Chapter 3: Organic Molecules
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Organic Molecules
Any molecule with a carbon and hydrogen backbone/skeleton
inorganic molecules
any molecule that is not based on a carbon and hydrogen backbone/skeleton.
- THESE MAY CONTAIN HYDROGEN AND CARBON but are not the C/H backbone
Monomer
smaller molecules that act as building blocks to build a polymer
Polymers
Larger molecules are made up of repeating units of monomers
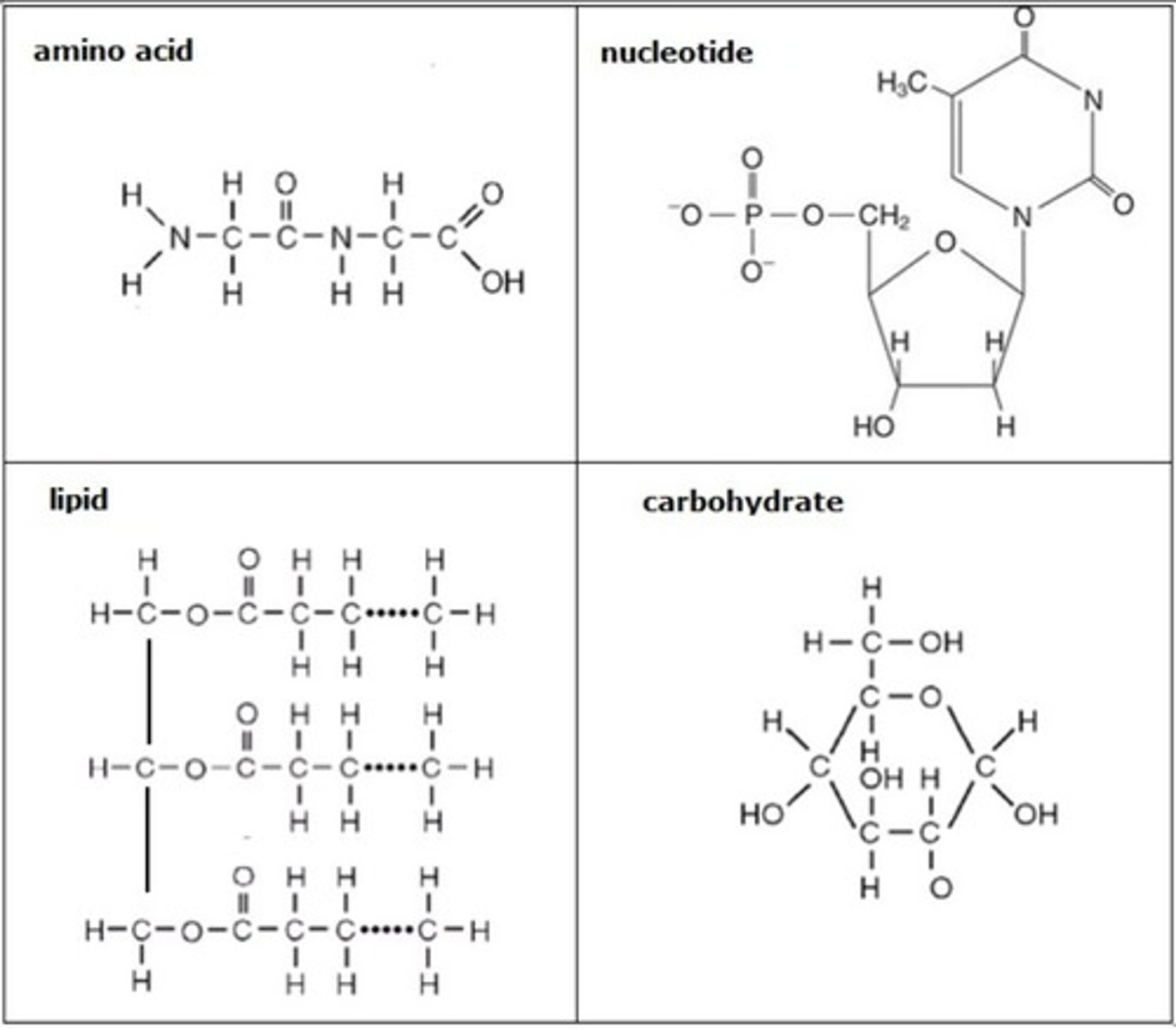
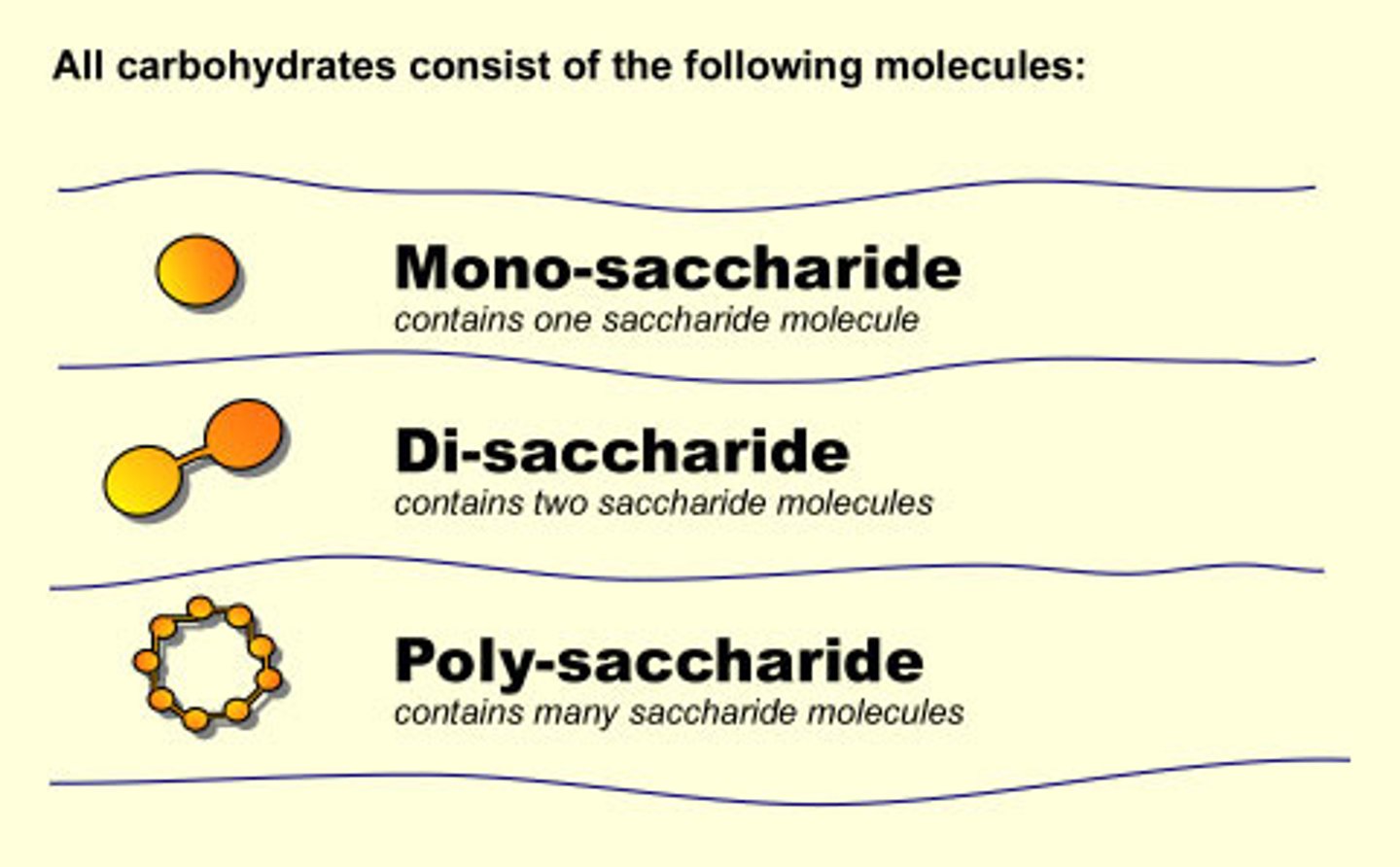
Carbohydrate (Monomer -- Polymer)
monosaccharide (glucose), polysaccharide (starch)
amino acids
monomers of proteins
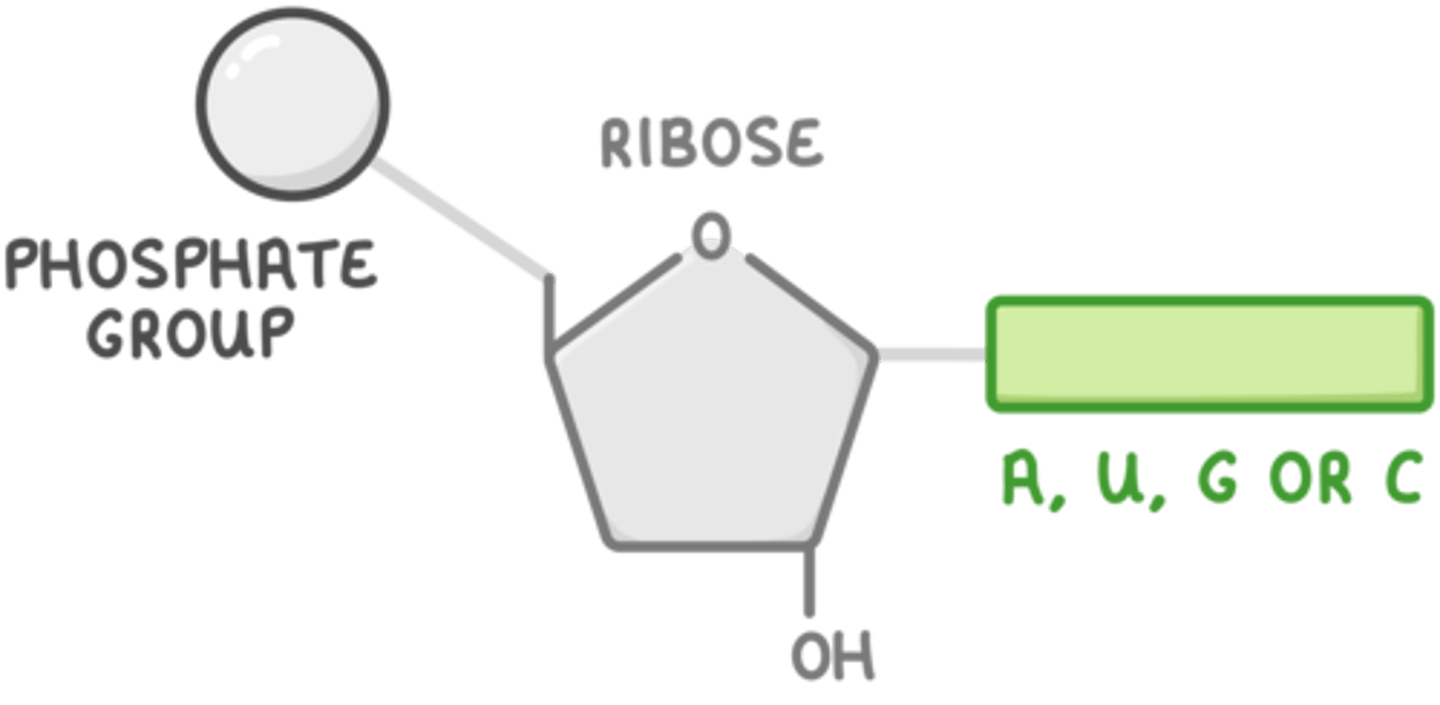
nucleotide
monomer to nucleic acid (DNA)
4 categories of organic molecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Role of Carbohydrates
provide energy
Monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
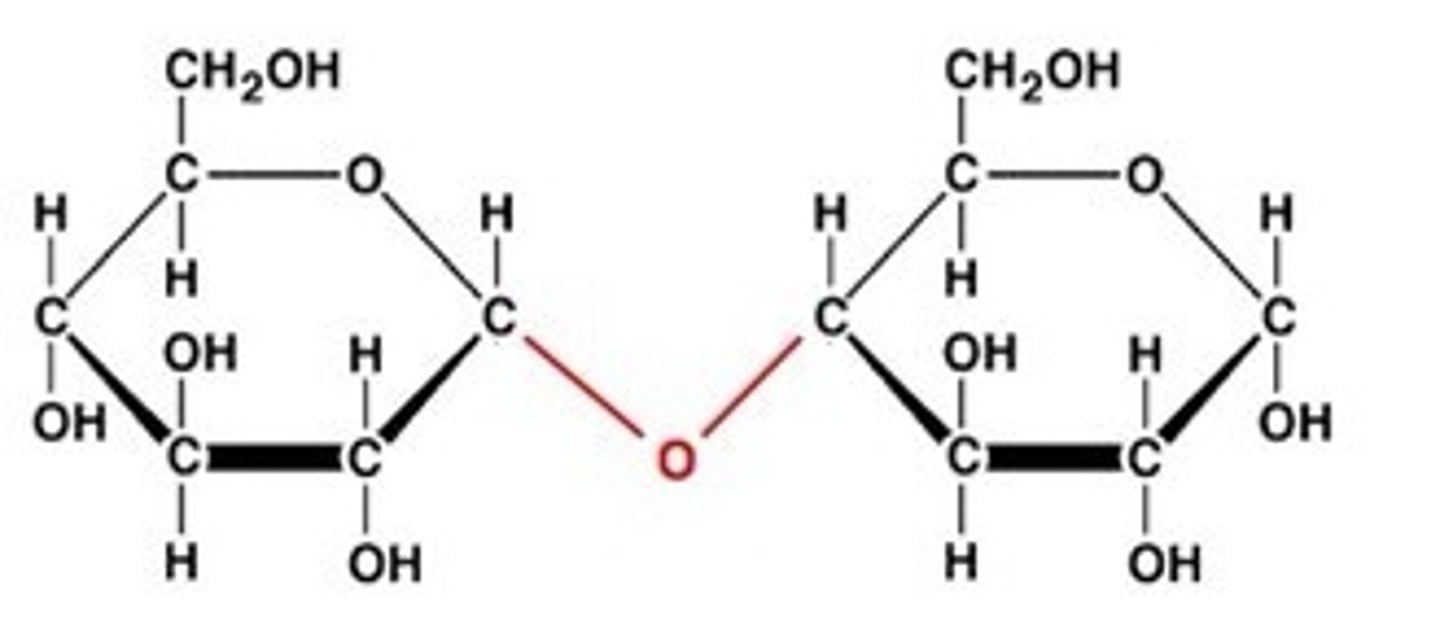
What holds carbohydrates together?
