biology classification
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
why do we use a binomial naming system?
common names can vary for a single species
how is a scientific name written?
The genus is capitalized, and the whole name is in italics or underlined
who invented binomical nomiclature?
carolus linneaus
7 levels of the Linnaean classification system
Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species
(King Phillip came over for great spaghetti)
What are some limitations of the Linnaean classification system?
- it only focuses on physical similarities
- bad because of convergent evolution
what is a phylogeny?
it shows how each member of the family is related to other members
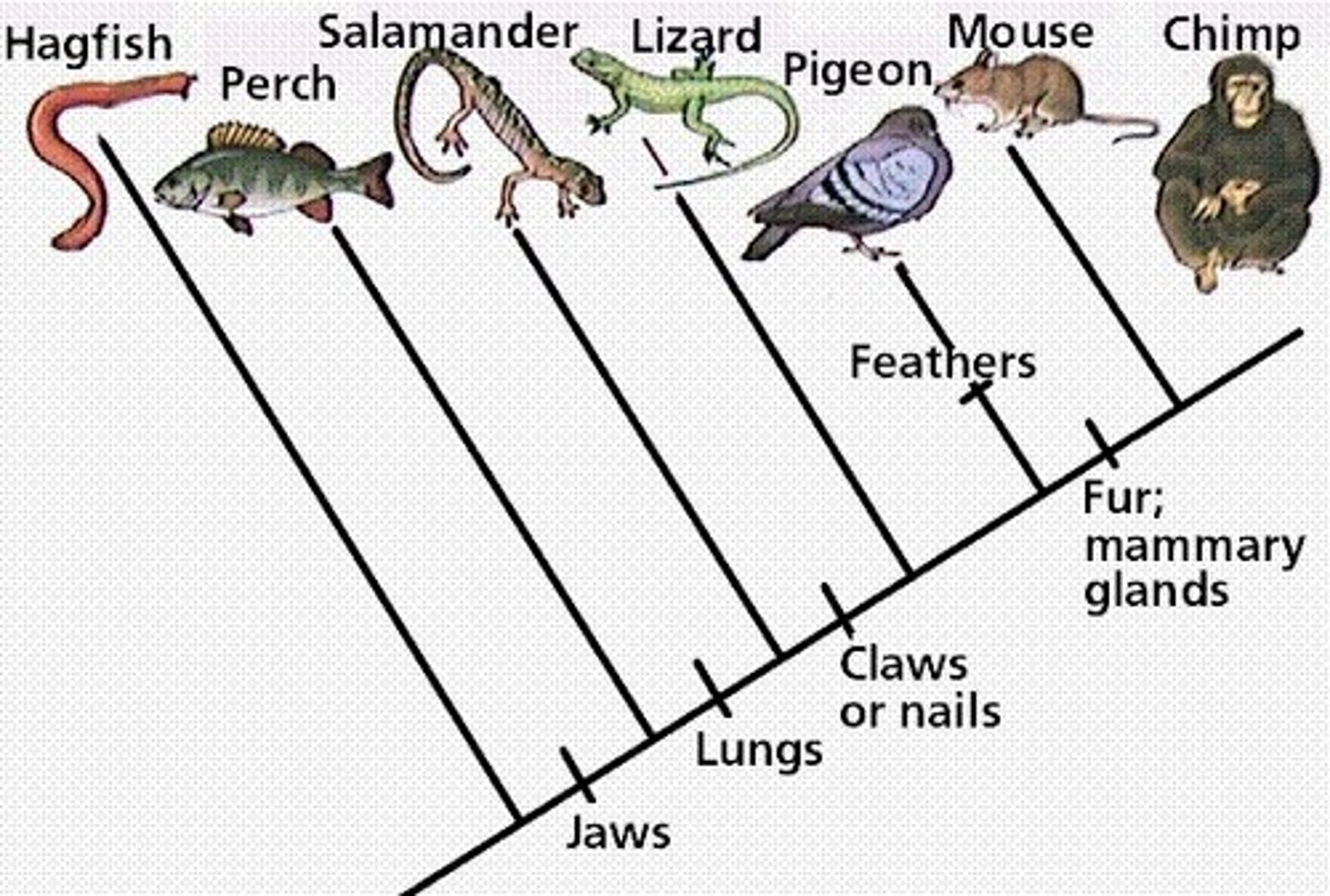
what are the three domains?
