OB Final Study Guide
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
A 28-year-old woman (non-smoker) is breastfeeding and asks what types of birth control are available for her and her husband. What would you tell her?
These specifically say can use with breastfeeding: progestin only pill, hormone implants (nexaplanon), IUDs, and depo-provera
Can pretty much use anything except those containing estrogen (combination pill, patch, ring, morning after pill)
What patient teaching is important when discussing different methods of contraception?
Condoms - don’t use male & female at the same time; no STI protection
Cervical caps must be fitted. Diaphragms must be fitted & refitted with growth changes. Both protect 24h - leave in place 6 hours
Depo-provera is a shot Q3m
Effectiveness lowest to highest: barriers/emergency contraceptive, hormonal, IUD, sterilization
Explain the purpose and significance of estrogen
◦ Aids in maturation of follicle and conception
◦ Increases vascularity
◦ Opens cervical os
◦ Causes cervical mucous to become abundant & slippery (egg-white consistency)
◦ Begins to build endometrial lining
Explain the purpose and significance of progesterone
◦ Hormone primarily responsible for maintenance of pregnancy
◦ Smooth muscle relaxant
◦ Closes cervical os
◦ Causes cervical mucous to thicken & become acidic
◦ Maintains endometrial lining in secretory phase
◦ Causes basal body temperature to rise
Explain the purpose and significance of hCG
First biochemical marker of pregnancy; Can be detected in urine or serum as early as 8d after ovulation
when does heart begin to beat
4 weeks
when does neural tube close
4 - 6 weeks
when can the heartbeat be heard by doppler U/S
10-12 weeks
when is fetal movement felt
16-20 wks
when does fetus begin to produce surfactant
24 wks
when is gas exchange possible in fetus
28 wks
Briefly describe the structure and function of the placenta
Maternal side (lobes) and Fetal side (umbilical cord)
◦ Provides oxygen/nutrients, rid waste/toxins & Hormone production
◦ Does NOT serve as filter- drugs, viruses, alcohol, & toxic substances can cross to fetus
Briefly describe the structure and function of the umbilical cord
◦ Connects placenta to fetus - waste and toxins are removed through it and placenta
◦ Umbilical vein (1) - blood to fetus
◦ Umbilical arteries (2) - blood away
◦ Wharton’s jelly - protects vessels from getting squished or pinched off
◦ Average length- 55 cm
Briefly describe the structure and function of the amniotic fluid
◦ Movement of fluid: Fetus swallows fluid, Flows in and out of lungs, Fetal kidneys excrete
◦ Amount: 700-1,000 ml at term
◦ Functions: Cushions fetus, prevents adhesion of membranes to fetus, allows fetal movement, provides constant body temp, barrier to infection, assists in the development of the digestive system
◦ Critical in fetal lung and kidney development
The fundus (uterus) becomes an abdominal organ at ___ weeks, is at the level of the umbilicus at ___ weeks, is at the ______ at 36 weeks, and then drops in a process called ______.
12
20
xiphoid process
lightening
Why is it important for the nurse to know the expected rate of uterine growth? Are there any conditions to monitor related to this?
It assesses the overall pregnancy process, gestational age, and fetal well-being. Tracking the growth helps identify potential compilations r/t abnormal fetal size (IUGR/FGR), amniotic fluid volume (oligohydraminos, etc), and other maternal or placental issues.
What is physiological anemia of pregnancy?
Due to hemodilution, there is more plasma than RBCs.
What is supine hypotensive syndrome? What are the potential problems and nursing interventions for this?
During the second half of pregnancy, the mother should not lay flat on back because pressure can be pushed down on the inferior vena cava and descending aorta.
This can cause hypotension, dizziness, and syncope.
Educate the patient on not laying on their back. During a c-section, can put a rolled towel or IV bag under their hip.
