Unit 4 - Earth Systems and Resources APES Vocab
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
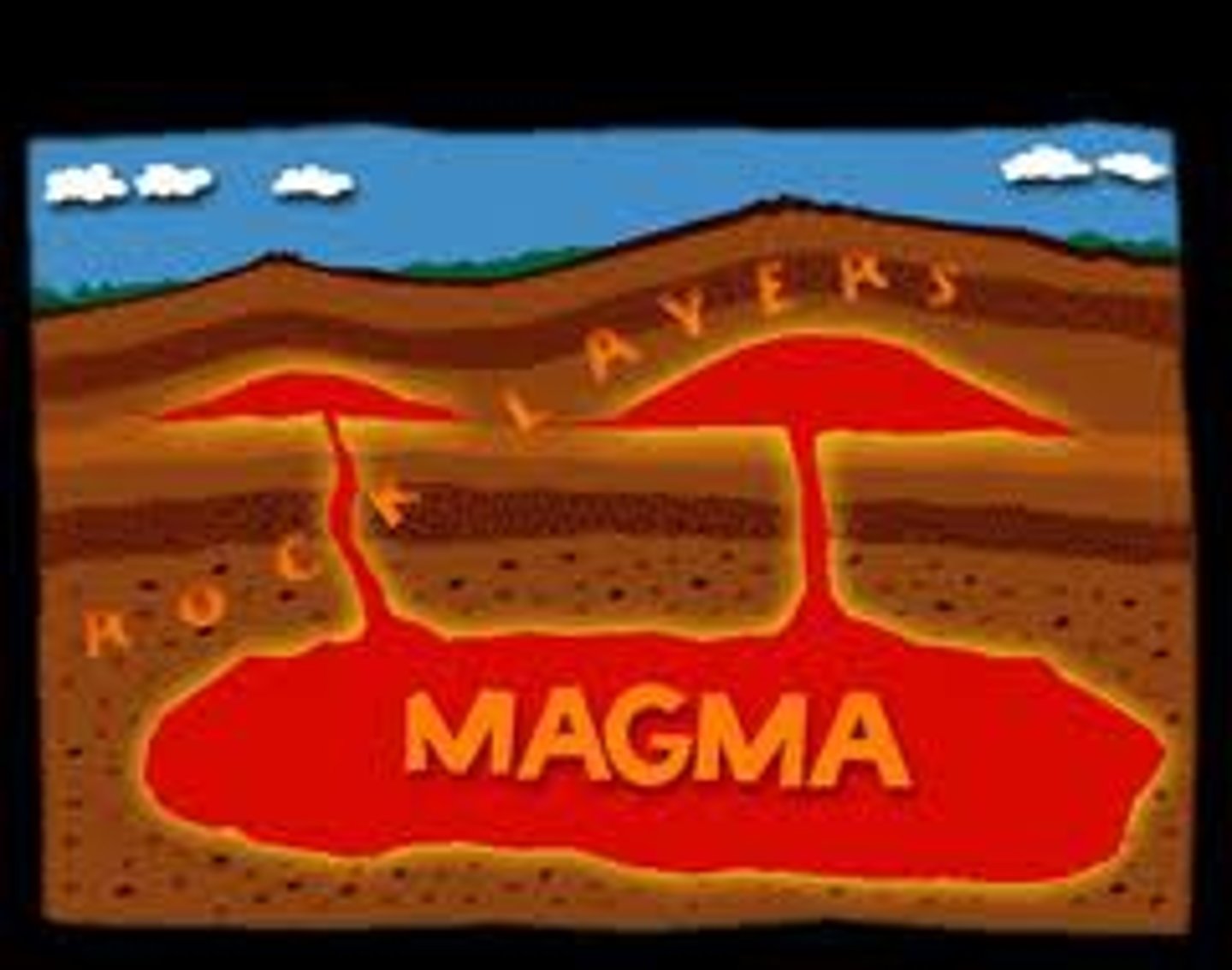
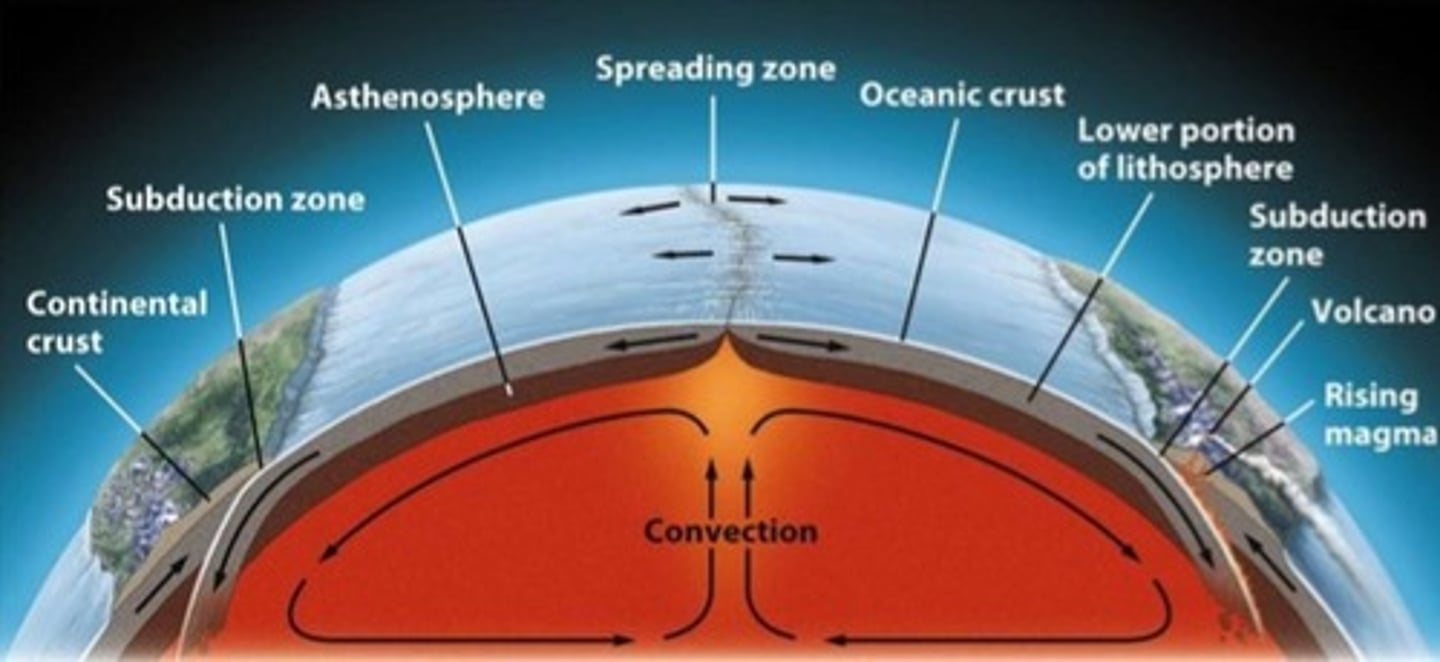
Magma
Molten rock beneath Earth's surface.
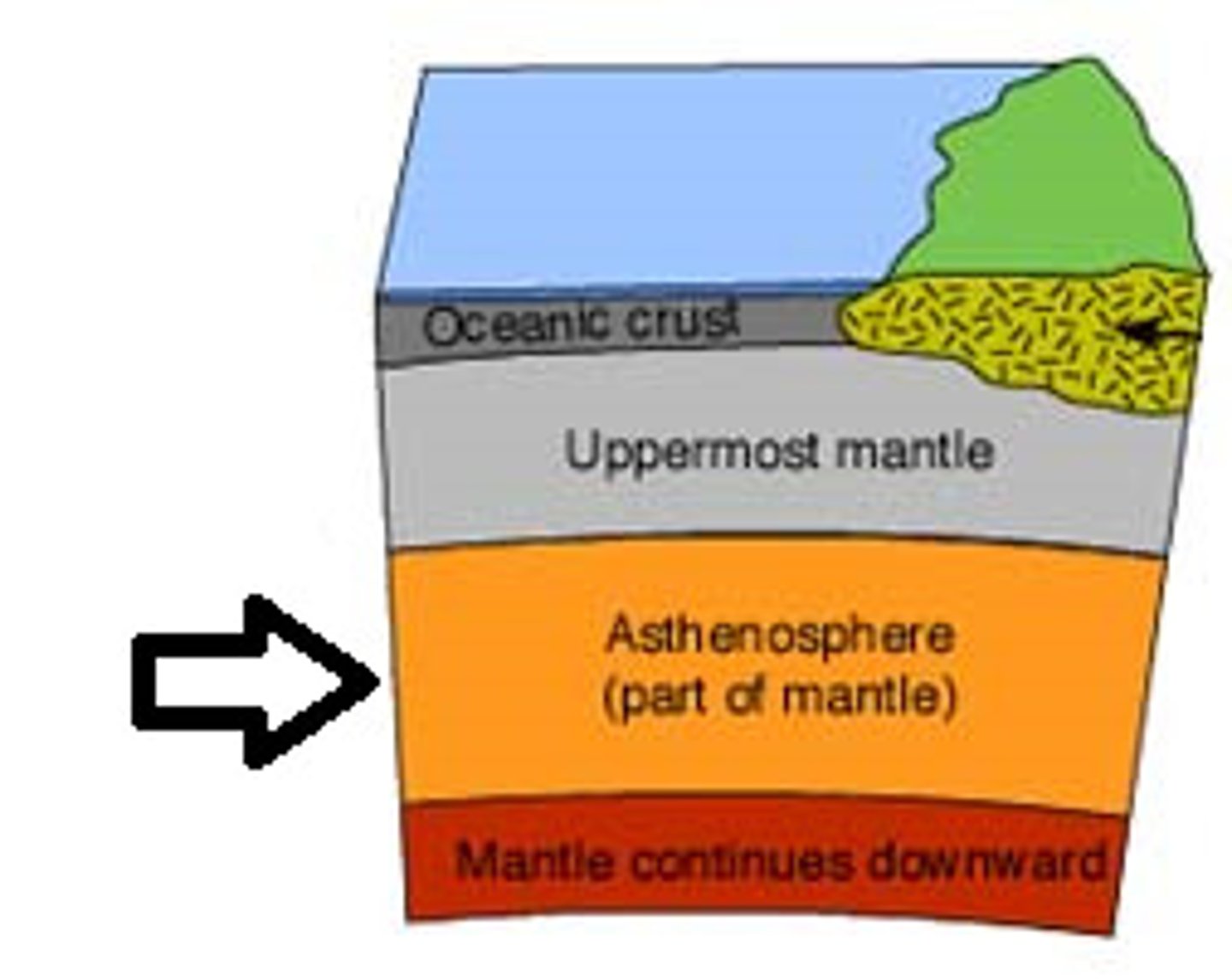
Asthenosphere
The semi-fluid layer of the mantle on which tectonic plates move.
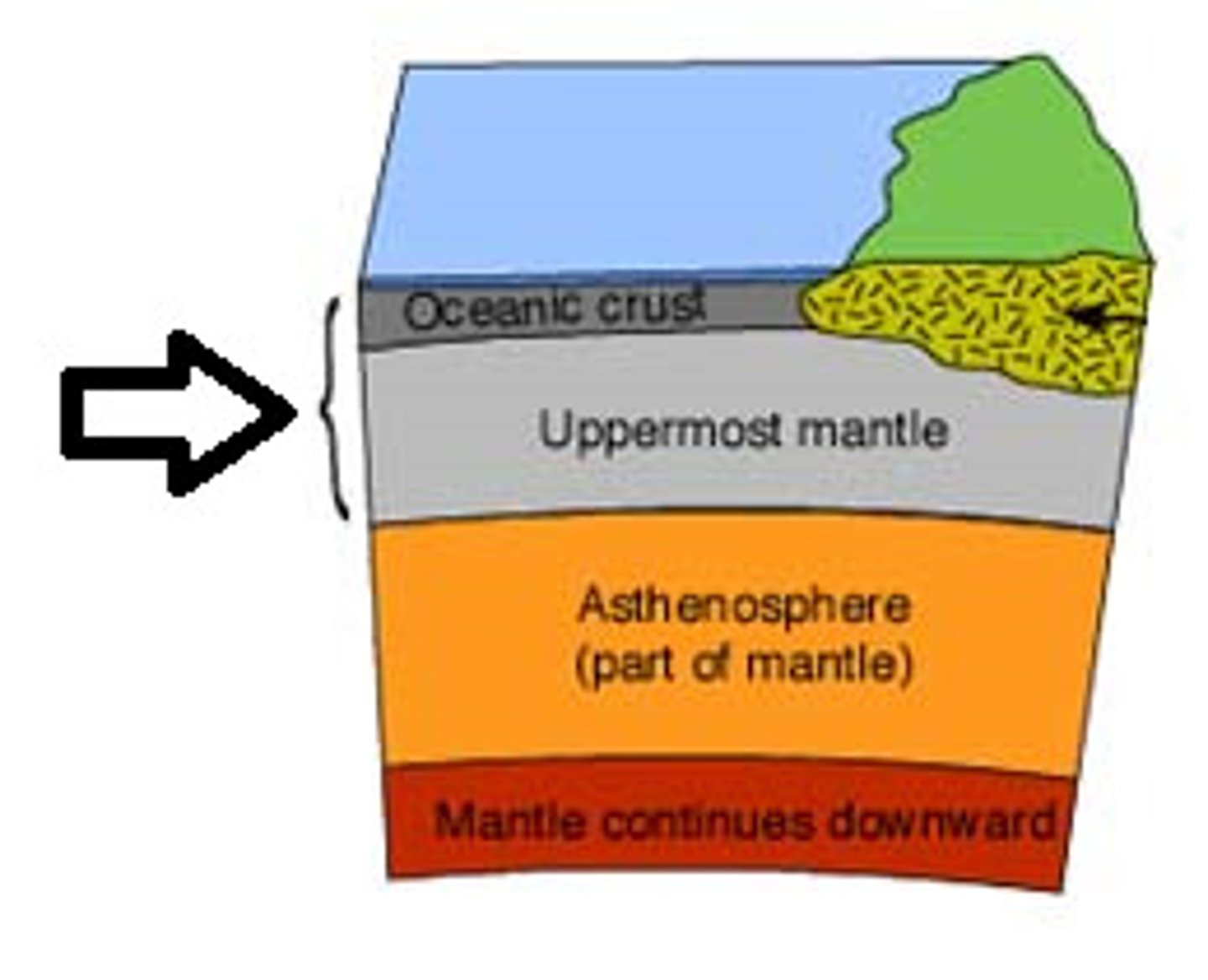
Lithosphere
The rigid outer layer of Earth, including the crust and upper mantle.
