Economics- Theme 2.2 + 2.3: Aggregate Demand and Supply
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:04 PM on 9/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
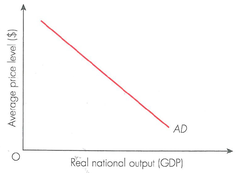
Aggregate Demand
The total level of demand in an economy at a given price level.
2
New cards
AD formula
C + I + G + (X-M)
3
New cards
Yield (Y)
Earnings generated and realized on an investment over a particular period of time.
4
New cards
Consumption
Consumer spending on goods and services
5
New cards
Disposable Income
Money consumers have left available after taxes and benefits added.
6
New cards
Investment
Increase in capital stock of an economy, leads to creating of real goods.
7
New cards
Wealth
The value/stock of assets owned
8
New cards
Government Spending
The expenditures of the Government
9
New cards
Fiscal Policy
The use of borrowing, government spending and taxation to manipulate the level of AD and improve macroeconomic performance
10
New cards
Types of Fiscal Policy
Discretionary- Implemented through policy change/ government action
Automatic stabilisers- Policies used to offset fluctuations in economic cycle but do not need government intervention or regular policy change.
Automatic stabilisers- Policies used to offset fluctuations in economic cycle but do not need government intervention or regular policy change.
11
New cards
Purpose of Fiscal Policy
Contractionary- Reduce AD
Expansionary- Increase AD
Expansionary- Increase AD
12
New cards
Exports (X)
Spending by foreign consumers on domestic goods and services.
13
New cards
Imports (M)
Spending by domestic consumers on foreign produced goods and services.
14
New cards
Net Trade (X-M)
The difference between the value of exports and imports of an economy.
15
New cards
Exchange rate
The price of a currency in terms of another
16
New cards
Aggregate Supply
The total amount of output of goods and services at a given price level in an economy.
17
New cards
Short-Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
At least one factor of production is fixed
18
New cards
Long-Run Aggregate Supply
A curve that shows the potential amount of real output that will be supplied in the economy in the long run at any given overall price level.
19
New cards
SRAS Shifts
Raw Material/ Energy/ Commodity prices- Increase= Inward, Decrease= Outward
Exchange Rate- Weak= Inward, Strong= Outward
Tax- Increase= Inward, Decrease= Outward
Exchange Rate- Weak= Inward, Strong= Outward
Tax- Increase= Inward, Decrease= Outward
20
New cards
LRAS types
Classical and Keynesian
21
New cards
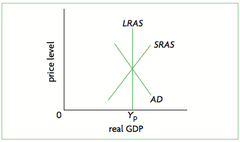
Classical LRAS
In the Long-Run AS is Inelastic and is determined by supply side policies rather than AD.
22
New cards
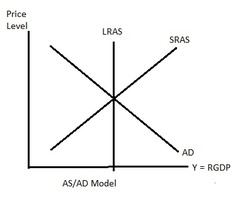
Relation Between SRAS and LRAS
SRAS will always shift during a boom or recession but will find a way to come back to LRAS (Perfect Inelastic)
23
New cards
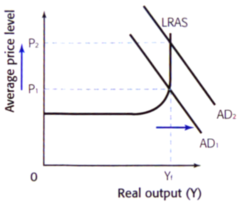
Keynesian LRAS
One Aggregate supply which is determined by the level of spare capacity within the economy.
24
New cards
Spare Capacity
When an economy is not fully utilizing its factors of production.
25
New cards
LRAS shifts
-Change in potential output or productivity
-Increase in quantity FOP
Increase in Education
-Increase in quantity FOP
Increase in Education
26
New cards
Strong Banking/ Financial sector
More money available for investment. Leads to increase in productivity. Therefore, LRAS and SRAS shift outwards.