oxygen

amine and carboxylic acid
amine, ketone, and carboxylic acid
amine, amide, and carboxylic acid
alcohol, amine, amide, and carboxylic acid
none of the above are correct
amine, amide, and carboxylic acid
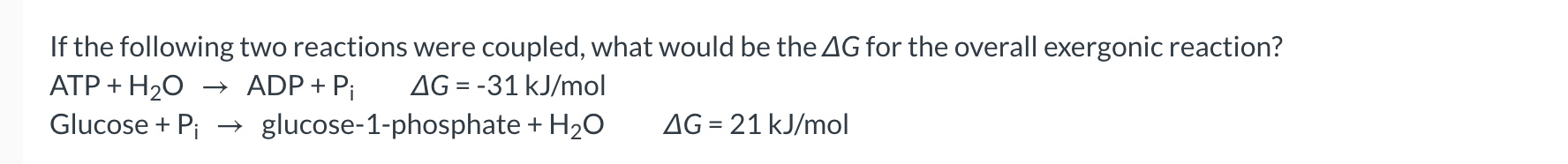
-52 kJ/mol
-10 kJ/mol
10 kj/mol
52 kj/mol
none of the above
-10 kJ/mol
Which of the following is a major difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus, prokaryotic cells do not
eukaryotic cells contain organelles, prokaryotic cells do not
eukaryotic cells are much larger than prokaryotic cells
eukaryotic cells often form multicellular organisms, prokaryotic cells do not
all of the above
all of the above
Which of the following correctly identifies the progression from individual molecules to a functioning multicellular organism?
molecules, organelle, organ, cell, organism
molecules, cell, organ, organelle, organism
molecules, organelle, cell, organ, organism
molecules, cell, organelle, organ, organism
molecules, organ, organelle, cell, organism
molecules, organelle, cell, organ, organism
Change in enthalpy (delta H) is best defined as
the sum of heat absorbed and work done
the heat content of a system
the pressure change at constant temperature
the measure of disorder in a system
none of the above
the heat content of a system
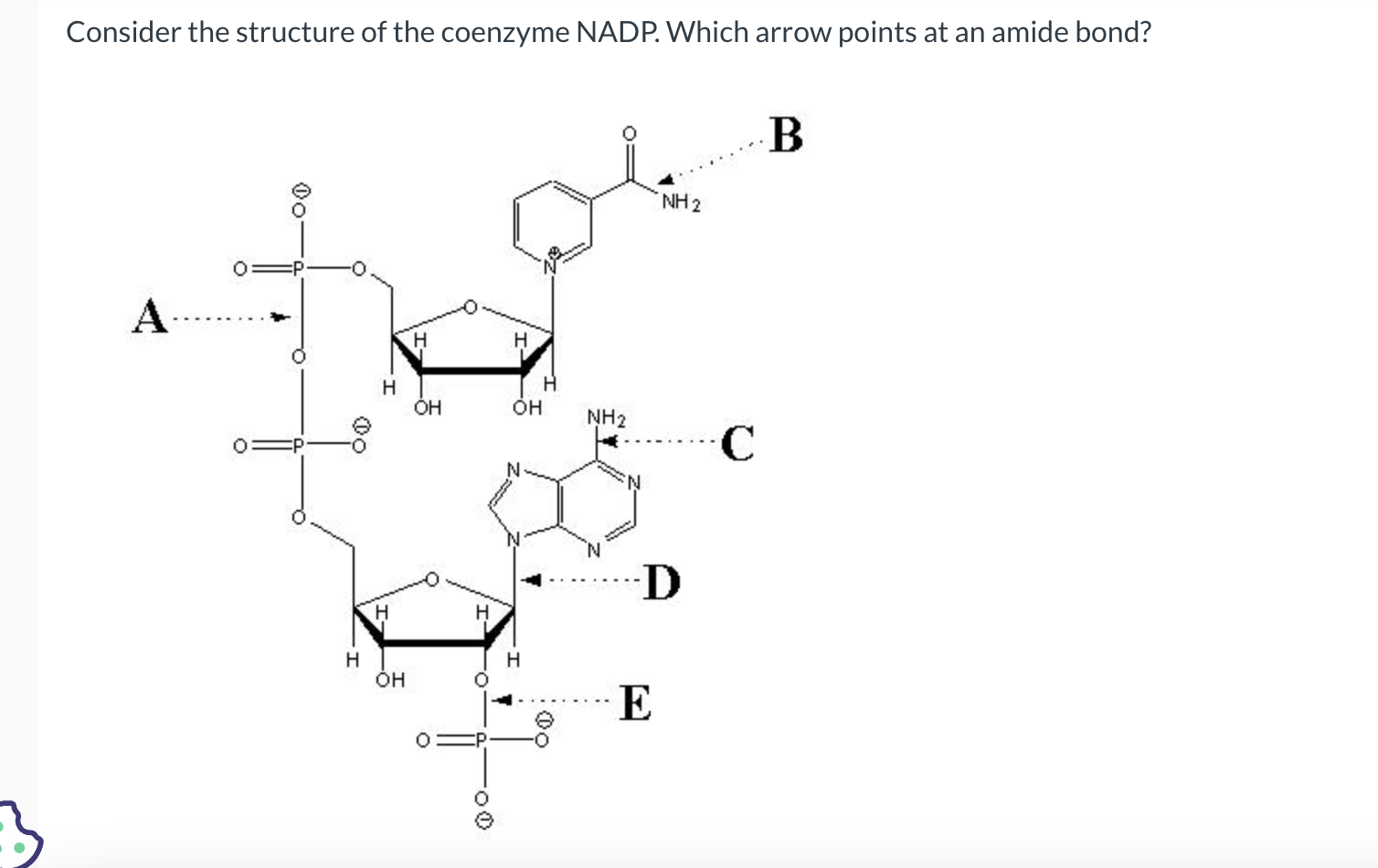
B
An endergonic reaction with a _ delta H _ and a _ delta S can be changed into an exergonic reaction by decreasing the temperature
negative, positive
positive, positive
positive, negative
negative, negative
negative, negative

spontaneous and endergonic
spontaneous and exergonic
nonspontaneous and endergonic
nonspontaneous and exergonic
none of the above
spontaneous and exergonic
in a water molecule, hydrogens are partially _ ; oxygens are partially _
negative, negative
negative, positive
positive, positive
positive, negative
none of the above
positive, negative
the strongest non-covalent interactions are _
hydrogen bonds
LDF
van der waals
dipole dipole
ionic interactions
ionic interactions