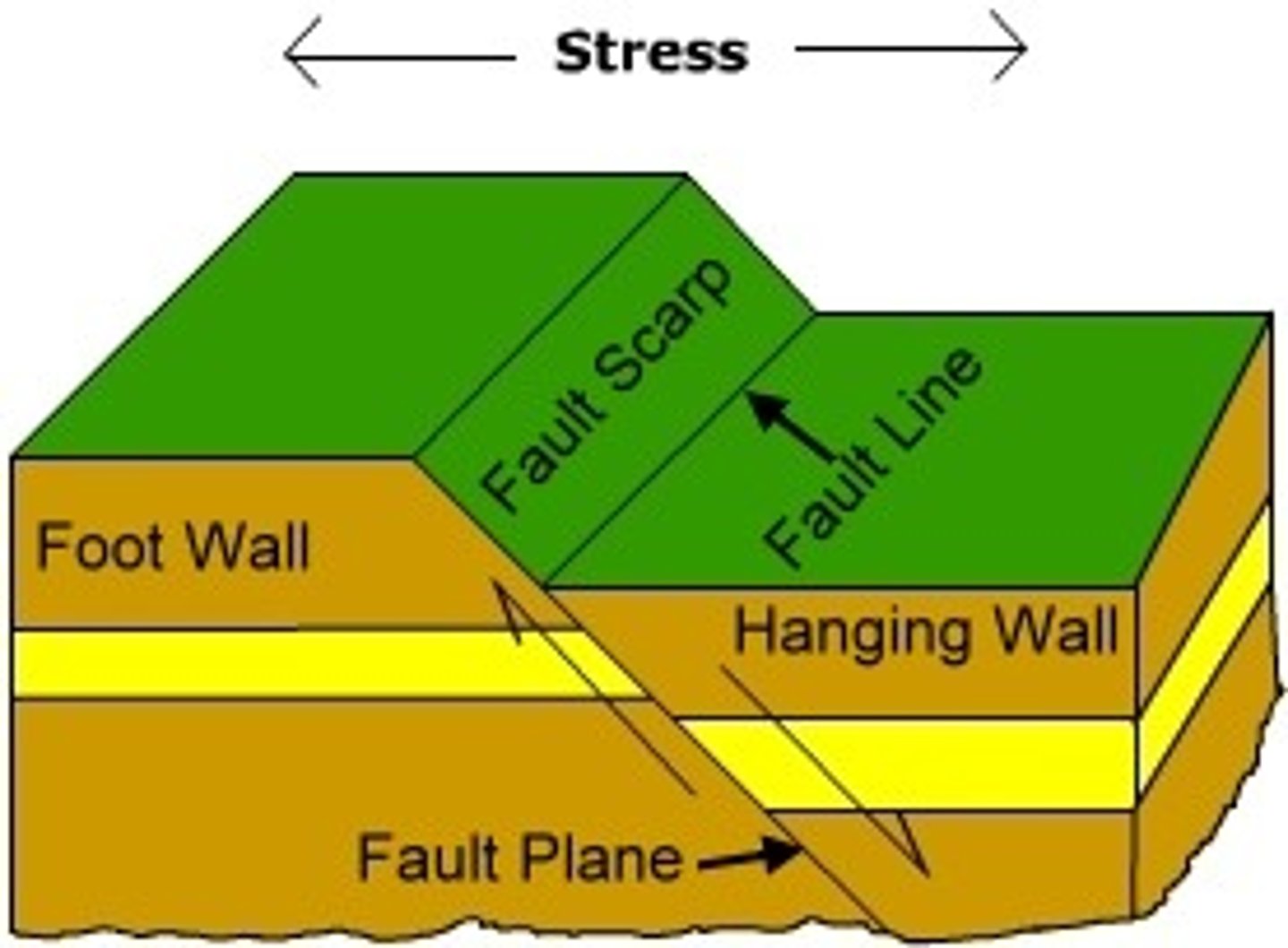
Fault
A fracture in Earth's crust where movement has occurred.
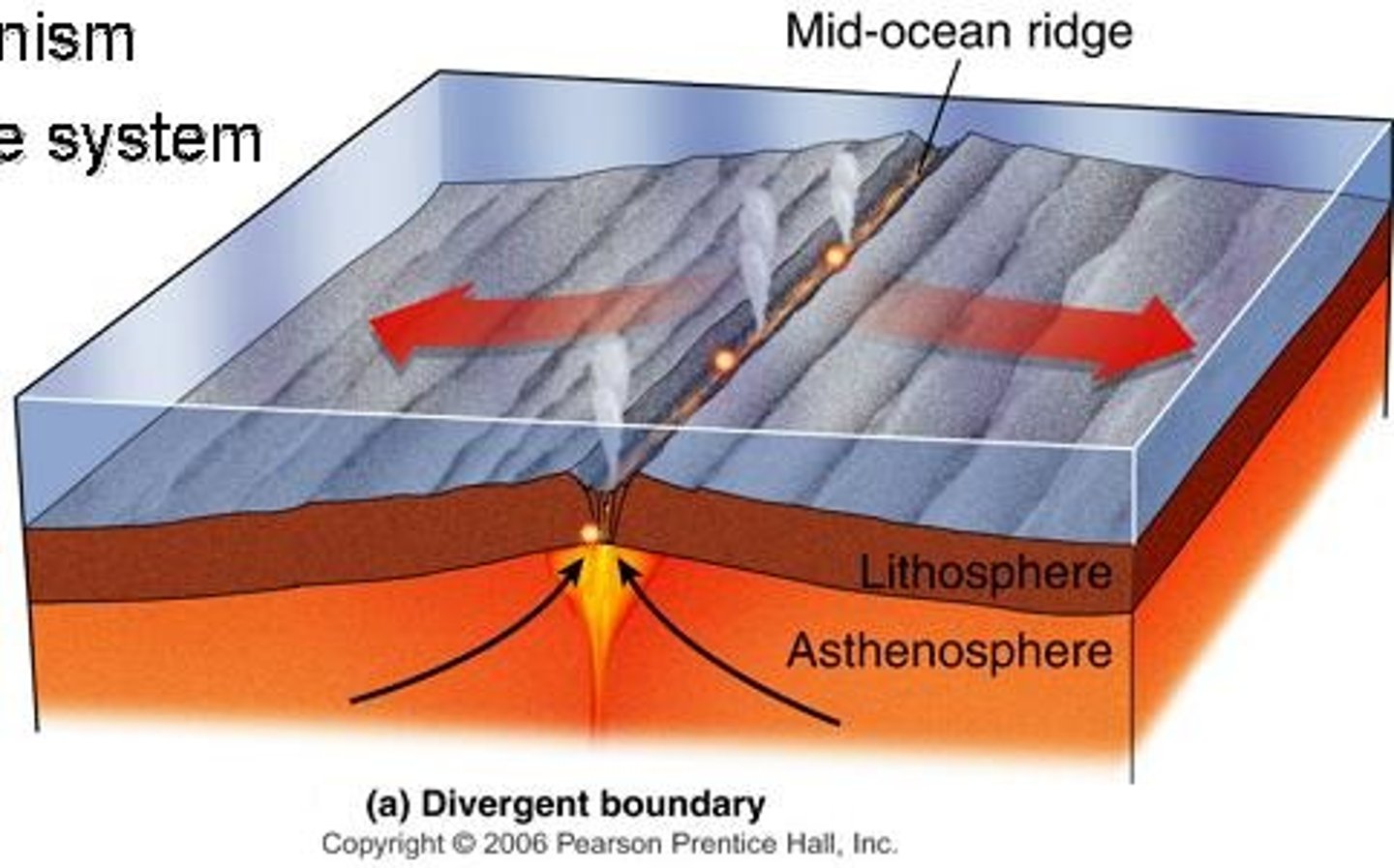
Divergent Boundary
A plate boundary where two plates move apart, creating new crust.
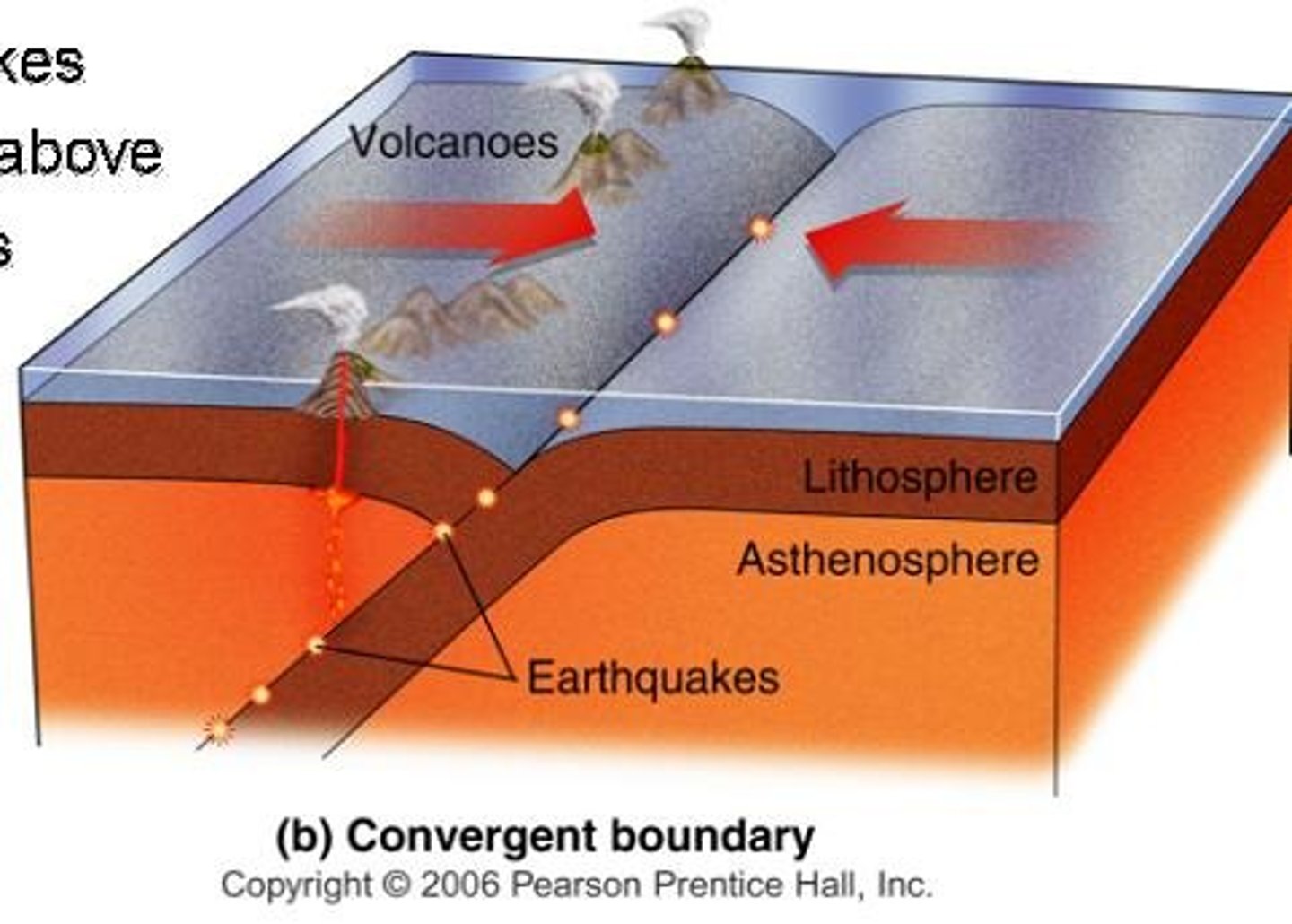
Convergent Boundary
A plate boundary where two plates collide, causing subduction or mountain building.
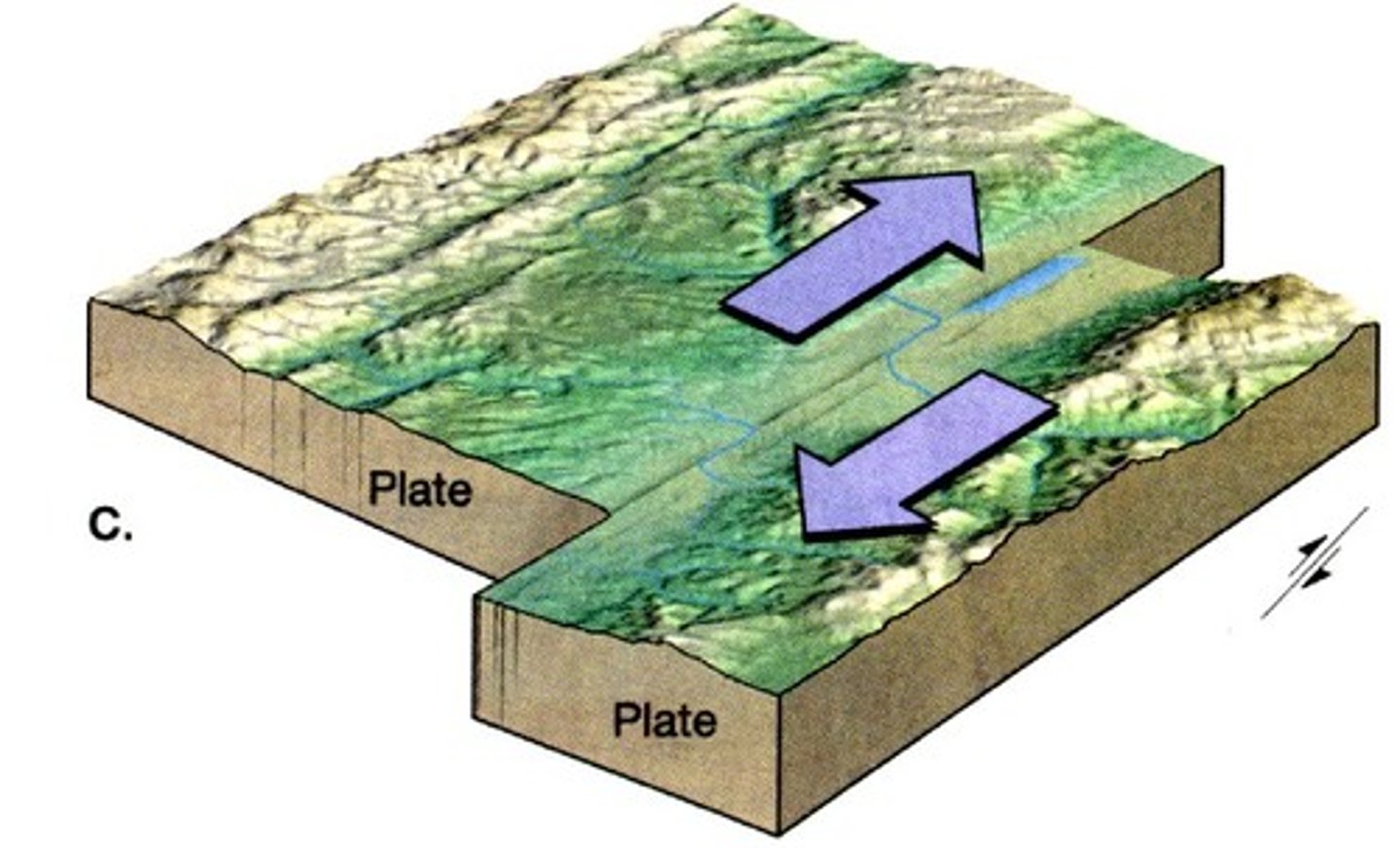
Transform Boundary
A plate boundary where plates slide past each other horizontally.
