Calorimetry
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
m
(1)
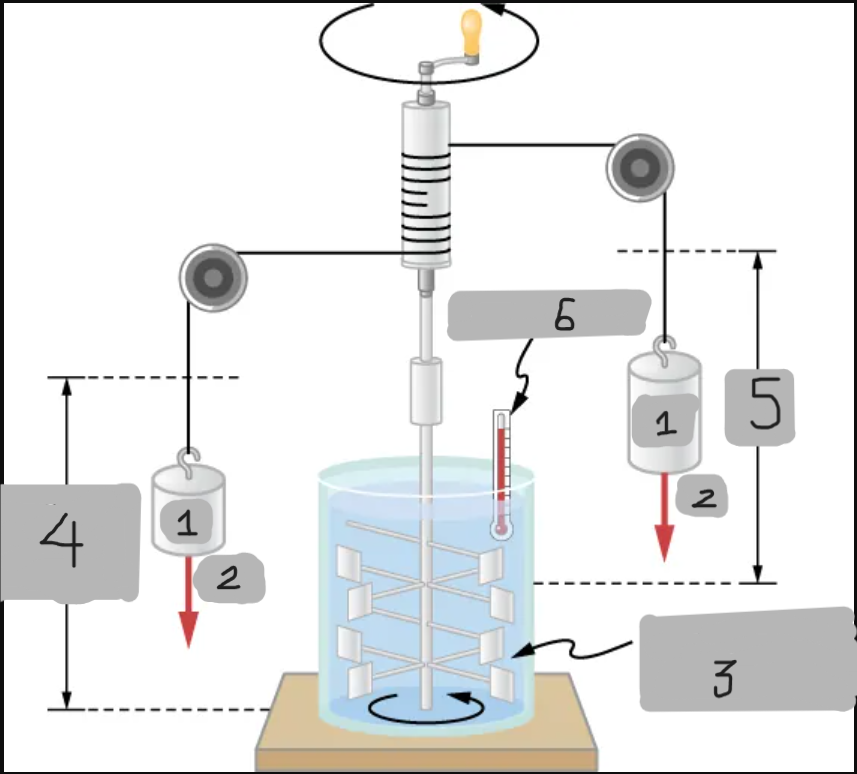
w
(2)

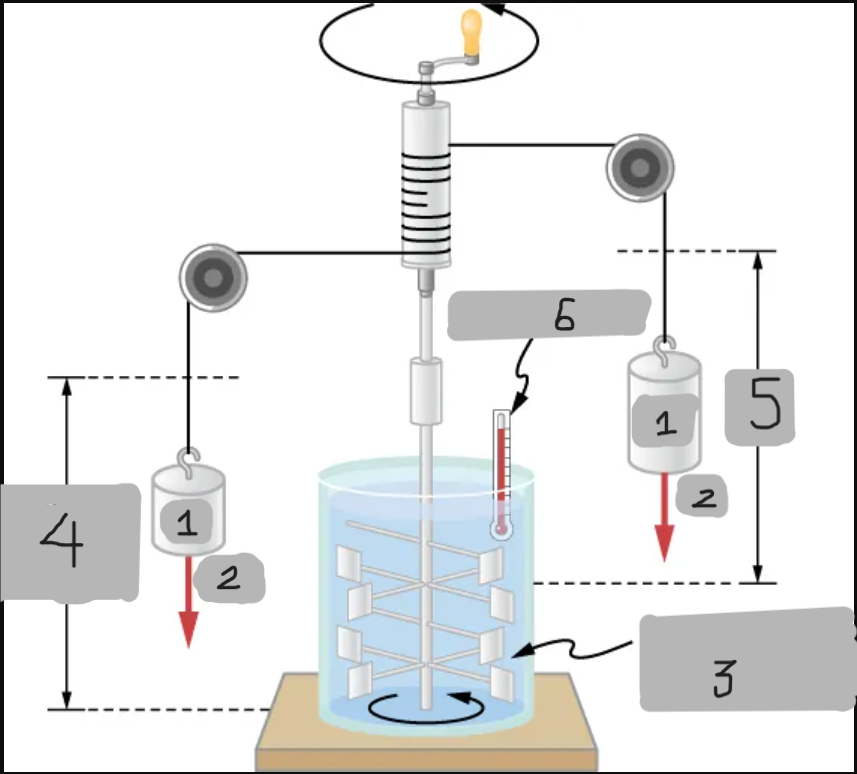
Insulated, known volume of water
(3)
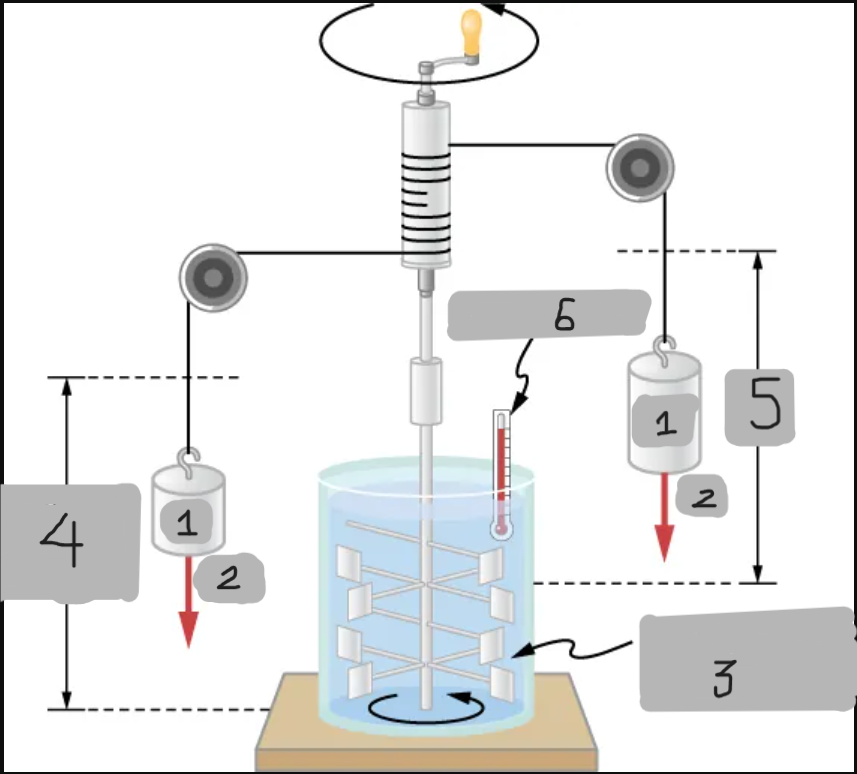
Measured height of descent
(4)
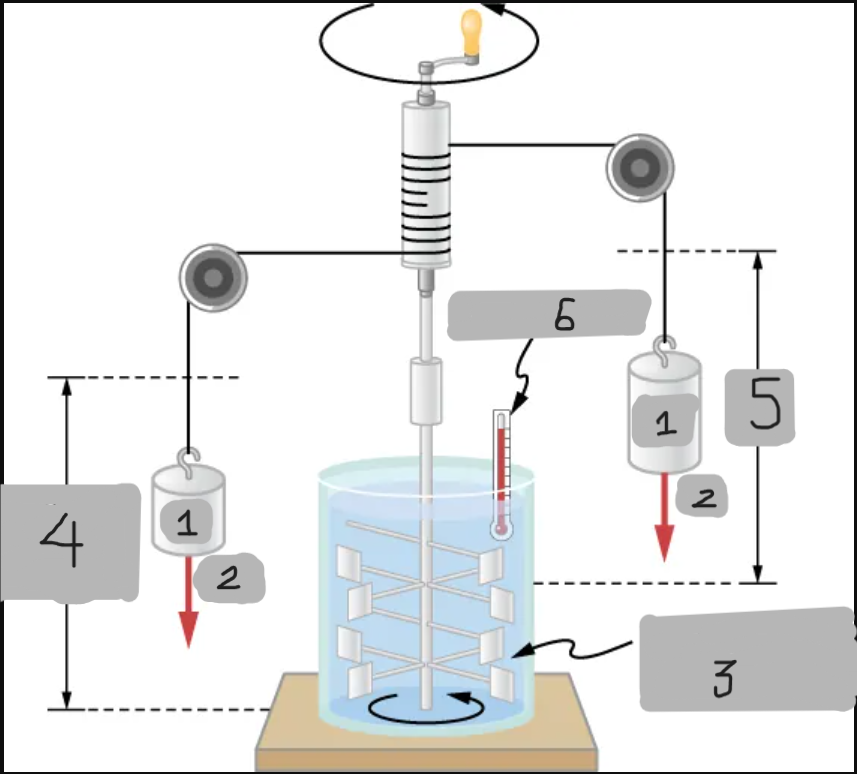
h
(5)
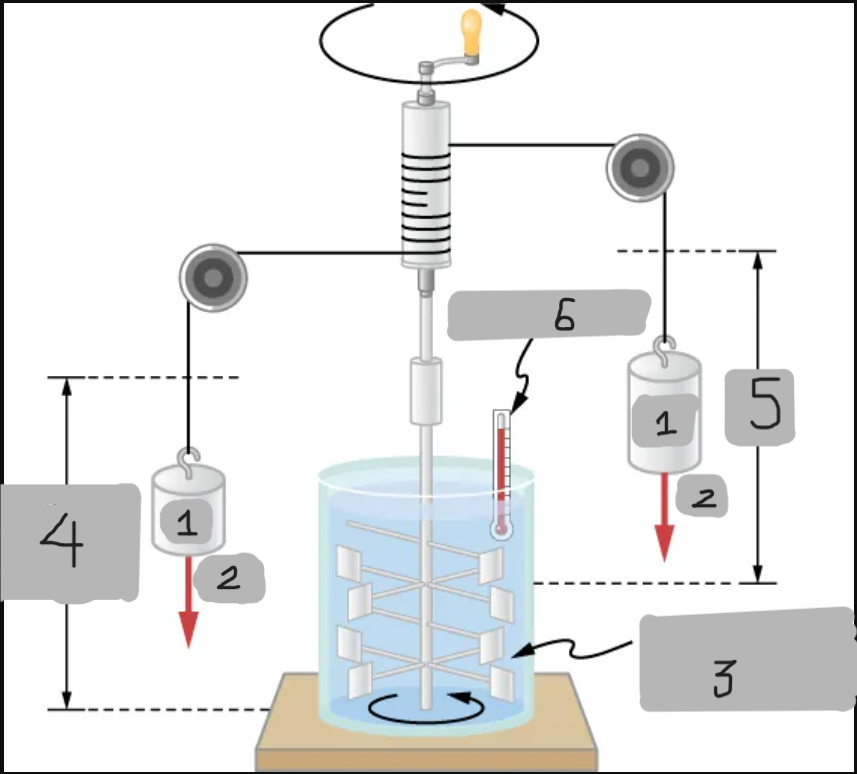
Thermometer
(6)
Internal Energy (U)
The total microscopic energy stored inside a system.
Includes molecular kinetic energy (due to motion)
Includes potential energy (due to interactions between molecules)
Heat
Energy in transit due to the temperature difference.
Temperature
A measurement of average kinetic energy, and not a form of energy flow.
Thermal Equilibrium
The state in which two systems have the same temperature and no net heat between them.
Heat as Energy Flow
Heat is defined only during transfer
A system never “contains” heat.
It contains internal energy, not a quantity of heat.
mechanical work
The amount of _______________ that produces the same temperature increases as heat transfer.
4186 J
1 kcal = ?
Joule’s Experiment
Demonstrated that mechanical work can increase internal energy and temperature.
Proving heat is a form of energy
Paddle wheels stirred up water as falling masses did work;
Raising the water’s temperature