glycosidic bonds
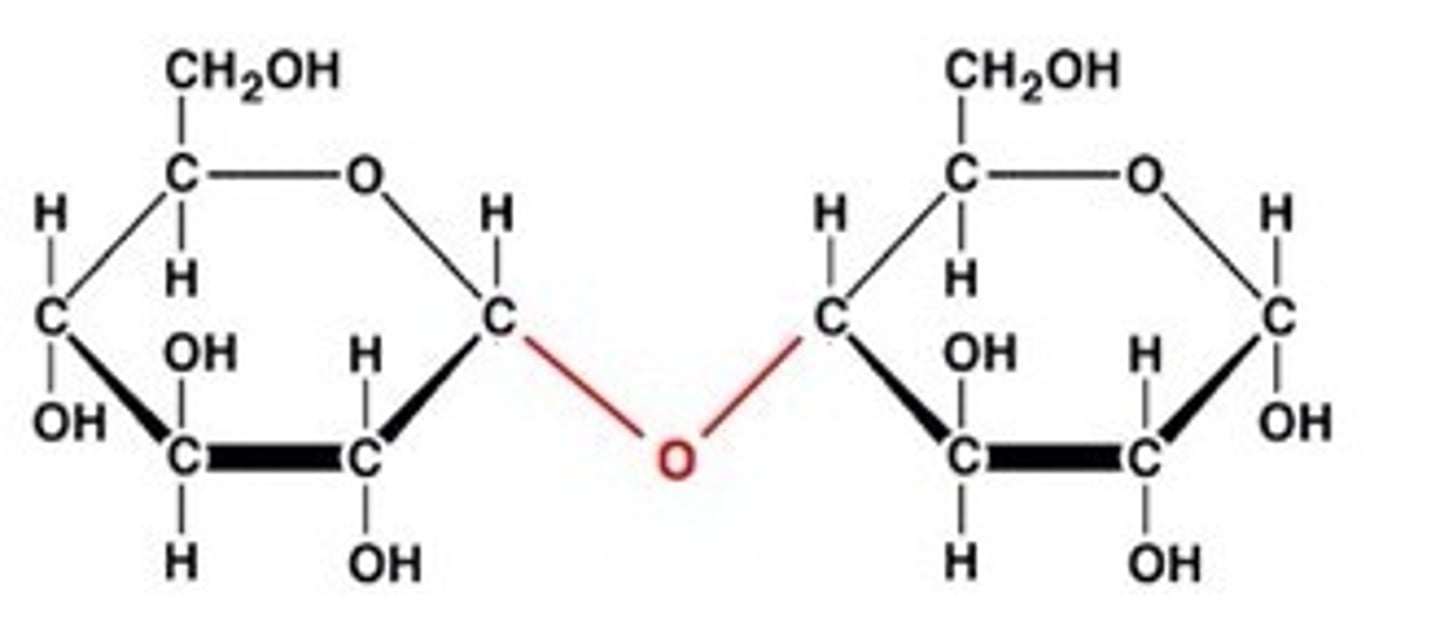
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
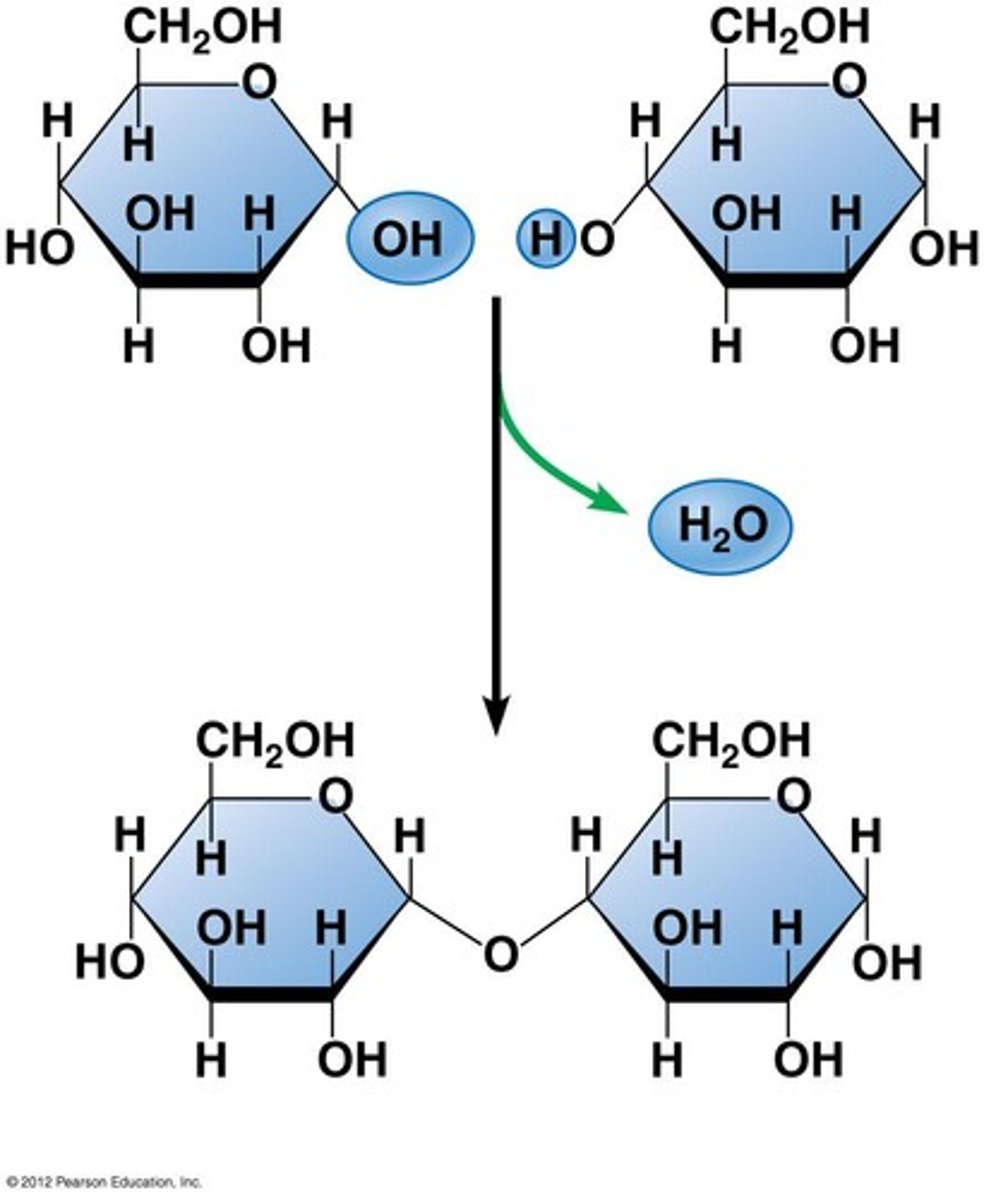
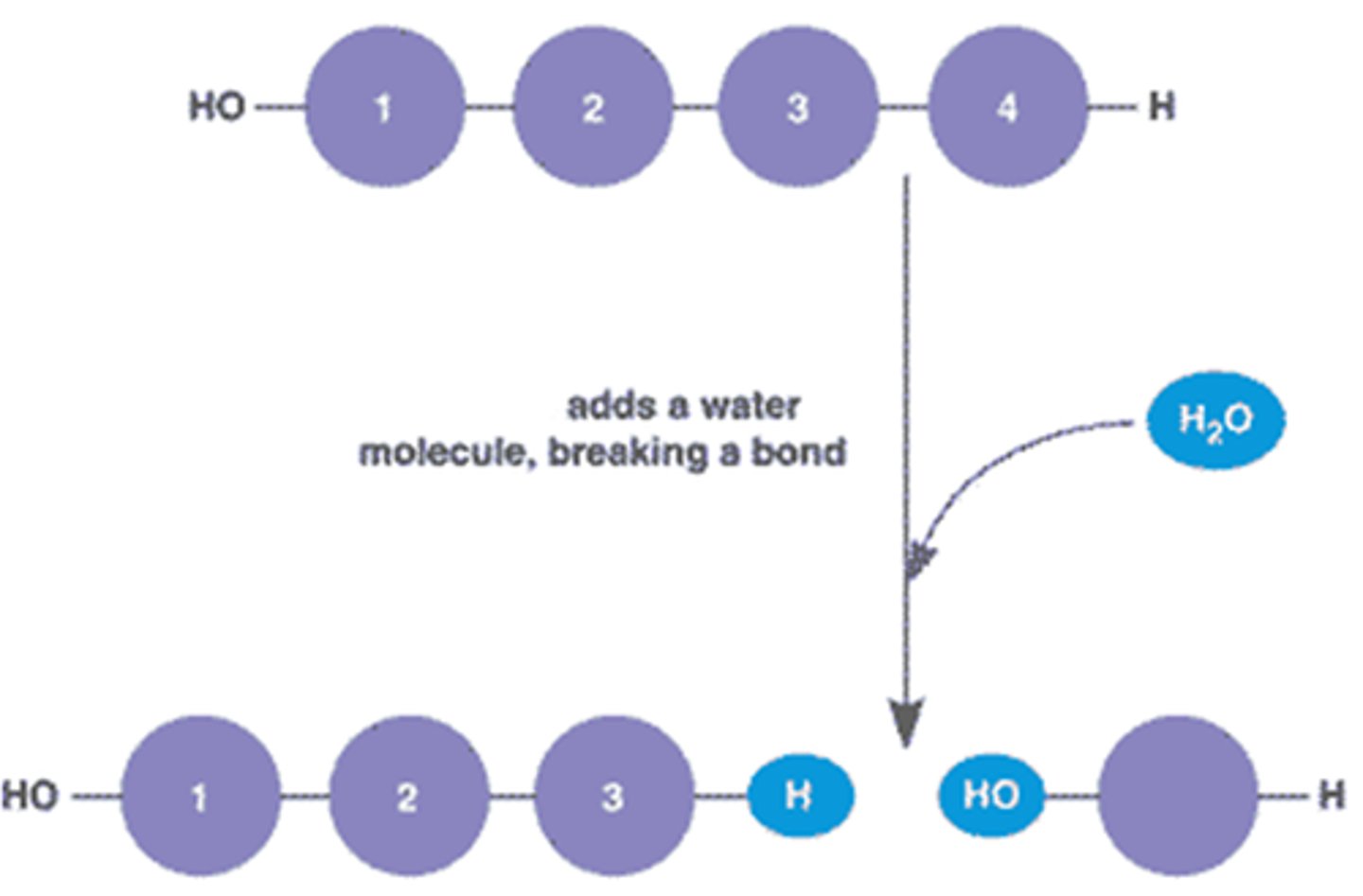
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
importance of lipids
- energy storage
- insulation
- Fat
- Organ protection
- Making hormones

fatty acid
Building Blocks of Lipids
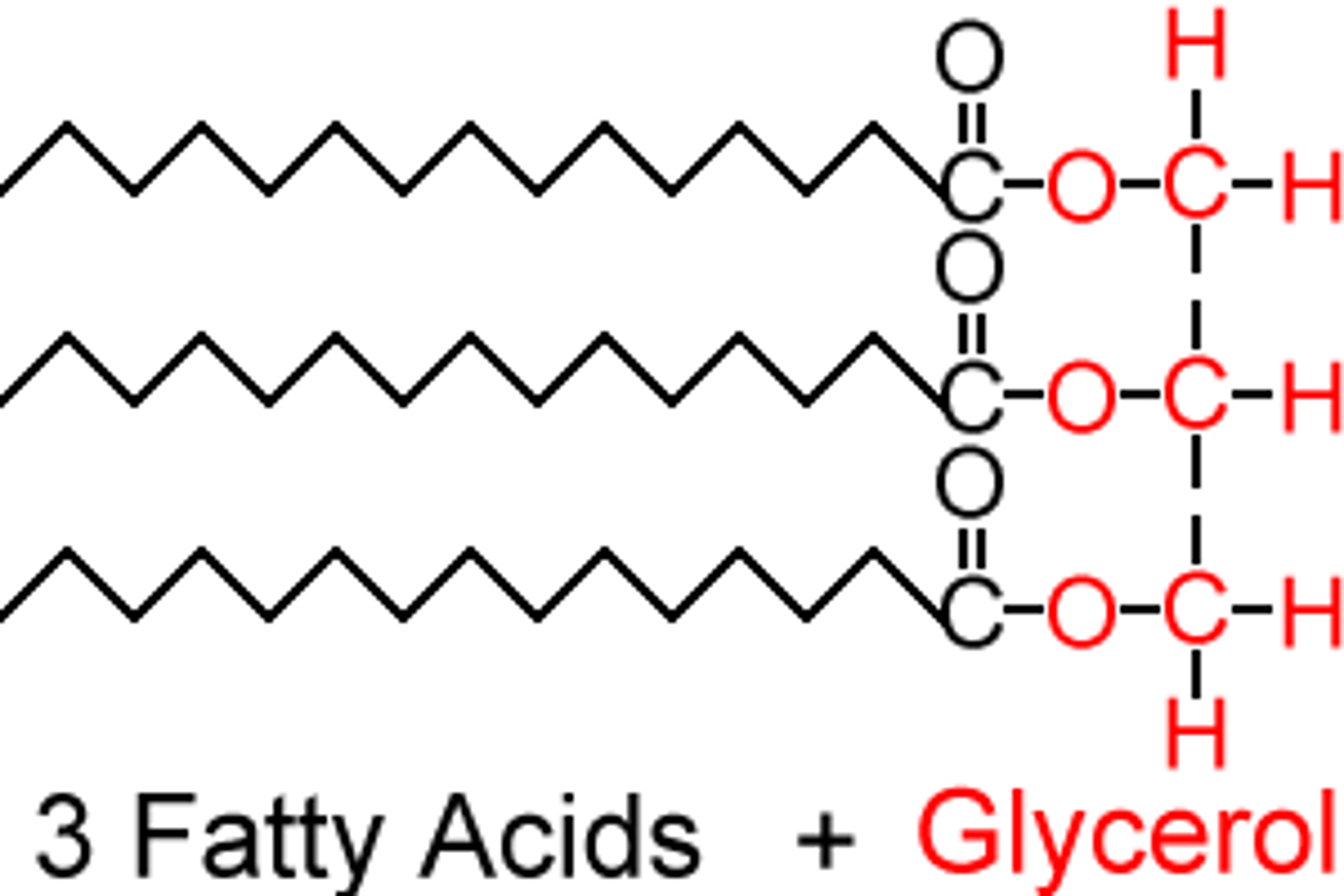