Which of the following explains the interactions that occur between the atoms of water molecules and the ions that form when sodium chloride dissolves in water?
hydrogens interact with the sodium ion, oxygens interact with the chloride ion
hydrogens interact with the chloride ion, oxygens interact with the sodium ion
hydrogens interact with the sodium ion and the chloride ion
oxygens interact with the sodium ion and the chloride ion
none of the above
hydrogens interact with the chloride ion, oxygens interact with the sodium ion
Which of the following explains the attractive forces between hydrophobic molecules in an aqueous solution?
in an aqueous environment, LDF between hydrophobic molecules become stronger
In an aqueous environment, LDF between hydrophobic molecules and water become stronger
since nonpolar molecules do not form hydrogen bonds with hydrogen bonds with water, they can form hydrogen bonds with other nonpolar molecules
there is no increase in attractive forces between nonpolar molecules in an aqueous environment
none of the above
there is no increase in attractive forces between nonpolar molecules in an aqueous environment
Which of the following is an example of an amphipathic molecule?
adenine, a base found in nucleic acids
glucose, a monosaccharide
serine, an amino acid
palmitic acid, a fatty acid
none of the above
palmitic acid, a fatty acid
Fatty acid anions most commonly assemble into _ in an aqueous solution
lipid bilayers
solvent-filled vesicles
micelles
liposomes
none of the above
micelles
Which of the following is true regarding hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar molecules or groups?
they depend on strong permanent dipoles in the nonpolar molecules
they result from the tendency to maximize water’s contact with nonpolar molecules
they are the result of strong attractions between nonpolar regions
they require the presence of surrounding water molecules
they are the result of strong repulsion between water and nonpolar regions
they require the presence of surrounding water molecules
What would be the resulting pH if one ml of 1.0 M NaOH was added to one liter of pure water (assume pH 7.0)?
