PD III E1- Casting & Splinting
1/89
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
What is the shaft of the long bone?
diaphysis
What is the end section of long bone prior to the growth plate (physis)?
metaphysis
What is the end of the long bone proximally and distally?
epiphysis
What is the growth plate?
epiphyseal plate
What condition is of low bone density and causes bones to become weak often resulting in fractures?
osteoporosis
What are the MC osteoporotic fracture sites?
wrist, hip, vertebra
What is a stress fracture in osteoporotic bone, MC in pelvis?
insufficiency fracture
What are stress fractures caused by repetitive motions or intensity of activity being increased too quickly, common among athletes?
overuse injuries
What is the MC location for overuse injuries?
tibia and foot
What are fractures that occur secondary to metastatic disease, commonly in the vertebra, pelvis, and proximal femur?
neoplastic pathologic fractures
What are the MC cancers to metastasize to bone?
lung, breast, thyroid, renal, prostate
When the bone is fractures and the skin is intact, this is ____
open fracture
When the bone is fractures and the skin has been disrupted, this is ____
open / compound fracture
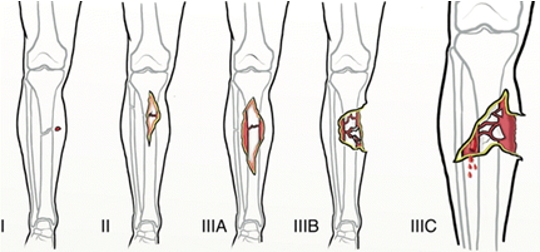
What classification system is for open fractures?
Gustilo-Anderson
What is the management for 3A open fracture?
orthopedics alone
What is the management for 3B open fracture?
orthopedics & plastics
What is the management for 3C open fracture?
orthopedics, plastics, & vascular
What kind of bone fracture is perpendicular to it’s length?
transverse
What kind of bone fracture is fractured diagonally through the width?
oblique
What is a complete fracture that occurs from rotational force?
spiral / torsion
What fracture results in 3 or more bone fragments?
comminuted
What fracture has 2 distinct fracture lines that create a completely separate cylindrical intermediate segment?
segmental
What is an incomplete fracture with a building of the cortex?
torus / buckle
What fracture occurs through one cortex only, causing a bend on the other side of the bone?
greenstick / break and bend
What fracture is a partial vertebral collapse?
compression
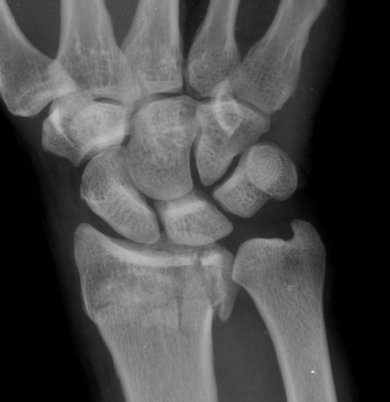
When the fracture extends into the joint, this is ____
intra-articular
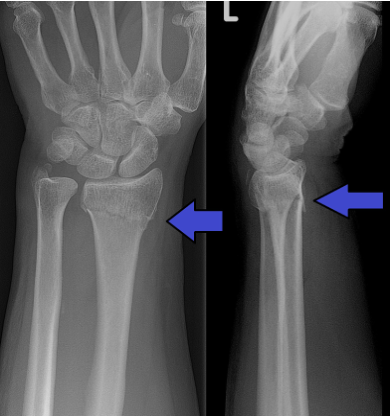
When the fracture does not extend into the joint, this is _____
extra-articular
What term refers to whether the broken portions of the bone have moved in relation to each other?
displacement
What is an extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation?
colles fracture
What is an extra-articular fracture of the distal radius with volar angulation?
smith frature
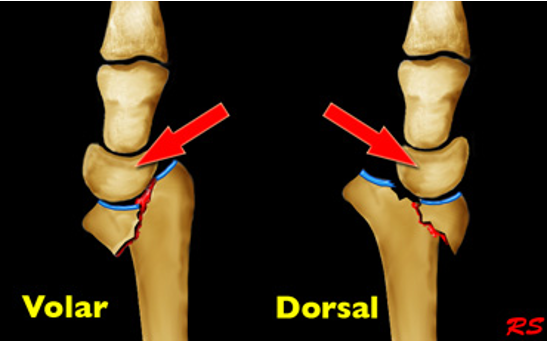
What is an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius w/ dislocation of the radoiocarpal joint?
