PATHO (E2) Chapter 24: Disorders of leukocytes and lymphoid tissues
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
How much blood do humans have?
5 liters (1.3 gallons)

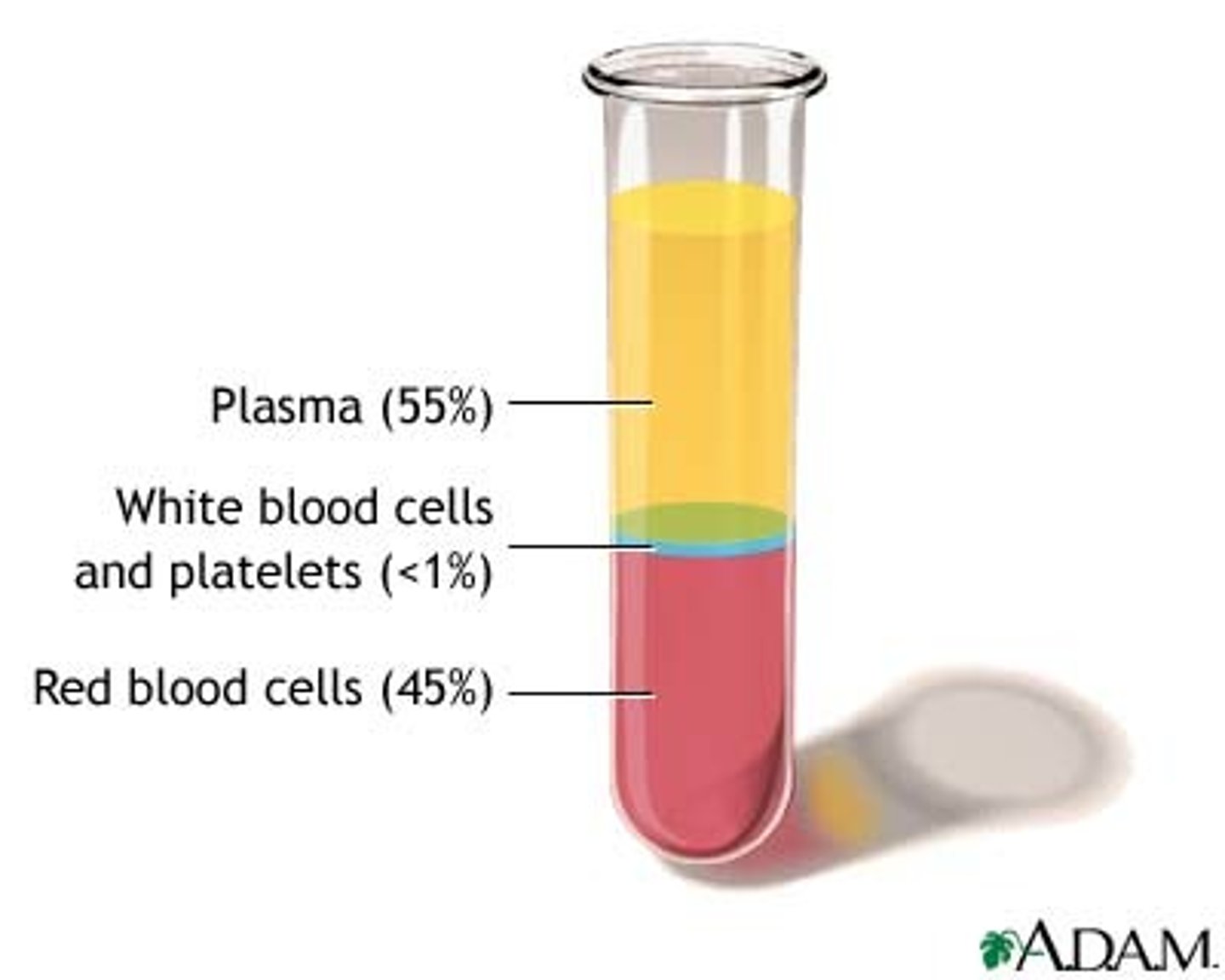
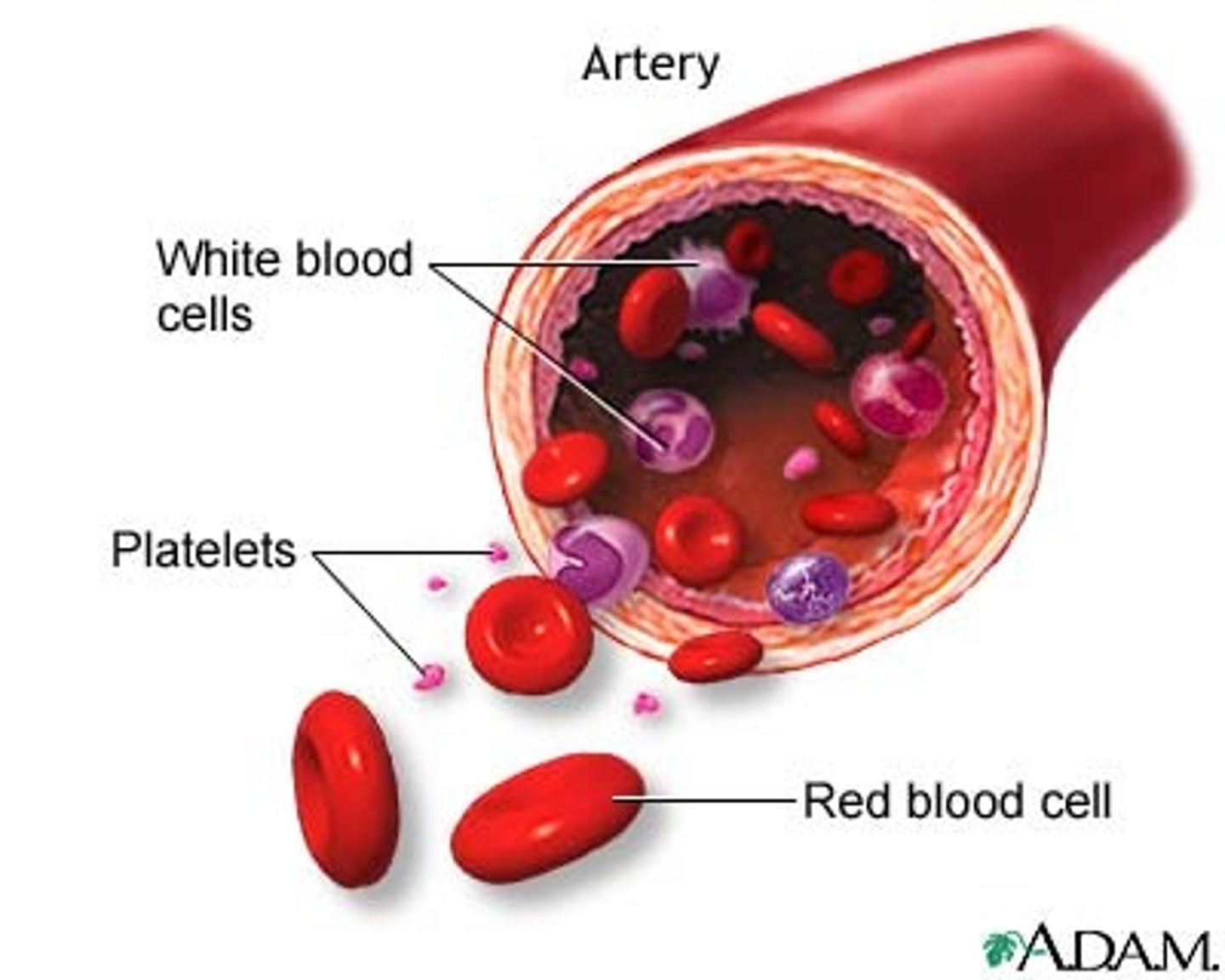
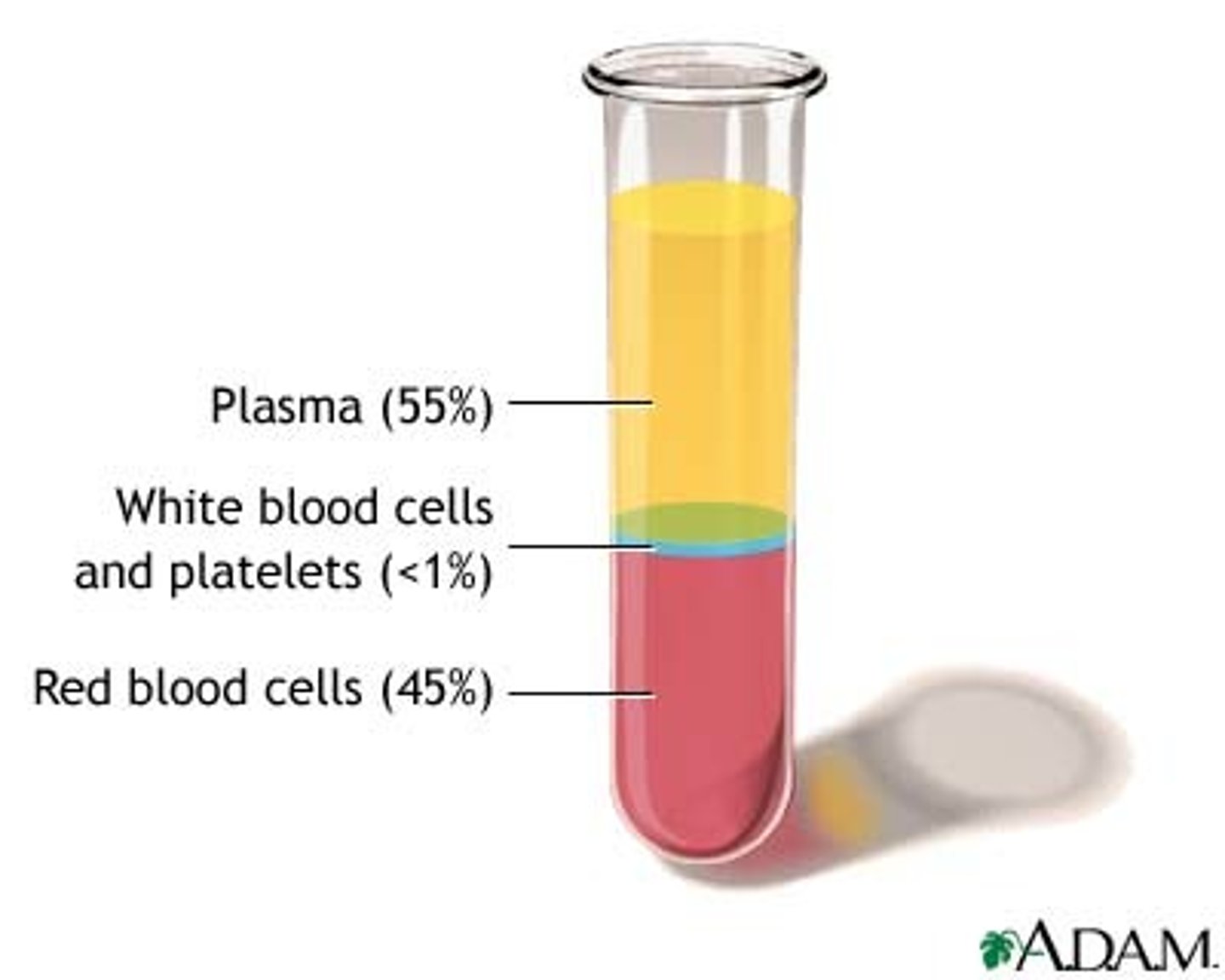
What is the cellular component of blood?
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes (45% of blood)
What is blood plasma?