triglyceride
3 fatty acid + glycerol
Lipids include
fats, oils, waxes, steroids, phospholipids
What bonds hold lipids together?
ester bonds
amphipathic
have a polar head and a nonpolar tail
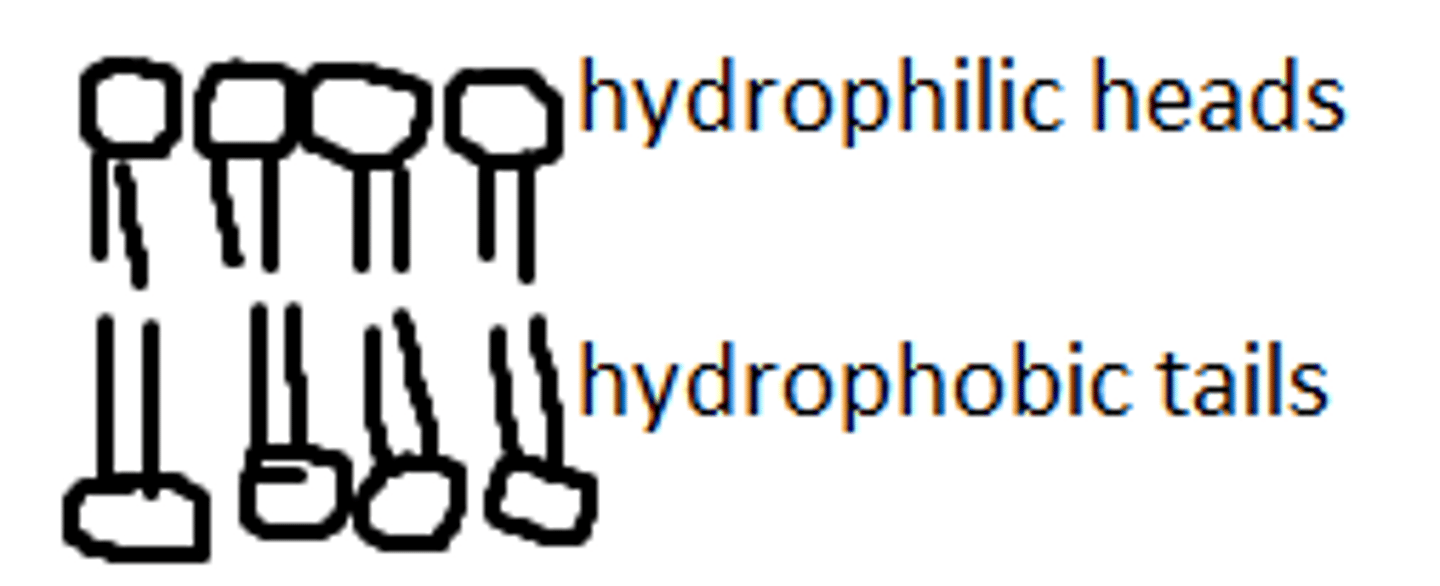
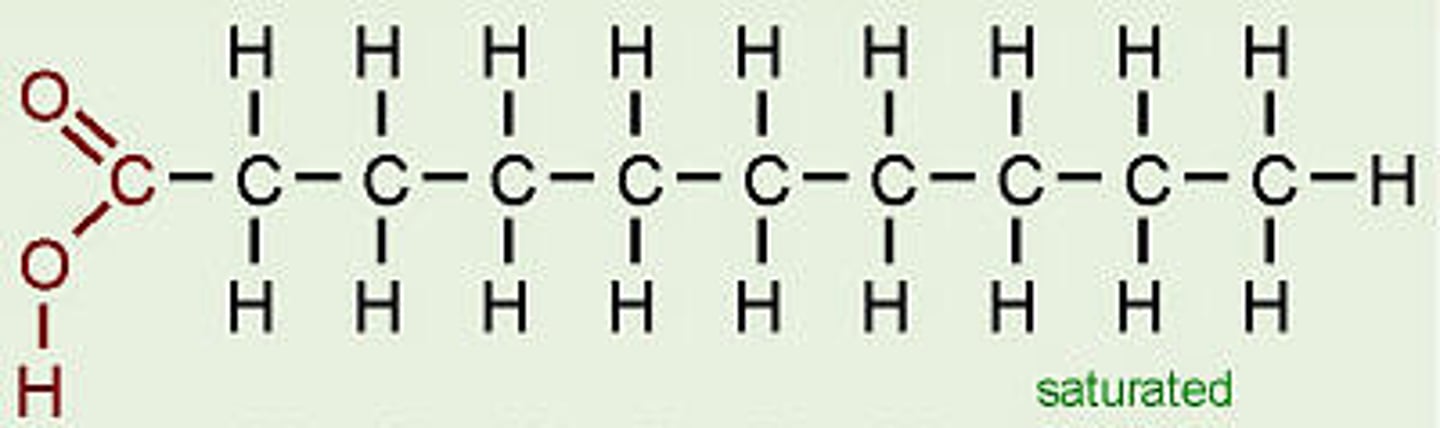
Saturated fatty acids
- no double bonds
- solid at room temperature
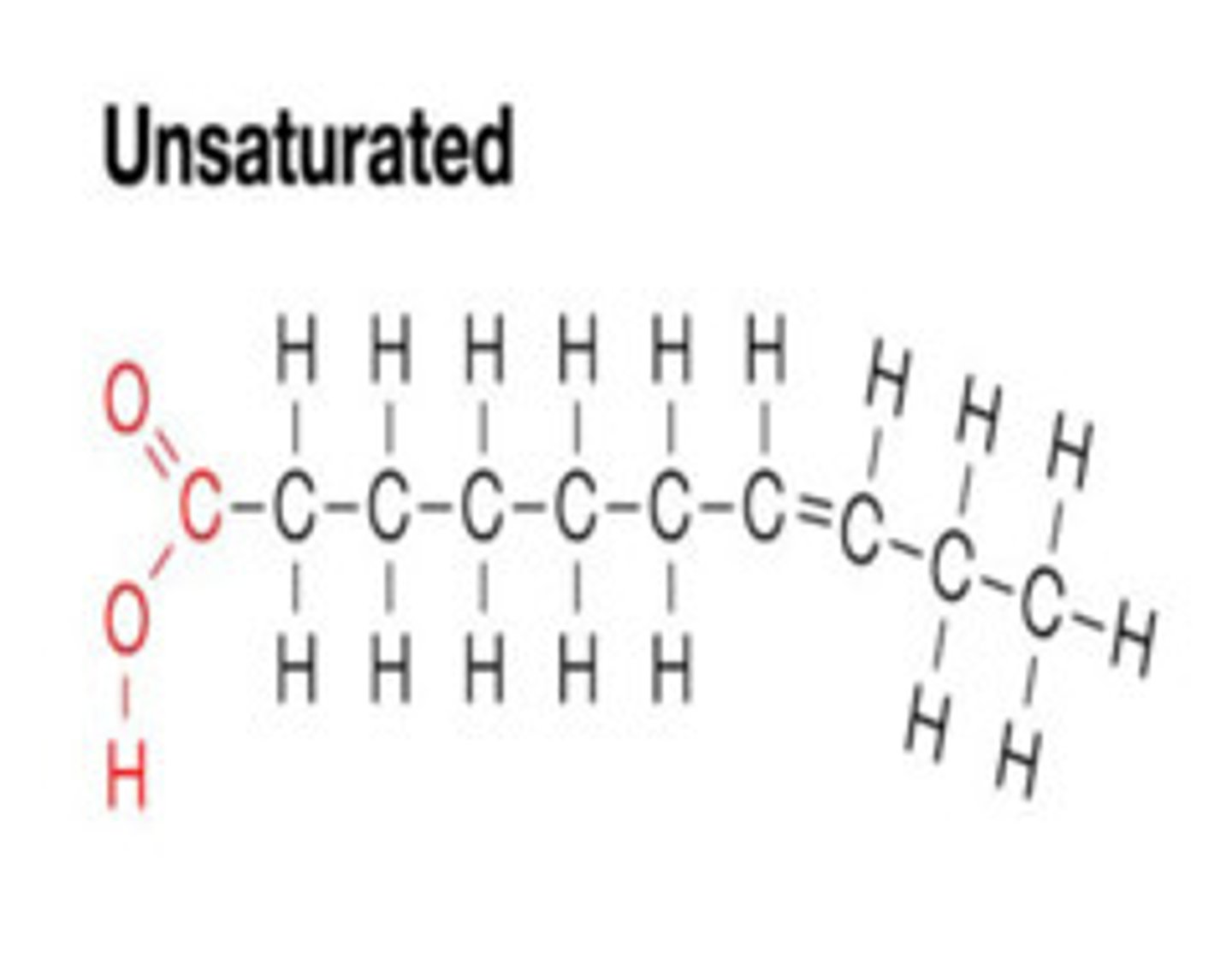
unsaturated fats
