GHS pictograms (MUST STUDY)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms

Explosive

Flammable

Oxidizing

Compressed Gas
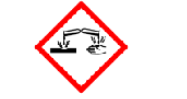
Corrosive

Toxic

Harmful

Health Hazard

Environmental Hazard
Fire
If hair or clothing catches on fire walk (DONT RUN) to the nearest safety shower or stop, drop, and roll.
If on bench, step back from the fire and notify your lab instructor
Evacuate the lab and the building immediately if necessary.
Chemical or Heat Burns
Small burns hold under cold water for 15 minutes.
Larger burns use safety shower
remove affected clothing
call for medical help if needed.
Chemicals in the Eye
Wash eyes at the nearest eyewash station
let your lab instructor know
keep eye open and rinse for no less than 15 minutes
follow up with an eye doctor and call for medical help if needed
Broken Glassware
inform the lab instructor immediately
DO NOT clean up glass or throw broken glass in the trash cans.
Handling chemical bottles
chemicals should not be handled outside of the designated areas/ fume hoods.
Never pick up a bottle by its lid
Never put any excess reagent back in the reagent container. If you remove more then needed place the extra reagent into a waste container.
Handling chemical spills
All unwanted material must be disposed of in an appropriate container (NO WASTE GOES DOWN THE SINK)
There are 4 waste categories all available in the fume hood designated for waste.
There are trash bins available outside the fume hood (NO CHEMICALS SHOULD BE PLACED IN THIS BIN)
4 chemical waste categories (HANDLING CHEMICAL SPILLS)
Organic, halogenated, solid, aqueous
Handling glass waste
Any broken general purpose glassware should be discarded in the broken glass boxes around the lab.
Any specialty glassware should be taken to the lab instructor immediately.
All other waste including, but not limited to, plastic pipets, paper towels, gloves,
filter papers, weigh papers should be discarded in general waste bin, NEVER in
the broken glass box.

First aid kit

Emergency gas shutoff

Telephone
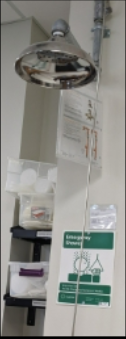
Safety shower

Fire extinguisher

Eyewash station

Beaker
used to measure the volume of liquid (not considered accurate)

Erlenmeyer flask
used to hold liquid, mixing liquids, transferring liquids, and you can boil liquids in it. It also measures approximate volumes of solutions (not considered accurate)

Graduated cylinders
used for precise measuring of volume of liquid (more accurate)
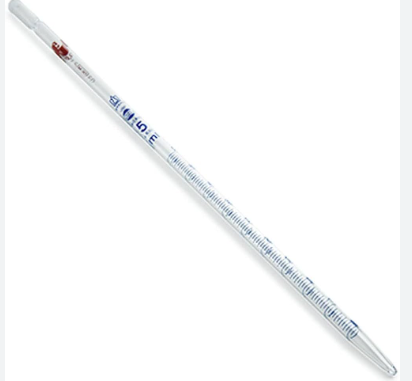
Graduated pipette
used to accurately measure and transfer a volume of liquid from one container to another (more accurate)

Vacuum/side-arm flask
used for vacuum filtration to rapidly separate solids from liquids by filtering liquids through a filter paper when connected to a vacuum via its sidearm

Buchner funnel
Used in vacuum filtration, where filter paper is placed inside to separate solids from liquids.

Spot plate
used to observe small-scale chemical reactions by holding tiny amounts of different substances in separate depressions (wells) on the plate, allowing for visual analysis of color changes or other reaction indicators without the need for precise volume measurements.

Glass stirring rod
Solid glass rods used to stir solutions, mix chemicals, and assist in transferring liquids by guiding flow.

Electronic balance
used to measure the mass of substances with high precision. Needed for accurately weighing chemicals for experiments.
Procedure for cleaning glassware
1.Gather the glassware from your assigned drawer.
2. Place paper towels at the bottom of your drawer.
3. Rinse each piece with tap water to remove visible residues.
4. Add a small amount of detergent to the glassware and scrub thoroughly with a brush.
5. Rinse the glassware with tap water until all detergent is removed.
6. Rinse the glassware with distilled water to remove any remaining impurities.
7. Place the glassware on a drying rack or dry with a clean towel.
8. After washing your glassware, have your TA check your drawer and initial the top of your lab manual.
Rules for significant figures
1. Any digit that is not zero is significant
2. Zeros located between nonzero digits are significant
3. Zeros to the left of the first nonzero digit are not significant
4. Zeros to the right of the last nonzero digit are significant if the number contains a decimal point
5. Zeros to the right of the last nonzero digit in a number that does not contain a decimal point are not significant
Density definition/ calculation
Density is the measure of mass per unit volume of a substance.
mass/ volume
Density units
g/mL (grams per milliliter) for liquids
g/cm³ (grams per cubic centimeter) for solids
kg/m³ (kilograms per cubic meter) for gases
How to accurately determine density in the lab?
Measure mass precisely using an electronic balance.
Measure volume accurately using a graduated cylinder, pipette, or water displacement.
Use proper significant figures in all calculations.
Repeat measurements to ensure precision.
Calculate density using mass/volume.