Liquid part of blood, mostly water and proteins (55% of blood)
What are the functions of blood?
Transportation of nutrients, protections against pathogens, regulation of homeostasis
Blood fractionation
The process of separating it into its component parts using a centrifuge
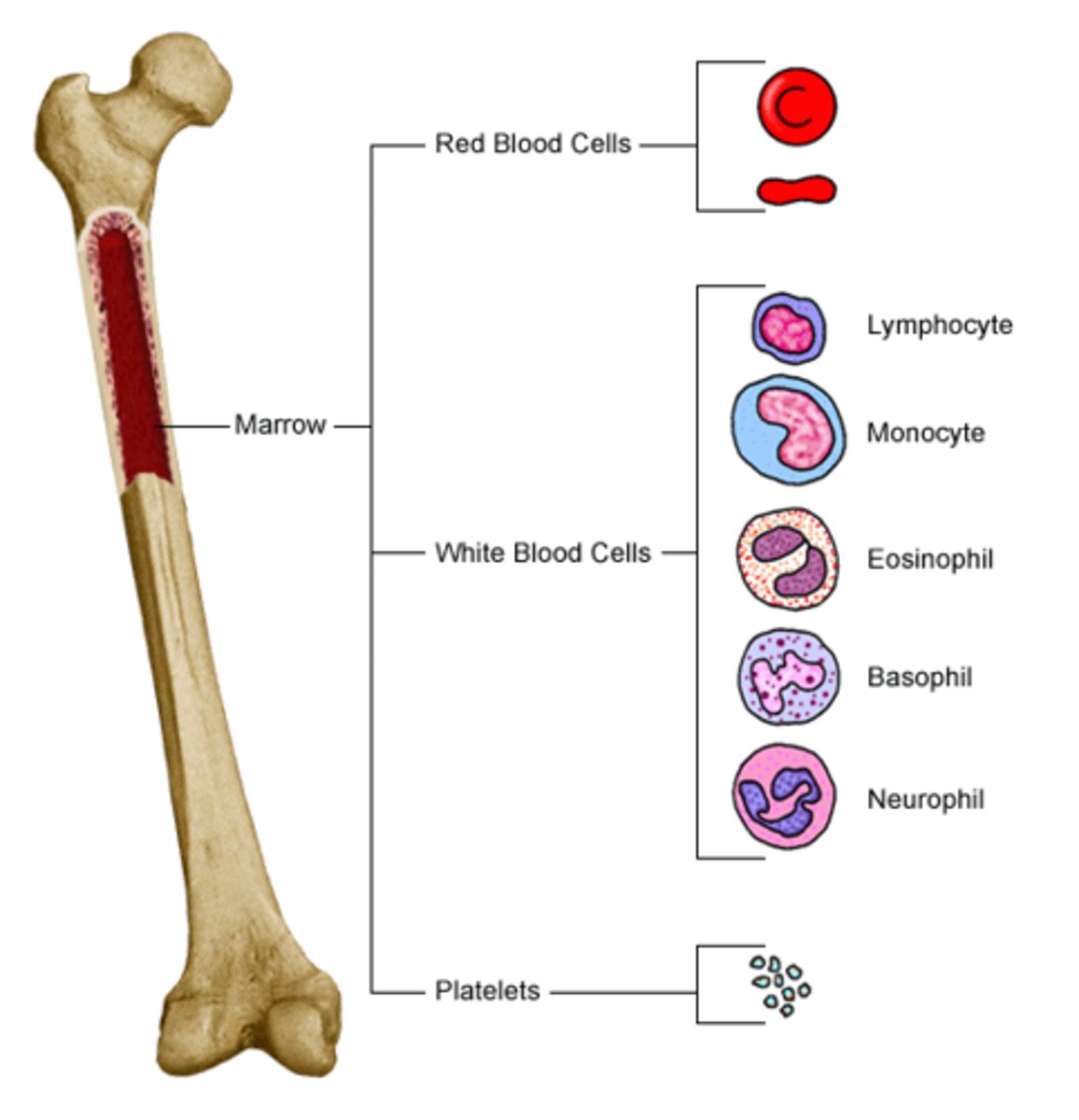
Hematopoiesis
The formation of blood cells from stem cells in the bone marrow
What are pluripotent cells?