- contain at least one double bond
- liquid at room temperature
- causes a kink
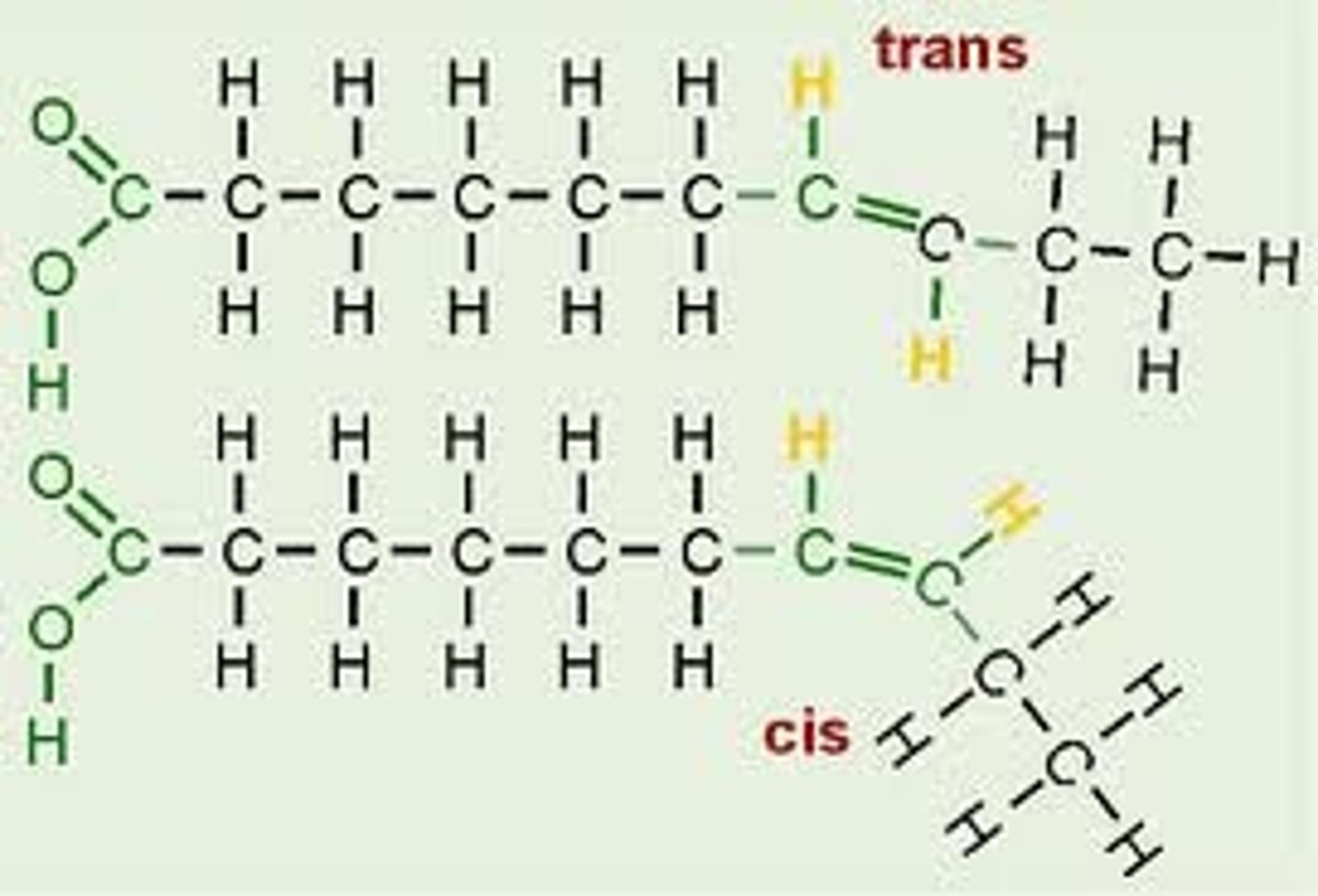
Cis or trans unsaturated fatty acids
cis= hydrogen atoms are bound to carbon atoms on the same side
trans= hydrogen atoms are bound to carbon on the opposite side
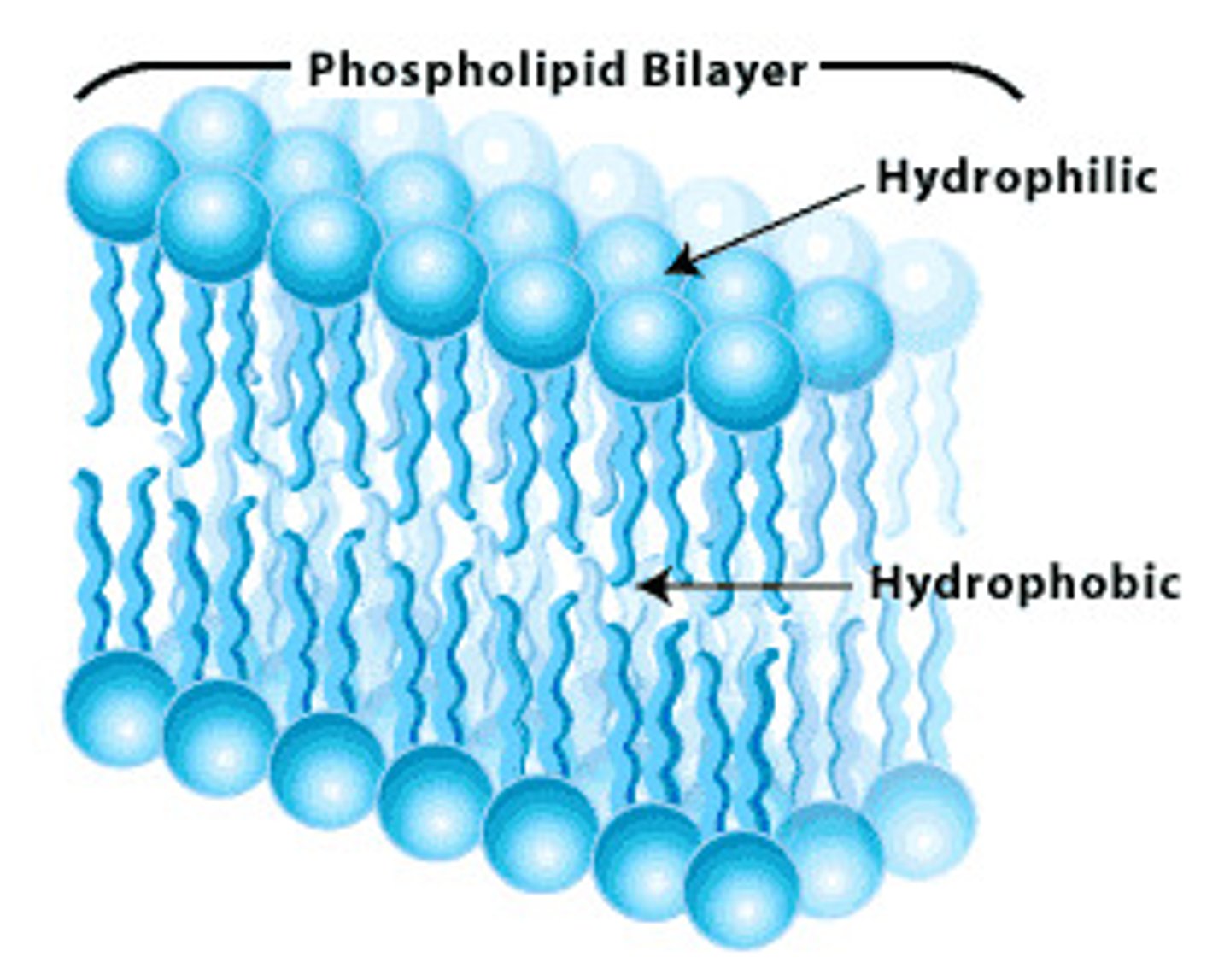
phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up plasma and organelle membranes.
