Nurs 307 (exam 2): nose, mouth, and throat
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
know anatomy of nose cavity
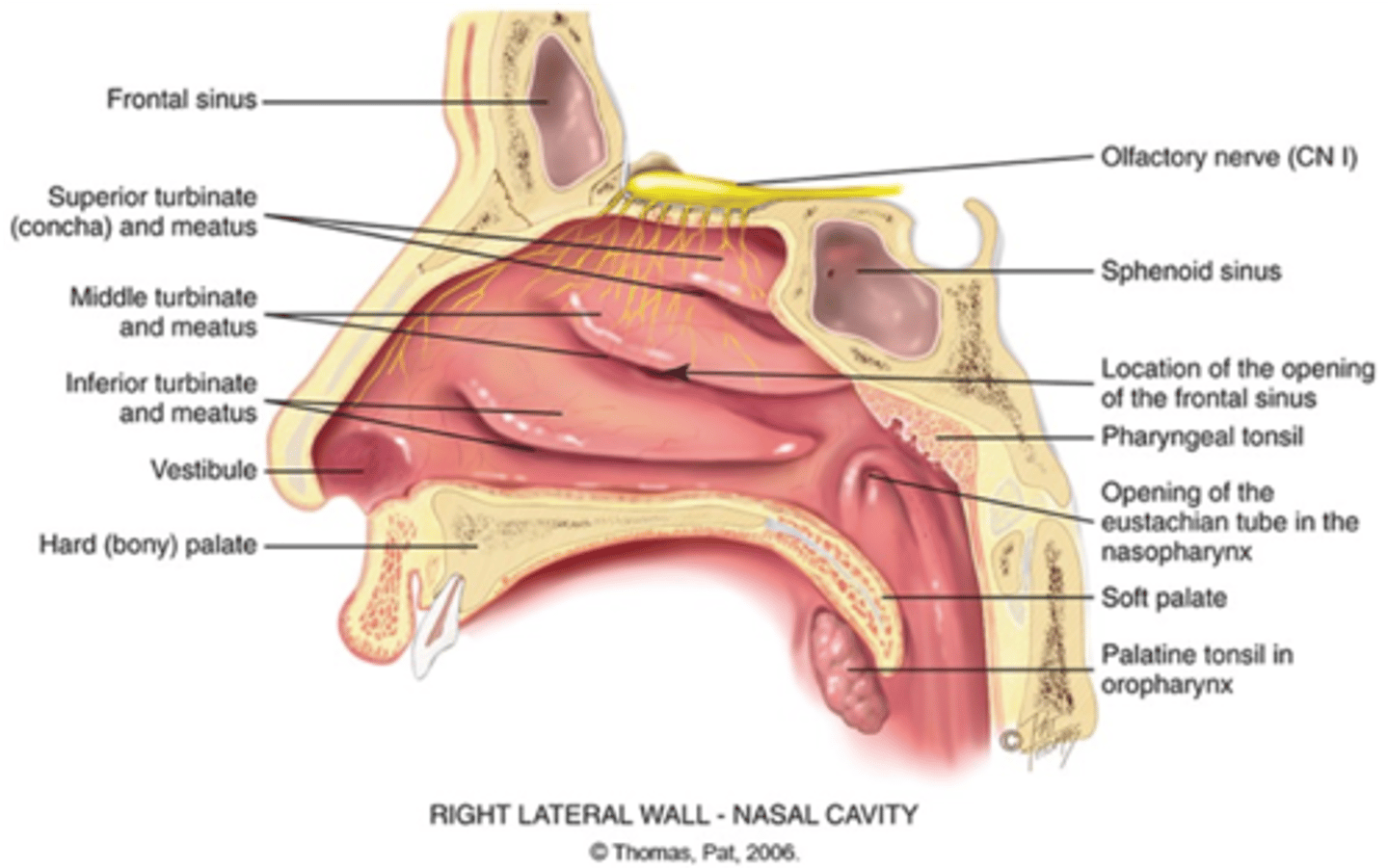
nose:
upper third made up of ____; the rest is ______
bone
cartilage
nasal cavity divided medially by ____ into two slit-like air passages
septum
sinuses drain into _____ meatus, and tears from nasolacrimal duct drain into _____ meatus
middle
inferior
Olfactory receptors, hair cells, lie at _____ of the nasal cavity, upper ___ of the septum
roof
third
receptors for smell merge into _______ nerve, ____ nerve I, which transmits to temporal lobe of brain
olfactory
cranial
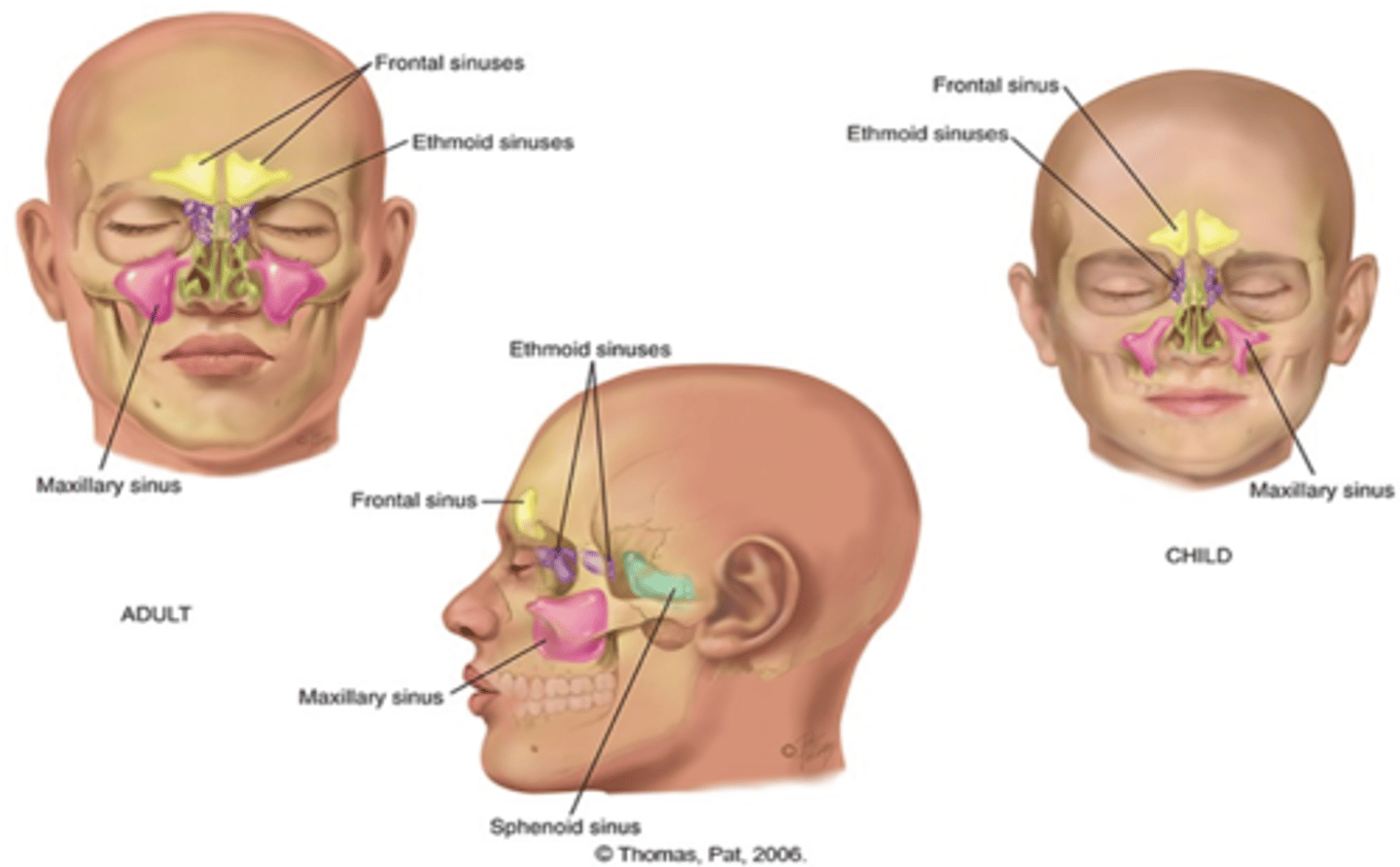
paranasal sinuses: air filled pockets within the cranium
lighten weight of skull bones provide _____, which drain into nasal cavity
mucus
sinus openings are ___ and easily occluded, which may cause _____ or sinusitis
narrow
inflammation
know the stars
The first segment of respiratory system is ____
nose