Stem cells that can differentiate into each of the different types of blood cells
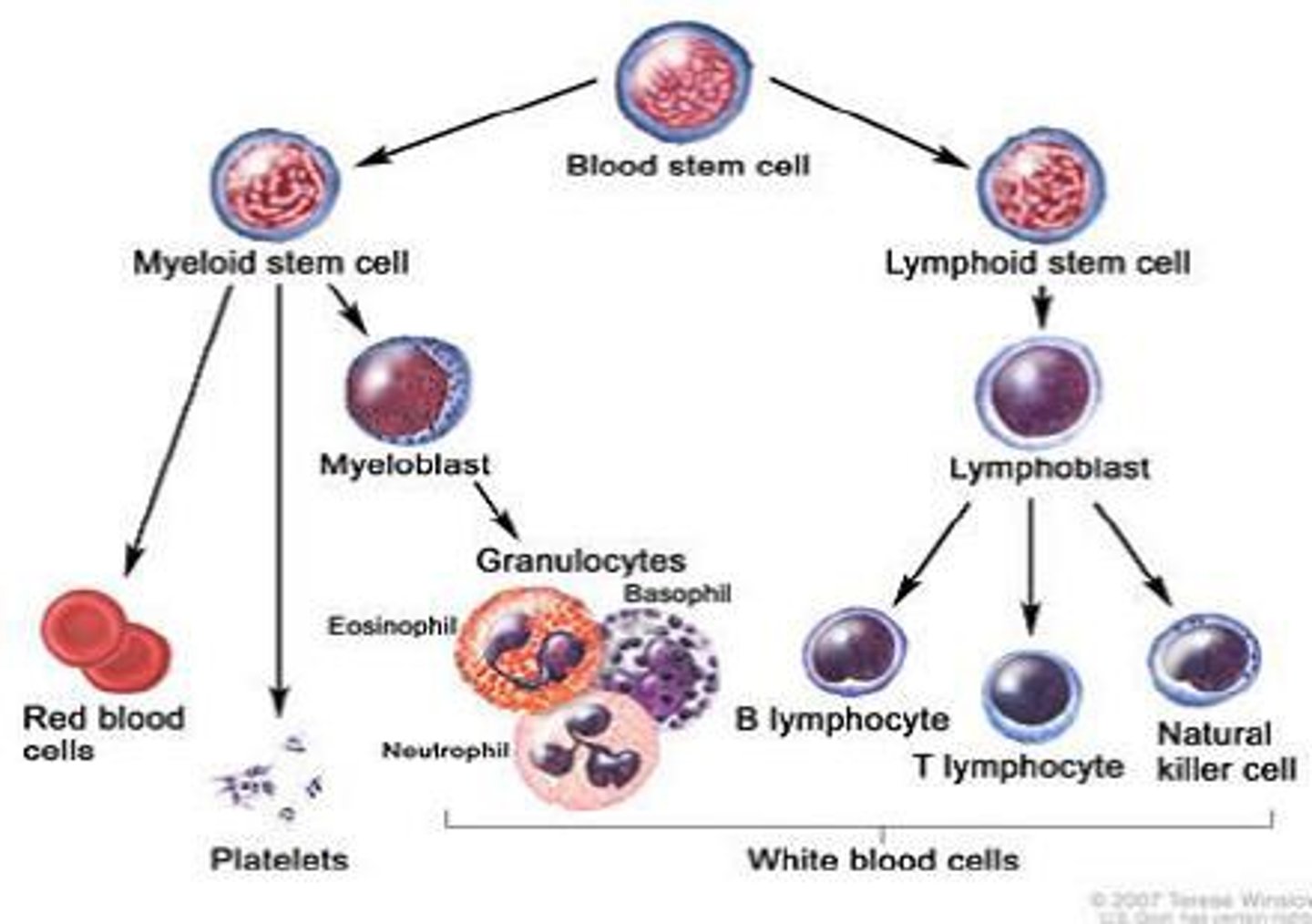
Lymphoid stem cell
Differentiates into the 3 types of lymphocytes (T cells, B cells, NK cells)
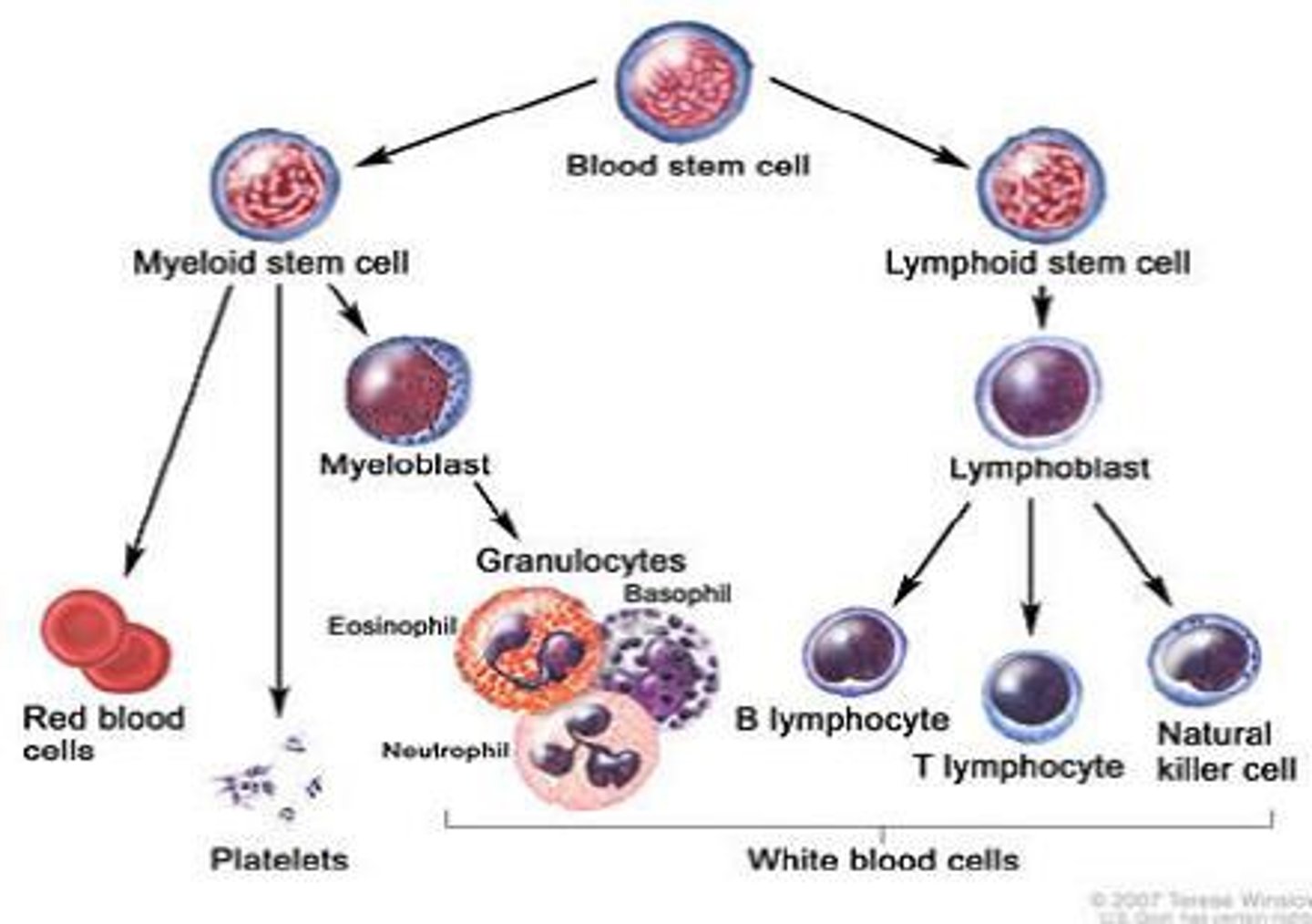
Myeloid stem cell
Differentiates into erythrocytes/platelets, and granulocytes/monocytes
