Microbiology 2 Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/189
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:07 PM on 3/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
190 Terms
1
New cards
Positive Supercoiling
Coiling of DNA that increases the number of base pairs per turn.
2
New cards
Negative Supercoiling
Coiling of DNA that decreases the number of base pairs per turn.
3
New cards
Replicon
portion of the genome that contains an origin and is replicated as a unit.
4
New cards
Replisomes
A complex of 12 proteins involved in replication
5
New cards
Clamp Loader Complex
A protein that holds DNA Pol at the DNA strand during DNA replication
6
New cards
Tau
Binds and organizes E.coli replication through distinct domains
7
New cards
\# of E.coli DNA Pol
5, Pol III plays the largest role
8
New cards
Bacterial DNA Replication Steps
1. DnaA binds oriC, bending and separating the strands
2. DnaB separates strands and SSB attach
3. Primase synthesizes RNA Primer
4. lagging + Leading synthesized
5. DNA Pol I removes primers and replaces with DNA
6. DNA Ligase joins Okazaki fragments (3’ OH of growing strand and 5’ P of fragment)
9
New cards
Catenanes
Two loops of DNA linked when topoisomerases break and rejoin DNA to ease supercoiling
10
New cards
TTGACA
\+35bp, recognized by sigma factor
11
New cards
TATAAT
\+10bp, where DNA starts to separate
12
New cards
tRNA
70-95nt RNA folded into an L shape that recognizes mRNA codons with anticodons
13
New cards
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
Catalyze AA attachment to tRNA. at least 20 exist for each amino acid.
14
New cards
16S rRNA
Binds SD sequence and 3’ RNA end
15
New cards
23S rRNA
Ribozyme that catalyzes peptide bond formation
16
New cards
t-RNA-fMet
Bacterial initiator tRNA that adds Met at AUG downstream of SD sequence. Commonly removed post-translationally
17
New cards
t-RNA-Met
Used by archaea and Euk, installs Met at elongating Aug codons using the 5’ cap as a reference.
18
New cards
Sec system
General secretion pathway. Moves unfolded proteins across the plasma membrane
19
New cards
Tat system
secretes only folded proteins
20
New cards
Two-step secretion
Type II, V, IX
21
New cards
One-step secretion
Type I, III, IV, VI, VII
22
New cards
Leader Sequence
Bacterial sequence transcribed into mRNA but not translated into AA
23
New cards
SD Sequence
Important for translation initiation
24
New cards
“Leaky Operon”
Operons have a low basal level of transcription
25
New cards
Genes for lactose metabolism
lacZ (Beta-galactosidase), lacY (lactose permease), LacA (Beta-galactoside transacetylase) . Inhibited by lacI when there is no lactose.
26
New cards
How does the lac repressor bind?
nonspecifically. Slides along major grove to reach an operator site recognizable by helix-turn-helix. Bends DNA to block RNA pol from accessing promoter.
27
New cards
How many operators can lacI bind to?
3
28
New cards
How many genes code for enzymes to synthesize tryptophan?
5
29
New cards
What control does the ara operon experience?
Positive and negative transcriptional control by araC
1. Inactive when ara present
2. Active when ara absent
1. Inactive when ara present
2. Active when ara absent
30
New cards
Attenuation
Early termination of transcription or translation caused by step-loop folding patterns in the long leader region of mRNA (control in trp Operon)
31
New cards
Riboswitches
A folding of mRNA leader sequence in response to a bound effector molecule that determines if transcription continues or terminates.
\
A form of transcription attenuation
\
A form of transcription attenuation
32
New cards
RNA thermometers
Regulate translation by folding 2\* structures in the leader sequence dependent on temperature
\
Measure temperature based on differences in thermal stability of GC and AU base pairs
\
Measure temperature based on differences in thermal stability of GC and AU base pairs
33
New cards
sRNA, ncRNA, Antisense RNA
May inhibit or enhance translation
34
New cards
Regulon
Genes/operons controlled by a common global regulatory protein
35
New cards
Two-component Signal Transduction
When exposed to a signal in the cytoplasm, a sensor kinase transfers phosphate to response regulator in the extracellular environment to elicit transcriptional changes.