barton fracture
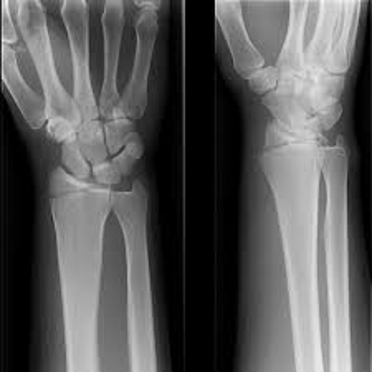
What is an intra-articular fracture involving radial styloid?
chauffer fracture
What is anatomic snuffbox tenderness highly sensitive (but not specific) for?
scaphoid fracture
What do you do if you suspect a scaphoid fracture, even if the xray is normal?
thumb spica splint
What is the most fractured carpal bone, commonly missed, less likely in young children, and occur in elderly secondary to relative weakness of distal radius?
scaphoid fractures
What is the MC location and LC location for scaphoid fractures, respectively?
waist > distal pole
What is there a high incidence of with scaphoid fractures?
nonunion and avascular necrosis in waist and proximal fractures ; may require bone grafting
What should be done for patients with persistent pain?
repeat xrays or CT
What are the most common fracture locations for > 65 y/o?
vertebra, wrist, hip
What are the most common fracture locations for < 18 y/o?
distal radius, forearm
What type of cast is made from gypsum, offers more moldability, has minimal amount of GIVE, is heavy and requires more layers?
plaster
What happens when plaster is wet?
exothermic reaction → recrystallizes (can burn patient)
What type of cast is lightweight, solid, comes in an assortment of colors and designs, has absolutely NO GIVE, and offers less moldability?
fiberglass
What tools are used to remove a cast?
cast saw (vibratory) and saw stop Zip stick
What are indications for splinting?
temporary stabilization of acute fracture, suspected fracture
accommodates swelling
definitive mgmt of specific stable fractures
joint instability or dislocation
immobilization of soft tissue injuries
What are contraindications to splinting?
none
What are possible complications of splinting?
burns, ischemia, pressure sores, infx
What are indications for casting?
immobilize and support bone fragments including post op immobilization
soft tissue injuries- ligamentous sprains & strains
deformity correction, clubfoot, scoliosis
What are contraindications to casting?
excessive swelling, skin infx, open wounds (esp draining), claustrophobia
What are possible complications of casting?
compartment syndrome, dermatitis, pressure sores, nerve injuries, DVT, joint stiffness & muscle atrophy
Is a stockinette or padding needed for a waterproof cast?
no; use aquacast liner prior to fiberglass
What should be included for patient education after casting/splinting?
cast care instructions
info ab potential complications
RICE: rest, ice, compression, elevation
FU appts for repeat imaging/monitoring
What must be checked immediately upon presentation with a dislocation or suspected fracture?
neurovascular & circulatory status
what should ALWAYS be obtained if fracture or dislocation suspected?
radiographs
What should be obtained after reduction and IMMOBILIZATION of a fracture or dislocation (before pt leaves ED)?
repeat radiographs / post reduction x rays
What is necessary after 2 unsuccessful attempts of reducing a dislocation (closed reduction)?
general anesthesia (closed) or during surgery (open reduction)
Which finger dislocations are more common- volar or dorsal?
dorsal dislocations
What finger dislocation more frequently requires open reduction?
lateral dislocation
How do you reduce dorsal PIP dislocation?
anesthetize w/ digital block at dorsal base of finger
apply longitudinal traction & pressure to Doral aspect of proximal phalanx (felt as a click)
eval joint for stability after reduction & obtain post reduction x rays
apply dorsal splint at 30 degrees flexion
What shoulder dislocations are most common?
anterior dislocations
What should you always asses for with shoulder dislocations?
axillary nerve function
What is a joint disruption in which the joint surfaces are maintained in some degree of apposition?
subluxation
When the radial head slips out from under the annular ligament, generally caused by sudden traction of forearm that extends & pronates elbow, this is _____
subluxation of radial head (nursemaids elbow)
What ages is nursemaid’s elbow most common in?