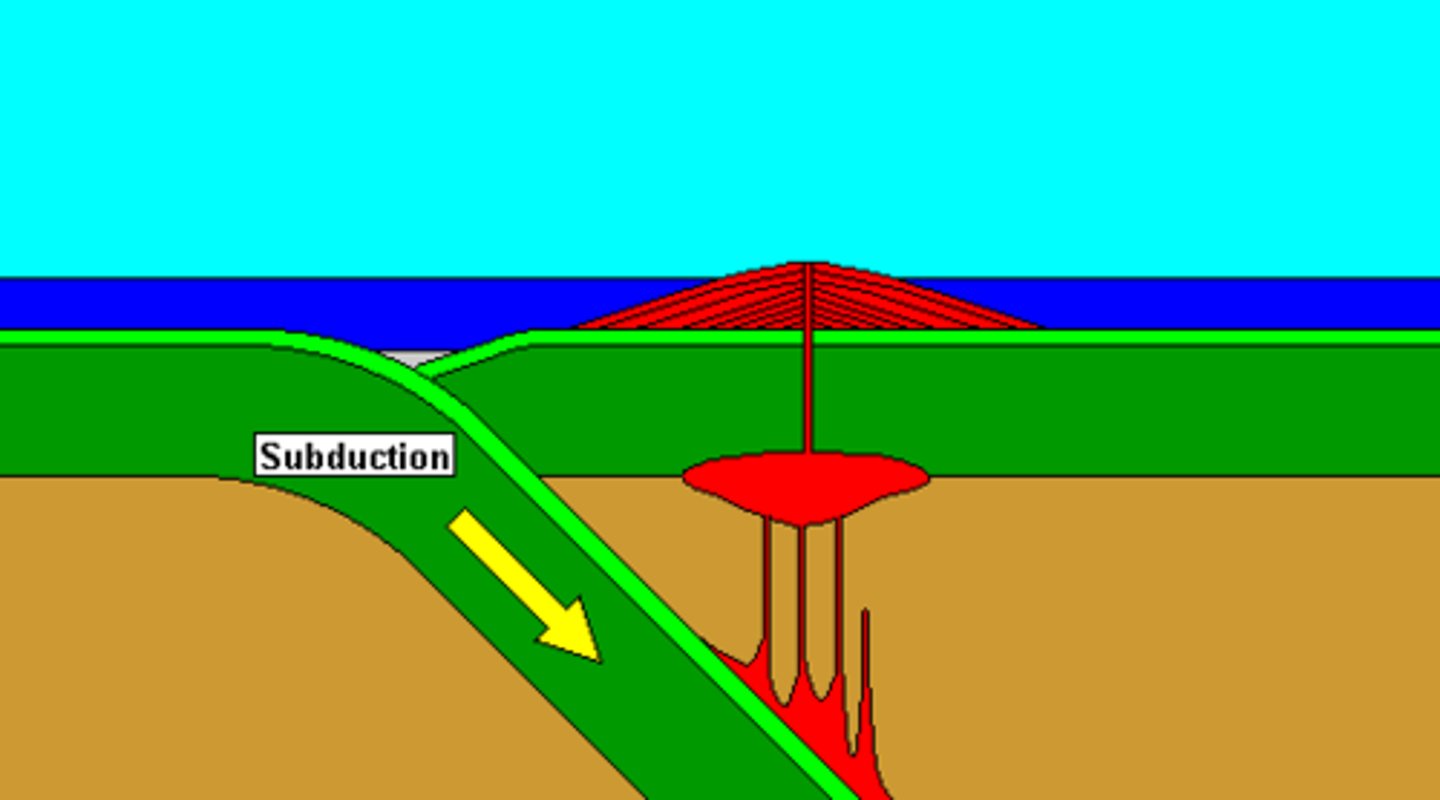
Subduction/Subduction Zone
Area where one tectonic plate sinks beneath another into the mantle.
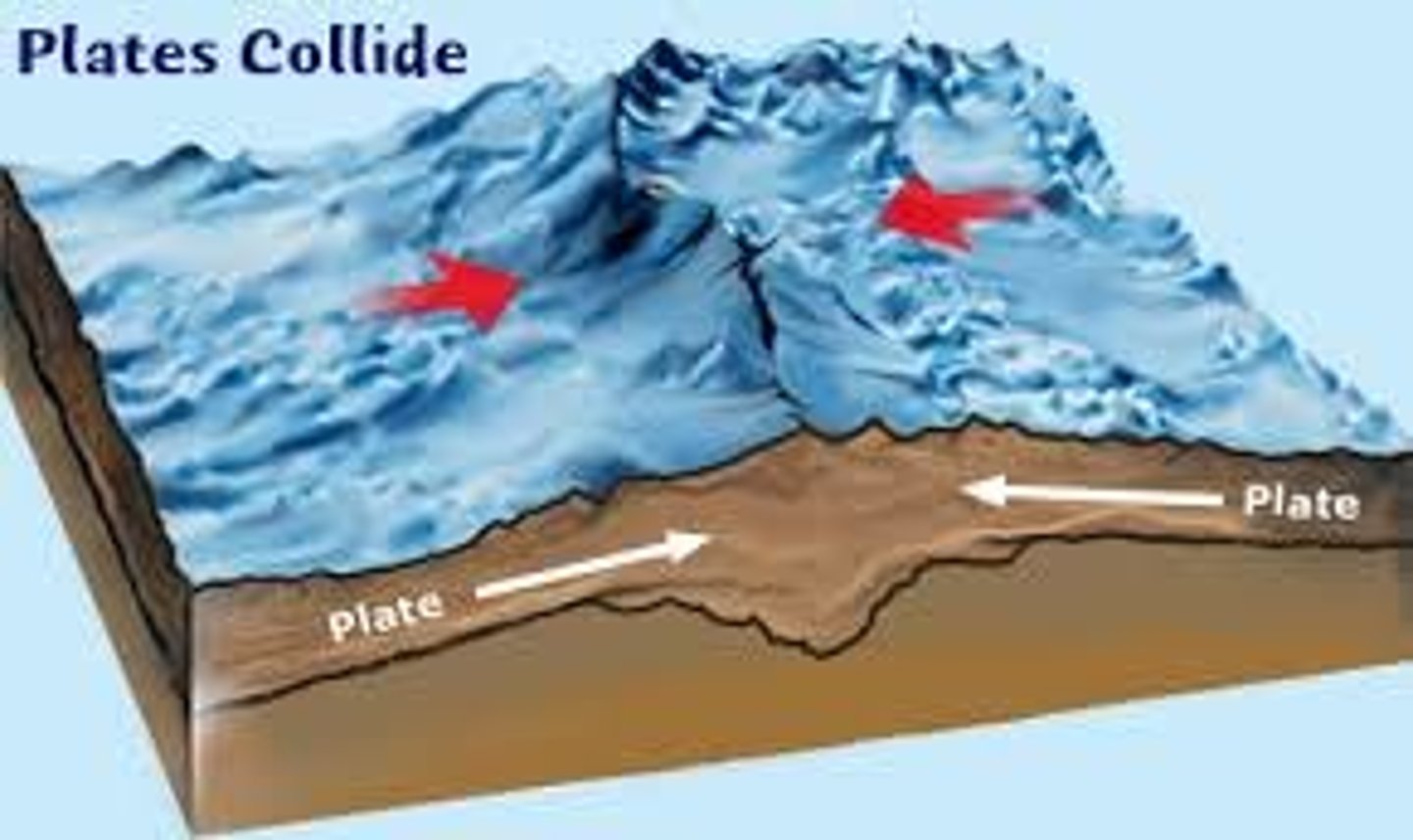
Collision Zone
Area where two continental plates collide, forming mountains.
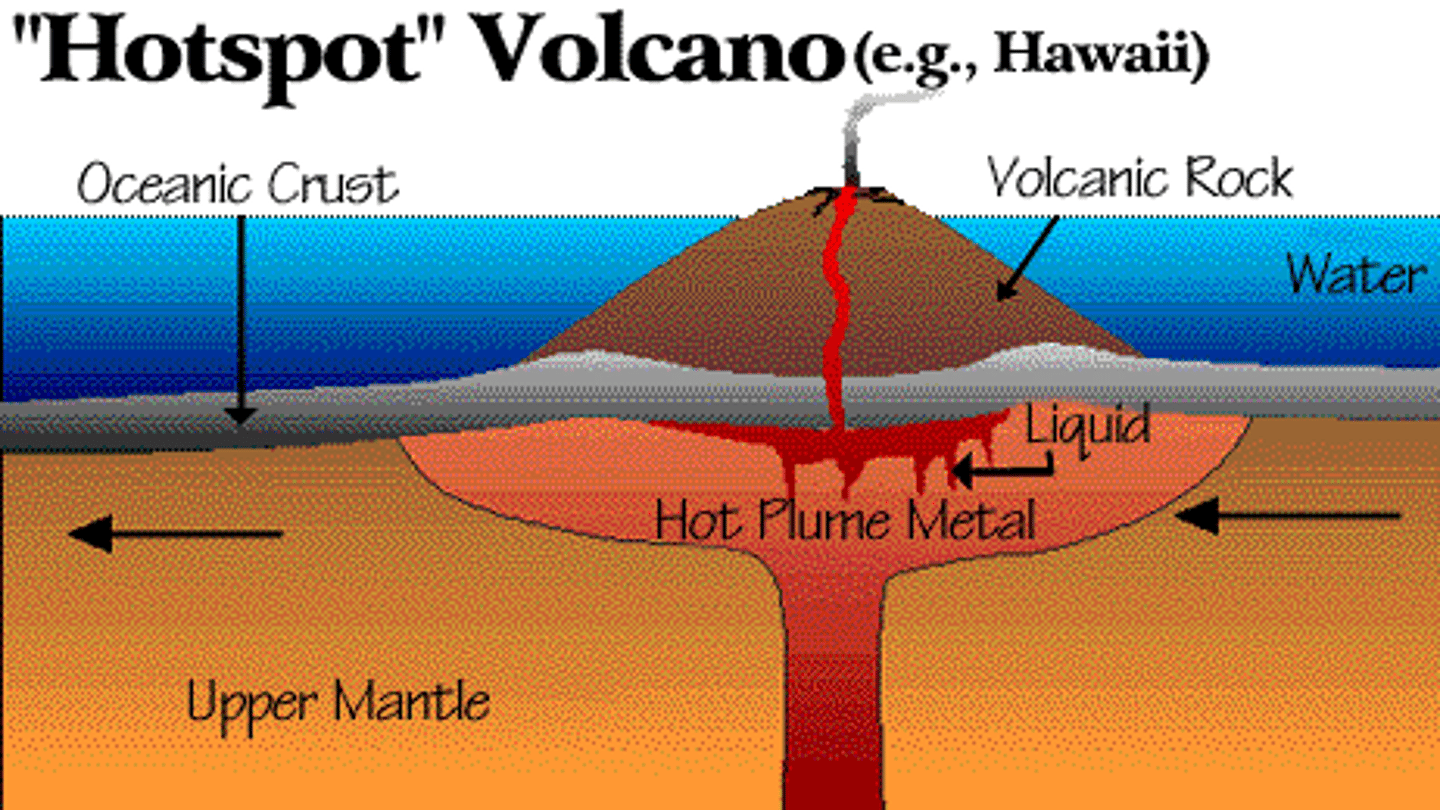
Hotspots
Areas of volcanic activity caused by plumes of magma rising through the mantle.
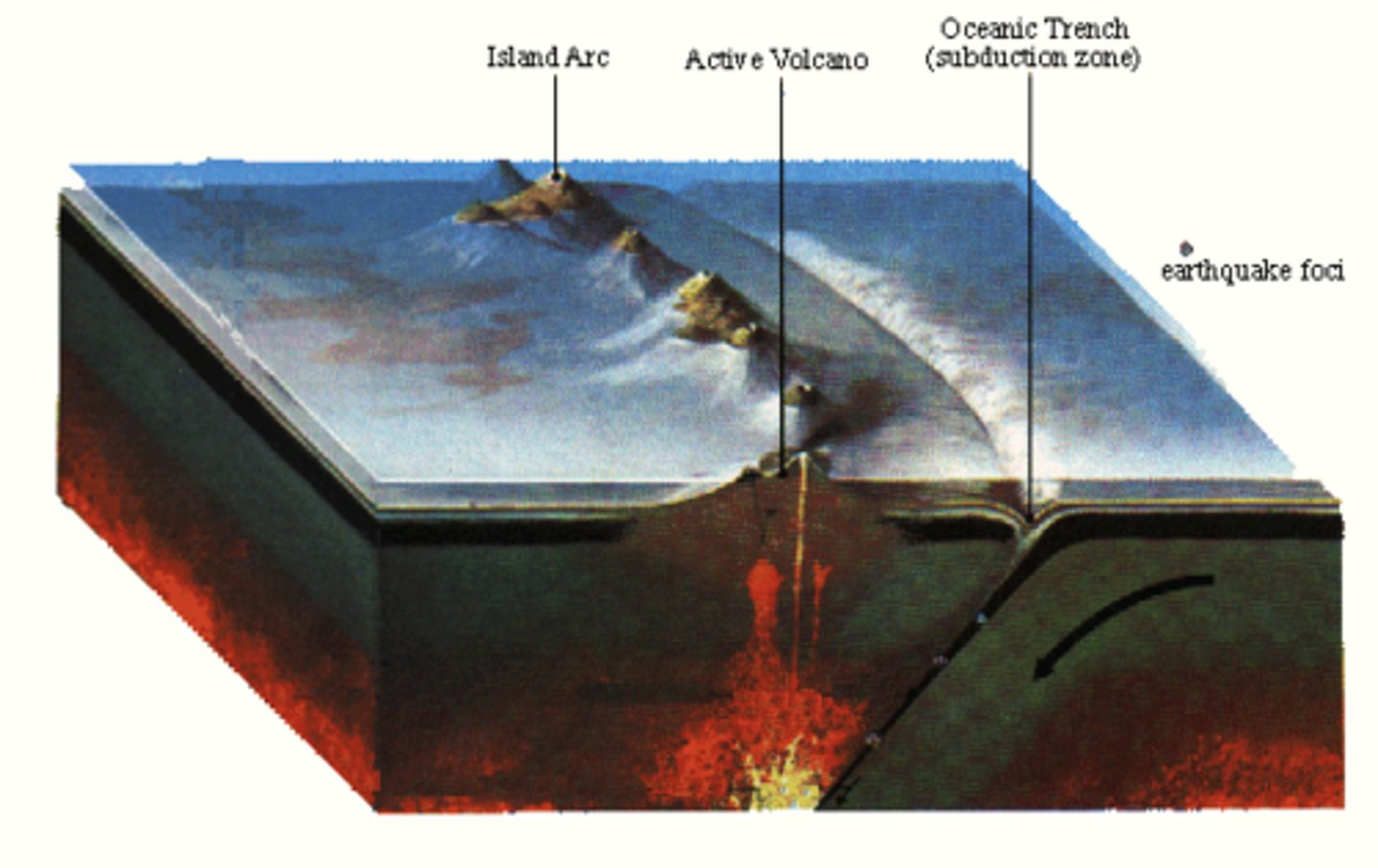
Island Arcs
Chains of volcanic islands formed along subduction zones.