Explain the cause and PT teaching for each:
N/V
Constipation / Bloating / Flatulence
Bleeding Gums / Sinus Congestion / Nosebleeds / ↑ Perspiration
Low Back, Pelvic Pain, ↑ Lordosis, ↑ falls
Heartburn
Increased Urinary Frequency / ↑ UTI Risk
Striae Gravidarum (Stretch Marks)
Shortness of Breath (SOB)
Varicose Veins / Edema
Nausea/Vomiting
Cause: Hormonal changes (↑hCG, estrogen)
Teaching: Small frequent meals, avoid strong odors, stay hydrated
Constipation / Bloating / Flatulence
Cause: Progesterone slows GI tract; iron supplements
Teaching: Increase fluids/fiber, activity, stool softener if prescribed
Bleeding Gums / Sinus Congestion / Nosebleeds / ↑ Perspiration
Cause: Increased vascularity and mucosal swelling from estrogen
Teaching: Soft toothbrush, saline spray/humidifier, gentle nose blowing
Low Back, Pelvic Pain, ↑ Lordosis, ↑ falls
Cause: Shift in center of gravity; loosened joints/ligaments
Teaching: Good posture, stretching, heat, massage, supportive shoes/belt
Heartburn
Cause: Relaxed esophageal sphincter from progesterone
Teaching: Small meals, avoid lying down after eating, avoid trigger foods, elevate HOB
Increased Urinary Frequency / ↑ UTI Risk
Cause: Hormone-related ureter dilation + uterine pressure
Teaching: Hydration, void often, proper hygiene, avoid bladder irritants
Striae Gravidarum (Stretch Marks)
Cause: Skin stretching from maternal weight gain and uterine growth
Teaching: Maintain healthy weight gain, moisturize, reassure they fade postpartum
Shortness of Breath (SOB)
Cause: Uterus pushes up on diaphragm in later pregnancy
Teaching: Upright posture, slow deep breathing, frequent rest
Varicose Veins / Edema
Cause: Impaired venous return from uterine pressure; fluid shifts
Teaching: Elevate legs, avoid crossing legs, compression stockings, stay mobile
Explain the difference(s) between presumptive, probable, and positive signs of pregnancy.
Presumptive is subjective findings, so things that the patient would report feeling (amenorrhea, n/v, breast changes, fatigue).
Probable signs are objective findings, so things that the nurse can actually assess (hyperpigmentation, abdominal enlargement, chadwick sign, braxton-hicks contractions, ballottement).
Both presumptive and probable signs can be caused by something else.
Positive signs are findings that are only caused by fetus (auscultation of heart tones, palpation of fetal movement, cardiac activity).
Explain Nagele’s Rule and calculate the EDD (due date) for LMP of March 14, 2024
Nagele’s Rule is estimating the EDD by taking the last menstrual period and subtracting 3 months and adding 7 days.
December 21, 2024
What does G-P mean?
It means Gravida/Para. Gravida means # of pregnancies. Para means # of deliveries after 20 weeks (giving birth to twins or triplets is still considered 1 delivery).
What does G-T-P-A-L mean?
G = total number of times pregnant (including current pregnancy).
T = number of term deliveries (number of deliveries after 38 weeks).
P = number of preterm deliveries (number of deliveries after 20 weeks but before 37 6/7 weeks).
A = number of abortions (induced or spontaneous [miscarriage]; <20 weeks [stillbirth before 20 weeks is considered a spontaneous abortion).
L = number of children currently living
For best absorption, iron should be taken with _________ or _________ but not with ________; _______ increases absorption.
orange juice/vitamin C
calcium, tea, coffee, antacids
vitamin C
Women of conceiving age that are sexually active should take at least _____ of folic acid. Why is this?
0.4mg
Can prevent neural tube defects
Women that have a history of neural tube defects or are high risk should take ___ mg of folic acid
4
The recommended weight gain during pregnancy for a woman of normal weight is?