Hematopoietic growth factors
"Hormones" that promote and regulate the differentiation and proliferation of blood cells
Colony-stimulating factors
Another name for Hematopoietic growth factors
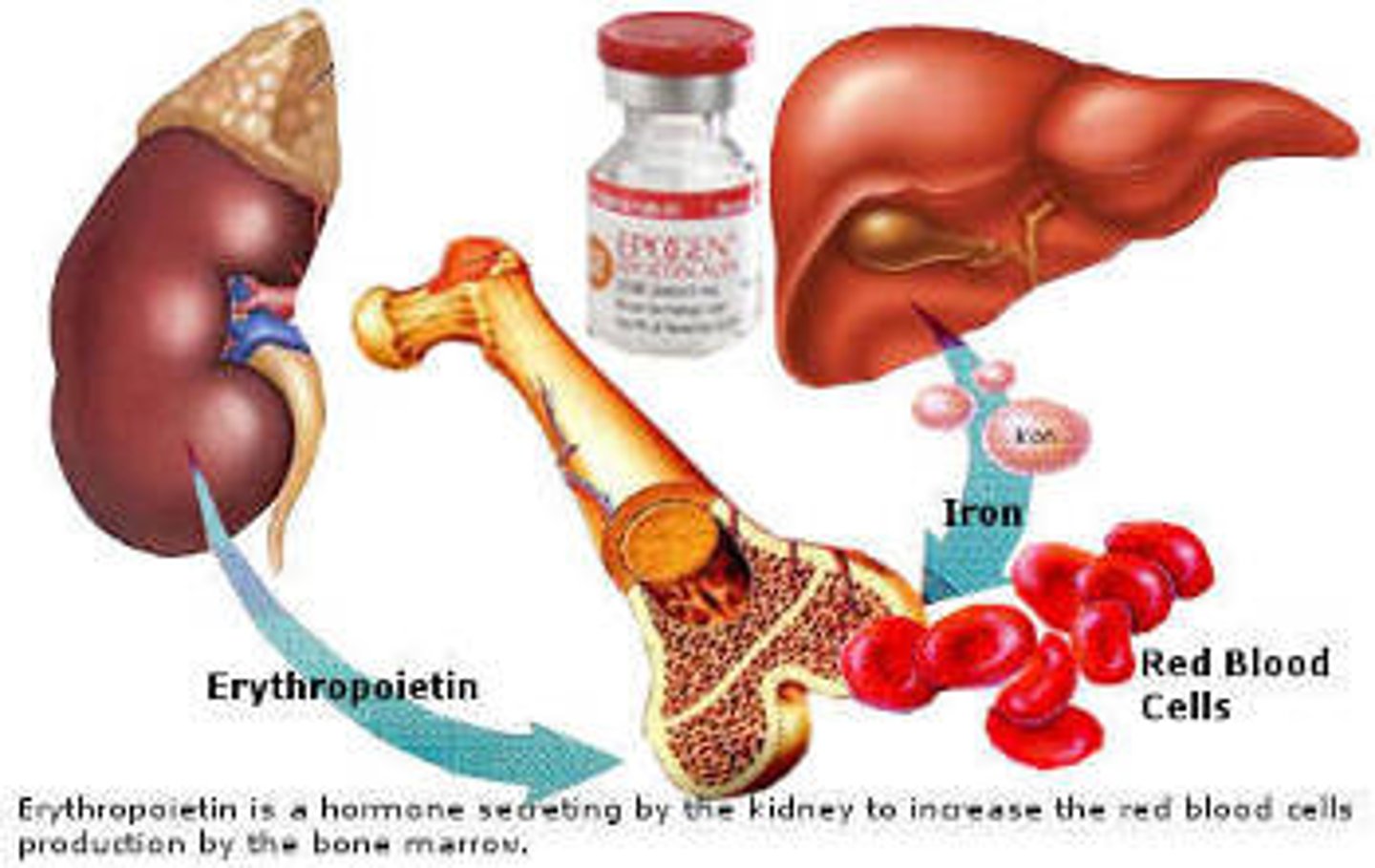
EPO
Erythropoietin; promotes growth of red blood cells