11
7.3
1
13
3
11

HPO4 2-
H2PO4
H3PO4
PO4 3-
none of the above
H3PO4
Hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar molecules _
depend on strong permanent dipoles in the nonpolar molecules
are the result of strong attractions between nonpolar molecules
require the presence of surrounding water molecules
are the result of strong repulsion between water and nonpolar molecules
result from the tendency of water to maximize contact with nonpolar molecules
require the presence of surrounding water molecules
Which of the following is a characteristic of Chargaff’s rules?
A+T = C+G
A+G = C+T
A+G = C+U
all organisms have identical amounts of all four nucleotides
none of the above
A+G = C+T
What type of bond is made between nucleotides?
ester
phosphate ester
phosphodiester
glycosidic
none of the above
phosphodiester
If instead of four different bases in DNA and RNA there were six, what is the minimum size of a codon to encode the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins?
1
2
3
4
cannot be determined
2
The presence of _ approximately one in every 1000 base pairs is what makes each individual human genome genetically unique
horizontal genes
transposable elements
single nucleotide polymorphisms
homologous genes
orphan genes
single nucleotide polymorphisms
The triplet code allows many amino acids to be specified by more than one codon. Such a code is said to be _
degenerate
An open reading frame is defined by
a start and stop codon
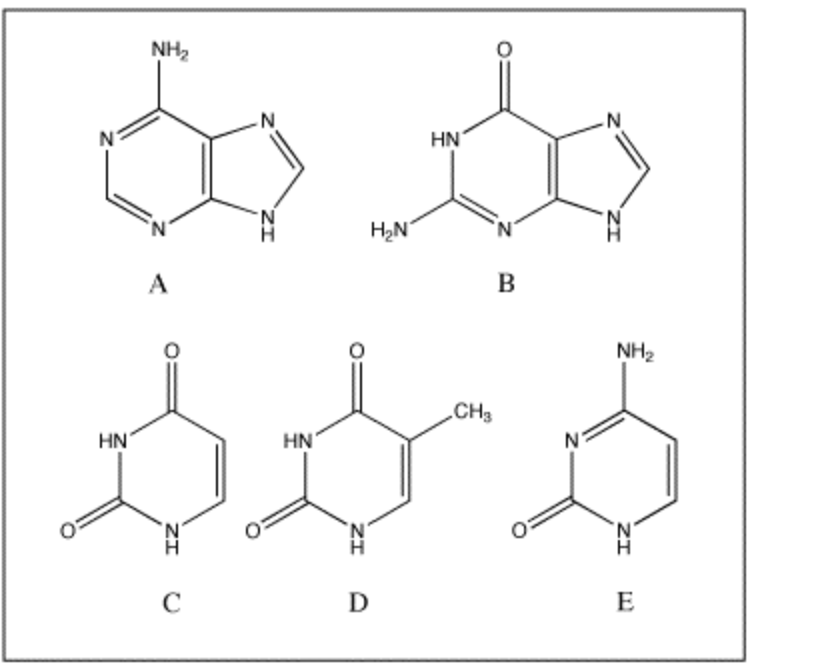
Which of the following bases pairs with guanine?