25 to 35 pounds
Describe the risk factors for preeclampsia
• Nulliparity
• Maternal age older than 35 years
• Prepregnancy obesity BMI greater than 30
• Multiple gestation
• Family history of preeclampsia
• Previous preeclampsia or eclampsia
• Chronic HTN, kidney disease, lupus, thrombophilia, antiphospholipid syndrome, or diabetes before pregnancy
• Gestational diabetes
• Assisted reproduction
Describe the s/s of preeclampsia
• Elevated BP
• Proteinuria may or may not be present (ACOG)
• Edema
• Elevations in liver function tests, diminished kidney function, altered coagulopathies
(severe headache, vision changes, sudden weight gain)
Describe the nursing management for preeclampsia
Environment: Quiet, decrease stimulation, decrease lighting
Seizure Precautions: Suction equipment, Oxygen equipment, Call button within reach, & Crash cart nearby
Emergency Medications: Magnesium Sulfate, Hydralazine, Labetalol, Nifedipine, Calcium Gluconate
Emergency Birth Pac
Constant maternal & fetal monitoring
Describe the s/s of eclampsia
Seizure Activity in the presence of preeclampsia (h/a, visual disturbances, increased DTRs)
Describe the nursing management of eclampsia
Immediate care
Call for help, remain at bedside
Maintain patient airway and safety during seizure
Side rail up, protect pt, roll to side to prevent aspiration
Post-seizure care
Stabilize mother, Suction as needed, O2 non-rebreather 10 L/min,
VS, EFM, Magnesium sulfate, diazepam, lorazepam
What is HELLP syndrome? What is the only cure?
• H: Hemolysis
• EL: Elevated Liver enzymes
• LP: Low Platelets
• Patient symptoms: N&V, epigastric pain, RUQ pain, headache, blurred vision, malaise, increasing BP
ONLY ONE CURE FOR HELLP! → Delivery!!
Which medications do we use to treat pregnancy induced hypertension (gestational hypertension) or preeclampsia?
Emergency Medications: Magnesium Sulfate, Hydralazine, Labetalol, Nifedipine, Calcium Gluconate
s/s and treatment of magnesium toxicity
• initial flushing, feeling hot, sedated, nauseate
• Notify if epigastric pain or trouble breathing. Will have pitting edema.
• DTRs- sluggish or absent, flaccidity/muscle weakness
• CNS depression
• Respirations <12/min (respiratory depression can occur when level >12)
• Decreased urine output <25-30ml/hr
• Chest pain, EKG changes, Cardiac arrest, Pulmonary edema
• Labs: Mag Level >8, Elevated liver enzymes (LFTs) and elevated renal function tests (BUN, Creatinine, albumin)
• Prepare to give Calcium Gluconate 10% 1G slow IVP (10ml over 3 minutes) for magnesium toxicity
What is an ectopic pregnancy? What are signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
• Fertilized ovum implants outside of uterus - 95% in fallopian tube
• Clinical manifestations: abdominal pain, missed menses, abnormal vaginal bleeding, rupture = cullen sign/bruise
What is gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD)? Diagnosis?
Types of hydatidiform moles: grape like clusters
Complete mole: fertilized egg where nucleus was not activated; no placenta, embryo, fetus, etc
Partial mole: one egg fertilized by 2+ sperm; may be some parts/sac; if fetus = anomolies
Clinical manifestations: really high HCG levels, may pass clusters
Vaginal bleeding, Significantly larger uterus, Absence of FHT’s
Diagnosed: Ultrasound & symptoms
List and describe the types of spontaneous abortions.
• Miscarriage: Loss of an intrauterine pregnancy before viability
• Spontaneous abortion: Nonviable, intrauterine pregnancy with either an empty gestational sac or a gestational sac containing an embryo or fetus without fetal heart activity within the first 12 6⁄7 weeks of gestation
• Early pregnancy loss: Spontaneous pregnancy demise before 10 weeks of gestational age
What is GBS? How do we screen for it? When? What is the treatment?
Part of normal fecal and vaginal flora for many women
Transmission rate low, but infected neonate carries high morbidity/mortality
Mom tested at 35-37 weeks usually by vaginal or rectal swab
GBS + : intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis
What is the antibody (Coombs) screen and who is tested? Would you anticipate administering any medication related to the results and at what time periods?
Coombs test is a blood test that checks for antibodies that attack red blood cells. There’s indirect and direct.