The first segment of the digestive system and respiratory system is _____
mouth
______ arching roof of mouth divided into two parts
palate
___ ____ : anterior part (roof of mouth)made of bone
hard palate
___ ___: posterior part (roof of mouth), an arch of muscle that is mobile
soft palate
______: free projection hanging down from middle of soft palate
uvula
______ are side walls of oral cavity
cheeks
_______(tongue): rough, bumpy elevations on its dorsal surface
papillae
______ ____ (tongue): smooth, shiny and has prominent veins
ventral surface
______ (ventral side of tongue): midline fold of tissue connecting tongue to floor of mouth
frenulum
glands secrete: _________ that moistens and lubricates the food bolus, starts digestion, and cleans and protects mucosa
saliva
adults have _____ permanent teeth; ____ in each arch
32
16
Each tooth has three parts:
-
-
-
crown
neck
root
gums:
different from the rest of oral mucosa because of their ____ ___ color and _____ surface
pale pink
stippled
know anatomy of mouth
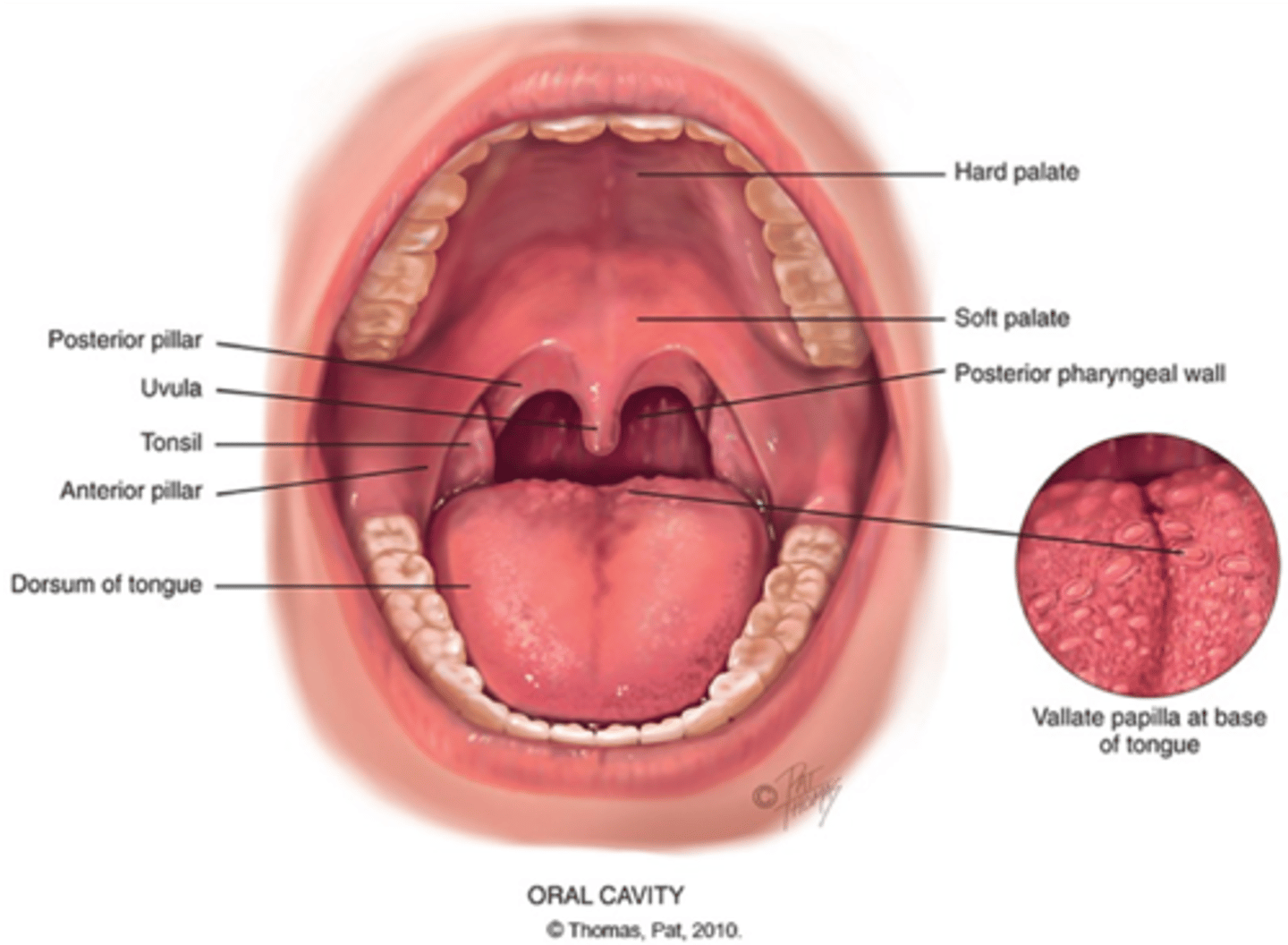
______: mass of lymphoid tissue; sits between anterior and posterior pillars
tonsils
______: continuous with oropharynx, above oropharynx, and behind nasal cavity
nasopharynx
_____ tonsils (adenoids) and _____ tube openings are located here
pharyngeal
eustachian
infants and children:
teeth, both sets and begins development in _____
utero
______ and _____ most common in asians, intermediate in whites, and least in blacks
cleft lip
cleft palate
_____ and _____ intermediate in whites
cleft lip
cleft palate
_____ and ____ least common in blacks
cleft lip
cleft palate
______ _____: infectious process leading to tooth decay due to interaction of bacteria is on the rise
Dental caries
Complications r/t periodontal disease linked to _____ ______
type two diabetes
increased incidence of oral cancers linked to _____ and changes in _____ norms
HPV
sexual
(allergies)
Do you use ______, _____ ____, or ____ drops? how often? which type?