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
bacteria
single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus; prokaryotes
archaea
single-celled prokaryotes
extremophiles
no organelles
differ from bacteria in cell wall structure and genetics
eukarya
eukaryotes
single-celled or multicellular
includes plants, animals, fungi, protists
what are the 6 kingdoms?
Plants, Animals, Protists, Fungi, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria
why is cladistics a work in progress and what information do we currently rely on for current data?
new findings can lead scientists to change how they classify organisms.
we rely on molecular data
why are viruses not considered alive?
they cannot reproduce on their own or carry out thier own metabolic processes
what are viruses made out of?
- DNA or RNA
- Double or single stranded
- Surrounded by a capsid (protein coat)
- Viral envelope (lipid bilayer)
- Surface proteins that aid infecting host cells
what are the different shapes of capsids?
helical (rod shaped), polyhedral, or more complex (bacteriophages)
what is a single virus particle called?
virion
How is the "host range" determined?
it fits in surface proteins to receptor molecules on the host cell surface
what does a virus do upon entering a host cell?
it manufactures viral proteins
what is a bacteriophage?
a virus that infects bacteria
lysogenic cycle
- replicated phages WITHOUT destroying the host
- viral DNA Is incorporated into host cell's chromosome and called a prophage
- replicates with the host
lytic cycle
- kills the host cell
- virus replicated and then leaves
- causes cell to lyse or burst
how do vaccines work to prevent illness?
vaccines are harmless versions of pathogenic microbes
they stimulate the immune system to mount defense against the actual pathogen
why can't you take antibiotics for a virus?
antibiotics are meant to kill bacteria, not viruses
viruses do not have a cell wall for the antibiotics to attack, they instead have a protective protein coat
what are some common viral diseases?
Common cold, influenza, pneumonia, and hepatitis
how does the structure of prokaryotes differ from the structure of eukaryotes?
prokaryotes are smaller and lack membrane bound organelles
what is the bacterial cell wall made out of?
peptidoglycan
structure of bacteria
unicellular prokaryotes
spheres (cocci), rods (bacilli), spirals (spirilla)
what does a gram stain result tell us?
gram-neg bacteria have less peptidoglycan and stain lighter than gram-pos bacteria
how do prokaryotes move?
flagella and pili
how can prokaryotes be grouped based off their need for oxygen?
obligate aerobe - requires oxygen
obligate anaerobe - no oxygen
facultative anaerobe - survives without oxygen when necessary
how do prokaryotes reproduce?
binary fission
- high diversity from mutations allows for rapid evolution
what is an endospore and why does it help bacteria survive?
an endospore is a thick and protective wall formed around a copy of the bacteria's DNA
it prevents it from drying out, temperature changes, and disinfectants
why do mutations build up so quickly in prokaryotes?
- short generation times
- haploid
what is conjugation and how does it impact bacterial evolution?
genetic material is transferred between bacterial cells and it increases genetic diversity
ecological roles of bacteria
- decomposing (break down corpses, dead vegetation, and waste products)
- nitrogen fixation (convert nitrogen in atmosphere to usable nitrogen for plants)
- bioremediation (breaking down of pollutants)
- photosynthesis (cyanobacteria produce oxygen through it)
what are some bacterial diseases?
Salmonella, gonorrhoea, strep, tetanus, tuberculosis
how does antibiotic work and why doesn't it affect human cells?
it interferes with the peptidoglycan cell wall of bacteria
animal cells don't have a cell wall so they don't impact our cells
what are two ways that bacteria can make us sick?
- by invading tissues and attacking cells
- making toxins (common cause of food poisoning)
what is antibiotic resistance and how does it occur?
when the bacteria stops responding to the antibiotic
it occurs with overuse, underuse, and misuse of the antibiotic.
what are prions and what animals are infected?
prions are slow acting, indestructible infections proteins that cuase brain disease in mammals
- they happen in sheep (scrapie), Cruetzfeldt-Jakob disease in human
why is kingdom protista so difficult to classify?
they aren't actually related to each other but they are all eukaryotic, and not animal, plant, or fungi.
characteristics of protists?
eukaryotic
unicellular/multicellular
autotrophic or heterotrophic
move or stationary
usually live in aquatic environments
how do protists move?
pseudopods, cilia, flagella
how do protists reproduce?
mitosis (limits genetic diversity)/ meiosis
conjugation
what is alternation of generations in protists?