State Variable
A property that depends only on the current state of a system;
Examples: Temperature and internal energy
And not on how the system arrived there.
Heat and Work are not classified as this.
Calorie (cal)
The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1°C (from 14.5°C to 15.5°C)
Kilocalorie (kcal or Calorie)
Energy needed to raise 1kg of water by 1°C.
1 kcal = 1000 calories
Food labels use Calories = kilocalories
Joule (J)
The SI unit of energy. Used to measure both mechanical work and Heat.
Specific Heat
The amount of heat needed to raise temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C or 1K.
J/(kg × K)
SI unit of the Specific Heat
mass × specific heat × temperature change
Heat transfer equals ?
Q = mcΔT
Mathematical representation of the Heat Capacity (Constant c)
Microscopic Basis of Heat Capacity
Temperature rise depends on how much internal energy is needed to increase the average kinetic energy of molecules.
Heavier or more strongly interacting molecules require more heat input.
c = (1/m)(dQ/dT)
Mathematical representation of the specific heat. Which is the heat needed per unit mass for an infinitesimal temperature change.
internal energy, temperature, constant
During the phase changes (e.g., melting, boiling) adding heat increases _______________ but __________ stays _______.
Calorimeter
A thermally insulated container used to measure heat transfer between substances while preventing heat flow to the environment.
Calorimeter Principle (Conservation of Energy)
Heat lost by the hot object = heat gained by the cold object.
Qcold + Qhot = 0
Mathematical representation of the Calorimetry Principle
Calorimetry Problem
Any problem where objects at different temperatures exchange heat while isolated from surroundings.
Q = m ∫(From T1 to T2) c(T) dT
General Heat Transfer Formula. Specifically used when heat changes significantly with temperature.
stored
Internal energy increases through heat transfer or work done on the system. Both method raise internal energy, but neither is ______ as “Heat” or “work” inside the system.
compressing, stirring
Doing mechanical work on a system (like ___________ gas or ________ liquid) increases internal energy, just like heating.
gravitational potential, kinetic
Brakes convert __________________ energy into ________ energy (heat).
If heat cannot escape quickly, brakes can overheat.
The reason engine braking is used.
Regenerative Braking
In hybrid/electric car, brakes convert mechanical energy into electrical energy stored in the battery, reducing heat production.
Q = ΔU
Key energy in heat transfer is no work is done.