E
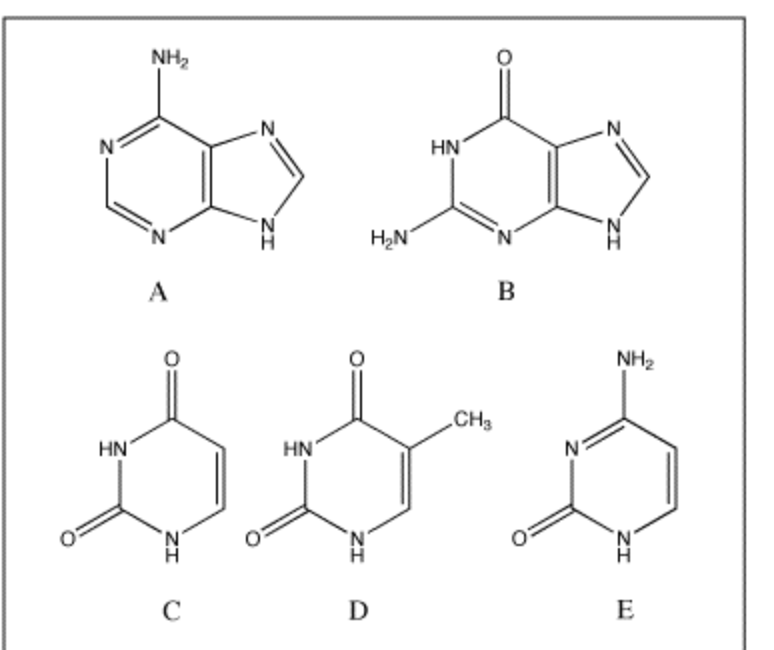
Which of the following bases is not present in RNA?
D
Nucleotides contain one or more phosphate groups that are usually attached to the __
C-3’ or C-5’ atoms
C-3 or C-3’ atoms
C-5 or N-3 atoms
C-1’ or N-3 atoms
none of the above
C-3’ or C-5’ atoms
Mutations leading to changes that can be inherited by the next generation have to be introduced at the _ level
mRNA
protein
DNA
tRNA
rRNA
DNA
When a peptide bond forms a(n) _ reacts with a carboxylate group
amide
amine
alcohol
ester
none of these choices
amine
At a pH above its pKA, the R-group of Asp is _
protonated and neutral
protonated and positively charged
deprotonated and neutral
deprotonated and negatively charged
none of these choices
deprotonated and negatively charged
Disulfide bonds form between two residues of which amino acid?
Met
Ser
Cys
Thr
Asn
Cys
What is the net charge of the pentapeptide Ala-Cys-Ser-Glu-Asn at pH 7?
-2
-1
0
+1
none of these choices
-1
Since there are 20 standard amino acids, the number of possible linear polypeptides of length N can be expressed as _
20^N

Which of the following best describes the peptide backbone in B-sheet?
highly extended
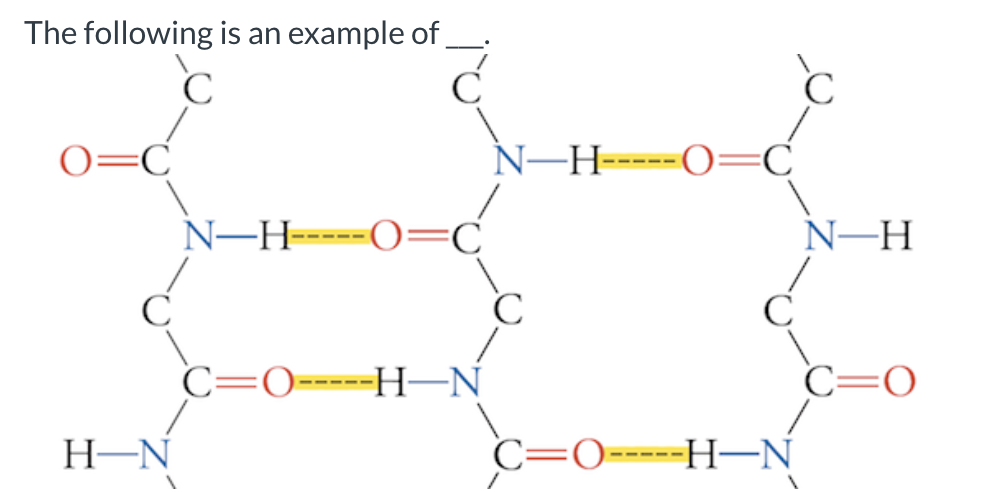
antiparallel B-sheet
The side chain of serine could interact with the side chain of _ using an _
Val; hydrophobic interaction
His; hydrogen bond
Gln; hydrophobic interaction
Asn; electrostatic interaction
none of these choices
His; hydrogen bond
Molecular chaperones assist proteins in the formation of _
aggregates
tertiary structure
peptide bonds
primary structure
none of these choices
tertiary structure
Given pKa values of 2.3 and 9.7, what is the pI of alanine?