• Indirect antibody screen or Coomb’s test performed on mom during pregnancy & after delivery
• Direct antibody screen performed on baby at birth
• RhoGam is indicated in these circumstances:
1st dose- in the 2nd trimester at 28 weeks if Rh -
2nd dose- administered to mom within 72 hrs of birth, if infant’s blood type is Rh+ and maternal antibody screen is negative
Key to optimizing outcomes for mothers with pre-existing and gestational diabetes and their infants is strict….
maternal glucose control.
Explain the insulin requirements of the Type I diabetic Mother during and immediately after pregnancy.
1st trimester: Insulin requirement is reduced from hormones.
2nd trimester: Hormones start increasing then insulin needs increase
3rd trimester: Insulin needs double or quadruple; hospitalized; may be on insulin drip - critical pts
After: Insulin needs drop significantly and breastfeeding helps stabilize them
When do we perform the 1- hour and 3 -hour GTT? Why? What is a positive test?
1 hour screening occurs between 24-28 weeks. Less than 140 is negative after the sugary drink.
>140 = they have to come in fasting and do a 3 hour test with glucose taken at every hour.
2 or more of the values must be met or more for it to be considered a positive test:
Fasting: 95
1 hr: 180
2 hr: 155
3 hr: 140
What is an NST? Describe a reactive NST.
◦Who: High-risk pregnancies (Hypertension, Diabetes, Multiples, trauma, lupus, renal disease)
◦What: Assess fetal well being (oxygenation & autonomic nervous system functioning)
◦When: Done alone or part of BPP (biophysical profile), > 32 weeks
◦How: Place on EFM x 20-30 min, often use vibroacoustic stimulator, patient pushes hand-held button
Reactive Strip (Normal/Good): 15 x 15 x 2 x 20 (15 beat acceleration for 15s twice in 20 min; at least 2 acels in 20m)
Daily Fetal Movement Count (DFMC) key fx
o Palpate abdomen & track fetal movements daily for 1-2 hours
o 10 fetal movements within 2 hours is normal and reassuring
o Can do at home. For high risk patients like GDM.
o Less activity could just mean the baby is sleeping. Having something to eat while doing this perks up baby.
o No fetal movement in 12 hours = fetal alarm signal. Bad!
Contraction Stress Test (CST) key fx & results
Assess fetus wellbeing and placental functioning by initiating uterine contractions
Types of CSTs & Adverse effects:
o Nipple stimulated contraction test - precipitate labor
o Oxytocin-stimulated contraction test - tachysystole & uterine rupture - terbutaline on standby
Negative: (normal) Zero late or variable decels
Positive: (abnormal) Late decels with >50% uterine contractions in 20m
Suspicious or equivocal: variable decels or late decels with <50
BPP- Biophysical Profile key fx
Who: Diabetic, High blood pressure, Small baby or baby not growing properly, Past due date, and Too much or too little fluid around baby
Assesses 5 Variables in 30 min: (BATMN)
1. Breathing movements
2. Amniotic fluid volume
3. Tone
4. Movement
5. NST
BPP Scoring
*8-10: reassuring, no fetal asphyxia, repeat weekly
6: possible fetal asphyxia; if >36 wks = deliver, if less repeat test in 12-24 hrs
4: nonreassuring, strongly suspect fetal asphyxia; Further investigation and highly consider delivery
2 or below: immediate delivery regardless of age
What is this? Explain why these occur. What are the nursing interventions?
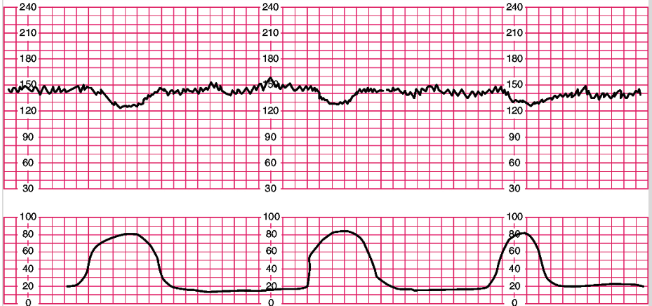
An early deceleration
The head is compressed by uterine contractions.
