physics - conservation of momentum (3.1 - 3.14)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
3.1 GPE equation
change in grav. potential energy (J) = mass (kg) x grav. field strength (N/kg) x change in height (m)
ΔGPE = mgΔh
3.2 kinetic energy equation
kinetic energy (J) = ½ x mass (kg) x speed2 (m/s)2
KE = ½mv2
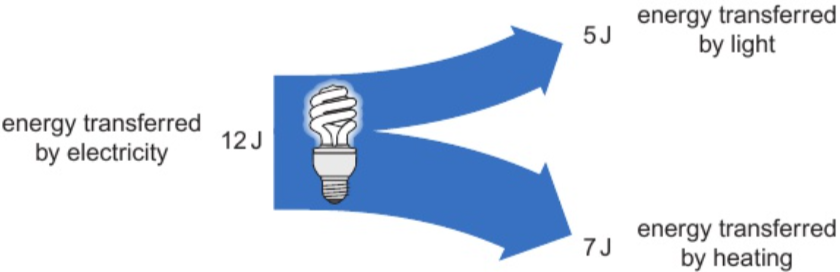
3.3 diagrams to represent energy transfers
3.4 conservation of energy
energy cannot be created/destroyed, only transferred from one store → another
total energy transferred by system = energy put into system
3.5 changes in energy stores - object projected upwards
energy in object (kinetic) —transferred mechanically→ energy in object (GPE)
3.5 changes in energy stores - moving object hitting obstacle
energy in moving object (kinetic) —transferred mechanically→ energy in object & obstacle (thermal & sound)
3.5 changes in energy stores - object accelerated by constant force
energy in moving object (kinetic) —transferred mechanically→ energy in moving object (kinetic)
3.5 changes in energy stores - vehicle slowing down
energy in moving vehicle (kinetic) —transferred by forces (braking)→ energy in hot brakes (thermal)
3.5 changes in energy stores - boiling water in electric kettle
energy in kettle (thermal) —transferred by heating→ energy in water & surroundings (thermal)
3.6 energy transfers in closed system
no net change to total energy in system - energy is conserved
3.7 mechanical processes - wasteful
moving parts touch → causes friction → rise in temperature
thermal energy in hot machine transferred to surroundings by heating - dissipates energy
energy can’t be used for other useful energy transfers - wasted
3.8 energy dissipated in all system changes
energy not always transferred into useful forms, stored in less useful ways
e.g. kettle - energy stored in hot water = useful, energy stored in kettle & surroundings = not useful
3.9 reducing unwanted energy transfer - lubrication
reduces friction between moving parts
conduction
vibrations passed on between particles in solid
convection
warmer part of fluid rises & sets up convection current
radiation
only way energy transferred through vacuum
infrared radiation can pass through gases & some solids
3.9 reducing unwanted energy transfer - thermal insulation
decreases rate of energy transfer by heating
low thermal conductivity = energy not transferred easily by heating
materials containing air are good insulators - air has low thermal conductivity
trapped air cannot form convection currents - doesn’t transfer much energy
3.10 effects of thickness & thermal conductivity of walls of building on rate of cooling
to decrease rate of energy transfer:
increase thickness
decrease thermal conductivity
decrease temperature difference
3.11 efficiency equation
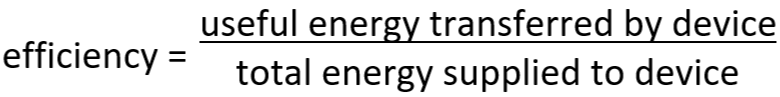
3.12 how can efficiency be increased?
reduce amount of wasted energy
mechanical processes - reduce friction
ensure all fuel put into engine is burned
use energy transferred by heating (otherwise wasted)
3.13 fossil fuels
store lots of energy
easy to store & use in engines
non-renewable
burning fossil fuels release CO2 & other gases
CO2 - contributes to climate change
other gases - contribute to pollution
expensive to reduce pollution
3.13 nuclear fuel
store lots of energy in small piece of material
useful for spacecraft - mass of fuel is important
don’t emit gases
non-renewable
produces radioactive waste
expensive to dispose of radioactive waste
expensive to decommission nuclear power station
major accident can have serious consequences
3.13 bio-fuel
renewable
used in same way as fossil fuels
made from animal wastes/any part of plants
carbon neutral - when burned, release same amount of CO2 as took from atmosphere growing
energy needed to grow, harvest & turn crops into fuel - not carbon neutral
uses lots of land
3.13 wind
renewable
wind turbines generate electricity (if wind not too fast/slow)
need lots of wind turbines to produce same amount of energy as fossil-fuelled power station
some think they spoil landscape
not always available - depend on wind speed
3.13 hydro-electricity
renewable
falling water (trapped in high reservoirs) generates electricity
always available
can be started & stopped very quickly
3.13 the tides
renewable
tidal power generates electricity - turbines in barrage across river estuary turn as tides flow in & out
available at predictable times
not always available
not many places in UK suitable for barrages
may affect birds & other wildlife that live/feed on tidal mudflats
3.13 the sun
renewable
solar cells generate electricity - convert solar energy directly into electrical energy
not always available - depend on sun
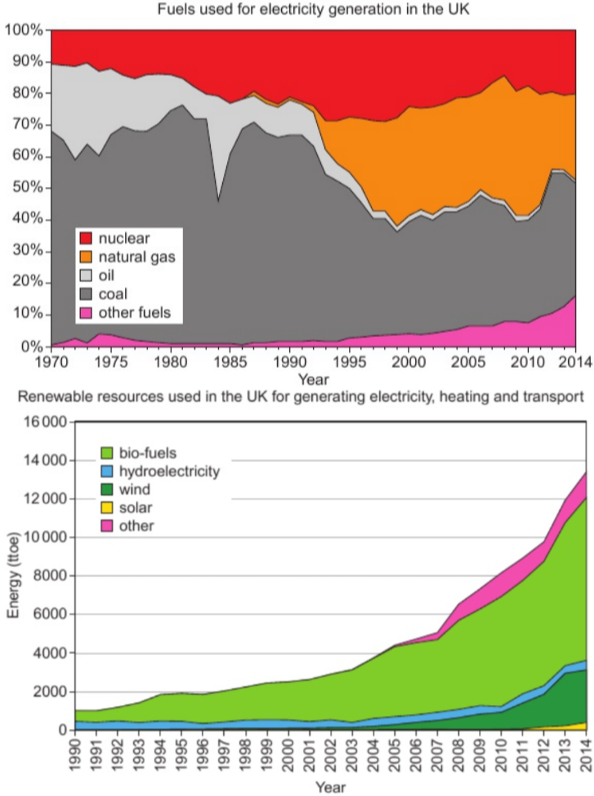
3.14 patterns & trends in use of energy resources