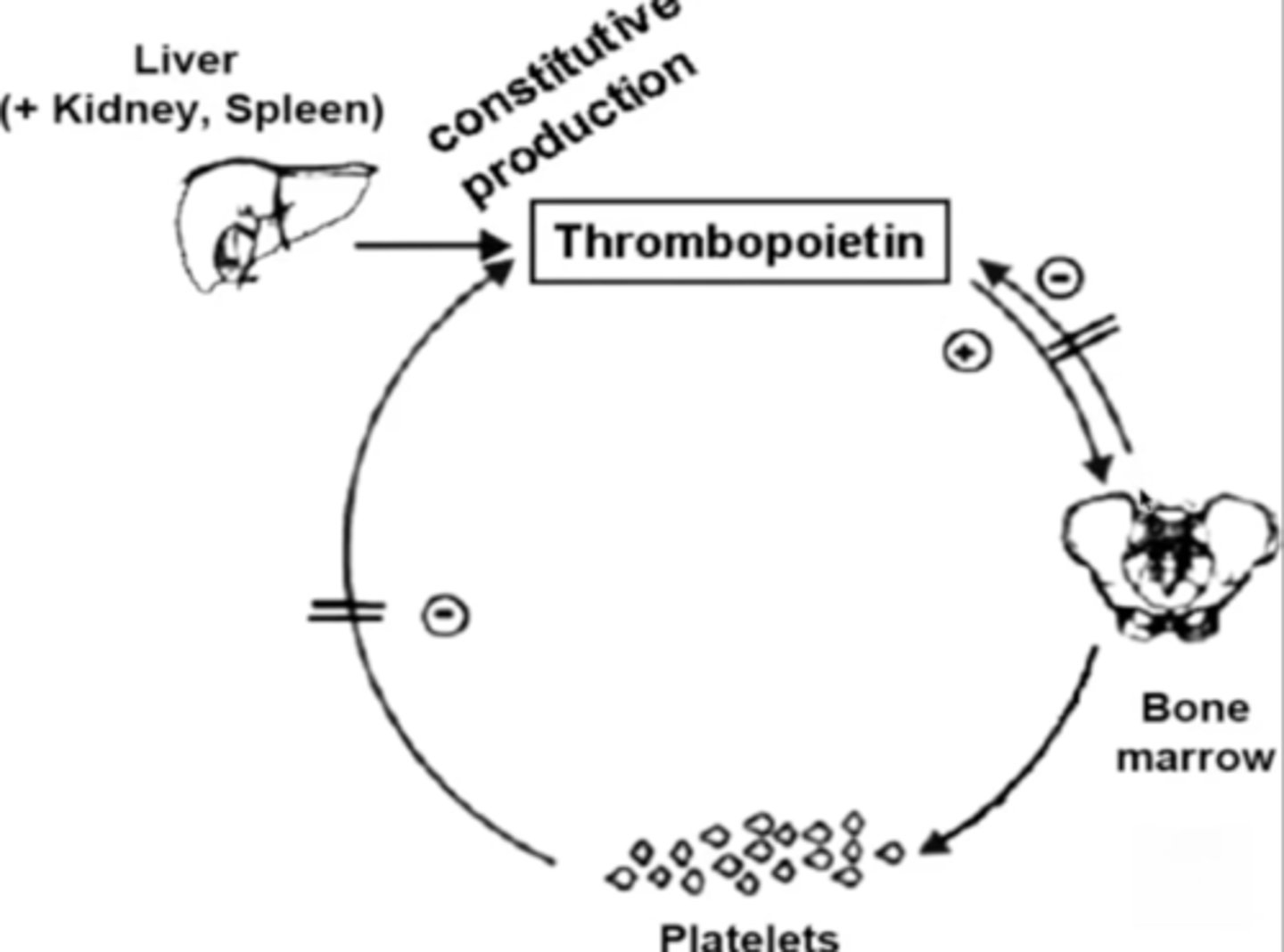
TPO
Thrombopoietin; stimulates platelet production
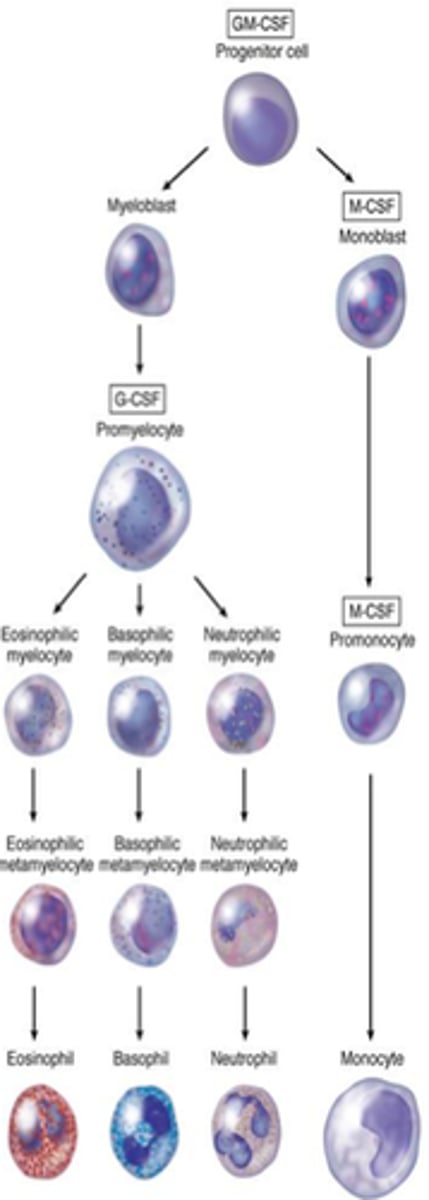
GM-CSF
Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; stimulates granulocytes and monocytes
Hematology
The study of blood and blood disorders

Hematology nurses
