Physiological Psychology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
evolutionary psychology
intends to provide the framework for approaching all areas of psychology to provide a unfiying theory (to be a science). tries to understand ultimate (why) causes and root origins of human psychology, rather than just proximate (how) causes
niko tinbergen’s four questions for understanding a phenomenon
mechanism (causation)
ontogeny (development)
phylogeny (evolution)
function (adaptation)
evolution
descent with modification, i.e. change in trait frequency within a population over time
evolutionary processes of modification
mutation, migration, genetic drift, selection
principles of natural selection
organisms in an environment are theoretically capable of producing more offspring than the environment can sustainably support
there will be variation in how well suited some individuals are to their environment, affecting their chances of survival
some of the variation will be heritable
classifications of selection
directional selection, stabilising selection, disruptive selection
directional selection
favours an extreme version of a trait, happens when there is change in the environment and new selection pressures are present
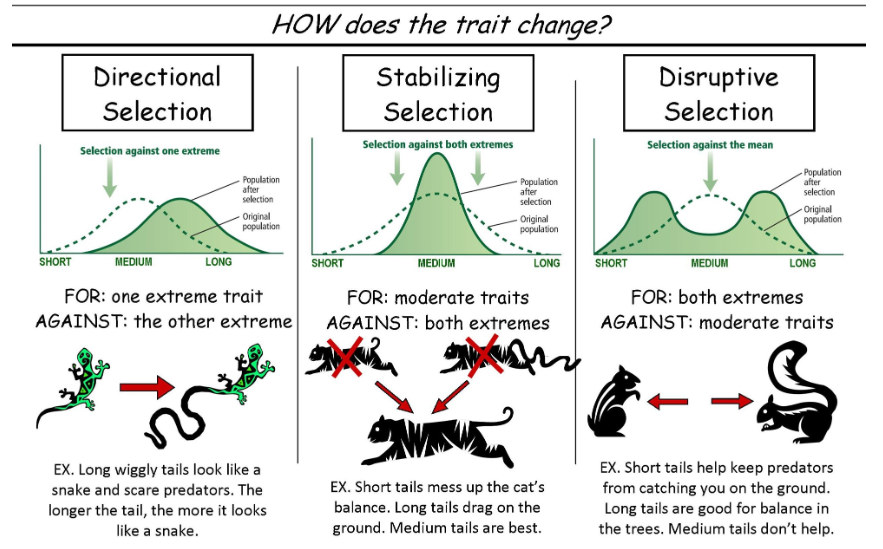
stabilising selection
favours neither extreme but finds moderate traits preferential, happens when there needs to be balance in trade offs between options
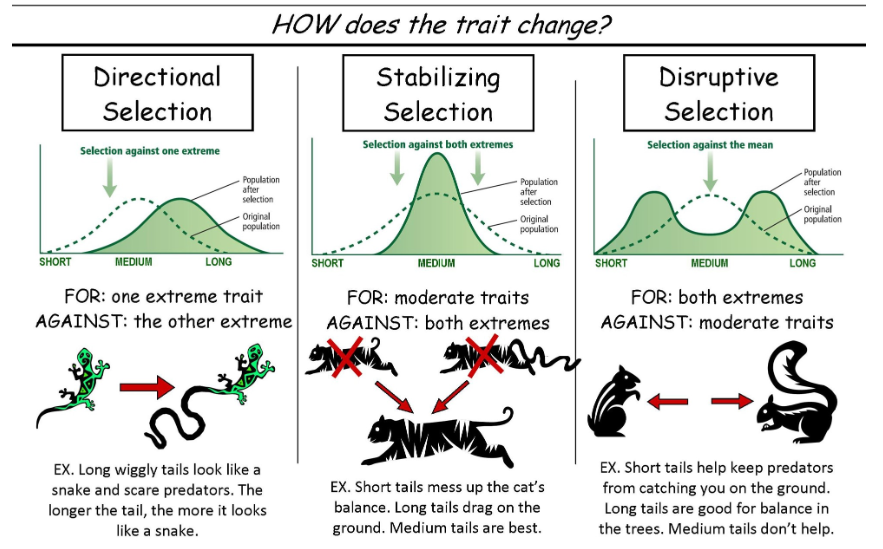
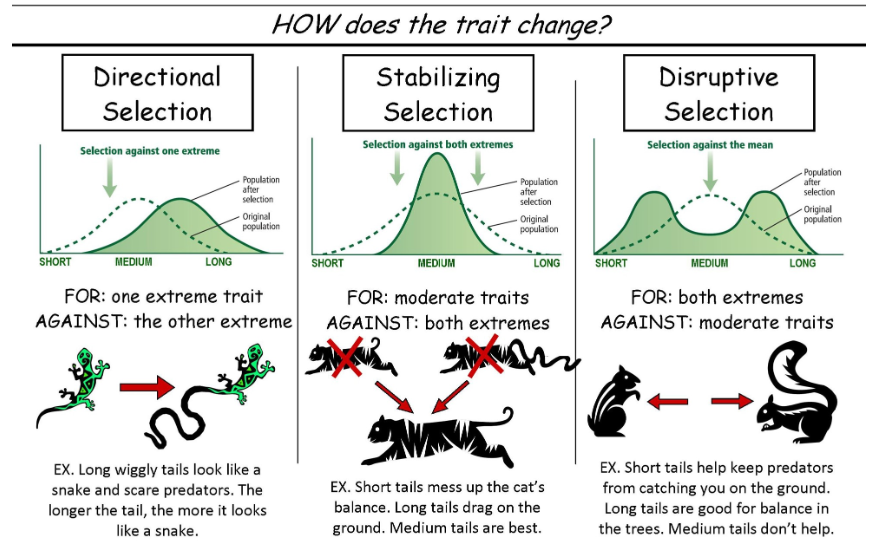
disruptive selection
favours more than one extreme version of a trait over more moderate versions when both extremes have advantages that may compensate for any disadvantages. most common in highly diverse environments with different ways to access resources or when a species splits in migration to slightly different environments
fitness
an organisms ability to survive and reproduce, leaving its genes in the next generation
sexual dimorphism
when there are large differences between organisms in the same species
sexual selection
the idea that traits that aide in reproduction are beneficial even at the risk of individual survival
intrasexual selection
when members of the same sex compete directly with each other for access to mates
intersexual selection
when members of one sex choose members of the other sex