The change in generation between haploid and diploid form (sexual and asexual)
ecological role of protists
algae
mutualistic symbiosis
parasitic protists
what are some common diseases caused by protists?
malaria, sleeping sickness, amoebic dysentery
how do plants and fungi differ structurally + how they obtain energy?
fungi do not have chloroplasts so they ABSORB food from their environment
plants have true roots, leaves, and stems, fungi do not
plant walls are made out of cellulose, while fungal cell walls are made out of CHITIN
are fungi multicellular or unicellular?
multicellular or unicellular (yeast)
anatomy of a fungus
- composed of long filaments called HYPHAE
- hyphae tangled underground is called a mycelium
- mycelia produce fruiting bodies (reproductive structures) above ground
how do fungi reproduce?
fungi reproduce sexually when conditions are harsh
they reproduce asexually when conditions are favorable
life cycle of fungi?
spores germinate into hyphae, forming mycelium, which can reproduce asexually or sexually, producing more spores
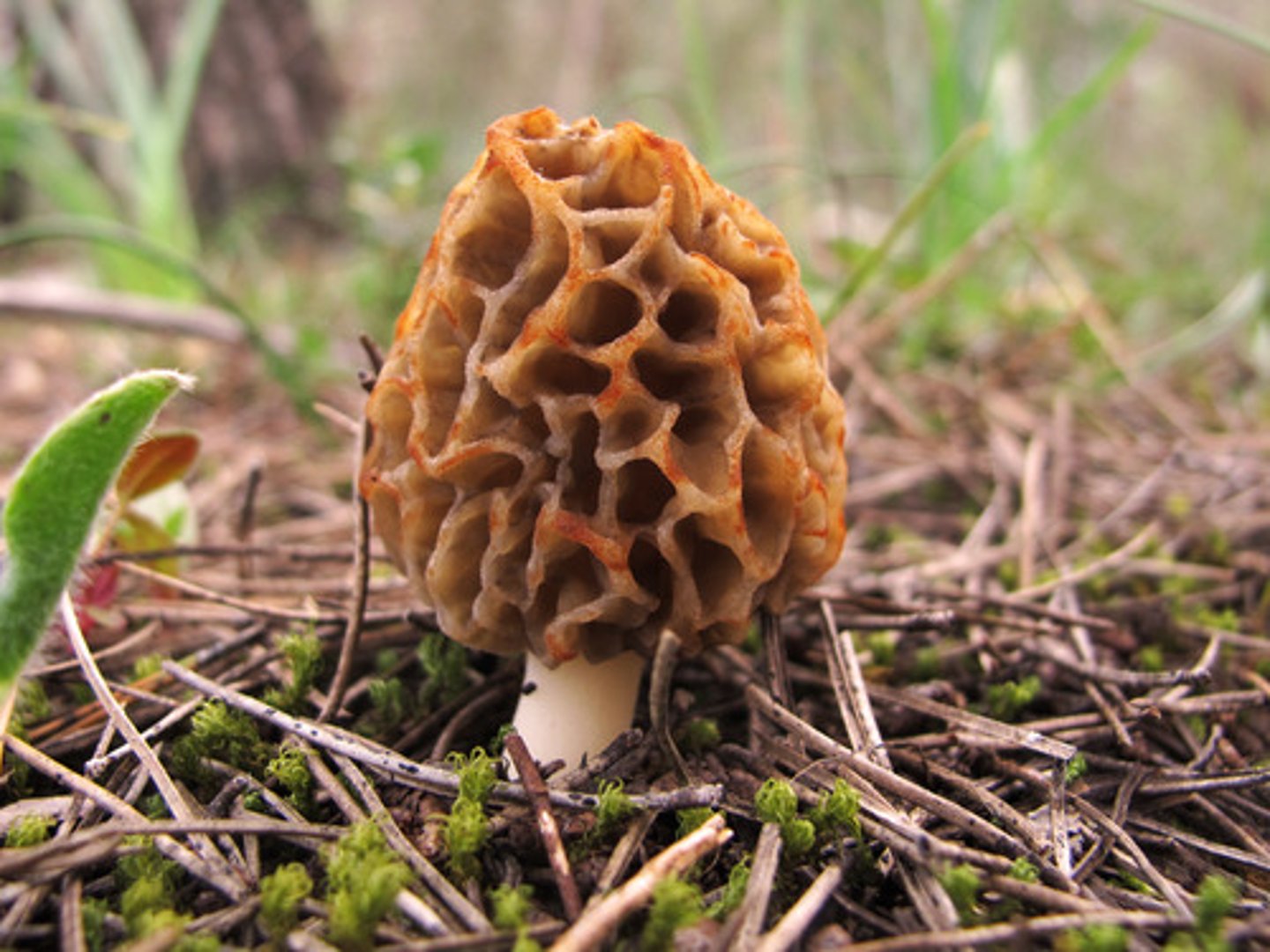
sac fungi
yeast, penicillium, morels, truffles
they have a sac called an ascus that contains spores for reproduction