12
7.4
6
4.2
none of these choices
6
Heme is considered a _
catalyst
prosthetic group
coenzyme
cofactor
none of the above
prosthetic group
The individual hemoglobin subunits and myoglobin share similar _ structure but have rather different _ structure
secondary and tertiary; primary
secondary; tertiary
primary; tertiary
primary and secondary; tertiary
primary; secondary
secondary and tertiary; primary
A plot of the binding of oxygen to myoglobin as a function of pO2 gives a _ shape; a similar plot for hemoglobin gives a _ shape
hyperbolic; sigmoidal
sigmoidal; sigmoidal
hyperbolic; hyperbolic
hyperbolic; exponential
sigmoidal; hyperbolic
hyperbolic; sigmoidal
Which of the following best explains the ability for carbon monoxide (CO) to bind to hemoglobin (Hb) despite the relatively low concentrations of CO?
CO binds to Hb about 250 times more strongly than oxygen
Hemoglobin S, the variant responsible for the misshapen red blood cells characteristic of the disease sickle-cell anemia, is potentially advantageous to heterozygotes because it confers some level of resistance to the disease _
malaria
When a cell moves along a surface, actin _ occurs at the leading edge while _ occurs at the trailing edge
polymerization, depolymerization
depolymerization, polymerization
denaturation, renaturation
renaturation, denaturation
none of the above
polymerization; depolymerization
The idea that binding of one molecule of oxygen to hemoglobin enhances further binding of oxygen to hemoglobin is called _
cooperativity
The helical structure of collagen contains:
three right-handed helices wound around each other in a right-handed triple helix
three right-handed helices wound around each other in a left-handed triple helix
three left-handed helices wound around each other in a left-handed triple helix
three left-handed helices wound around each other in a right-handed triple helix
none of the above
three left-handed helices wound around each other in a right-handed triple helix
Which of the following correctly describes the sequence of events in the myosin-actin cycle?
myosin release from actin, ATP binds to myosin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, release of Pi and ADP, stretched myosin returns to original conformation
ATP binds to myosin, myosin release from actin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, stretched myosin returns to original conformation, release of Pi and ADP
ATP binds to myosin, myosin release from actin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, release of Pi and ADP, stretched myosin returns to original conformation
myosin release from actin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, ATP binds to myosin, stretched myosin returns to original conformation, release of Pi and ADP
myosin release from actin, ATP binds to myosin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, stretched myosin returns to original conformation, release of Pi and ADP
ATP binds to myosin, myosin release from actin, myosin binds to another actin subunit, release of Pi and ADP, stretched myosin returns to original conformation
Which of the following correctly describes the sequence of events in the kinesin reaction cycle? For simplicity, the two heads are referred to as head 1 and head 2. Head 1 starts as the leading head.
ATP binds to head 1, head 2 swings forward, ADP release from head 2, ATP hydrolysis in head 1, head 2 binds to tubulin, head 1 releases tubulin
none of the above
ATP binds to head 1, head 2 swings forward, head 2 binds to tubulin, ADP releases from head 2, ATP hydrolysis in head 1, head 1 releases tubulin
head 1 releases tubulin, ATP binds to head 1, head 2 swings forward, head 2 binds to tubulin, ADP release from head 2, ATP hydrolysis in head 1
ATP binds to head 1, head 2 swings forward, head 2 binds to tubulin, ATP hydrolysis in head 1, ADP release from head 2, head 1 releases tubulin
ATP binds to head 1, head 2 swings forward, head 2 binds to tubulin, ADP releases from head 2, ATP hydrolysis in head 1, head 1 releases tubulin
Which of the following biopolymers is correctly paired with the bond that forms between the monomers?
protein; ester bond
polysaccharide; glycosidic bond
DNA; phosphate bond
RNA; phosphate bond
all of the above
polysaccharide; glycosidic bond
Which of the following elements are found in simple carbohydrates?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and phosphorus
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur
none of the above
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
If a reaction at 37 degrees Celsius has a delta H of 23 kJ/mol and a delta S of 337 kJ/Kmol, what is the delta G for the reaction?