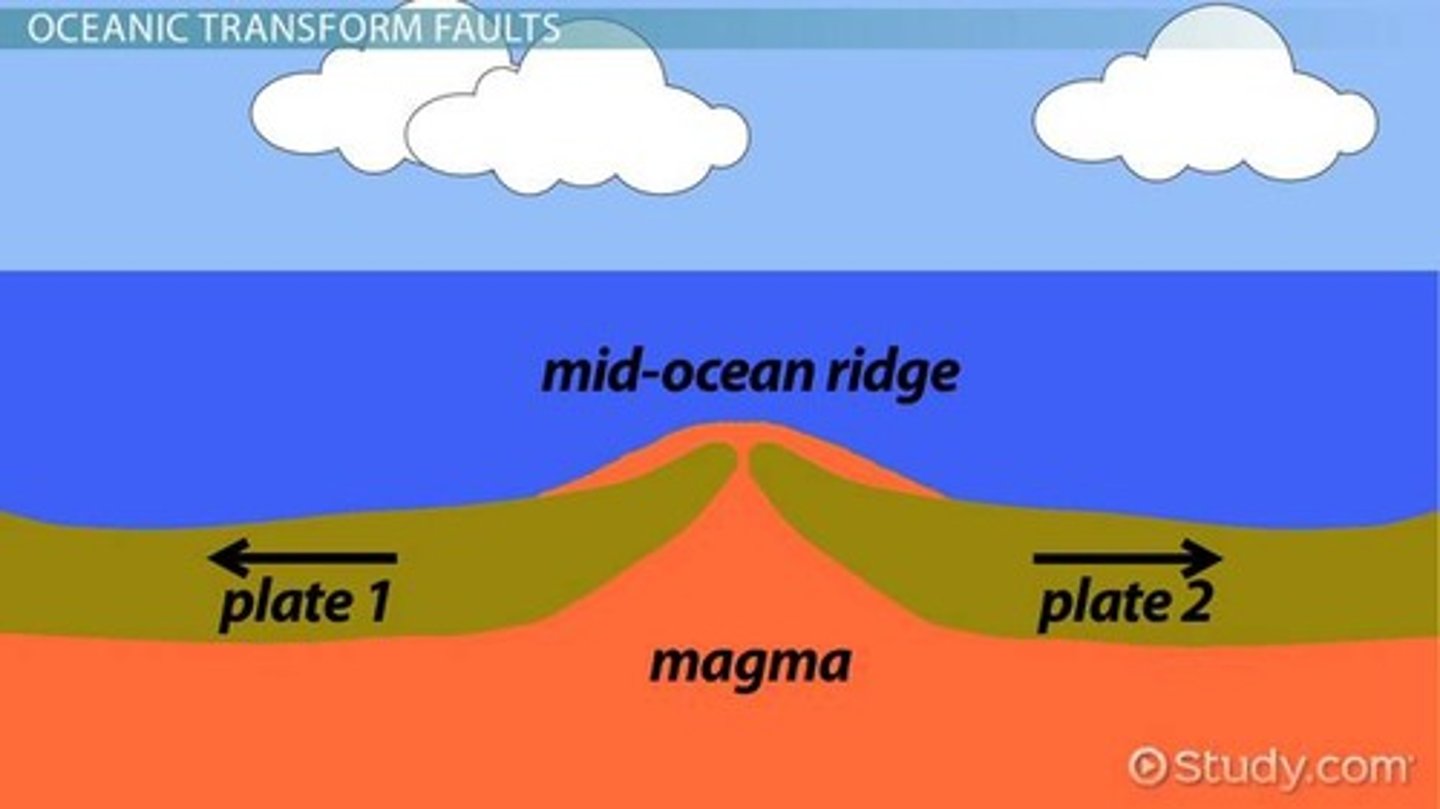
Seafloor Spreading
The process of new oceanic crust forming at mid-ocean ridges and moving outward.
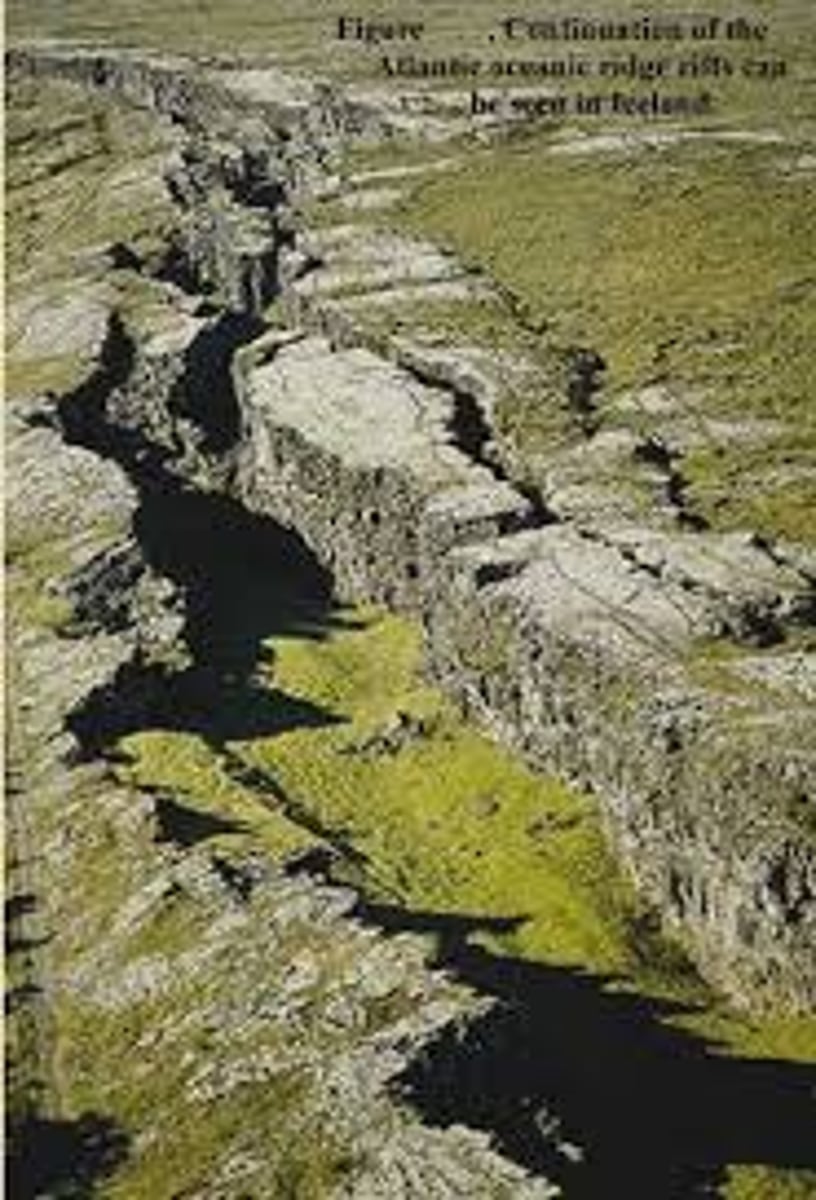
Rift Valleys
Deep valleys formed where tectonic plates diverge on land.

Mid-Oceanic Ridges
Underwater mountain chains formed by seafloor spreading.
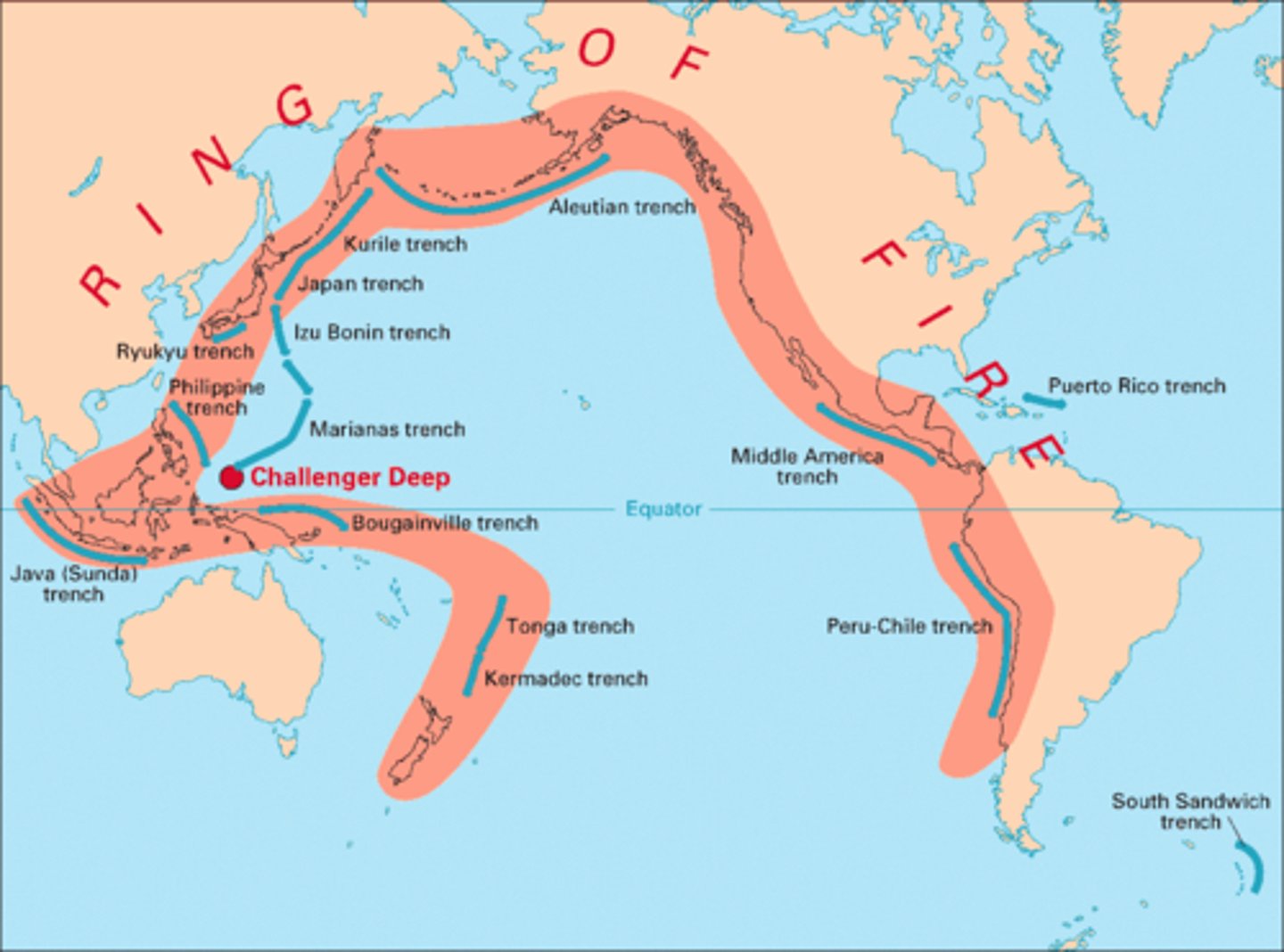
Ring of Fire
The zone of frequent earthquakes and volcanoes around the Pacific Ocean.
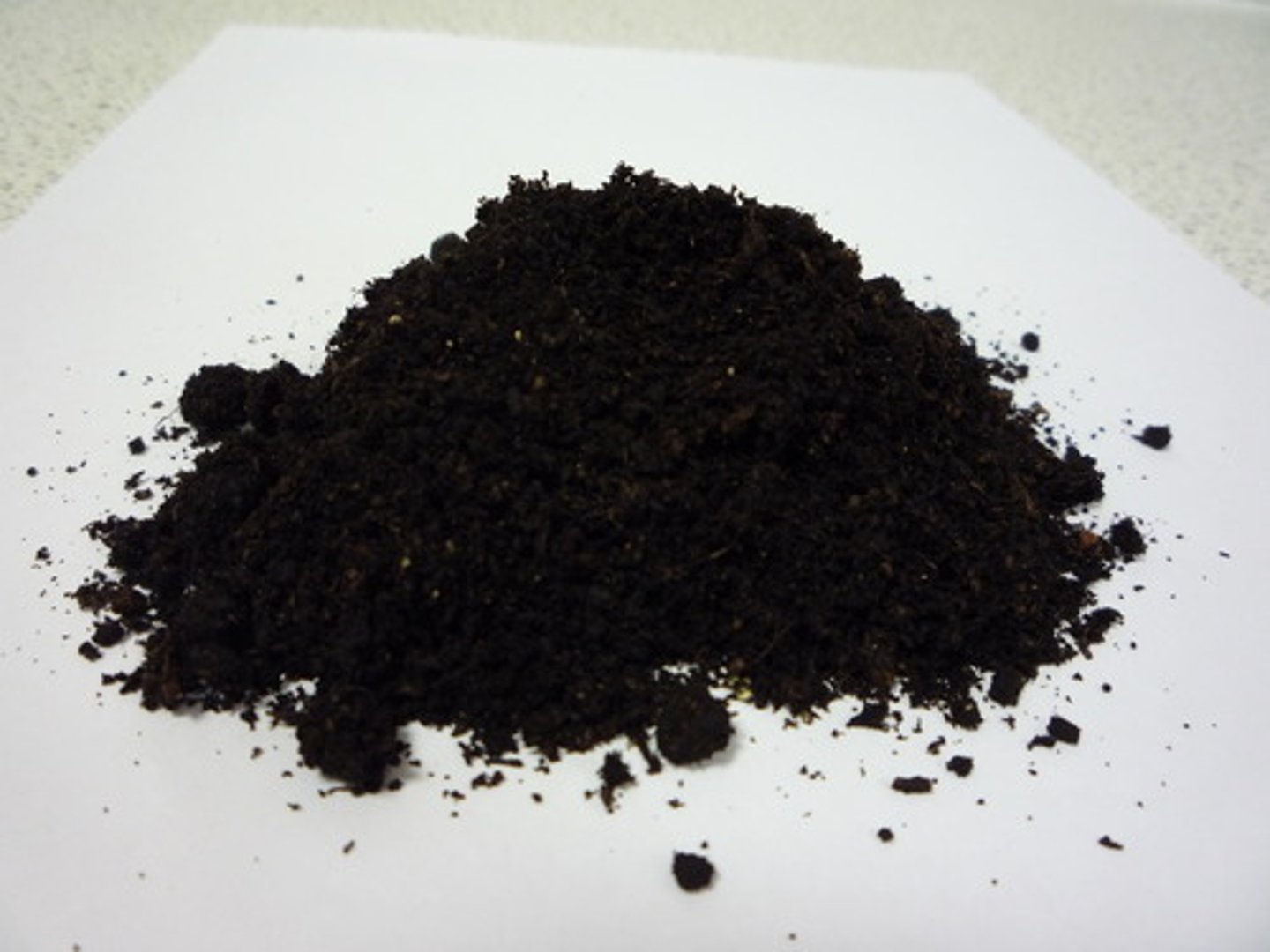
Humus
Decayed organic matter in soil that improves fertility and water retention.

