16.1 plant hormones and growth in plants
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
limitations of plants responding to their environment
they are not mobile and do not have a rapidly responding nervous system
roles of auxins
control cell elongation
prevent leaf fall
maintain apical dominance
involved in tropisms
stimulate release of ethene
involved in fruit ripening
role of gibberellin
cause stem elongation
trigger the mobilisation of food
stored in a seed at germination
stimulate pollen tube growth in fertilisation
role of ethene
causes fruit ripening
promotes abscission in deciduous trees
role of ABA
maintains dormancy of seeds and buds
stimulates cold protective responses eg antifreeze protection
stimulated stomatal closing
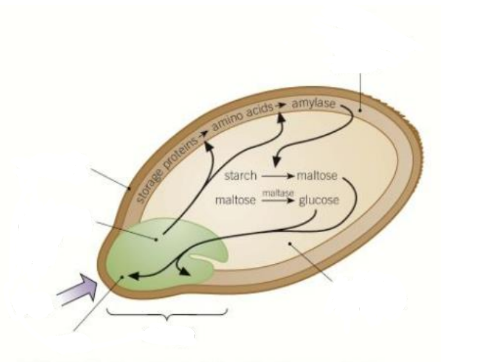
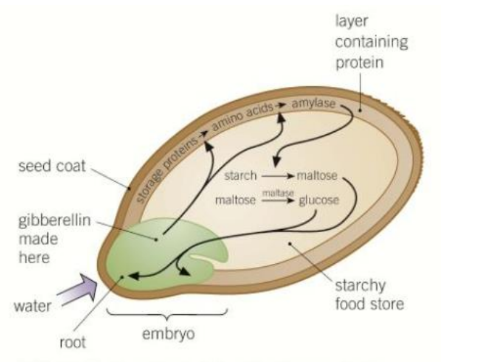
what happens during seed germination
for a seed to germinate the seed needs to absorb water
this activates the embryo to produce gibberellins
gibberellins stimulates the production of enzymes to breakdown tghe food stored insdie of the seed
the food stores are then used to produce ATP for building materials so the embyro can grow and break through the seed coat
evidence for the action of gibberellin
mutated seed produced which lack the gibberellin gene - they don’t germinate and if gibberellin is then artificially added to the mutant seeds they germinate
if gibberellin inhibitors are added to non mutant genes - no germination, if the inhibition is removed or gibberellin is artificially added they germinate
where are auxins made and how do they move around the plant
made in cells at the tip of the roots and shoots, and in the meritstems
auxins move down the stem and up the root both in the transport tissue and from cell to cell
the effect of auxin depends on its concentration and interaction with hormones
what is apical dominance
auxin is produced in the meristem cells at the top of the apical shoot
higher levels of auxin stimulates the growth of the apical shoot but inhibits the growth of the lateral shoots
lateral shoots near the top where there is more auxin will be shorter
shoots further down with less auxin will be longer
apical shoot growth
auxins bind to receptor sites on the plant cell membrane
this causes a fall in PH to PH 5
this is the optimum PH for the enzymes that keep the walls very flexible and plastic
as the cells mature auxin is destroyed, so auxin levels fall and PH rises
the enzyme maintaining plasticity becomes inactive
as a result, the wall becomes rigid and more fixed in shape and size and the cells can no longer expand and grow
effect of auxin on the root + experimental evidence for this
low concentrations of auxin promote root growth
auxin produced by root tips diffuses down from the growing shoot tops
experimental evidence
remove the apical shoot
auxin reaching the root reduced so root growth slows
replace the auxin at the shoot and root growth restarts
synergism
different hormones working together to produce a greater response
antagonism
different hormones working in opposite directions
outcome will depend on the relative levels of each hormone