65 kJ/mol
-47 kJ/mol
18 kJ/mol
-81 kJ/mol
none of the above
-81 kJ/mol

-52 kJ.mol
-10 kJ/mol
10 kJ/mol
52 kJ/mol
none of the above
-10 kJ/mol
Photosynthetic organisms use energy from the sun to reduce _ to _
formaldehyde; ethanol
CO2; ethanol
CO2; carbohydrates
CO2; oxygen
none of the above
CO2; carbohydrates
The similarity of one organism to another (for example a bacteria versus a human) is most easily done by comparing which biopolymer?
nucleic acids
polysaccharides
proteins
lipids
all of the above
nucleic acids
The second law of thermodynamics states _
that spontaneous processes are characterized by the overall conversion of order to disorder
Calculate the delta G for a reaction with delta H = 20 kJ/mol and delta S=20 J/Kmol that is carried out at 27 degrees C.
14 J/mol
140 J/mol
1,400 J/mol
14,000 J/mol
none of the above
14,000 J/mol
hydrogen bonds within liquid water are _
ion-induced dipole interactions
attractions between the protons of the oxygen nuclei
dipole-dipole interactions
attractions between the H+ and OH- ions of the liquid
attractions between two oxygen atoms
dipole-dipole interactions
What is the C-terminal amino acid in the pentapeptide Val-Leu-Arg-Ser-Gly?
Arg
Leu
Ser
Gly
Val
Gly
Which of the following amino acids contains a side chain that is polar and uncharged from pH 1-13
Tyr
Phe
Ile
Gln
Asp
Gln
Which of the following is generally absent from an alpha helix?
Trp
Ser
Ile
Pro
none of these choices
Pro
Lysine can form a salt bridge by interacting with the side chain of:
Glu
Ser
Asn
Gly
Pro
Glu
If the following mixture of proteins was applied to a size-exclusion chromatography column, what would be the order of elution? Proteins with molecular weights: myoglobin (17.7 kDa), hemoglobin (64.5 kDa), lysozyme (14.3 kDa), and triose phosphate isomerase (57.4 kDA)
lysozyme, myoglobin, triose phosphate isomerase, hemoglobin
triose phosphate isomerase, hemoglobin, lysozyme, myoglobin
hemoglobin, myoglobin, lysozyme, triose phosphate isomerase
hemoglobin, triose phosphate isomerase, myoglobin, lysozyme
cannot be determined
hemoglobin, triose phosphate isomerase, myoglobin, lysozyme
A technique for determining protein structure where the protein is in solution is:
NMR spectroscopy
X-ray crystallography
electron crystallography
mass spectrometry
none of these choices
NMR spectroscopy
Noncovalent forces that stabilize protein structure include all of the following except:
the hydrophobic effect
hydrogen bonding
disulfide bridges
salt bridges
electrostatic interactions with metal ions
disulfide bridges
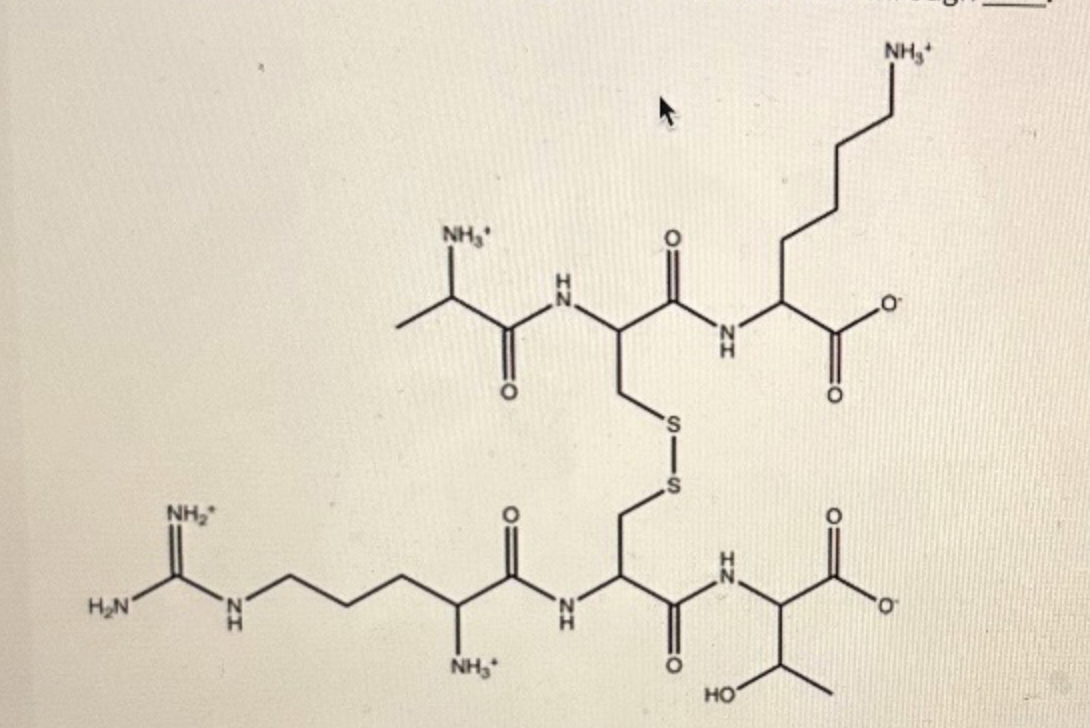
The two peptides shown in the diagram below are linked through:
a hydrogen bond
an ester linkage
a glycosidic bond
a disulfide bond
a peptide bond
a disulfide bond
Which of the following explains the conversion of hemoglobin subunits from deoxy to oxy state?
all four subunits switch simultaneously
each subunit switches only upon oxygen binding to the particular subunit
both alpha subunits simultaneously switch first followed by both B subunits
both B subunits simultaneously switch first followed by both alpha subunits