function of proteins
- serve as structural support
- serve as a backbone
- formation of enzymes
- structure behind antibodies
amino acids form a
peptide bond and form a polypeptide chain
primary structure
long string of amino acids
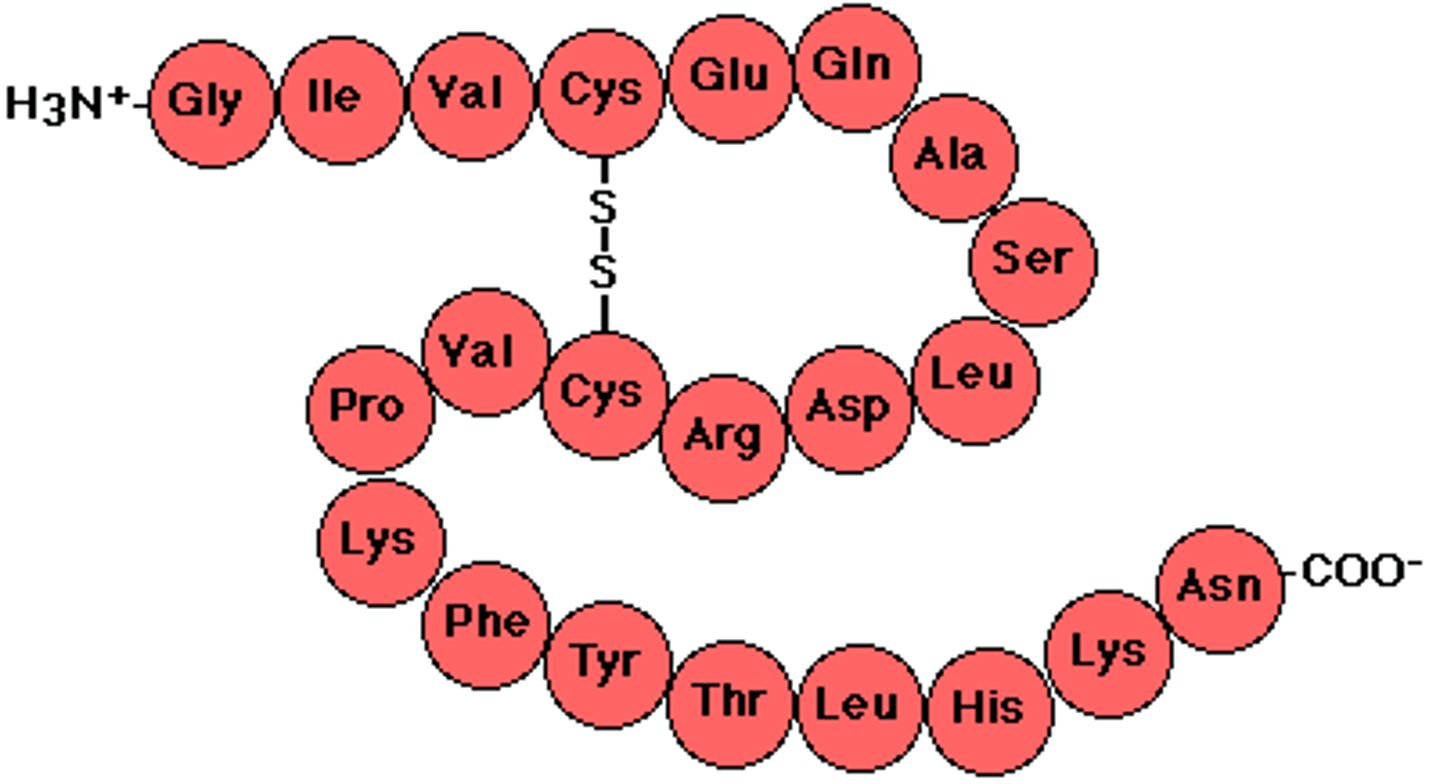
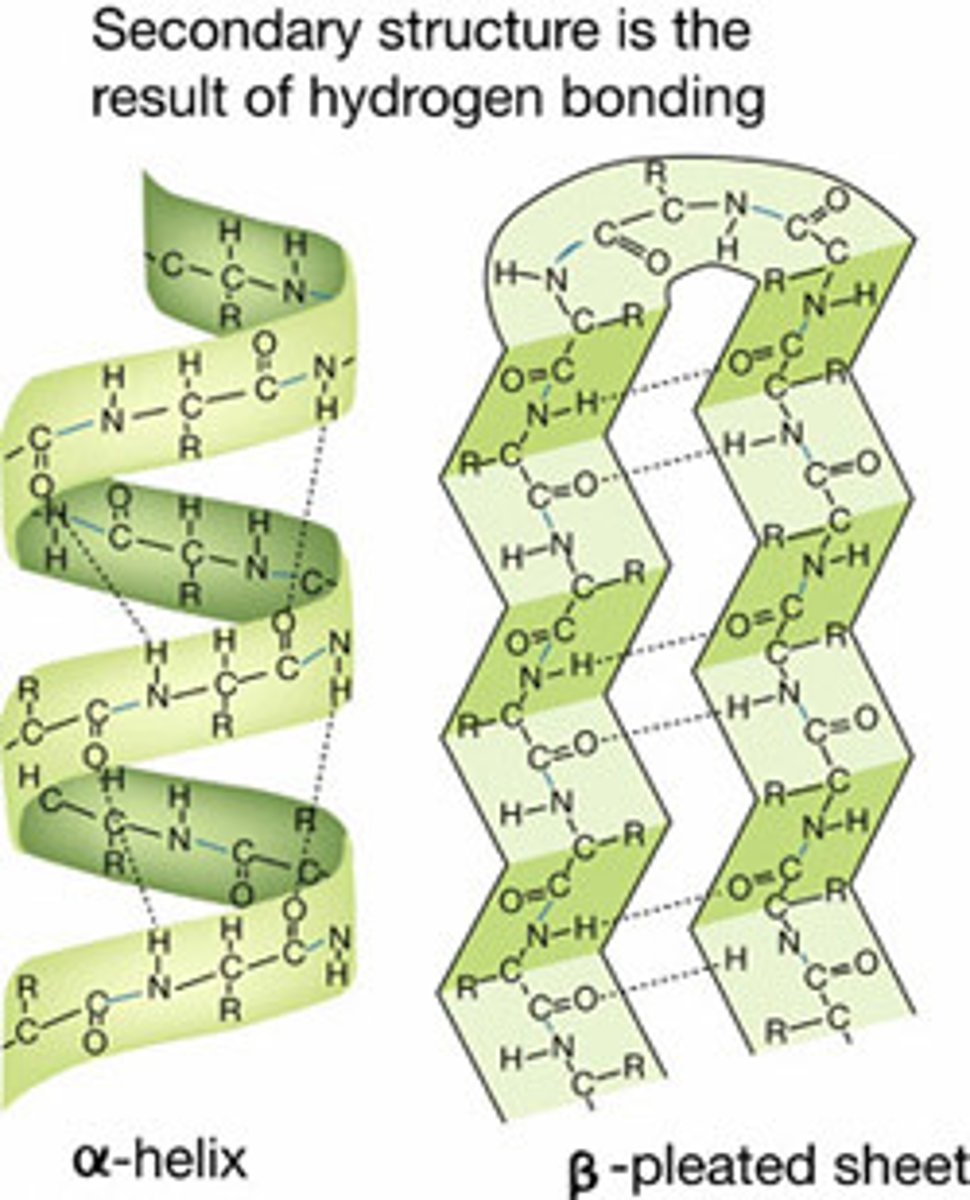
secondary structure
Either an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet.