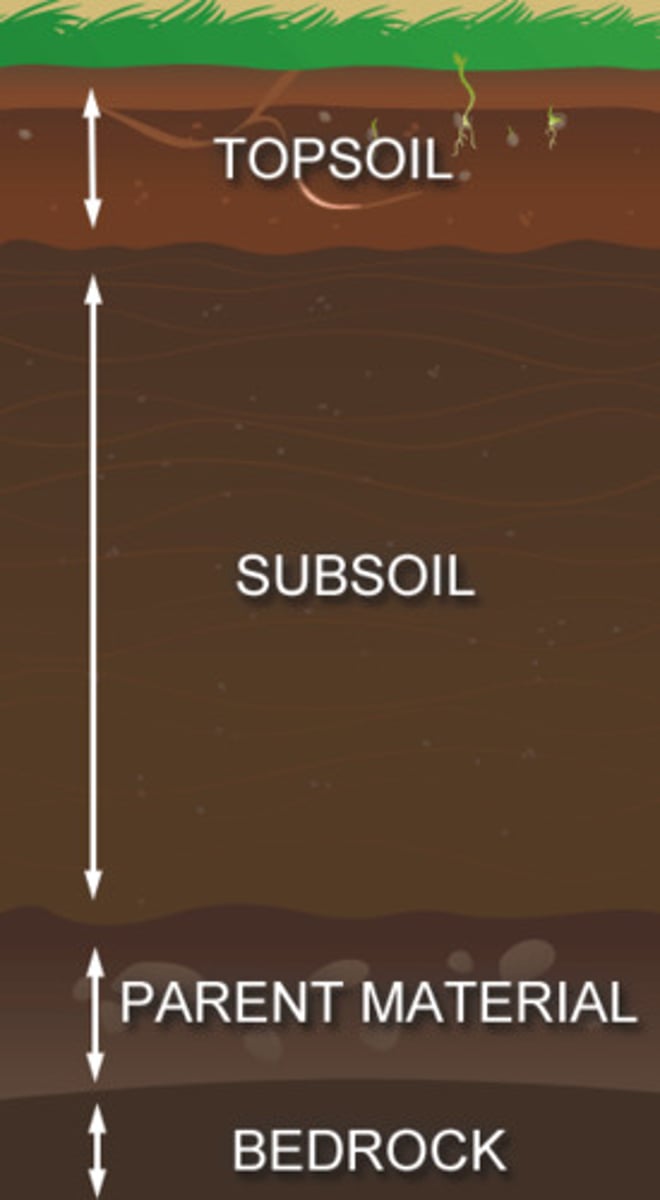
Parent Material
The original rock or sediment from which soil forms.

Topography
The shape and features of Earth's surface, influencing soil and water movement.
Topsoil
The nutrient-rich upper layer of soil where most plant roots grow.
Soil Degradation
The decline in soil quality due to erosion, compaction, or nutrient loss.

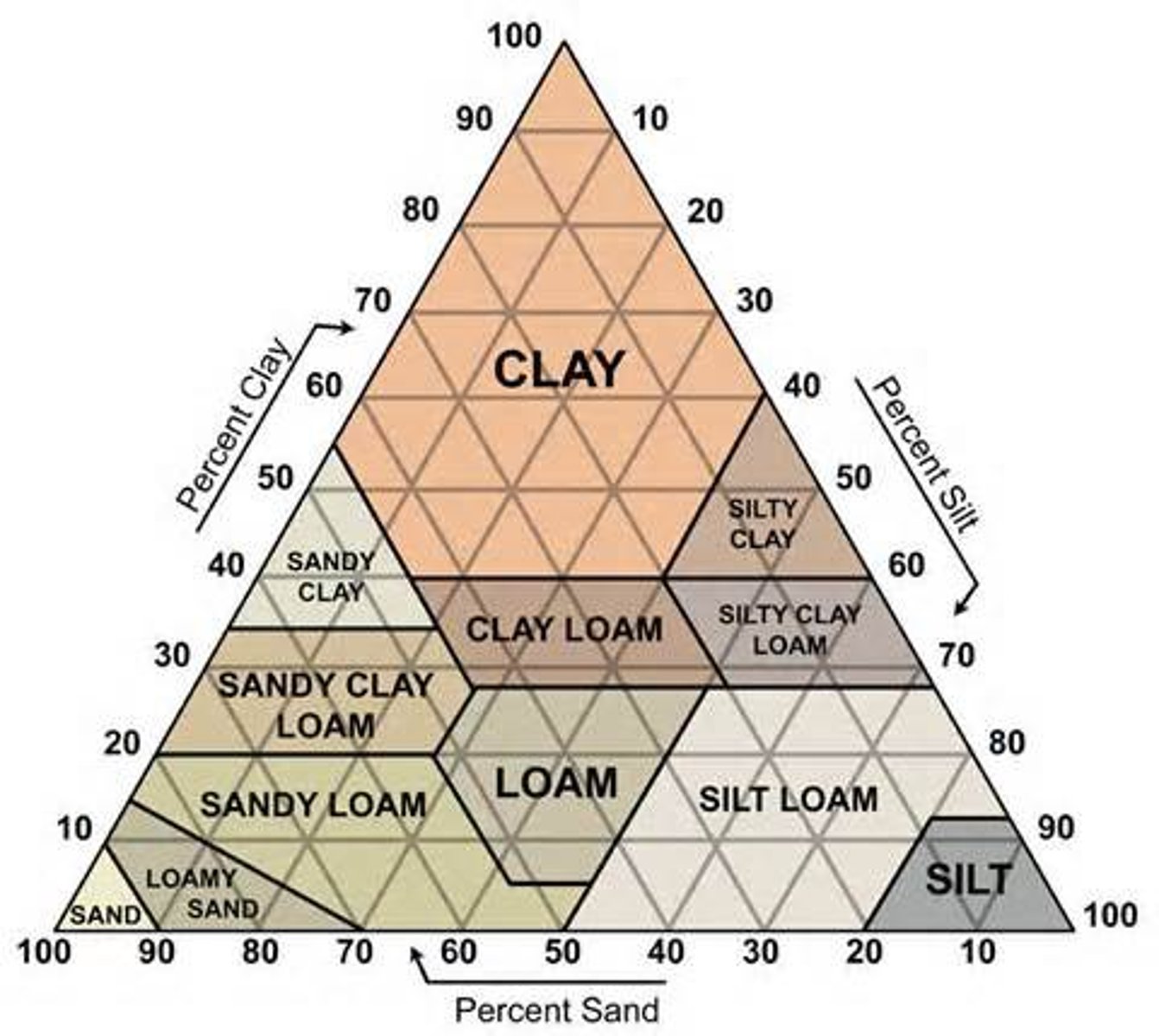
Soil Texture
The relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay in soil.
Porosity
The amount of pore space in soil that can hold air or water.
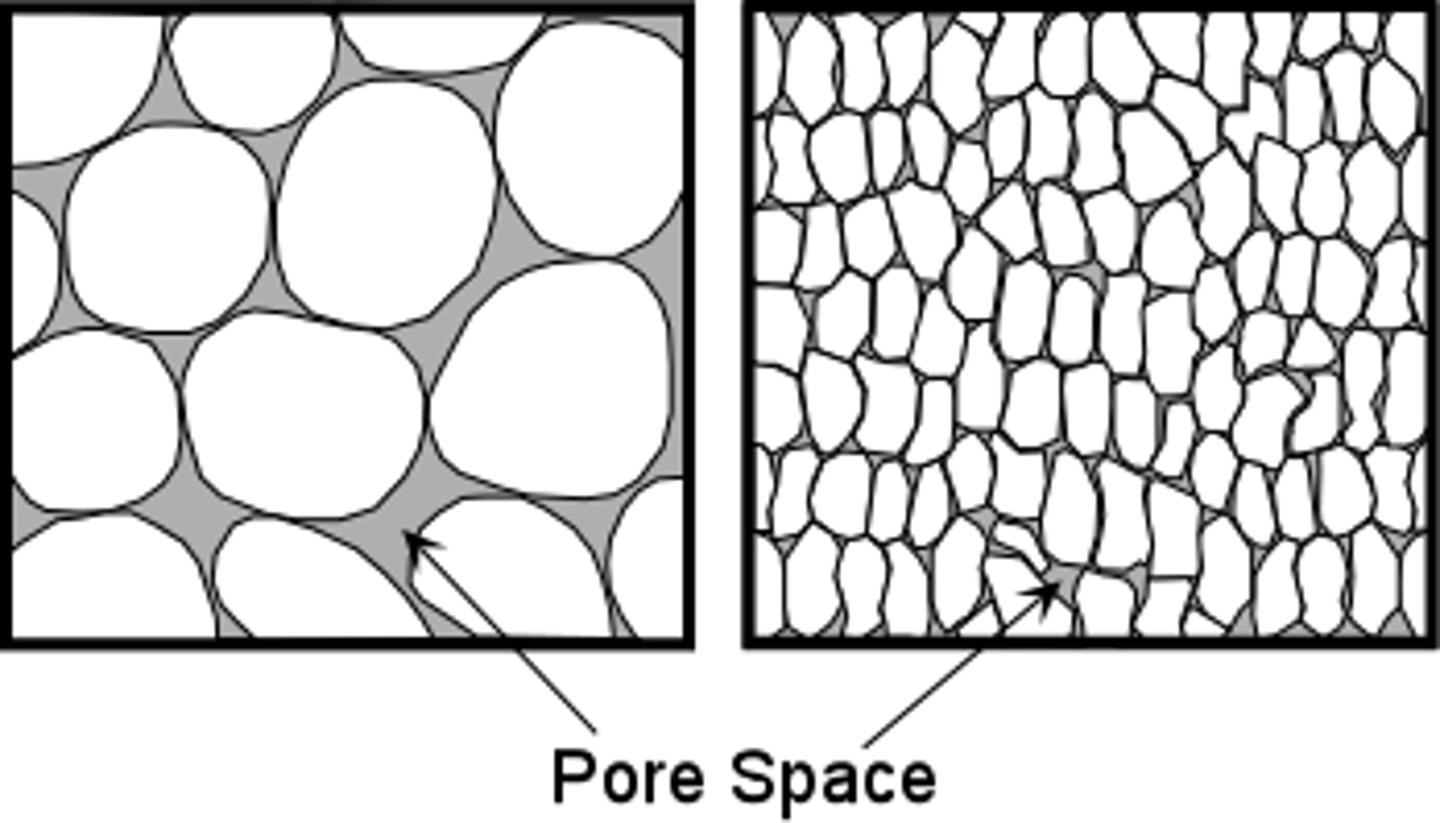
Permeability
The ability of soil to transmit water.

Water Holding Capacity
The ability of soil to retain water for plant use.
Solar Radiation
Energy emitted by the sun reaching Earth.
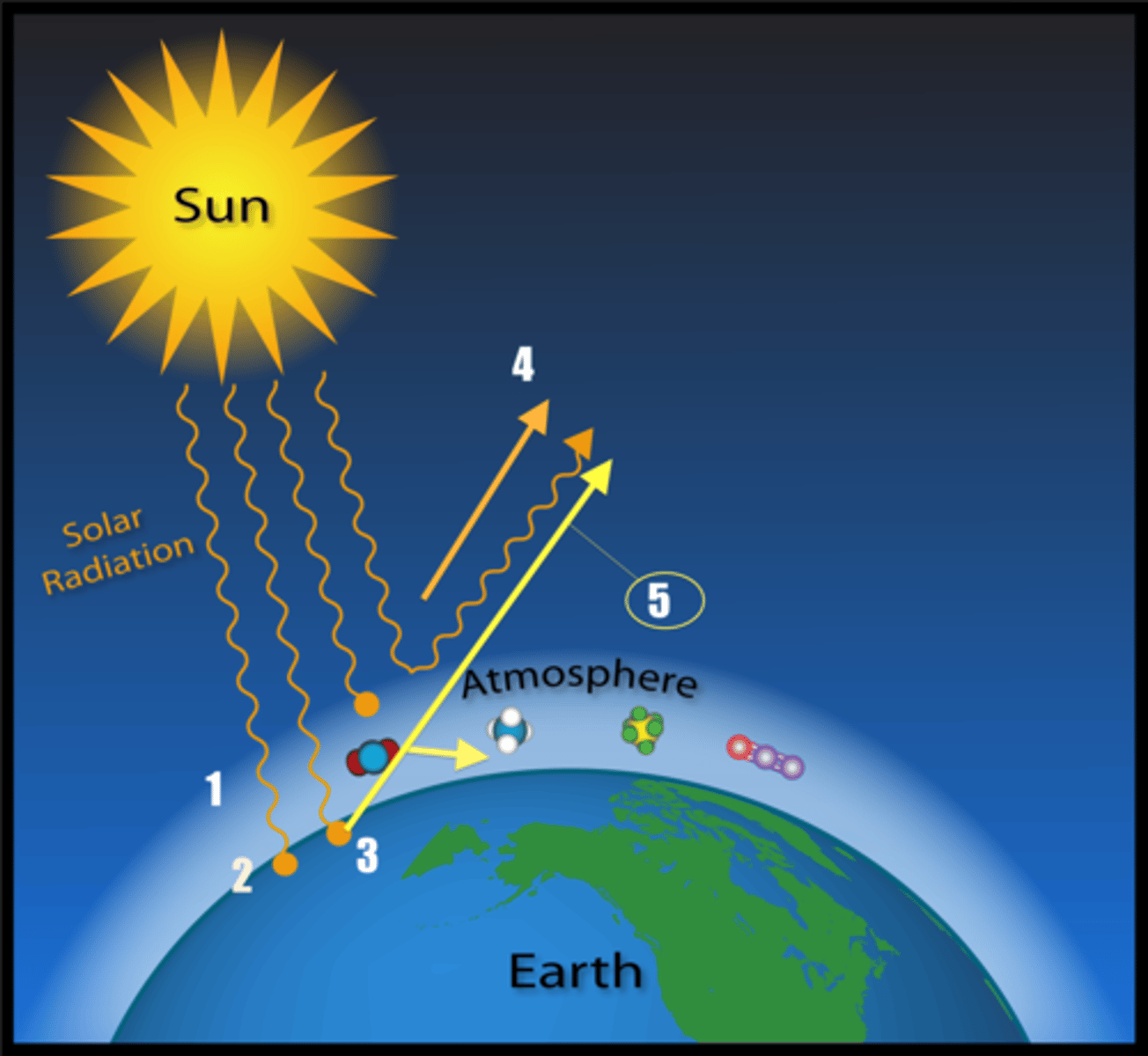
Insolation
The amount of solar radiation received by a specific area.