children 1-4 (bc lip of radial head is not well formed and may slip out with more ease)
When is pain felt with subluxation of radial head?
minimal when stationary
pain felt upon flexing or supinating arm
What two techniques are used to nursemaid’s elbow reduction?
supination-flexion & hyperpronation
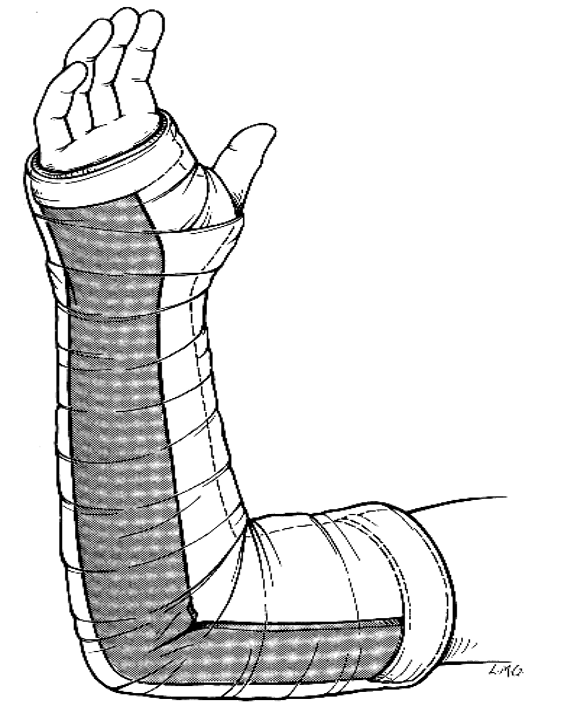

What are indications for a long arm posterior splint?
elbow & forearm injuries - distal humerus fx, both-bone forearm fx, unstable proximal/distal radius or ulna fx
What splint doesn’t completely eliminate supination / pronation?
long arm posterior splint
What splint should be used for complex or unstable distal forearm fracture?
long arm posterior + anterior split OR double sugar-tong
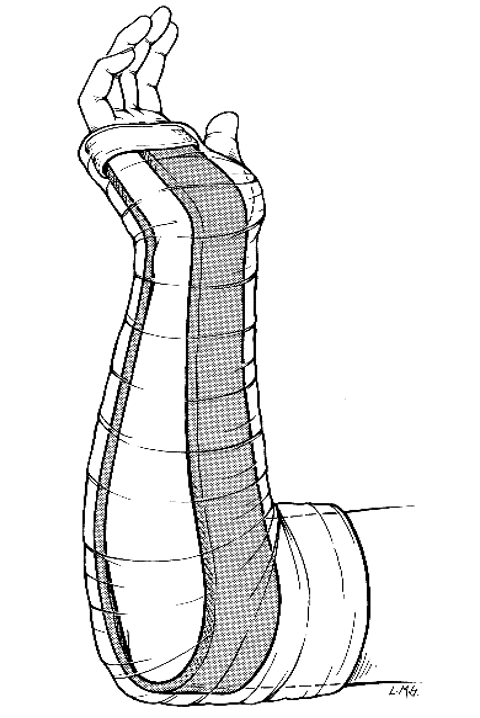

What are indications for forearm sugar tong splint?
distal radius & ulnar fracture
What splint prevents pronation, supination, and immobilizes elbow?
forearm sugar tong splint
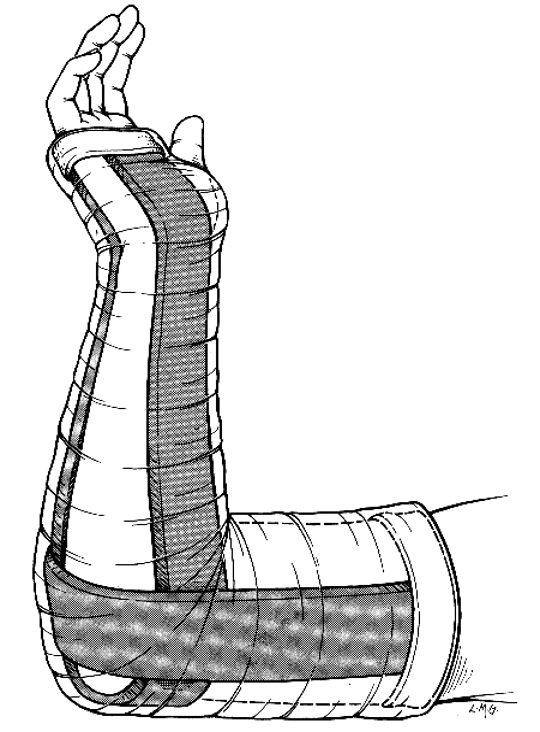
What are indications for double sugar tong splint?