36
New cards
Second Messengers
* cAMP - CRP/CAP
* ppGpp/pppGpp
* Cyclic dinucleotides (c-di
* ppGpp/pppGpp
* Cyclic dinucleotides (c-di
37
New cards
Catabolite Repression
Regulation of transcription by both repressors and activators
38
New cards
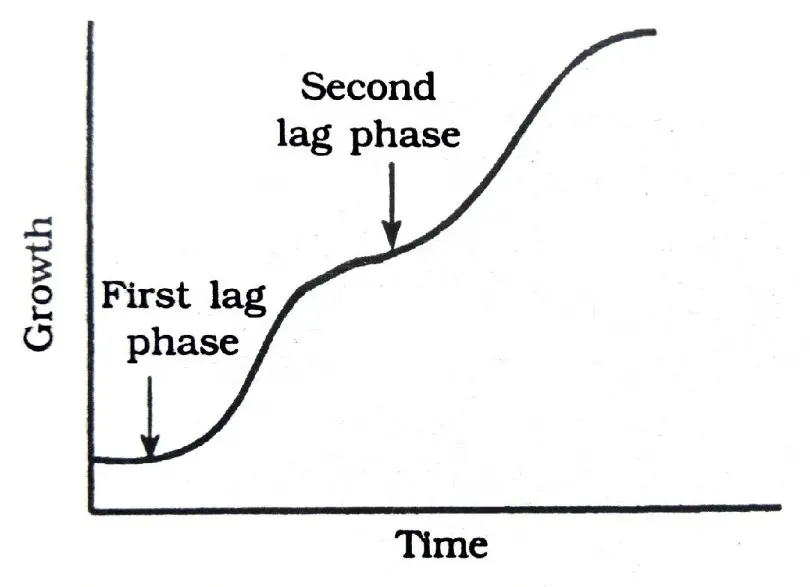
Diauxic growth
Preferential use of one material over another. Lag occurs when preferred substrate is exhausted, then growth resumes using the second substrate.
39
New cards
CAP/CRP
Catabolite activator protein. Active when cAMP bound and interacts with RNAP to stimulate transcription.
\
ALL catabolite operons contain a CAP binding site
\
ALL catabolite operons contain a CAP binding site
40
New cards
Stringent response
Bacterial response to stress conditions. AA biosynthesis genes are transcribed, tRNA/rRNA transcribed less.
41
New cards
How does Chemotaxis work in E.coli?
MCPs bind to chemical signals in the encironment and activates sensor kinase CheA which autophosphorylates before relaying the phosphate to CheY.
\
if MCP is more methylated (as analyzed by CheR and B), and CheY is active, CW rotation = tumbling
\
If MCP is not methylated and CheA/Y are inactive, CCW rotation = running.
\
if MCP is more methylated (as analyzed by CheR and B), and CheY is active, CW rotation = tumbling
\
If MCP is not methylated and CheA/Y are inactive, CCW rotation = running.
42
New cards
What regulation controls sporulation?
Phosphorelay, posttranslational protein modification, transcription factors, sigma factors.
* alt. sigma factors produce in response to starvation
* Phosphorelay begins with KinA when nutrient depletion detected
* Spo0A controls sporulation initiation
* alt. sigma factors produce in response to starvation
* Phosphorelay begins with KinA when nutrient depletion detected
* Spo0A controls sporulation initiation
43
New cards
Quorum Sensing
Cell-cell communication mediated by signaling mols essential for virulence, symbiosis, biofilm production, and differentiation.
44
New cards
Restriction-modification
Innate system to restrict the growth of viruses.
45
New cards
Restriction endonucleases
Recognize and cut specific DNA sequences.