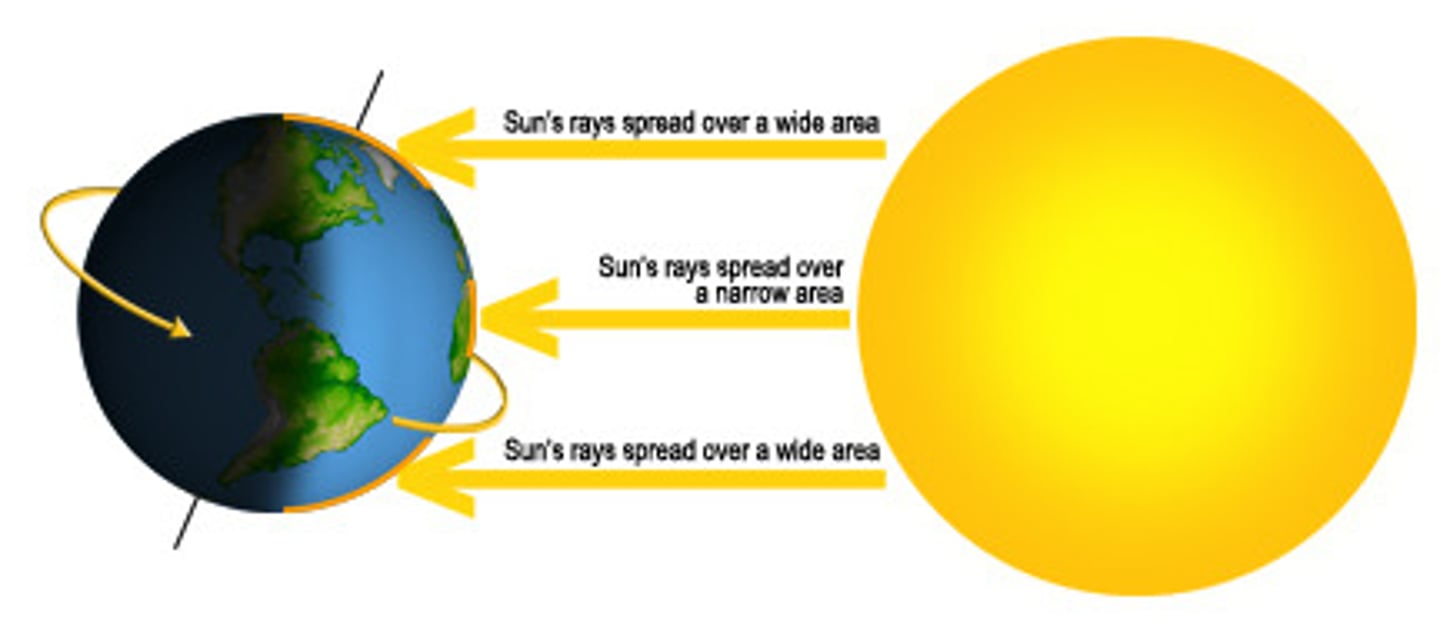
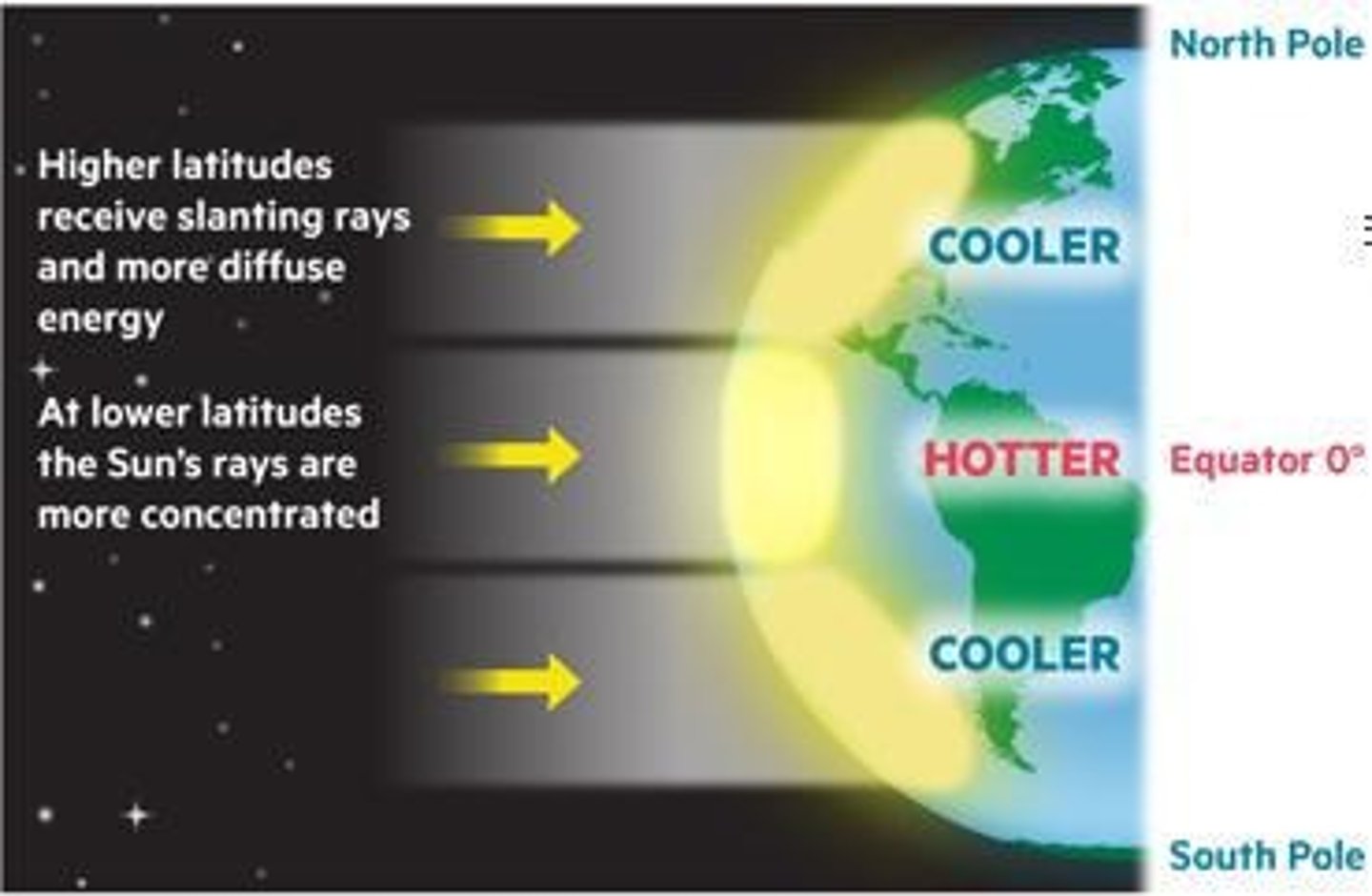
Latitude
The distance north or south of the equator, affecting climate and sunlight intensity.
Equinox
The time of year when day and night are equal in length.
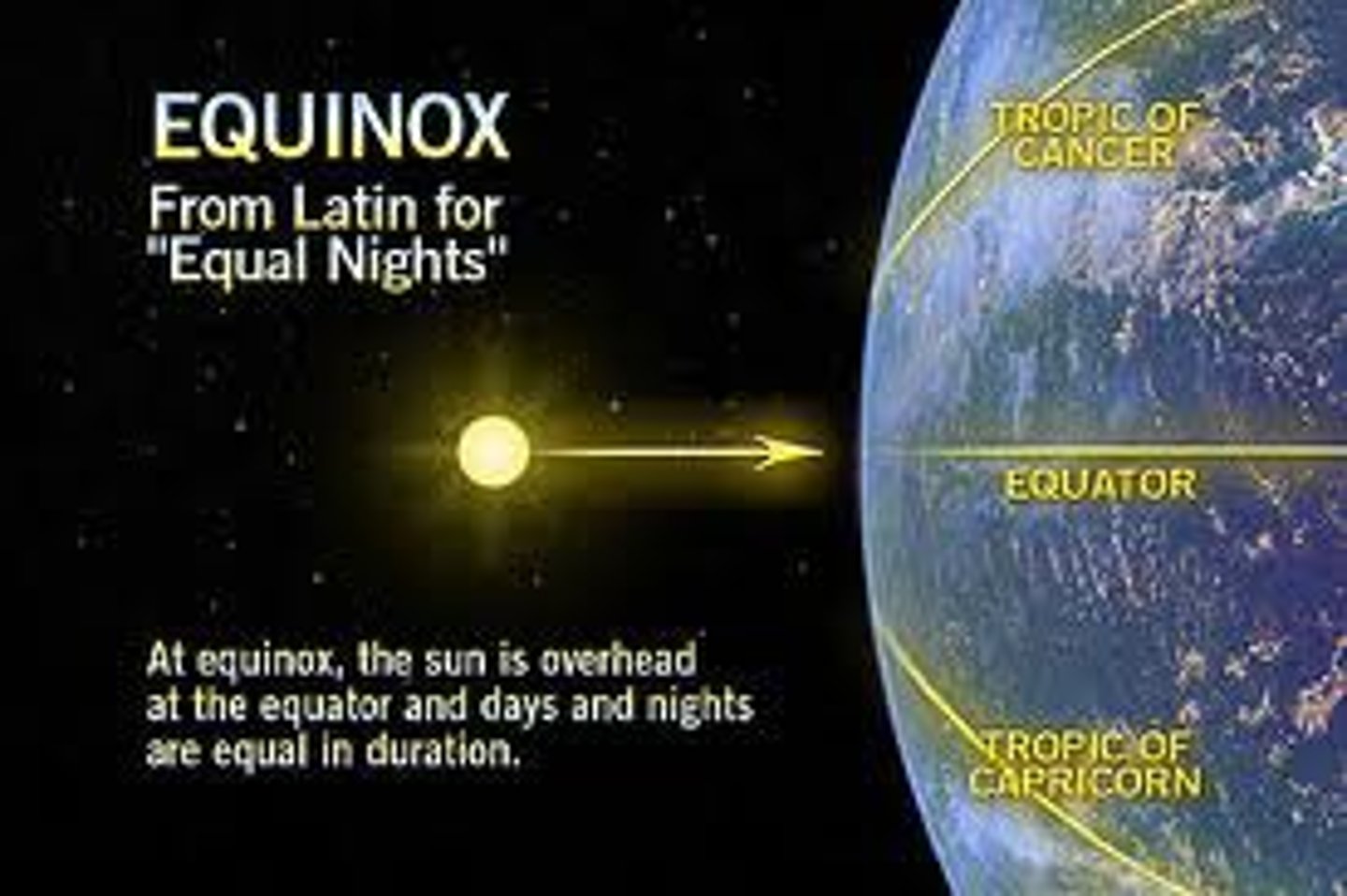
Solstice
The time when the sun is at its highest or lowest point in the sky, marking seasonal change.
Convection cycles/current
Circular movement of fluids caused by heat rising and cool material sinking.
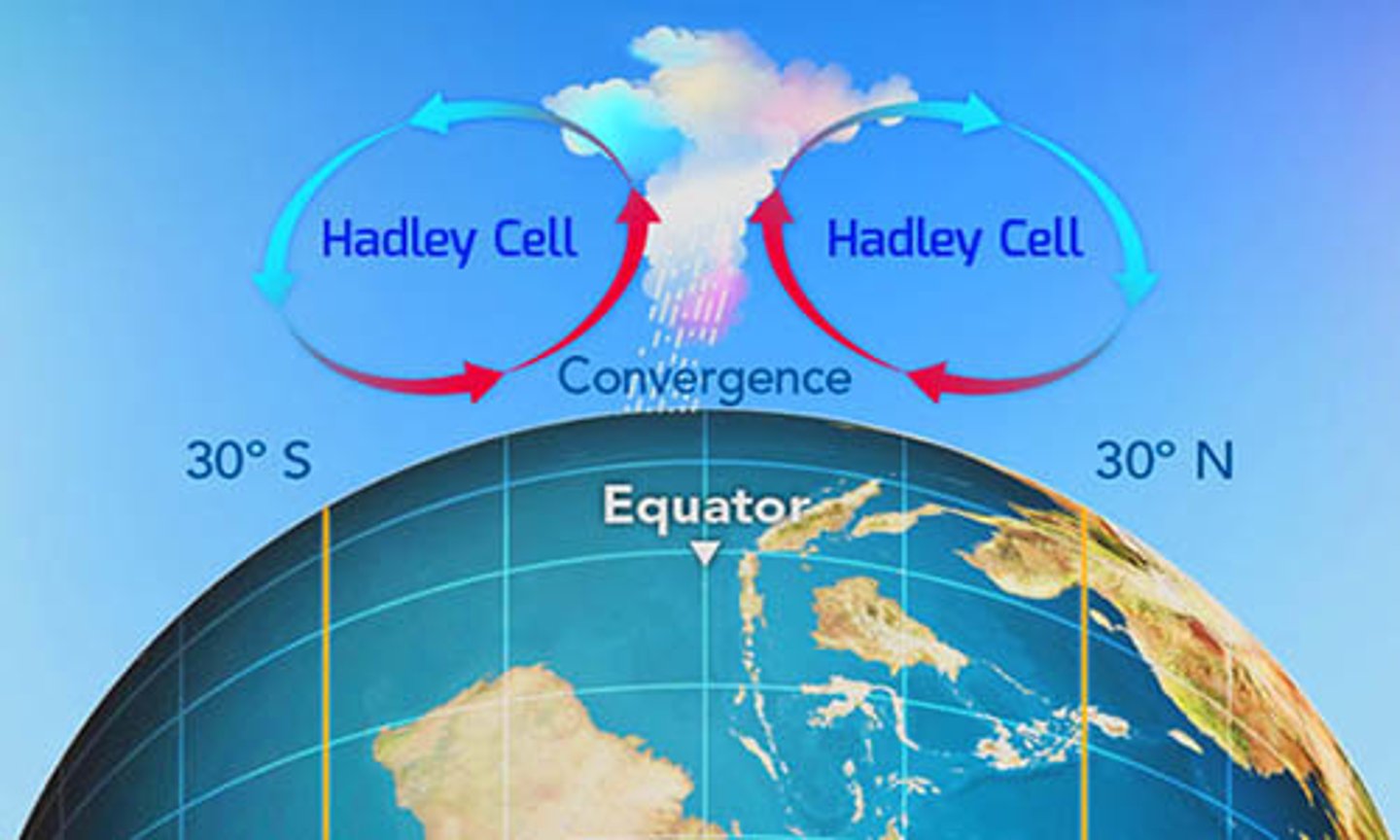
Hadley Cells
Atmospheric convection cells that move warm air from the equator to about 30° latitude.