elbow & forearm fx- prox/mid/distal radius & ulnar fx
What splint is better for most distal forearm and elbow fractures because it limits flexion/extension and pronation/supination?
double sugar tong splint
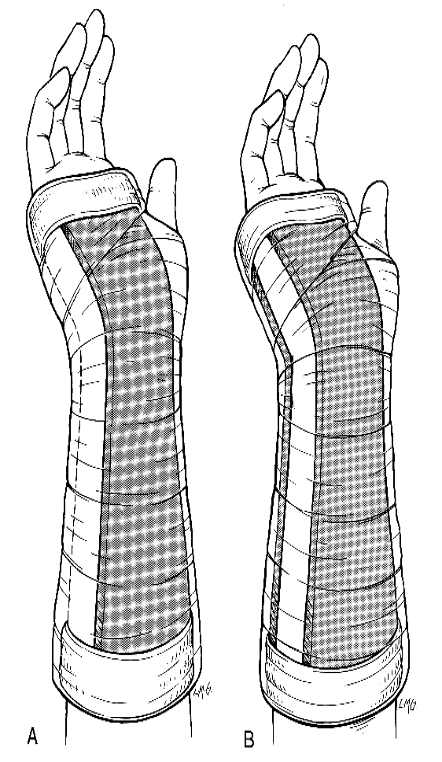
What are indications for a forearm volar / cockup splint?
soft tissue hand/wrist injuries, most wrist fx, 2-3 metacarpal fx
What splint requires a dorsal splint addition for increased stability (sandwich splint) and is not used for distal radius or ulnar fractures because you can still supinate/pronate?
forearm volar / cockup splint
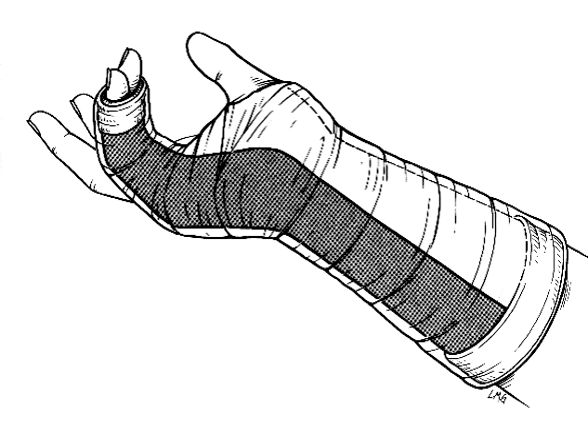
What are indications for ulnar gutter splinting?
phalangeal and metacarpal fractures & soft tissue injuries of little and ring fingers
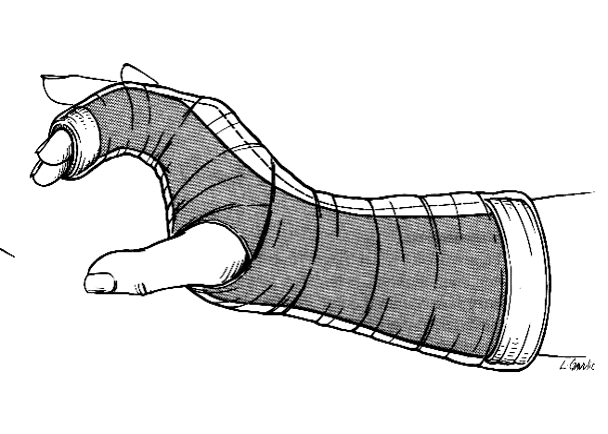
What are indications for radial gutter splinting?