none of the above
all four subunits switch simultaneously
Which allosteric effector has the greatest ability to stabilize the deoxy state of hemoglobin?
BPG
CO2
O2
H+
all of the above have equal ability
BPG
Which of the following details the nucleotide-binding site when tubulin dimers assemble into microtubules?
both alpha and beta sites are bound to GTP
the alpha site is bound to GDP, the B site is bound to GTP
both alpha and B sites are bound to GDP
the alpha site is bound to GTP, the beta site is unoccupied following GTP hydrolysis and release of GDP
the alpha site is bound to GTP, the B site is bound to GDP
the alpha site is bound to GTP; the beta site is bound to GDP
Which amino acid is critical for crosslinking of keratin fibers?
Cys
Which amino acid is critical for crosslinking of collagen fibers?
Lys
Which of the following represents the longest distance traveled by a kinesin-vesicle complex?
movement of a mitochondria in a cardiac cell
movement of a neurotransmitter vesicle down the axon of a nerve cell
movement of a lipid-filled vesicle within an intestinal cell
none of the above
movement of a glucose filled vesicle to the membrane of a liver cell
movement of a neurotransmitter vesicle down the axon of a nerve cell
an exergonic process:
occurs without the addition of free energy
will have more products than reactants at equilibrium
all of the above
is spontaneous
has a delta G < 0
all of the above
entropy is used to measure
randomness
A gaseous mixture of hydrogen, water, ammonia, and methane can produce which of the biomolecules when exposed to an electrical discharge (such as lightning)
amino acids
The biological classification system categorizes organisms into which of the following domains:
bacteria, eukarya, prokarya
bacteria and eukarya
prokarya and eukarya
archaea and eukarya
bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
bacteria, archaea, and eukarya
A reaction with a _ delta H and a _ delta S will never be spontaneous
positive, negative
Nucleoside triphosphates carry energy in the form of
amide linkages
glycosidic bonds
phosphoester bonds
phosphoanhydride bonds
hydrogen bonds
phosphoanhydride bonds
In living organisms, genetic information is most often stored in the form of _
deoxyribonucleic acid
The DNA strand that serves as the template for the synthesis of RNA is often called the _
messenger strand
coding strand
transfer strand
noncoding strand
transcription strand
noncoding strand
Which of the following correctly describes the B-DNA double helix?
antiparallel strands
right-handed helix
base pairs are located in the center of the helix
one helical rotation has a rise of 3.4 nm
all of the above
all of the above
The coenzymes known as NAD+, FAD, and coenzyme A all contain a derivative of _
thymidine
guanosine
cytidine
adenosine
uridine
adenosine
In aqueous solution, globules of up to several thousand amphiphillic molecules arranged with the hydrophilic groups on the surface and the hydrophobic groups buried in the center are called _
micelles
In an aqueous solution, if the [OH-] is 3.0×10^-5 M, what is the [H+]?