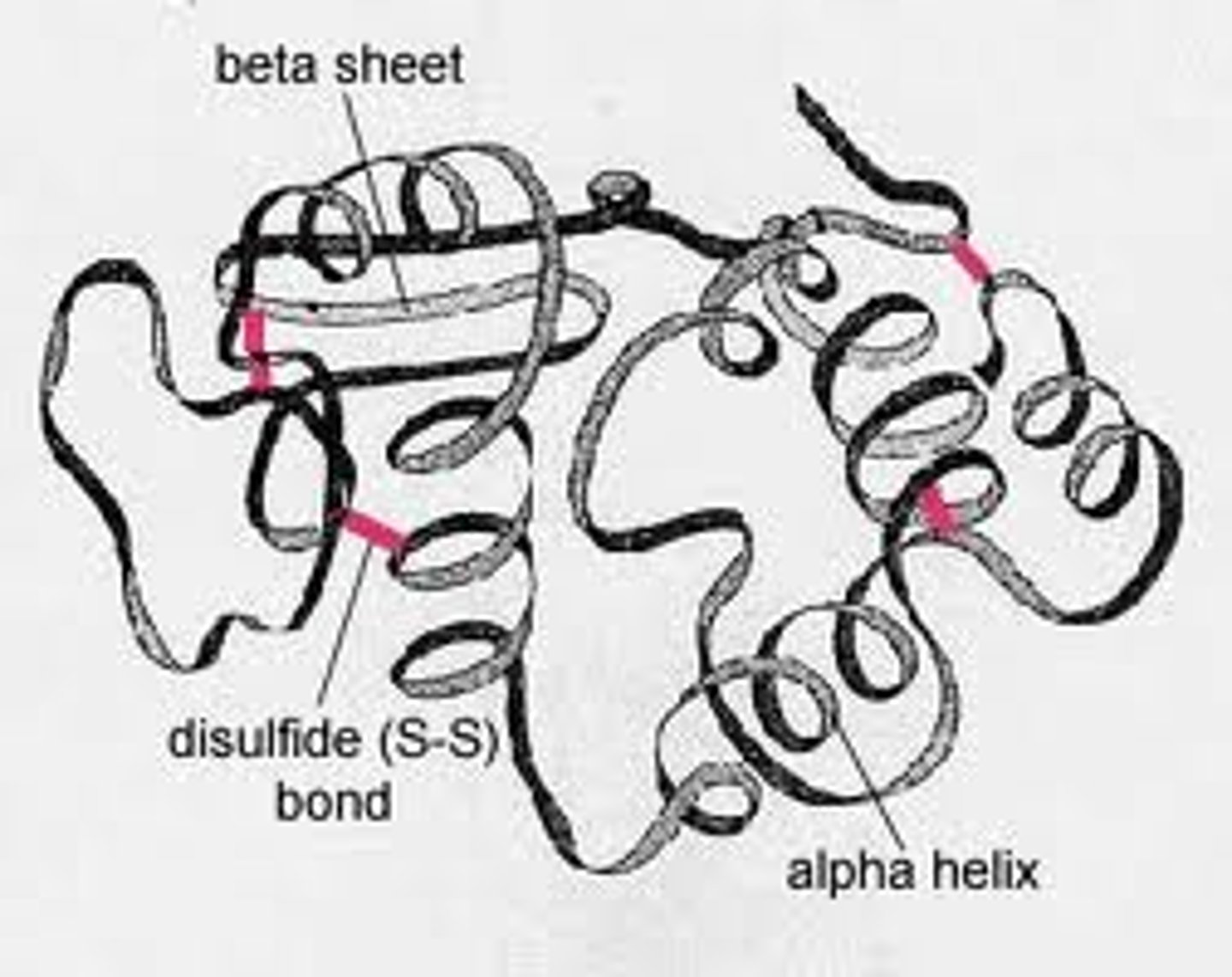
tertiary structure
multiple secondary structures
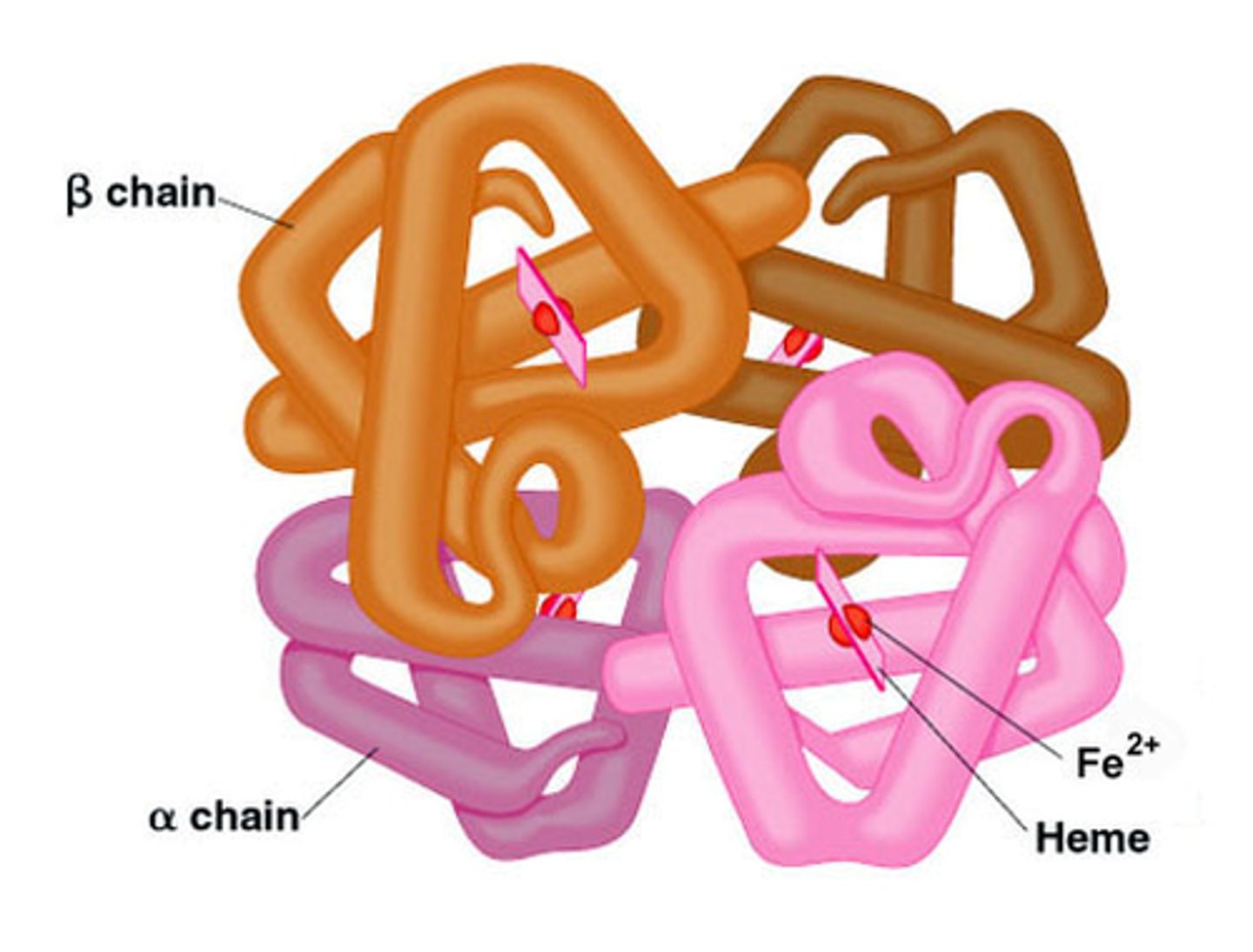
quaternary structure
multiple tertiary structures
organic catalysts
enzymes
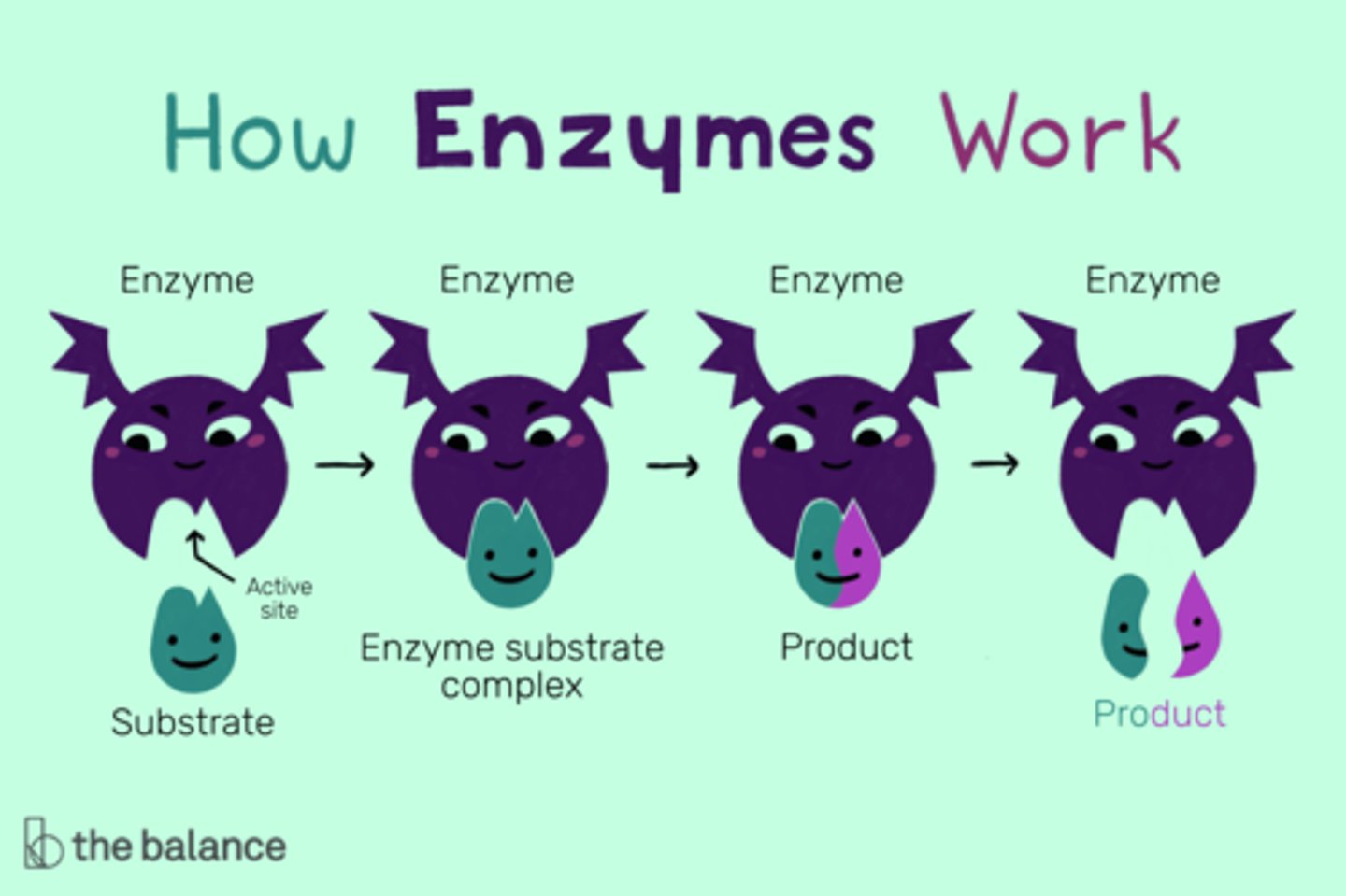
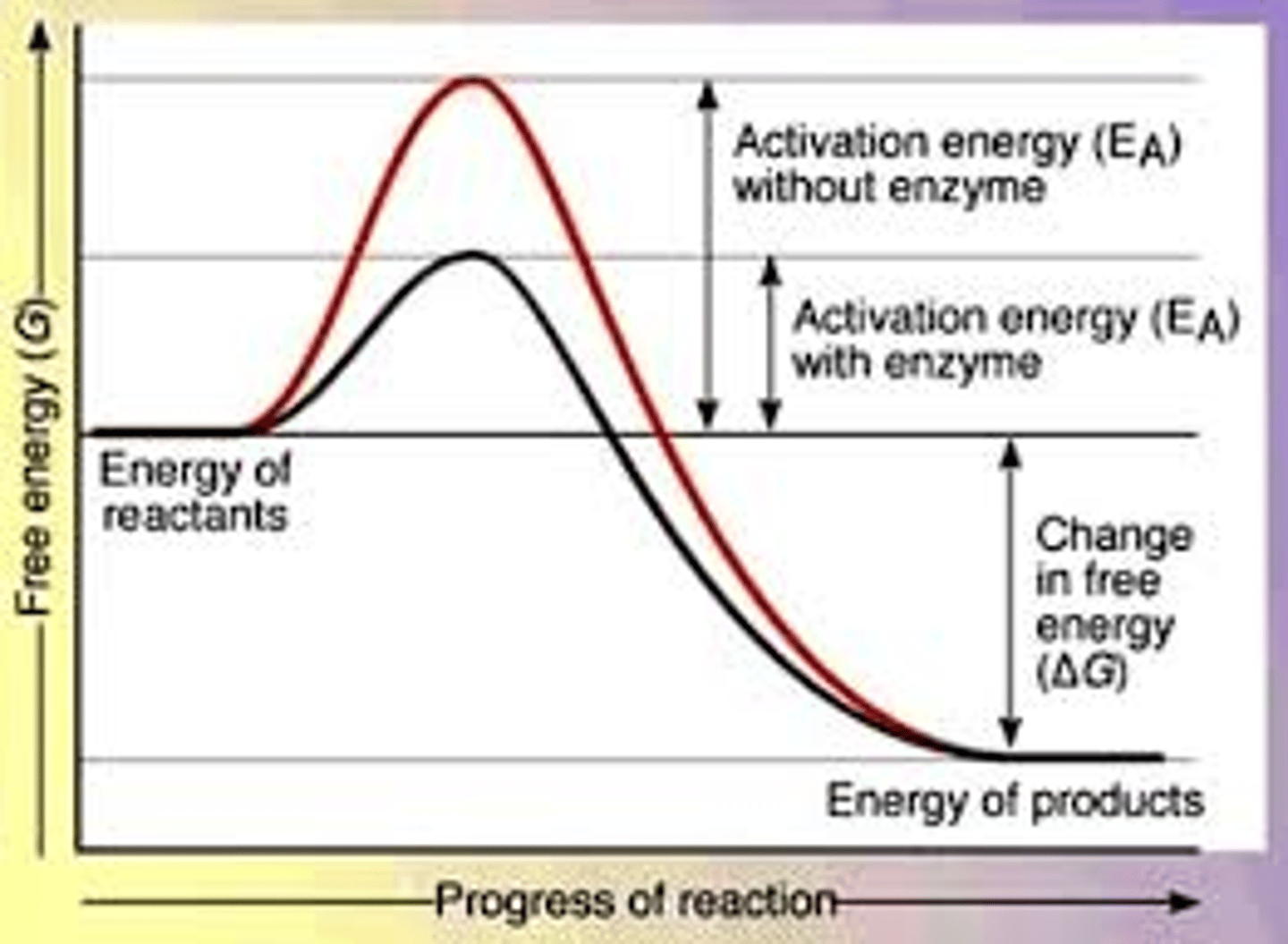
Enzymes work by _____.