inhalers
nasal spray
nose drops
Patient-centered care children:
how are child's ____ habits?
use a ______ regularly?
how often does child see a ____?
dental
toothbrush
dentists
Patient-centered care children:
Do you use ______ water or ______ supplement?
fluoridated
fluoride
Patient-centered care children:
are ______ up to date?
vaccinations
Hx Aging Adults:
any ____ in mouth?
dryness
Hx Aging Adults:
are you taking any _______?
medications (note px or OTC)
Hx Aging Adults:
Have you had any loss of ____?
Can you ____ all types of food?
teeth
chew
Hx Aging Adults:
are you able to care for your _____ teeth or dentures
own
Hx Aging Adults:
Have you noticed a change in your sense of ______ or _____?
taste
smell
Position a person sitting ___ ___ with his or her head at your eye level.
up straight
if person wears dentures, offer a paper towel and ask the person to _____ them
remove them
Equipment to inspect mouth:
-
-
-
-
-
otoscope
penlight
two tongue blades
4x4
gloves
nasal cavity inspection:
alternatively use ____ _____
pen light
Palpation of SINUS areas:
using thumbs, press frontal sinuses by pressing ____ and ___ the eyebrows and ____ Maxillary sinuses _____ cheeckbones
up
under
over
below
Normally African Americans may have ____ lips and ____ line on gingival margin
bluish
dark
observation of uvula:
ask the patient to say"______"and note soft palate and uvula rise in midline
ahhhh
Tonsils graded:
1+
visible
tonsils graded:
2+
halfway between tonsillar pillars and uvula
tonsils graded:
3+
touching uvula
Tonsils graded:
4+
touching each other
Normally which grade will you see when grading the tonsil size?
1+ or 2+
touching the posterior wall with tongue blade elicits _____ reflex
gag
gag reflex tests cn?
IX (glossophyngeal)
X (Vagus)
asking a person to stick out the tongue; should protrude _____; note any ____, _____ of movement, or _____ to side
midline
tremor
loss
deviation
asking person to stick out tongue tests which CN?
XII hypoglossal nerve
Halitosis: breath smelling fruity- scented can indicate _______
DKA
(DM2) High blood sugar levels increase glucose in saliva providing food for bacteria and plaque build up, if not removed then tooth decay and gums disease may occur causing ________
Halitosis
Newborns are obligate ______ breathers
nose
with a toddler, be alert for possible foreign body lodged in _____ cavity
nasal
normal finding in infants is _____ _____, a small pad in middle of upper lip from friction of breast feeding or bottle-feeding
sucking tubercle
sucking tubercle can be caused by friction of ____ ____ or ____-_____
-breast feeding
-bottle-feeding
_______ ______ on palate are normal findings in newborns and infants
Epstein pearls
Small, whitish, glistening, pearly papule along median roof of hard palate and on gums, where they look like teeth are called?
Epstein Pearls
Gum ______ may occur normally at puberty or during pregnancy
Hypertrophy
pregnancy gingivitis may cause gum _______
gum hypertrophy
Aging Adult:
nose may appear more ____ on face from loss subcutaneous fat
prominant
Aging Adult:
in edentulous (aka lacking teeth) person; mouth and lips fold in, giving a " ______-____" appearance
purse-string
Aging Adult:
teeth may look slightly yellowed, but the color is _____
uniform
Aging Adult:
Teeth may look ____ as gum margins recede
longer
Aging Adult:
tongue looks _____ as a result of _____ atrophy
smoother
papillary
epistaxis
nosebleed
sinusitis
sinus infection
acute rhinitis
(stuffy nose)
(nonallergic)
Lip abnormalities
-
-
-
cleft lip
Herpes simplex 1
Carcinoma
Teeth and Gum Abnormalities:
- ____-______ tooth decay
-_________ caries
- baby bottle tooth decay
- dental
Buccal Mucosa Abnormalities:
- ________ in adults
-______ _____ 1
Candidiasis
Herpes simplex 1
Tongue abnormalities:
- Enlarged Tonge aka ______
macroglossia
oropharynx abnormalities:
- acute ______ and _____
- ____ palate
- tonsillitis and pharyngitis
- cleft
Tongue's ability to change shape and position enhances its functions in:
-
-
-
-
mastification
swallowing
cleansing of teeth
formation of speech