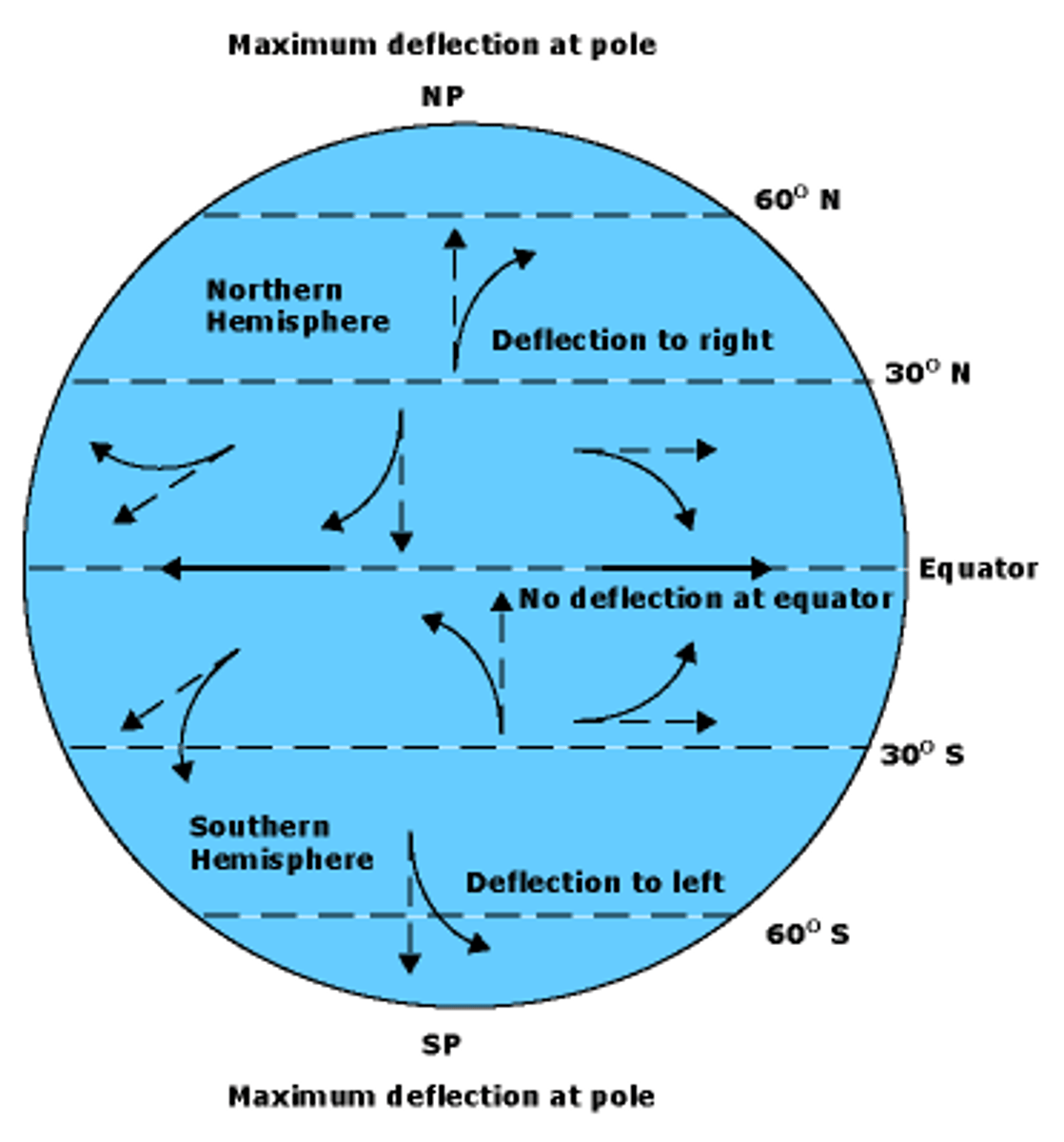
Coriolis Effect
The deflection of moving air and water due to Earth's rotation.
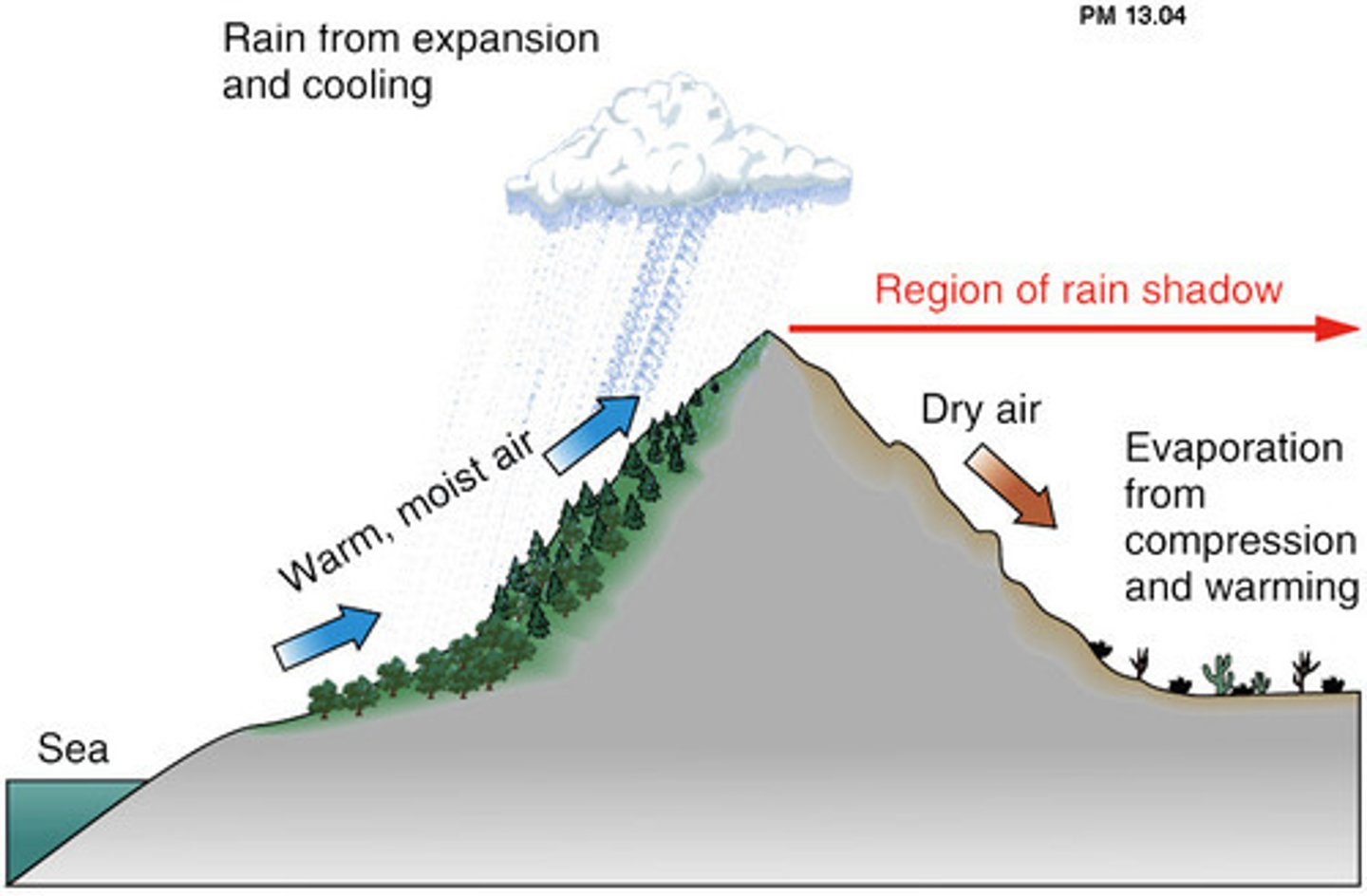
Rainshadow effect
Dry conditions on the leeward side of a mountain caused by moisture loss on the windward side.
ENSO (El Niño Southern Oscillation)
Climate pattern involving changes in Pacific Ocean temperatures and wind patterns.
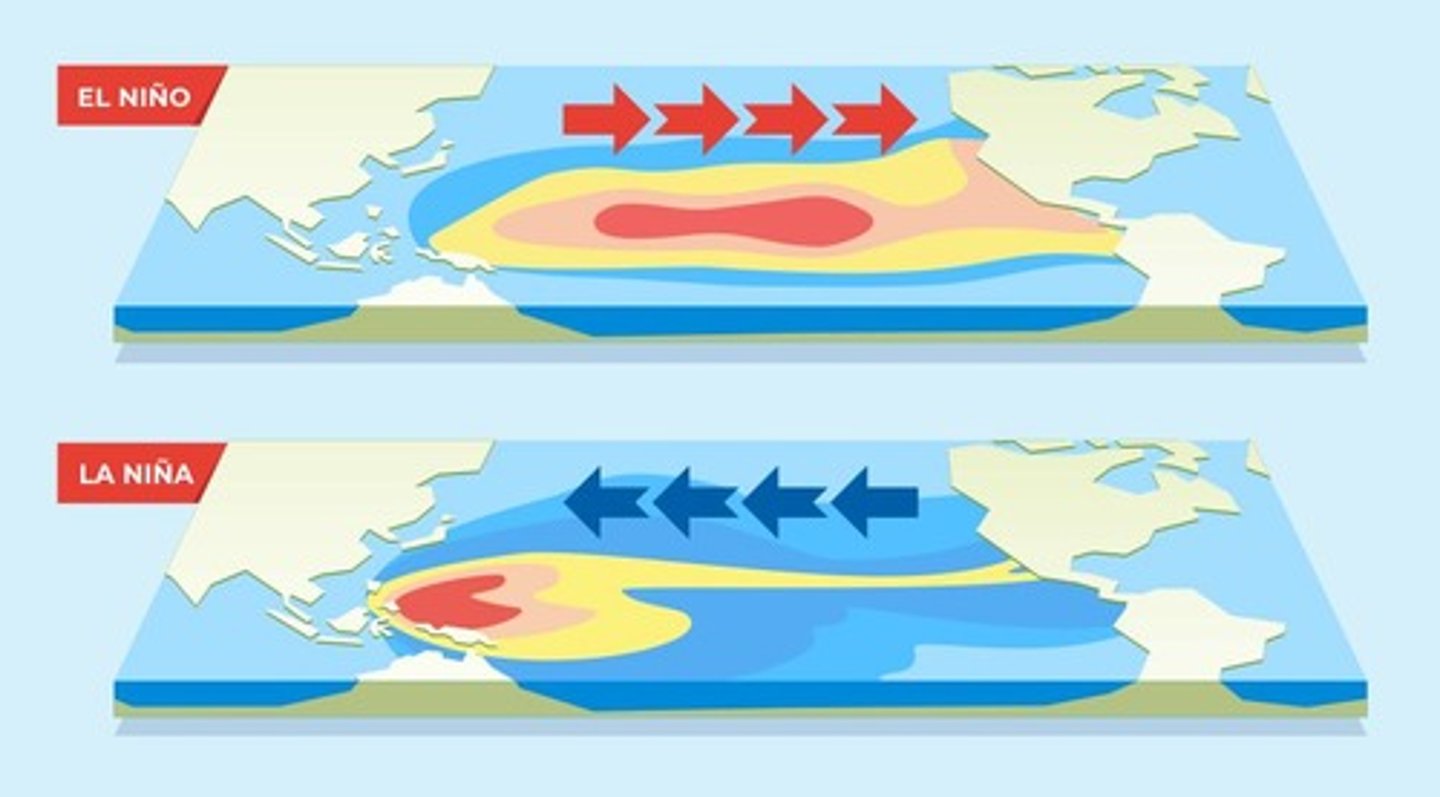
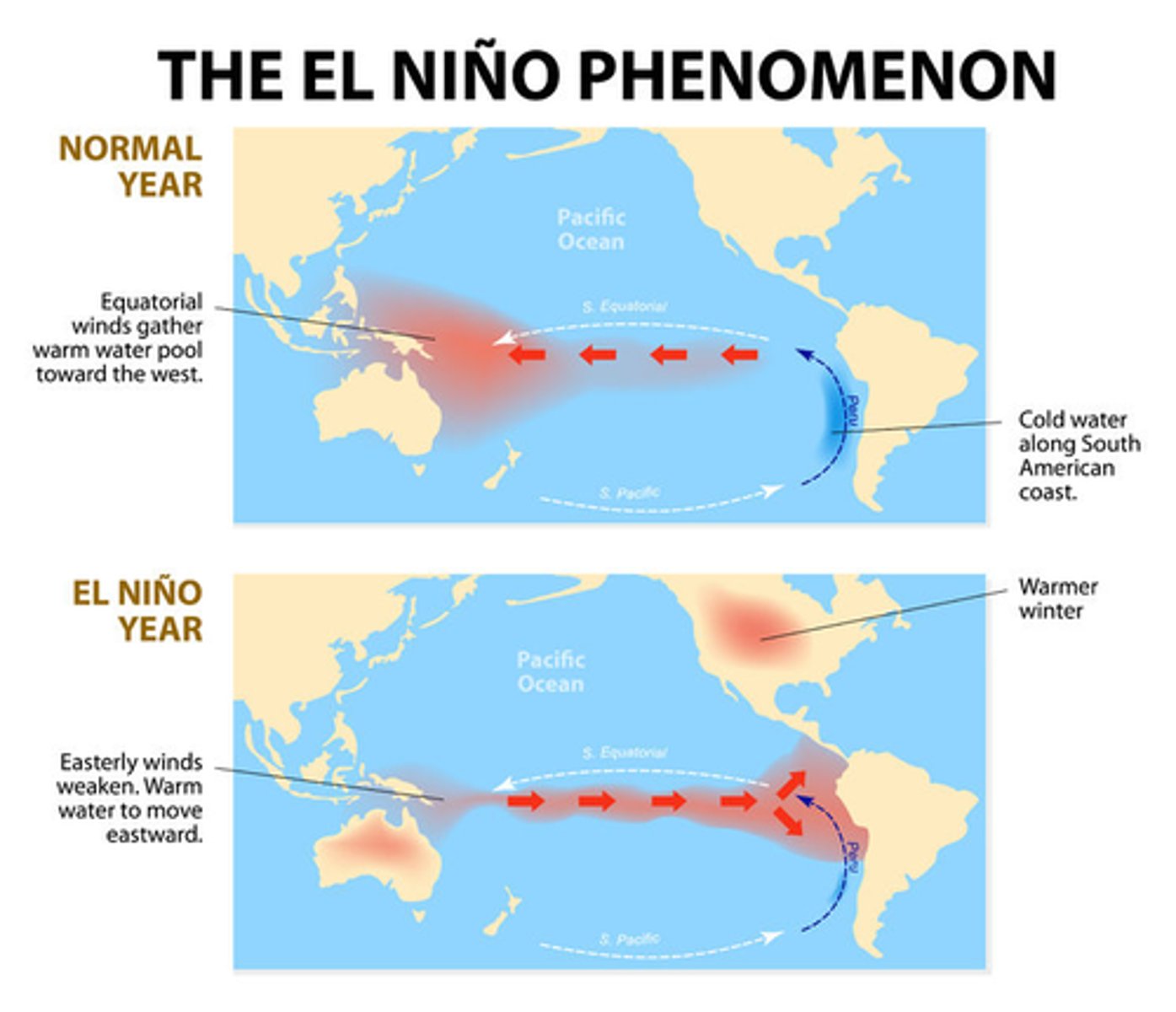
El Niño
Warming of Pacific waters causing weakened trade winds and global weather changes.