lowering the activation energy
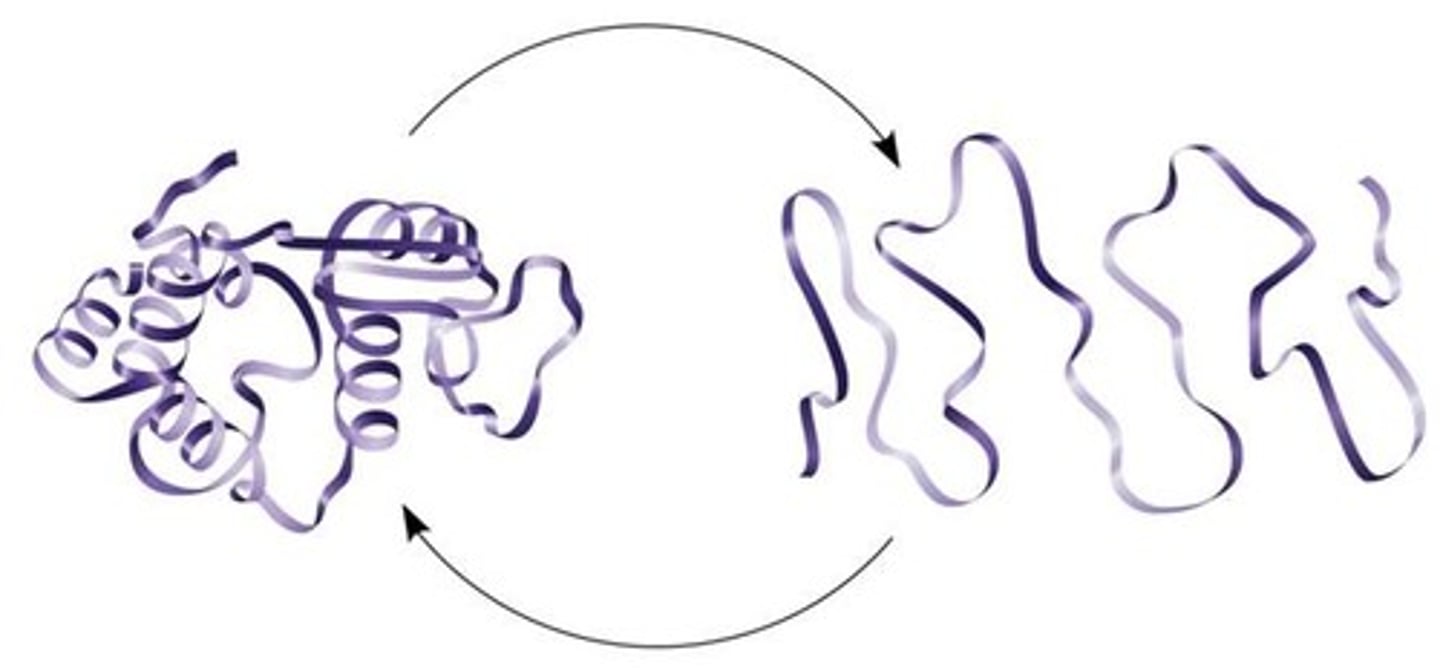
denaturation of proteins
loss of their 3D shape, and stops functioning
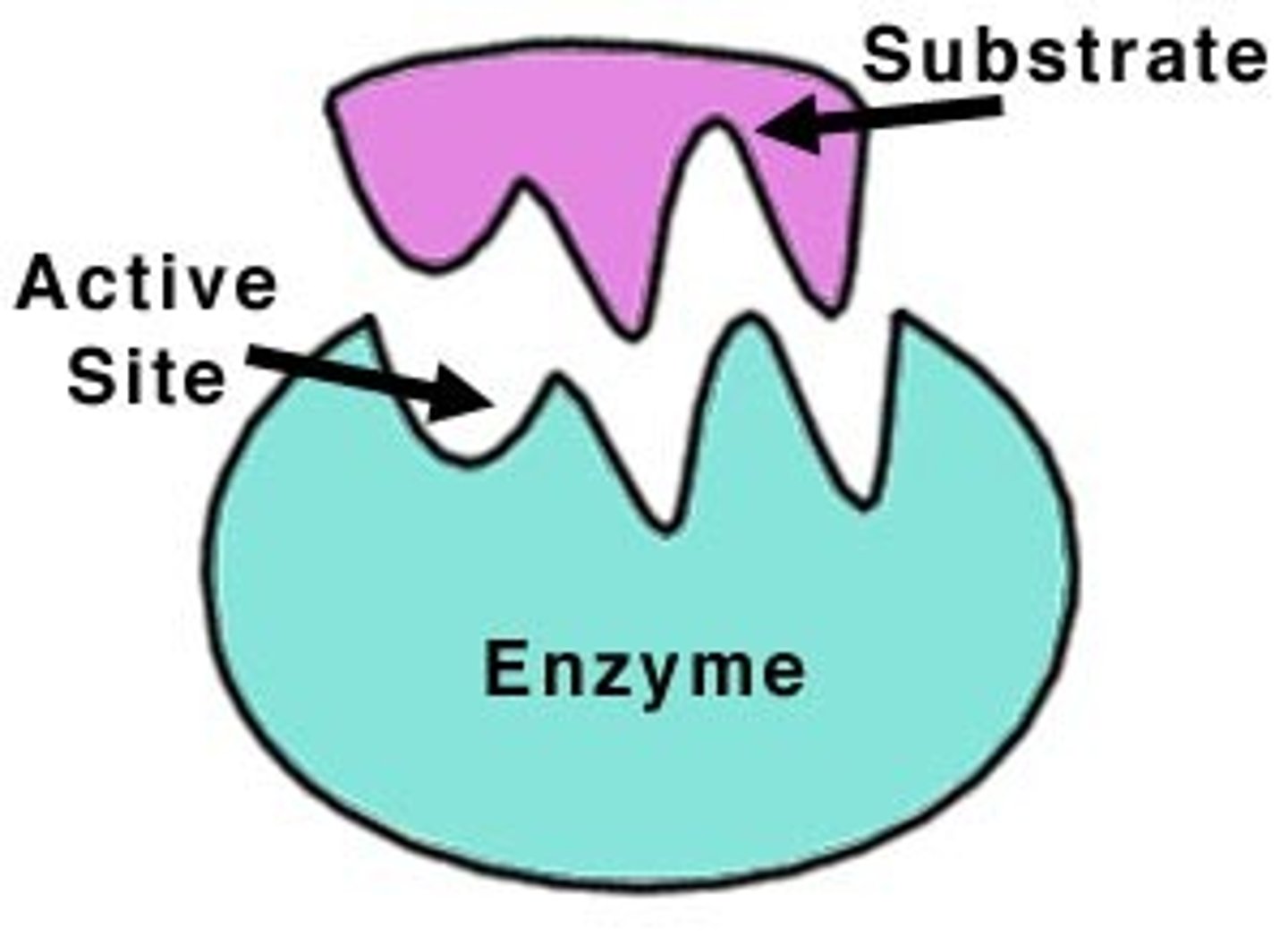
True or False: Enzymes are specific for one reaction
True, determined by their active site
True or False: Enzymes are used up in a reaction?
False, enzymes are not used up in the reaction
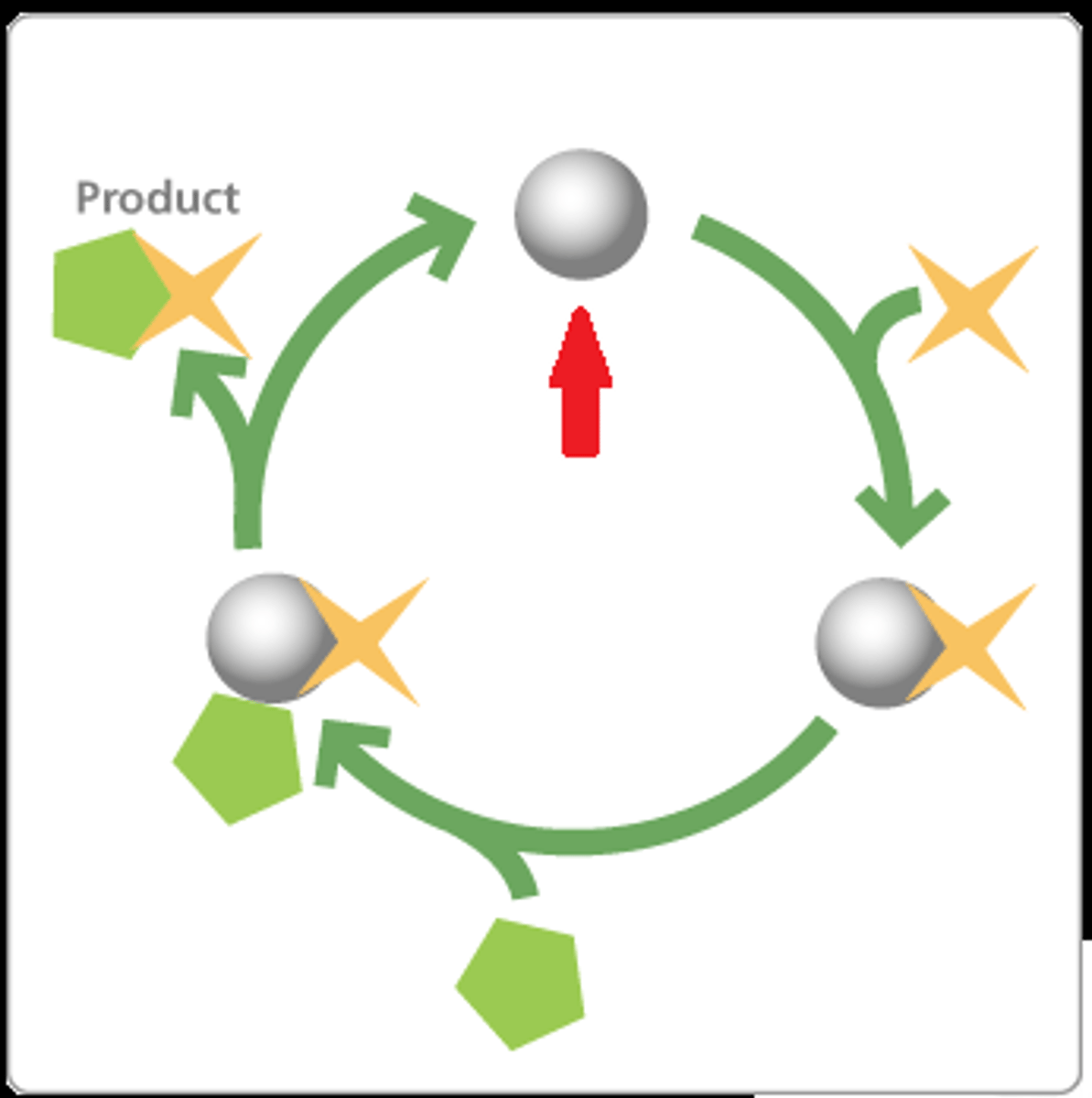
Factors that affect rates of enzymatic reactions?