Nursing interventions are to reposition the mother, continuous EFM, and support labor
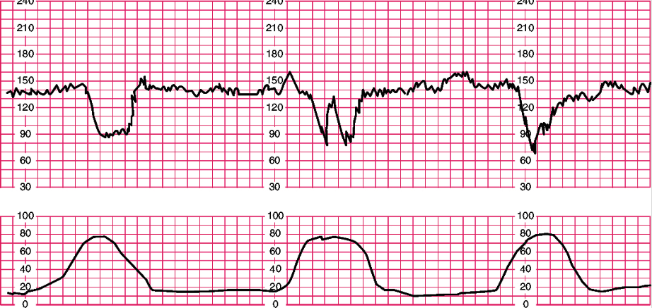
What is this? Explain why these occur. What are the nursing interventions?
Variable decelerations
This occurs because the cord is compressed.
Nursing interventions are to reposition the mother, amnioinfusion to flush fluids up to help float cord, give IVF, turn oxytocin off, and notify provider.
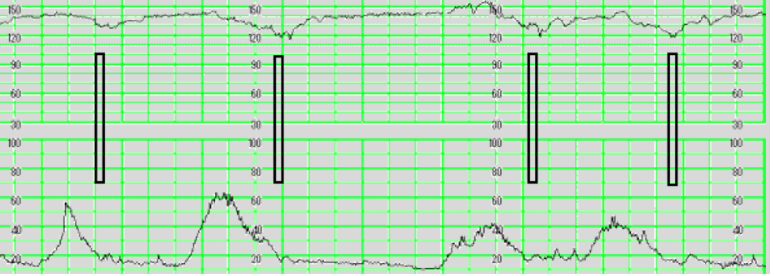
What is this? Explain why these occur. What are the nursing interventions?
Late decelerations
They occurs because there is placental insufficiency.
Nursing interventions are to turn oxytocin off, position change, IVFs, sterile vaginal exam, notify provider, consider oxygen, and prepare women for potential C/S delivery.
Explain variability and how it is measured; what does this indicate?
Variability is the irregular waves or fluctuations in the baseline FHR of two cycles per minute. It does not include accelerations or decelerations in the baseline.
Absent is no detection from baseline; same bpm over and over again; not good.
Minimal would only go up or down half of a block.
Moderate would be fluctuating 1-2 blocks up and down.
Marked would be above 2 blocks of fluctuation up and down
Category 1 FHR interpretation
Category I - Includes ALL of the following: Normal things (want to see this)
• FHR 110-160bpm
• Variability- Moderate
• Late or variable Decelerations- ABSENT
• Accelerations- present or absent; want to see them, but okay if not
• Early decels- present or absent
Cause: Well oxygenated & non-acidotic
Intervention: Continuous EFM & support labor
Category II FHR interpretation
all FHR not included in I or III:
• Bradycardia- not accompanied by absent variability
• Tachycardia- not accompanied by absent variability
• Baseline variability- minimal, absent, or marked
• No accelerations produced with fetal stimulation
• Recurrent Variables decelerations with “overshoots” or “shoulders”
• Late decels, prolonged decelerations >2 min but < 10 minutes
Cause: Not predictive
Intervention: Continuous EFM & initiate some intrauterine resuscitation
Category III FHR interpretation
includes the following: worst one
• Absent baseline variability and recurrent late decels, recurrent variable decels, or bradycardia
• Sinusoidal Pattern
• Get the baby out!
Cause: Acidosis, uteroplacental insufficiency, & fetal hypoxia
Intervention: Initiate intrauterine resuscitation
What are the factors that affect labor (5 P’s)?
Powers (contractions/pushing), passageway (pelvis/birth canal), passenger, psyche, position of mother.
Fetal presenting parts and positions
Cephalic - Head down first; what we want to see
Brow Presentation - Head is tilted back some, and brow is descending first
Face Presentation - Head is tilted all the way back
Breech - Sacrum or feet presenting first
Frank breech - Sacrum is presenting down with legs folded up
Single footing breech - Sacrum presenting with one leg extended.