bread molds
- spoil food
- during sexual reproduction they form a zygospore which rises to a sporangium which releases spores
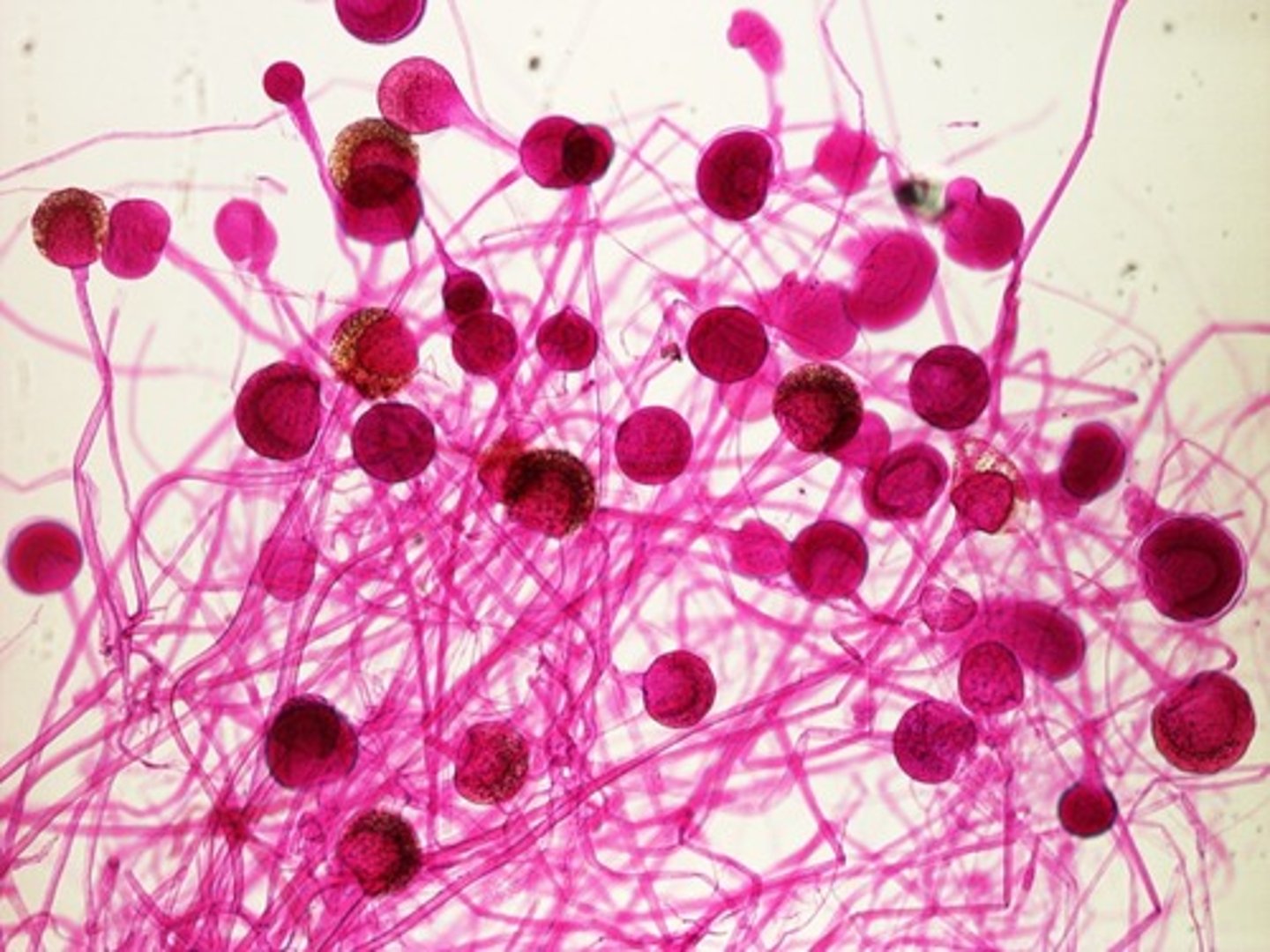
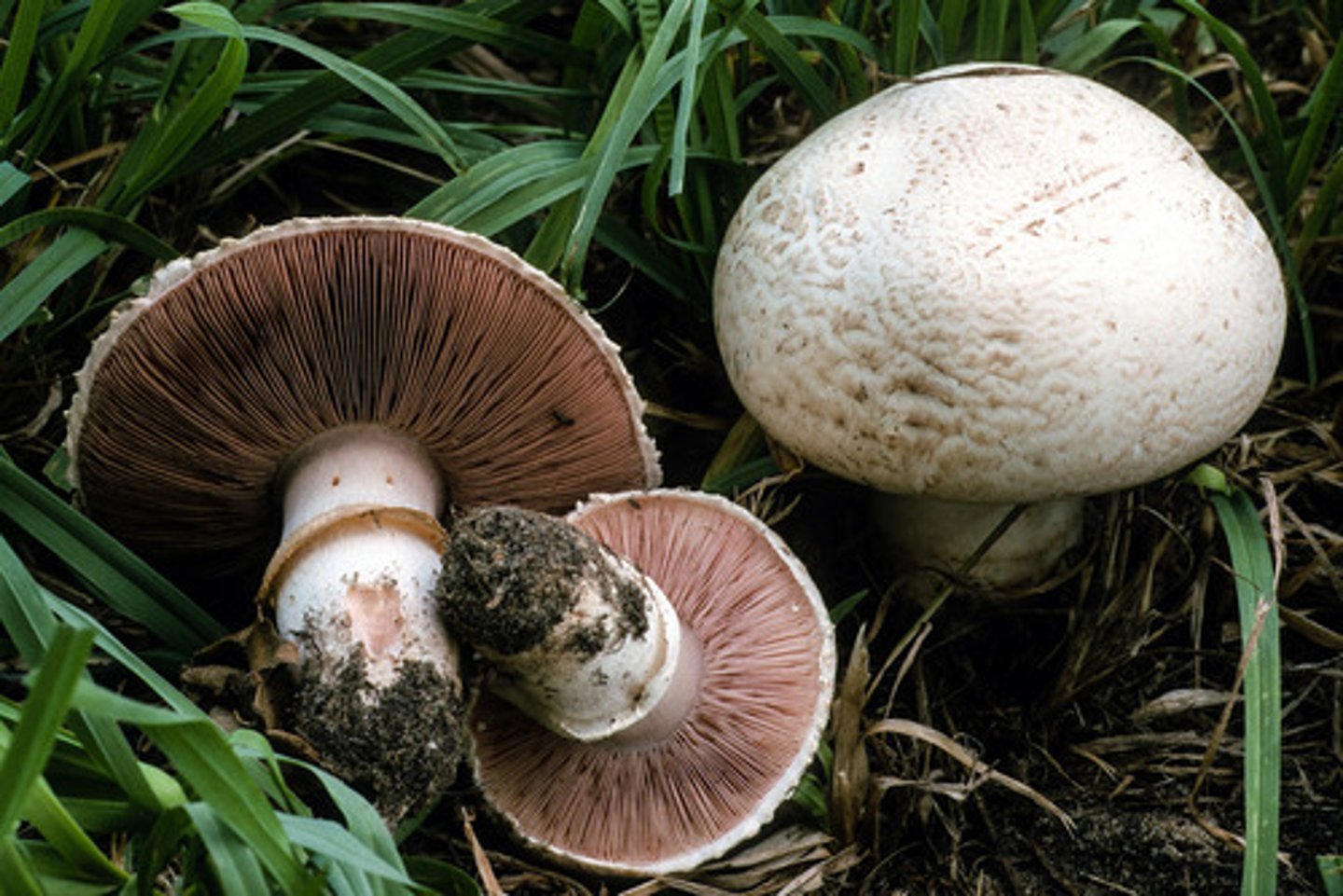
club fungi
- mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi)
- during sexual reproduction, they form basidia that contain spores

ecological role of fungi
- decomposers
- pathogens
- mycorrhizae is a mutualist to plant roots
- lichens provide minerals to photosynthetic partner
common diseases caused by fungi?
athlete's foot, ringworm, peach scab, gray mold, Dutch elm disease