Temperature: if heated, it loses its 3D shape
pH- most enzymes function best at a particular pH
- Pressure, Concentration, Inhibitors
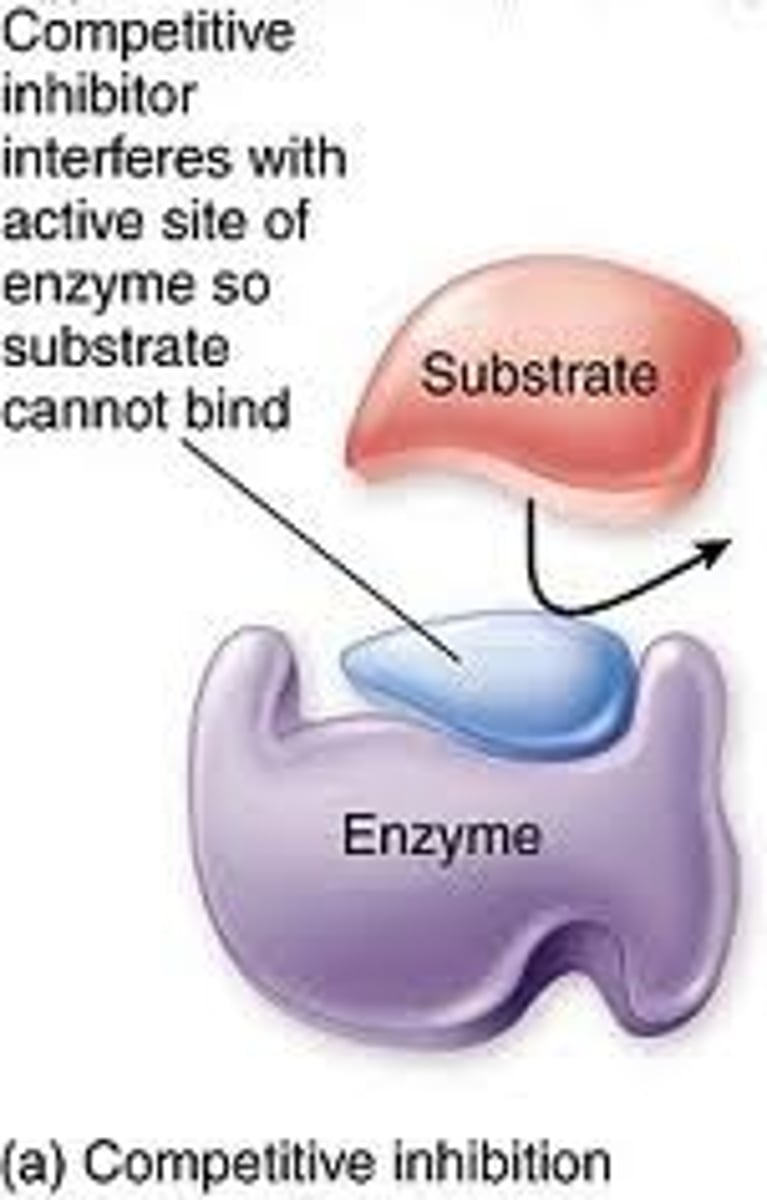
competitive inhibitors
act like substrate impostors and bind to the enzyme's active site, competing for the site with the true substrate.
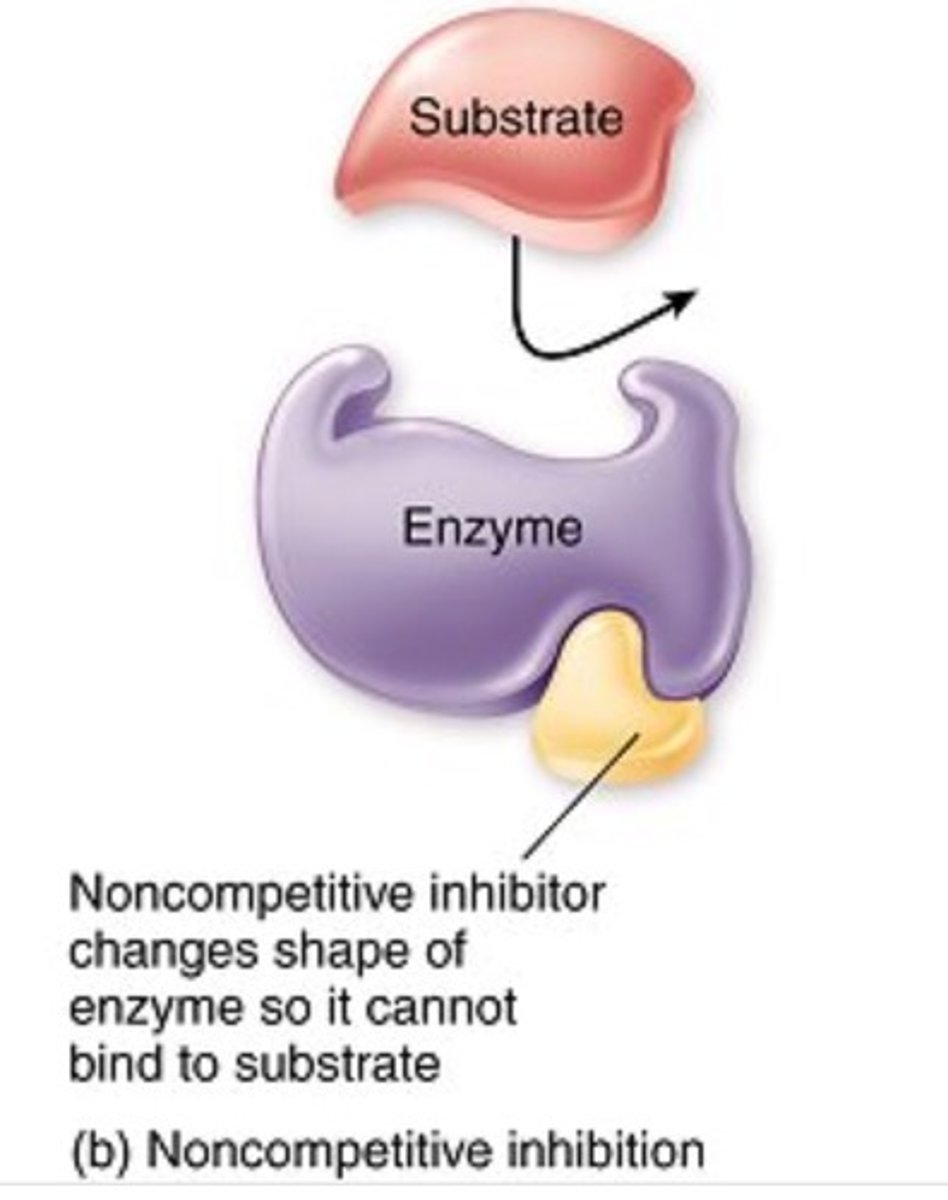
Non competitive inhibitors
bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective
Once proteins denature
THERE IS NO GOING BACK
Nucleic acids are
cellular
information storage, functionality and reproduction
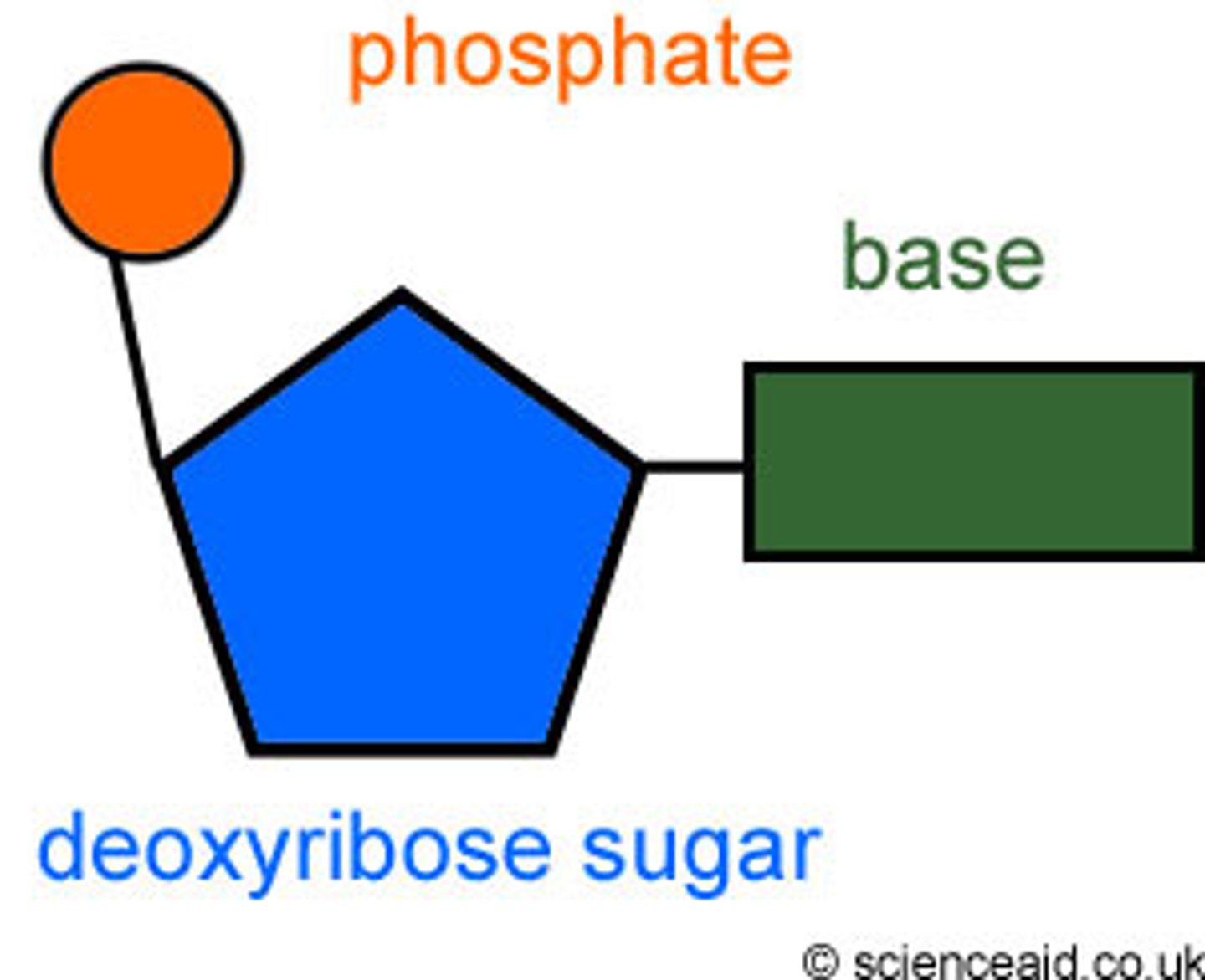
Nucleotide is made up of
1) deoxyribose 2) phosphate group 3) nitrogenous base