46
New cards
CRISPR/Cas System
Adaptive immunity
1. Adaptation: pieces of viral genome added to CRISPR array in surviving cell
2. Expression: CRISPR region transcribed, RNA matured by Cas proteins to create crRNAs
3. Interference: Cas-crRNAs block viral DNA/mRNA during infection
1. Adaptation: pieces of viral genome added to CRISPR array in surviving cell
2. Expression: CRISPR region transcribed, RNA matured by Cas proteins to create crRNAs
3. Interference: Cas-crRNAs block viral DNA/mRNA during infection
47
New cards
Condensates
Protein complexes that segregate and concentrate specific molecules to increase efficiency of biochemical reactions.
48
New cards
How many DNA polymerases function in Euk DNA replication?
at least 3
49
New cards
What are Telomerases important features?
* Internal RNA template (bps to G-tail)
* Reverse transcriptase activity (to maintain length of chromosome end)
* Reverse transcriptase activity (to maintain length of chromosome end)
50
New cards
How many RNA Polymerase do bacteria use?
1 - 5 subunits(polypeptides)
51
New cards
How many RNA Polymerases do eukaryotes have?
3
* RNAP I: rRNA
* RNAP II: mRNA
* RNAP III: tRNA and 5S rRNA
* RNAP I: rRNA
* RNAP II: mRNA
* RNAP III: tRNA and 5S rRNA
52
New cards
TATA Box
t absent for regulated genes. In eukaryotes, present at -31 to -26 for housekeeping genes.
\
Transcription initiation by binding to TFIID.
\
Transcription initiation by binding to TFIID.
53
New cards
What are the uses of 5’ cap?
Stabilizes and facilitates translation and splicing.
54
New cards
What are the uses of the 3’ Poly-A tail?
Aids in recognition, prevents degradation, and signals for transport
55
New cards
Is alternative splicing an option for bacteria and archaea?
No.
56
New cards
Translation in Bacteria
30S + 50S makes ribosome. Start codon binds 16S rRNA and initiator N-fMet-tRNA SD sequence. Termination may occur with or without Rho protein.
57
New cards
48S Complex
Forms when 43S binds to the bridged mRNA in eukaryotic translation initiation
58
New cards
80S ribosome
60S + 48S Subunit in eukaryotes
59
New cards
Vesicular transport
Moves proteins directly across a membrane in eukaryotes. Places proteins into ER, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
60
New cards
Twin-arginine translocation
Functions in chloroplasts and mitochondria
61
New cards
What does gene expression regulation look like in Archaea
* Rarely two-component regulatory systems
* TF can be positive or negative
* Histone-DNA complexes vary in size
* No post-translational modification
* TF can be positive or negative
* Histone-DNA complexes vary in size
* No post-translational modification
62
New cards
Apurinic site
A site in DNA where a base is missing (purine or pyrimidine). In the next replication round, one strand keeps the AP site and the other gets an incorrect random nucleotide.
63
New cards
Base analogs
Mutagens. Structurally similar to normal bases- mistakes when incorporated.
64
New cards
Intercalating agents
Mutagens that distort DNA to induce single nt pair insertions/deletions
65
New cards
Forward mutation
WT > Mutant
66
New cards
Reversion mutation
Mutant > WT
67
New cards
Suppressor mutation
WT phenotype restored by a second mutation at a different site than the original mutation.
68
New cards
Excision repair
Corrects damage that distorts the DNA double helix (base or nucleotide)
69
New cards
Recombinational Repair
Corrects DNA that has both bases of a pair missing or damaged with recombination with an undamaged chromosomal copy.
\
Done by RecA.
\
Done by RecA.
70
New cards
SOS Response
Inducible repair system when damage is great.
* RecA destroys LexA to increase production of excision repair enzymes
* RecA initiates recombination repair >50 genes.
* RecA destroys LexA to increase production of excision repair enzymes
* RecA initiates recombination repair >50 genes.