Complete breech - Sacrum presenting with feet; criss-cross
• Shoulder - Scapula (shoulder) presenting; with transverse baby
What is meant by fetal station? Dilation? Effacement?
Fetal station is the descent of the presenting part. It is measured by the descent of the fetal head in relationship to the ischial spine of the pelvis. The negatives mean that the head is up higher; the positives mean the head is further down (+4/+5 means fetal head is crowning).
Dilation is the amount that the cervix is enlarged or widened. (1-10cm)
Effacement is the amount that the cervix has shortened or thinned. (0-100%)
What are the stages and phases of labor?
The first stage of labor consists of the latent and active phase. This is when the labor starts to progress from 0 cm dilated to 10 cm. The labor itself gets to be more difficult because contractions increase, the cervix dilates, etc.
The second stage of birth consists of an early and active phase. This is the delivery of the fetus.
The third stage of labor lasts from birth of the baby to complete delivery of the placenta.
The fourth stage of labor is recovery.
What happens during the latent (early) phase of the first stage of labor (dilation, effacement, contractions)?
Dilation 0–5 cm with effacement progression; contractions mild → moderate, frequency 2–5 min, duration 30–40 sec progressing to 40–60 sec.
How quickly do nulliparas vs multiparas dilate during the latent phase?
Nulliparas dilate ~1 cm/hr; multiparas ~1.5 cm/hr and may skip centimeters. More pregnancies and closer spacing = faster labor/birth.
Maternal behavior during the latent phase?
Excited, talkative, able to talk/walk through contractions → progresses to apprehensive, anxious, less social, focused on breathing, needs more support.
What are the cervical and contraction changes in the active phase of the first stage of labor?
Dilation 6–10 cm, usually 100% effaced; contractions moderate–strong, every 2–3 min, lasting 60–90 sec.
Maternal behaviors/symptoms during the active phase?
Irritable, frustrated, restless, wants to give up, rectal pressure, nausea/vomiting, shaking.
Nursing care during the first phase of the first stage (latent)?
Admit; assess VS q30–60 min, FHR, and uterine activity; SVE as needed; clear liquids or NPO; pain management; draw & compare labs; ambulate/shower; encourage voiding hourly.
Nursing care during the active phase of labor?
Hygiene (cleanse perineum, change linens/chux), nutrition (ice chips/clear liquids, IV LR, oral care), elimination (monitor bladder esp. w/ epidural), movement (frequent position changes), comfort (pain relief, fetal monitoring, VS, SVEs, breathing, relaxation, massage, counterpressure, effleurage, reassurance).
What occurs during the second stage and what are nursing actions?
Fetal head descends; nurse encourages and assists patient to push with contractions.
Perineum bulges/flattens; strong contractions q1–3 min; may feel out of control; Ferguson’s reflex (involuntary pushing); crowning/ring of fire; birth of head; note time of delivery.
What defines the third stage of labor and how long does it last?
What are signs of placental separation in the third stage?
From birth of baby to delivery of placenta; usually lasts 5–10 minutes.
Placenta separates from uterus; umbilical cord descends further; a gush of blood occurs once placenta detaches.
What occurs during the fourth stage of labor (timing and blood loss)?
Priority assessments during the fourth stage of labor?
First 1–4 hours after birth; normal vaginal delivery blood loss is 250–500 mL.
Fundus contracted and firm at midline; assess VS, fundus, bladder, lochia, and perineum every 15 min for 1 hr, then every 30 min × 2 hrs.
Determining true and false labor? And how do we determine which one mom is in?
TRUE Labor: Contractions are longer, stronger, and closer together. Cervix dilates and effaces. There is no change in contractions.