phalangeal and metacarpal fractures & soft tissue injuries of index and long fingers
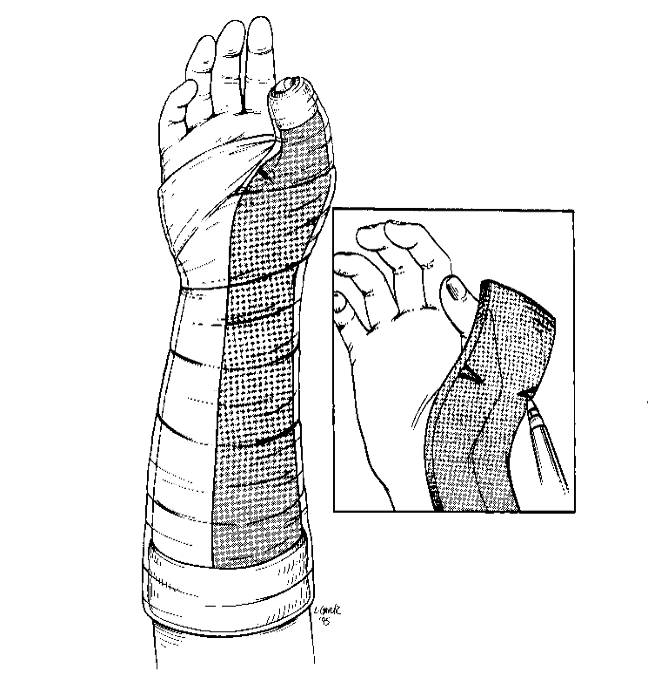
What are indications for thumb spica splints?
scaphoid fx, De Quervain tenosynovitis
What splint prevents buckling when notching the plaster when wrapping around the thumb, and is in wine glass position (thumb slightly flexed and abducted)?
thumb spica splint
What is the correct position for most hand splints?
neutral (position of function)
What position is with the wrist slightly extended (10-25°) with fingers flexed?
beer can
To what degree should the MCP joint be flexed when immobilizing metacarpal neck fractures?
90°

What are indications for finger splints?
sprains- dynamic splinting (buddy taping)
phalangeal fx- dorsal/volar splints
What are indications for jones compression dressing (aka bulky jones)?
short term immobilization of soft tissue and ligamentous injuries to knee or calf
What is compression dressing that helps control post-op swelling & allows slight flexion and extension?
jones compression / bulky jones
What is the procedure for jones compression dressing?
stockinette and webril
several layers of thick cotton padding
6 inch ace wrap
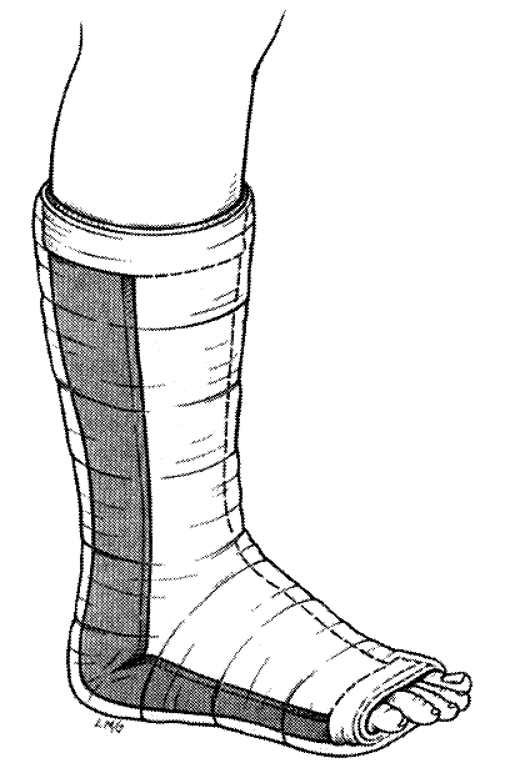

What are indications for posterior ankle splints?
distal tibia/fibula fx, reduced dislocations, severe sprains, tarsal/metatarsal fx

Adding what to a posterior ankle splint eliminates inversion/eversion & is especially useful for unstable fractures and sprains (great for ankle sprains)?
coaptation splint (stirrup)
When is a bledsoe brace used?
ligamentous knee injuries & post op
When are hard shoes used?
foot fractures or soft tissue injuries