These nurses specialize in caring for patients with blood disorders
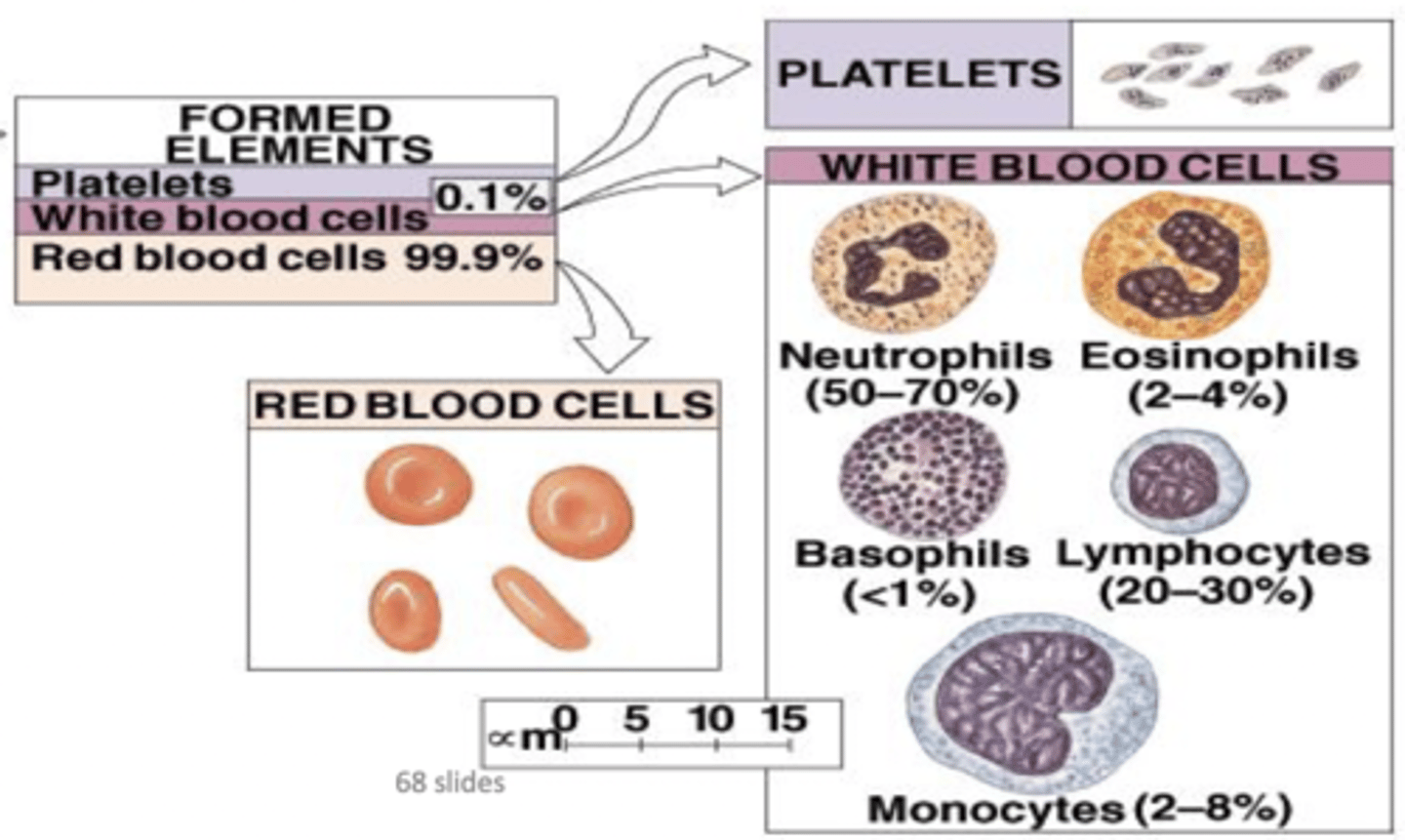
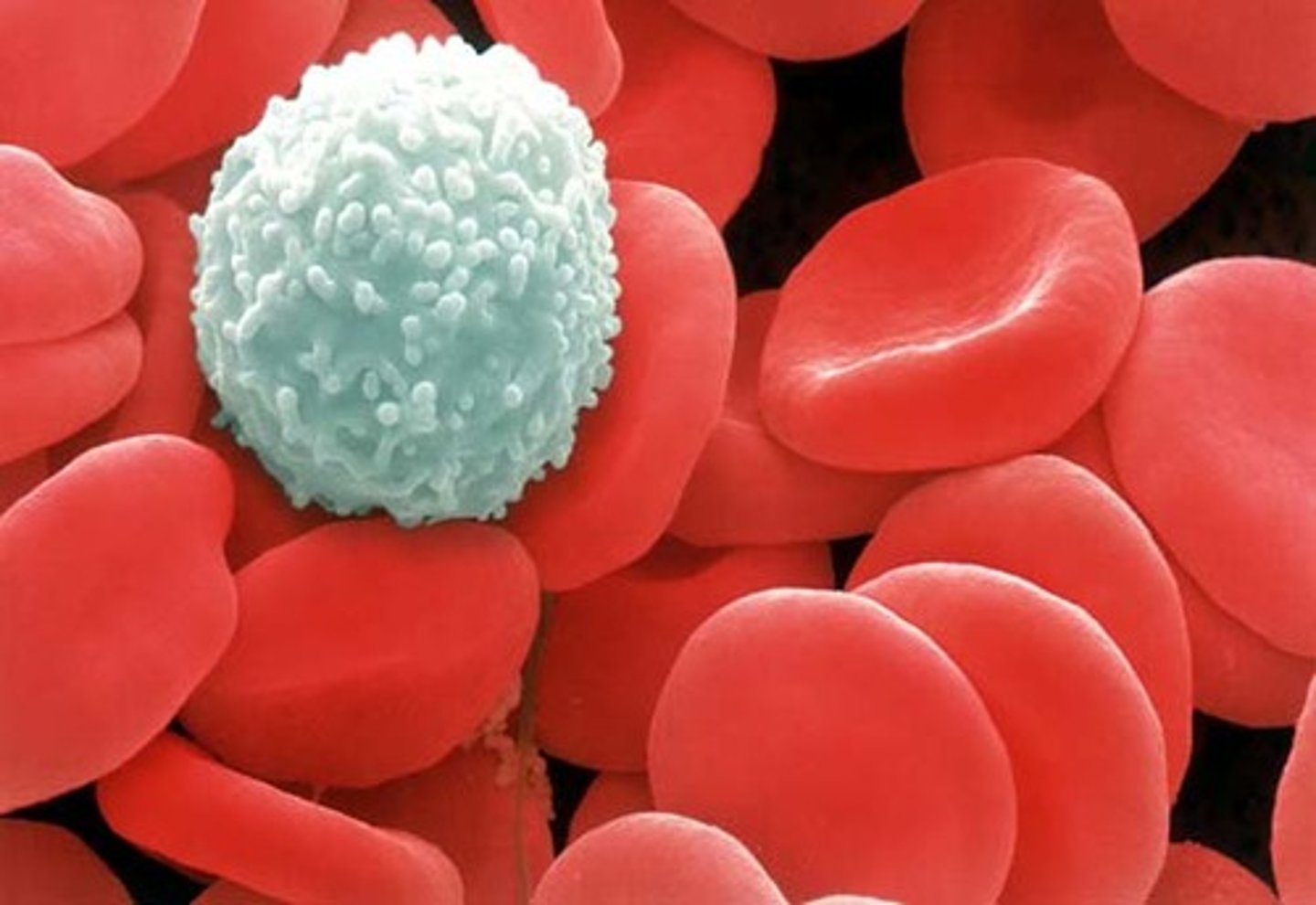
Leukocytes
White blood cells
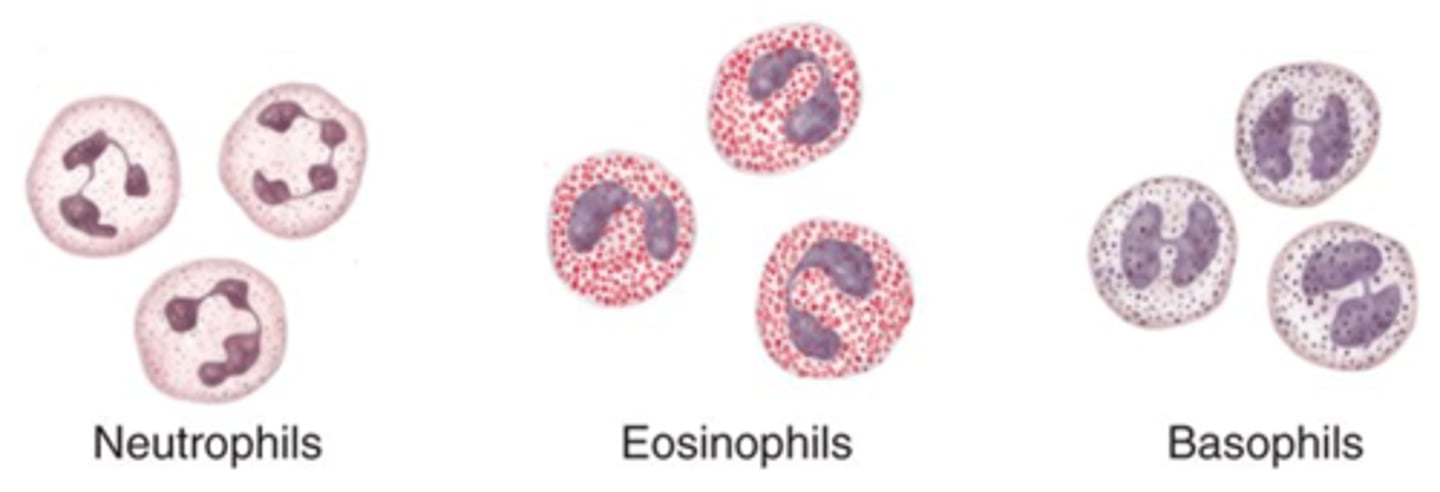
Granular leukocytes
Neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
PHILLED (filled) with granules (enzymes)