7.0×10^-9
7.0×10^-2
3.3×10^-3
3.3×10^-10
none of the above
3.3×10^-10
Which of the following could be used to formulate 100 mls of a .10 M acetate buffer (pK=4.76) at pH 5 if you start with 64 mls of .10 M sodium acetate
3.6 mls of 1 M HCl
34 mls of .10 M NaOH
34 mls of .10 M HCl
3.6 mls of 1 M NaOH
36 mls of .10 M acetic acid
3.6 mls of .10 M acetic acid
Considering the energetics of transferring nonpolar molecules from water to a nonpolar solvent, the factor T delta S is generally _, causing delta G to be _
negligible; either positive or negative
negative, negative
positive, positive
positive, negative
positive, negative
Which of the following molecules would be prevented from readily crossing a lipid bilayer?
glucose
sodium ions
potassium ions
water
all of the above
all of the above
If the pK values for phosphoric acid are 2.15, 6.82, and 12.38, _ would predominate at pH 5 while _ would predominate at pH 10
H3PO4, HPO4 2-
H3PO4; PO4 3-
H2PO4 - ; HPO4 2-
H3PO4; H2PO4-
H2PO4- ; PO4 3-
H2PO4-; HPO4 2-
If a phosphate buffer (pK= 6.82) was formulated such that its pH was 7.3, it would be best suited to buffer against _. If instead, it was formulated such that its pH was 6.3, it would be best suited to buffer against:
base; acid
acid; base
acid; acid
a buffer with a pH that far from the pK would not be an effective buffer
base; base
acid; base
During vigorous exercise, hydrogen ions are produced within cells as a result of increased metabolism. what component of the intracellular buffer would increase as a result of the increased H+ production?
H3PO4
H2PO4-
PO4 3-
HPO4 2-
none of the above
H2PO4-
urea is a water-soluble product of nitrogen metabolism. how many hydrogen bonds can one urea molecule donate to surrounding water molecules?
4
2
3
5
6
4
In DNA, the ribose derivative lacks an _ on carbon _
amine; 3
none of the above
alcohol; 2
alcohol; 3
amine; 2
alcohol; 2
What type of bond is made between nucleotides?
phosphodiester
Which term describes the process of converting the information found in DNA into the sequence of a protein?
transcription
translation
expression
replication
none of the above
expression
The replication of DNA is made possible by the presence of _ strands in the double helix of DNA
genomic
complementary
antiparallel
none of the above
hydrogen bonded
complementary
Bacteria and archaea typically have fewer than _ genes while plants and animals typically have greater than _ genes
1,000; 5,000
10,000; 500,000
5,000; 10,000
200; 1,000
500; 2,500
5,000 ; 10,000
In humans, approximately _% of the genome encodes proteins
1.5
Nucleotides play a central role in living organisms because
they mediate transport of energy within the cell
they are involved in intracellular signaling
all of the above
they function as building blocks for nucelic acids
they are involved in oxidation-reduction reactions
all of the above
Which of the following explains how cell division is blocked by drugs that prevent proper microtubule function?
division of organelles between daughter cells requires organelle movement along microtubules
chromosome separate along a microtubule spindle
none of the above
production of new membranes for organelles and nucleus requires microtubules
the condensation of chromatin requires a microtubule skeleton
chromosomes separate along a microtubule spindle
During the formation of microfilaments, which of the following occurs?
F-actin polymerizes, becoming G-actin
none of the above
ATP hydrolysis is catalyzed by F-actin
polymerization proceeds quickly at first, then slows after about ten actin monomers have polymerized
ATP binds to F-actin
ATP hydrolysis is catalyzed by F-actin