FALSE Labor: irregular and less frequent than real contractions; contractions end with change in activity and hydration; no change in cervix
signs of impending labor
Lightening (engagement - head distending down into the pelvis about 2 weeks before birth; more pressure lower - having to pee more, pain in thighs/buttocks from sciatic nerve)
Braxton Hicks (strengthens uterus; irregular & less frequent)
Surge in energy (from hormones: nesting instinct - get everything ready)
GI changes (nausea, maybe some diarrhea - body emptying out GI system)
Backache/sacroiliac discomfort (more pressure on pelvis, bladder, muscles, etc)
SROM (spontaneous rupture of membranes) - broke on its own (may be thick and the provider has to break it w/ amni hook)
Profuse vaginal and cervical mucus (may lose mucus plug - may go into labor within about 1-2 weeks; labor isn’t eminent)
Weight loss of 1-3lbs (shifting of fluids)
Bloody show (from dilation and effacement - things are moving along)
How to assess for amniotic fluid/ROM; what is it supposed to look like, what will it look like if infection present or possibly post-dates?
• Will continue to leak amniotic fluid after rupture
• Need to note color (clear is normal; green/brown if baby has pooped meconium in utero; can be light green and thick), odor (strong/bad odor can indicate infection), amount, time of rupture.
Techniques to confirm ROM:
• Speculum exam
• Nitrazine paper - get fluid from pad or pool; bright/indigo blue if amniotic fluid; yellow/green if urine
• Ferning - sample of fluid on microscopic slide; fern pattern seen as fluid starts to dry if it is amniotic (has glucose and crystallization)
• AmniSure testing kit - amniotic protein detected in vaginal secretions; won’t be amniotic protein if it is urine
What is augmentation versus induction of labor? What medications do we use for each?
Augmentation: Causing contractions after labor has already started but isn’t progressing appropriately
Medications: Prostaglandins (misoprostol, cervadil)
Induction: Stimulating contractions to start labor before spontaneous onset
Medications: Oxytocin
How do we control labor pain? What are the nursing interventions during an epidural?
We can control labor pain by administering opioids, nitrous oxide, and different types of anesthesia (local, nerve block, spinal block, epidural, general)
Monitoring v/s (BP), FHR monitor, placing indwelling catheter.
how to manage prolapsed cord
• Continuously relieve pressure of cord from presenting part (push up on presenting part) until delivery
• Put mom in trendelenburg position or in knee-chest position where butt is in the air if possible
• Call for help!
• STAT/Emergency Cesarean Section
• Assess fetal heart rate
how to manage shoulder dystocia
McRoberts maneuver - pull and flex the legs back out of the stirrups to their chest/abdomen opened wide
Suprapubic pressure - pressure straight down on anterior shoulder to roll it over under pelvis (to OA position)
Doctor is also corkscrewing the baby’s shoulder and head at the same time
Describe abruptio placentae, signs/symptoms, risk factors, and nursing management
It is premature separation of placenta from the uterine wall.
S/S are painful board-like abdomen, painful bleeding, uterine tenderness (feels like knife), and late decelerations.
The main management is to prepare for emergency C/S.
Expectant- pad count, labs, IV, Foley
Active- PREPARE FOR EMERGENCY C/S
Describe placenta previa, the signs/symptoms, risk factors, and nursing management
This is when the placenta lays lower than normal.
The S/S are abnormal placental attachment and painless bright red bleeding in the 2nd or 3rd trimester.
Nursing management is to monitor FHR, s/s of hemorrhage, obtain IV access, no vaginal exams, and to anticipate C/S (>250mL of bleeding).
How do we use Pitocin (oxytocin) what are the complications of using Pitocin? What are the contraindications and side effects
Oxytocin is given to stimulate uterine contractions. It can be used to induct labor and treat postpartum hemorrhage. It is given prophylactically following labor to prevent PPH.
Potential maternal complications are uterine tachysystole, placental abruption, uterine rupture, water intoxication, PPH, and infection.
Potential fetal complications are category II or III FHR pattern, hypoxemia, and acidosis.
What is the s/s of preterm labor? Which medications could we use to stop preterm labor? What medication do we administer to mature the neonate’s lungs?
Regular contractions of the uterus that is causing cervical changes before 37 weeks.
Magnesium sulfate, terbutaline, infometacin, and nifedipine.
Betamethasone
Describe the 3 fetal shunts: where are they? What do they do?