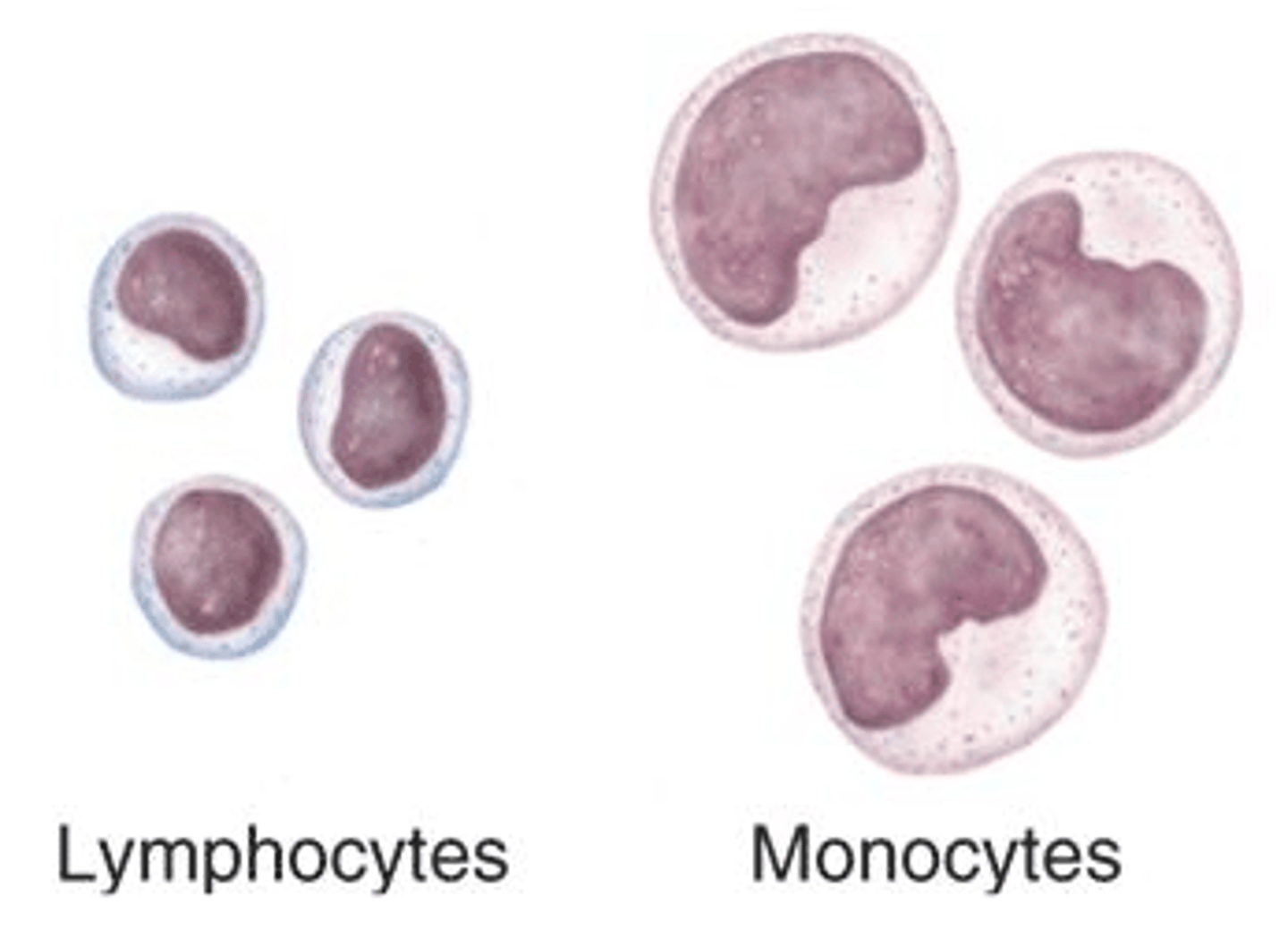
Agranular leukocytes
Lymphocytes and monocytes
No granules
What is unique about lymphocytes?
They can move between blood and lymphatic tissue, whereas all others only circulate in blood
That's why they're called LYMPHocytes silly goose
What are the two most common leukocytes?