La Niña
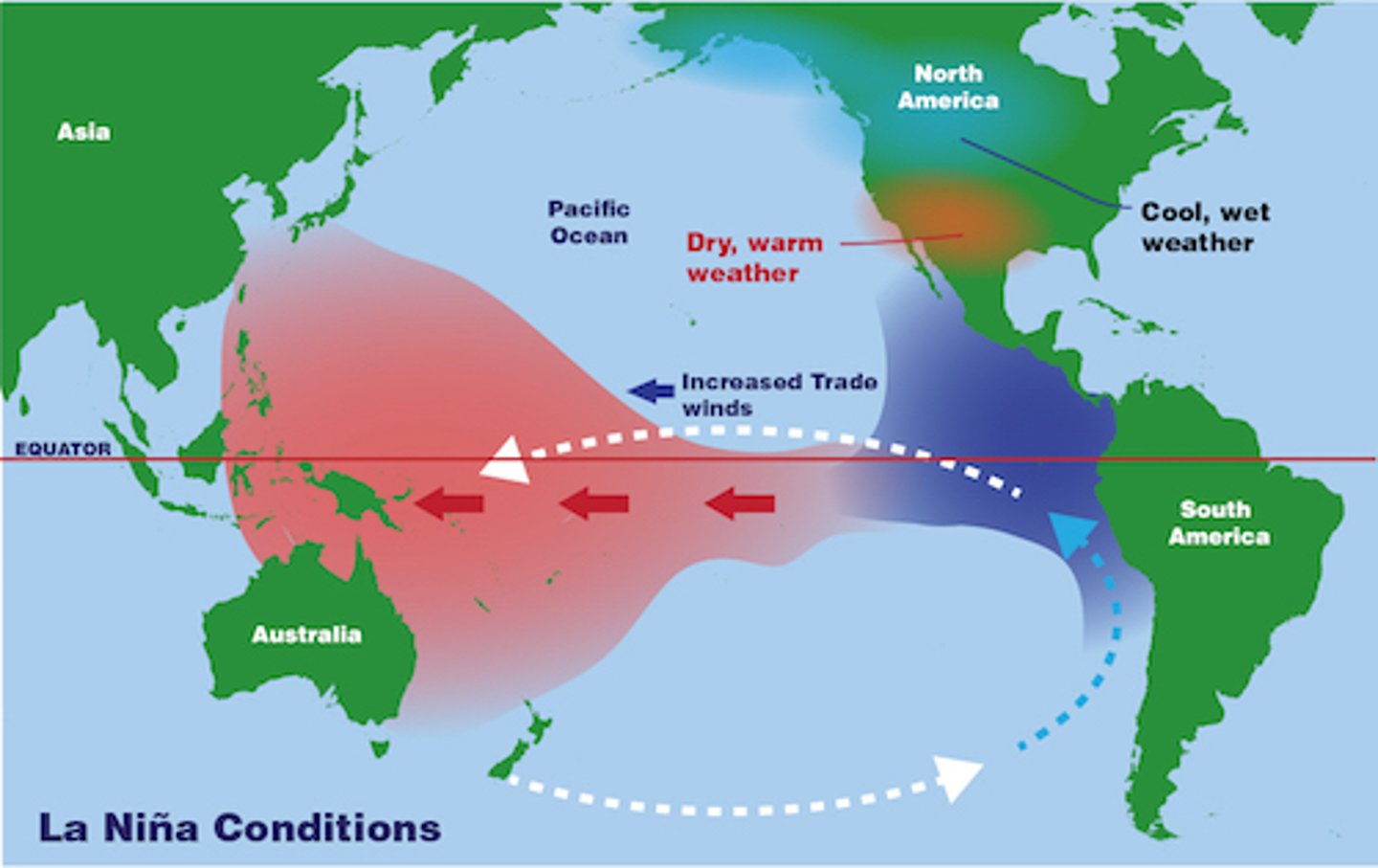
Cooling of Pacific waters causing stronger trade winds and opposite weather effects of El Niño.
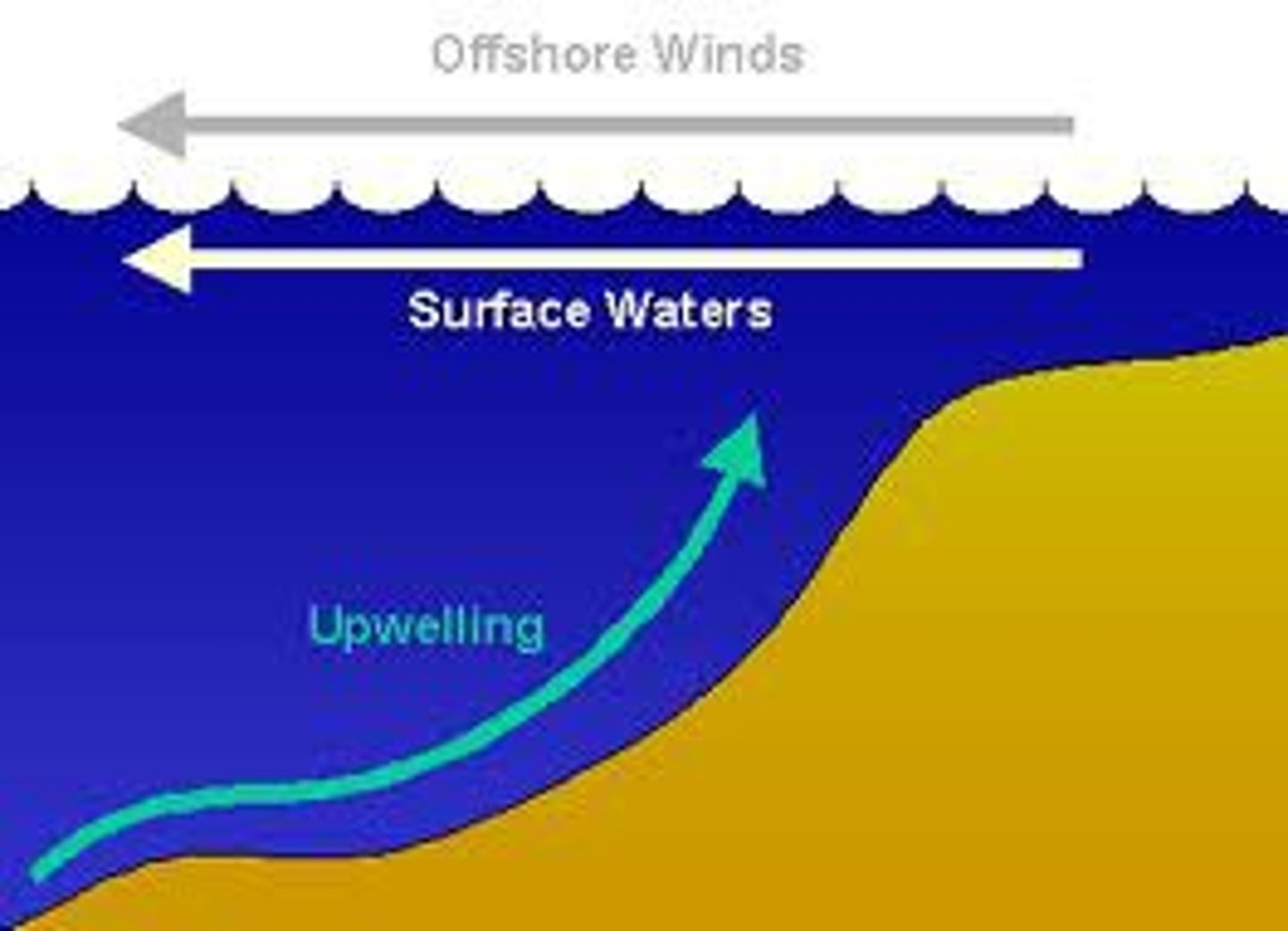
Upwelling
The rise of cold, nutrient-rich water to the ocean surface.
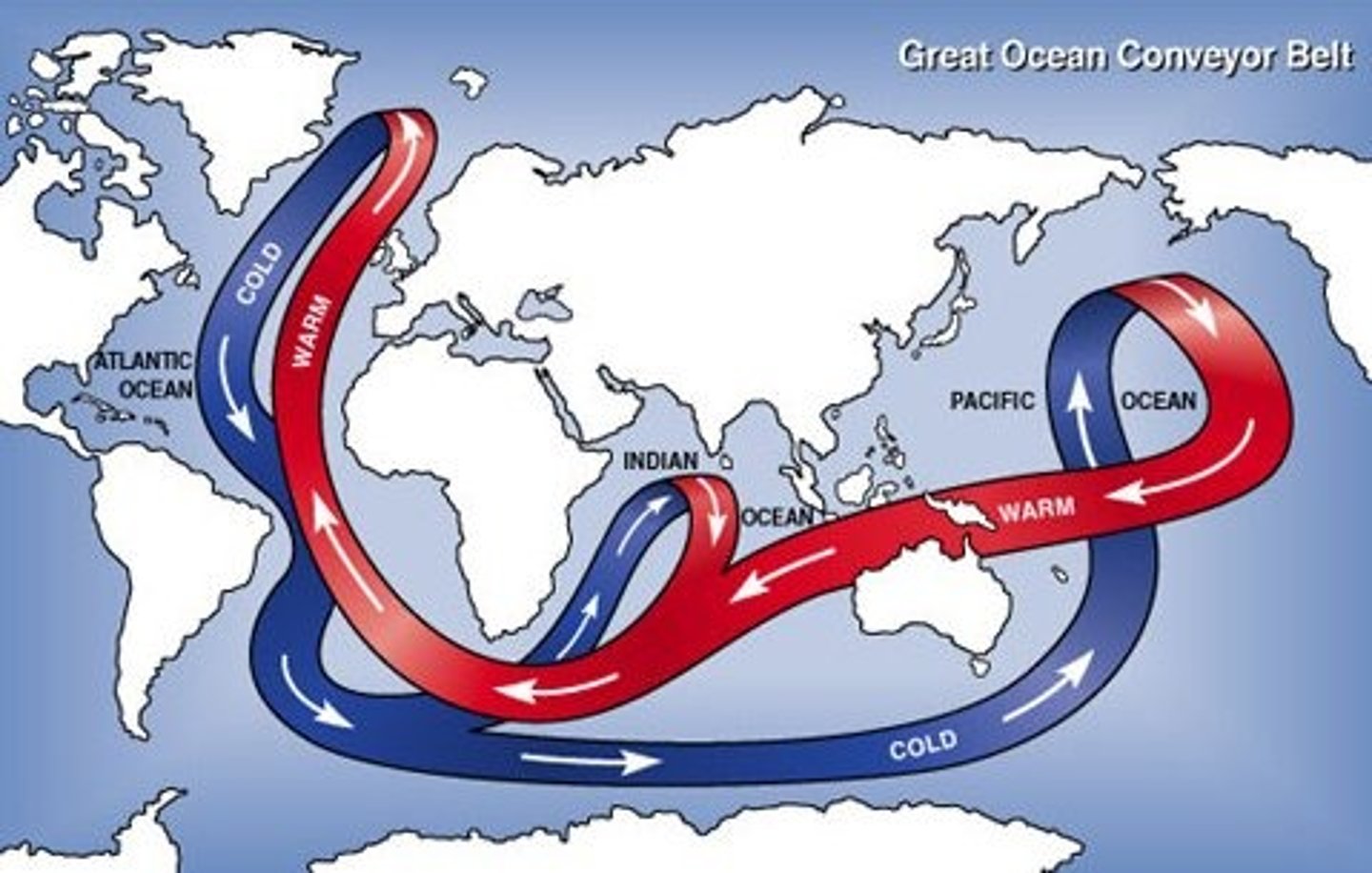
Thermohaline Circulation
Global ocean circulation driven by differences in temperature and salinity.
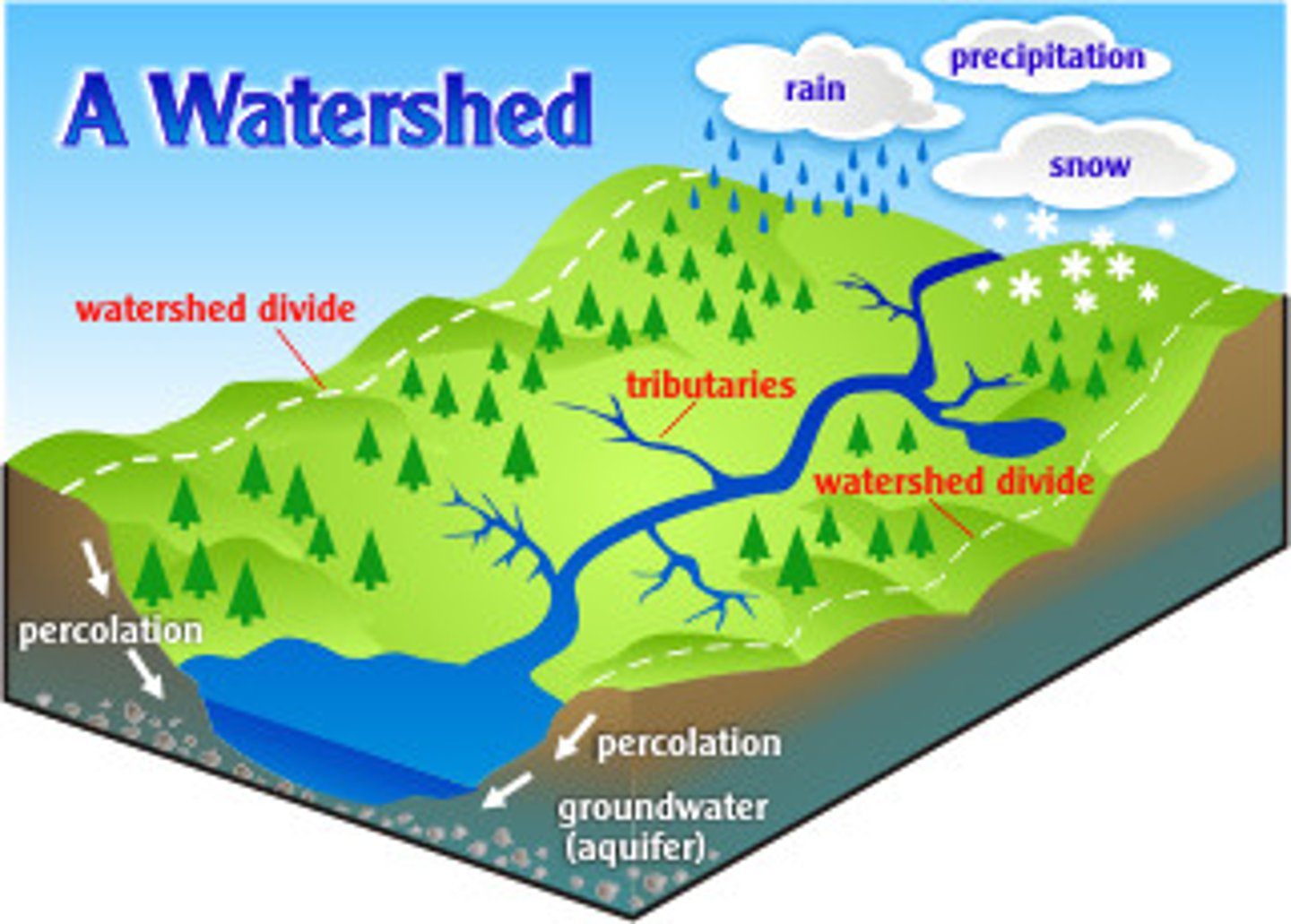
Watershed
The land area that drains into a particular river, lake, or ocean.
Riparian Buffer
Vegetated area along waterways that protects against erosion and filters pollutants.