71
New cards
Fate of DNA in Horizontal Gene Transfer
* Integration (recombines)
* Separate (persists as a plasmid)
* Remains in cytoplasm (donor DNA can’t replicate
* Degradation (By CRISPR/Cas)
* Separate (persists as a plasmid)
* Remains in cytoplasm (donor DNA can’t replicate
* Degradation (By CRISPR/Cas)
72
New cards
Homologous Recombination
RecA breaks DNA double stranded, reunion causes crossing over between long DNA regions with similar nt sequences
73
New cards
Site-specific Recombination
Recombination occurs by Recombinase at specific target sites in DNA mols.
74
New cards
Replicative transposition
Copy-and-paste
75
New cards
Simple transposition
Cut-and-paste
76
New cards
Rolling-Circle Replication
Unidirectional nucleic acid replication with polymerase and recombinase that rapidly synthesizes multiple copies of circular mols of DNA/RNA
77
New cards
Hfr Conjugation
F factor transfers itself in conjugation and drags the rest of the genome bridge, where process is often incomplete and connection breaks, breaking a portion of the copied genome into the F- cell.
\
Resultant cell is still F-
\
Resultant cell is still F-
78
New cards
Generalized Transduction
fragment of host same length as phage genome is mistakenly package and transfered in next infection, where it can be incorporated into the new host cell.
79
New cards
Specialized Transduction
Integration of phage takes place at a special attachment site in phage genomes called att sites.
80
New cards
Replica Plating
Screens for auxotrophic vs prototrophic parent based on ability to grow in the absence of a particular biosynthetic end product.
81
New cards
Conditional Mutations
Different phenotype under certain environmental conditions
82
New cards
Auxotrophic mutant
Unable to make an essential macromol (AA or nt)
83
New cards
MDA
Multiple Displacement Amplification
\
Occurs at a single temperature and uses DNA pol from phi29 to synthesize new DNA
\
Occurs at a single temperature and uses DNA pol from phi29 to synthesize new DNA
84
New cards
Metagenomics
Study of microbial genomes based on DNA extracted directly from the environment.
Each DNA fragment comes from a COLLECTION of genomes
Each DNA fragment comes from a COLLECTION of genomes
85
New cards
Bioinformativs
Convert raw nt data into location and potential of genes
86
New cards
in silico analysis
locates genes in a genome map by identifying an ORF.
87
New cards
BLAST
base by base comparison of 2+ gene sequences, tentative function of gene or protein structure
88
New cards
Orthologues
Genes from different organisms with similar ORFs
89
New cards
Paralogues
2+ genes with similar nt sequences (duplication event)
90
New cards
Conserved hypothetical proteins
match known sequences in databases without understanding assigned function
91
New cards
Proteins of unknown function
Proteins of genes unique to an organism.
92
New cards
DNA Microarray Analysis
Determines what genes are expressed at a specific time.
93
New cards
RNA-Seq
Quantifies mRNA by measuring reads matching each gene. mRNA > cDNA, sequenced using NGS.
94
New cards
Metatranscriptomics
Describes transcriptome of an entire ecosystem
95
New cards
Proteome
Entire collection of proteins that an organisms produces.
96
New cards
Protein Modeling
Assumes proteins fold into a limited number of shapes and can be grouped into families. Determines 3D structure of proteins
97
New cards
Lipidomics, Glycomics, and Metabolomics
A cell’s lipid, carb, and small molecule metabolite profile
98
New cards
ChIP
Surveys protein DNA interactions in living cells.
1. Crosslinking
2. Sonication
3. Antibodies added and bound, + Sonication
4. Immunoprecipitation
5. Reverse cross linking
6. DNA Sequencing after proteins removed
1. Crosslinking
2. Sonication
3. Antibodies added and bound, + Sonication
4. Immunoprecipitation
5. Reverse cross linking
6. DNA Sequencing after proteins removed
99
New cards
Functional Genomics
Puts genomic information in a biological context
100
New cards
Systems Biology
Holistic study of cells for interactions.