• Ductus venosus - located by the liver; the blood bypasses the liver because it doesn’t need all of the functions yet; blood comes from placenta through umbilical vein and bypasses liver to the inferior vena cava
• Foramen ovale - hole between right and left atria
• Ductus arteriosus - between pulmonary artery and aorta
Name the 3 most common signs of respiratory distress in the newborn
Grunting, nasal flaring, and retractions.
Heat loss can result in cold stress in the newborn. Why is this?
When exposed to cold, newborns increase both glucose and oxygen consumption to generate heat through the metabolism of brown fat.
Are glucose and oxygen consumption increased or decreased in a newborn?
The consumption is increased because it is needed for metabolism of brown fat and heat production.
Name 3 nursing measures to decrease heat loss in the newborn
Dry baby with dry towel immediately after delivery, ensure baby is dressed appropriately for room temperature, put under radiant warmer if the baby gets too cold.
Normal blood glucose levels in the newborn
40-60
First void/stool should occur..?
within the first 24 hours.
Failure to pass medium within 48-72 hours of age is a GI problem.
What are the 5 components of the APGAR score?
Appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, respiration.
What do the APGAR scores reveal? What is the score range?
• Scores of 7 to 10 – The infant is having little to difficulty transitioning to life outside the womb
• Scores of 4 to 6 – Infant is having a moderate amount of difficulty transitioning -> provide some resuscitation
• Scores of 0 to 3 – Infant is in severe distress -> full resuscitation
• These scores determine how much or how little resuscitation is required at birth -> <7 is concern
A baby is born with the following: blue all over, heart rate of 96 bpm, grimaces when the bulb syringe is used to clear the nares of mucous, has flaccid extremities and has gasping/weak respirations. What APGAR score do you assign? What is the priority action for this newborn?
3
Start full resuscitation for the newborn. Immediate positive pressure ventilation should be started to support oxygenation and improve HR and respirations.
What are the 2 newborn admission medications; why are they administered?
Erythromycin is an eye gel administered to prevent complications from potential diseases that might have been given to the fetus through vaginal delivery. Vitamin K is administered because newborns lack clotting factors, so it prevents bleeding.
What is the preferred IM injection site in the newborn/infant? Why is this?
Vastus lateralis because it is the largest and most developed muscle that contains no major nerves or vessels.
List the normal ranges for newborn vital signs:
Temperature: 97.7-99 axillary
Respiratory rate: 30-60 breaths/min
Pulse:110-160 bpm
Normal weight for a full-term newborn is
2500-4000 g
What is the gestational age assessment? How is it especially helpful?
It refers to the number of completed weeks of fetal development. It is calculated from the first day of the last normal menstrual period.
It helps determine how far along the mother should be, and what the fetus should be at developmentally.
Be able to describe the following: vernix, lanugo, milia, Mongolian spots & why it is important to document size and location.
Vernix covers the skin, and protects the skin from the amniotic fluid, moisturizes, and helps regulate body temperature.
Lanugo is hair that covers the body in the womb. It aids in insulation and skin protection.
Milia are tiny white bumps that appear on the face. They occur when dead skin cells become trapped.
Mongolian spots are flat, bluish-gray spots that appear at birth. It is important to document the size and location of findings to differentiate normal from abnormal, prevent misdiagnosis like abuse, monitor changes, etc.
Name the two fontanelles and when they should close. What does it mean if they are bulging? Sunken?
Anterior one closes by 18m
Posterior one closes by 2-4m
Should be soft and flat
Bulging - increased ICP
Sunken - dehydration
what is caput succedaneum
• Localized edema from pressure against cervix - whole head is squishy because of fluid
• Crosses suture lines - if they lay head on one side, it’ll be more squishy on that side
• Soft, dependent
• Resolves quickly
what is cephalohematoma
• Bleeding between skull & periosteum
• One or both sides
• Does NOT cross suture lines - only on one side at all times
• Firm, develops within 1-2 days
• Takes weeks or months to resolve - a big knot
• Increases risk for jaundice - when RBC get destroyed, bilirubin gets released
List 3 things you would teach parents of a newborn about cord care?
It will fall off in 7-10 days, do sponge baths until it falls off/don’t submerge in it water, and fold the diaper under it.