Neutrophils and lymphocytes
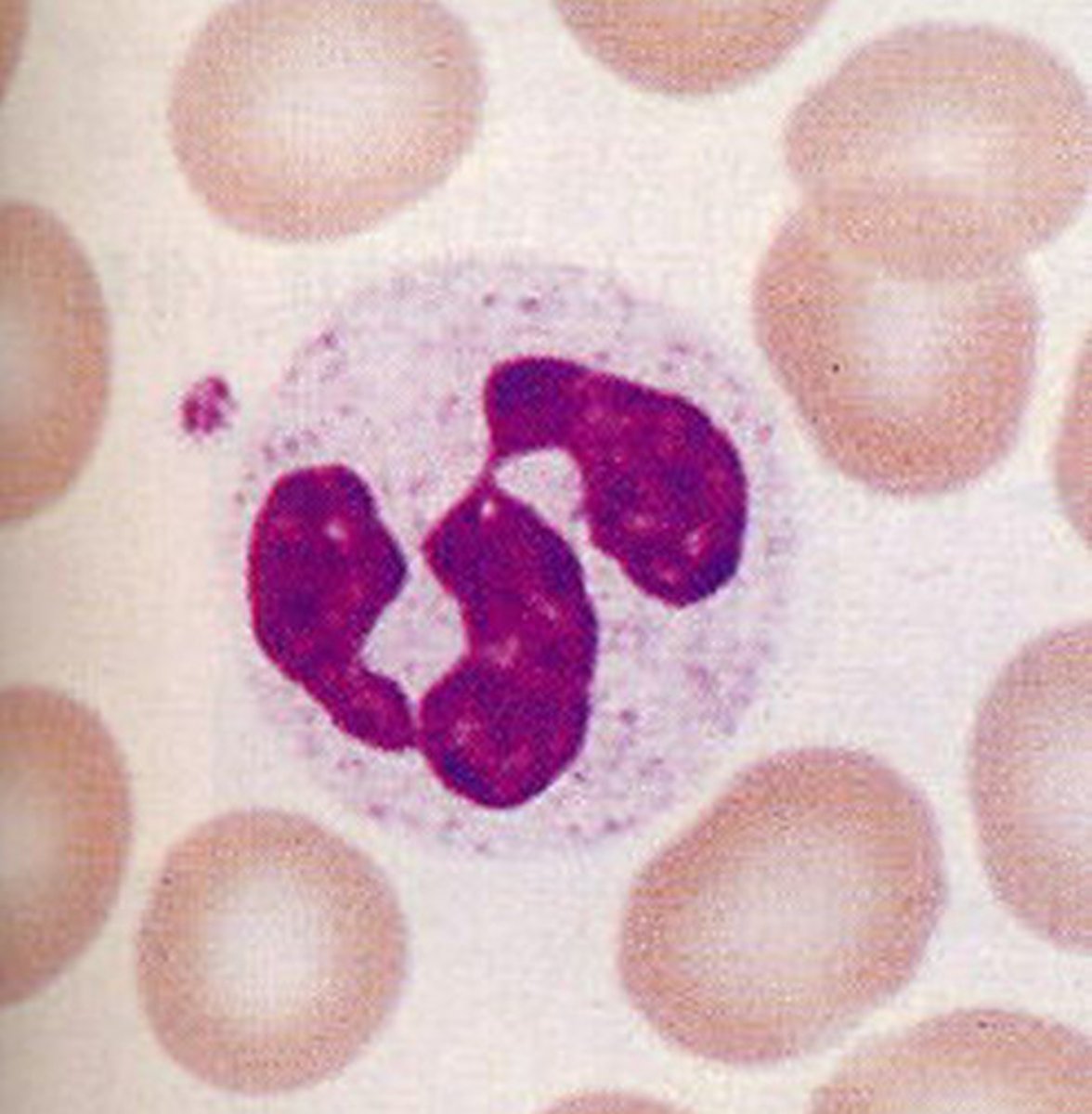
Neutrophils
Structure: Nuclei has three or more lobes
Function: The most common WBC; fights bacterial infections by engulfing bacteria by phagocytosis
Where does the name neutrophils come from?
Their granules do not stain with acid or basic dye
Other name for neutrophils
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (bc they have many lobes)
Eosiniphils
Structure: Nuclei has two lobes, granules stain pink
Function: A WBC that digests and destroys parasitic worms, they also play a role in allergy and immune response
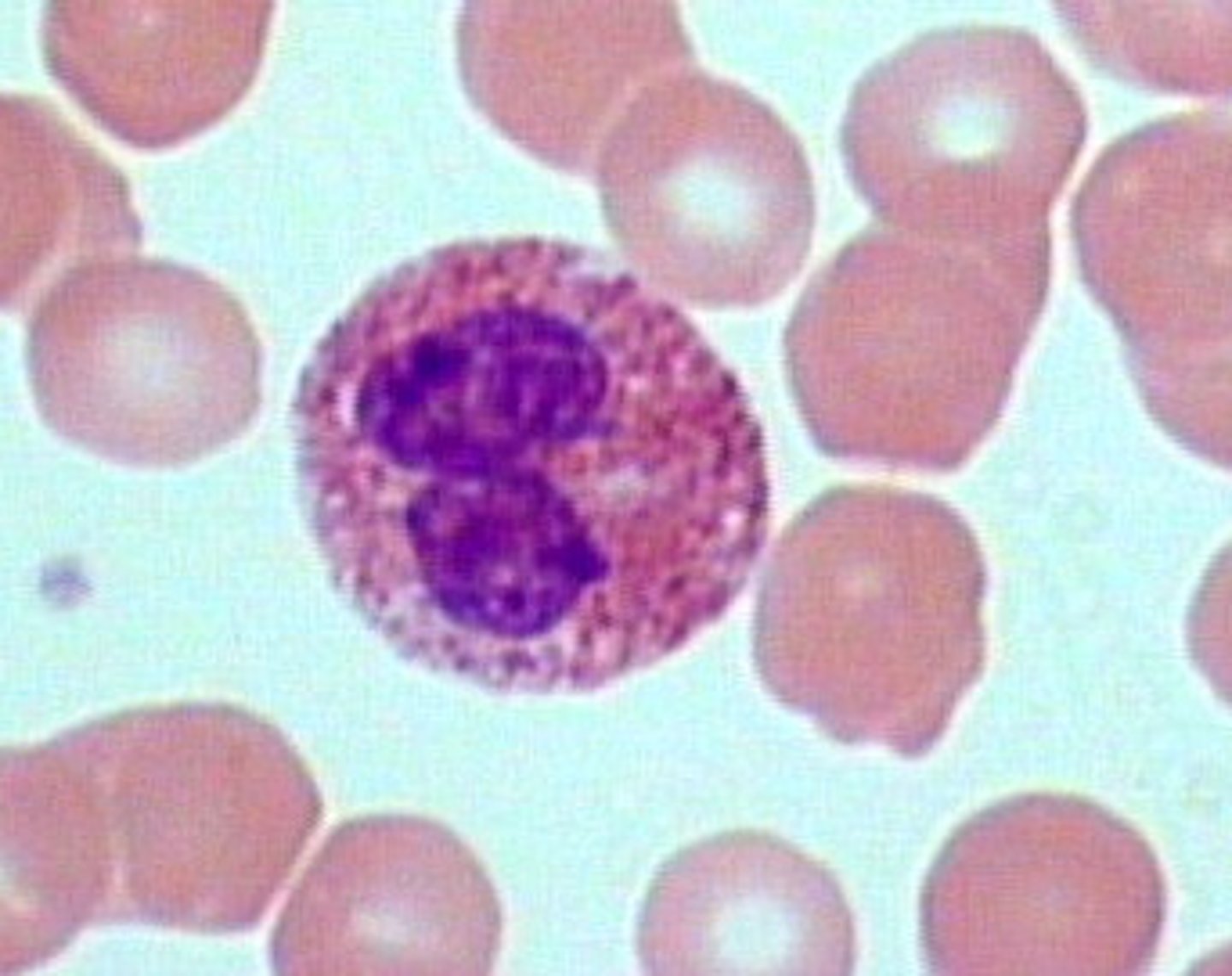
Where does the name eosinophils come from?
Their granules stain pink with acidic dye called eosin
Basophils
Structure: Nuclei is U or S shaped but is obstructed by HUGE blue granules
Function: A WBC that produces histamine --> causing inflammation during an immune response
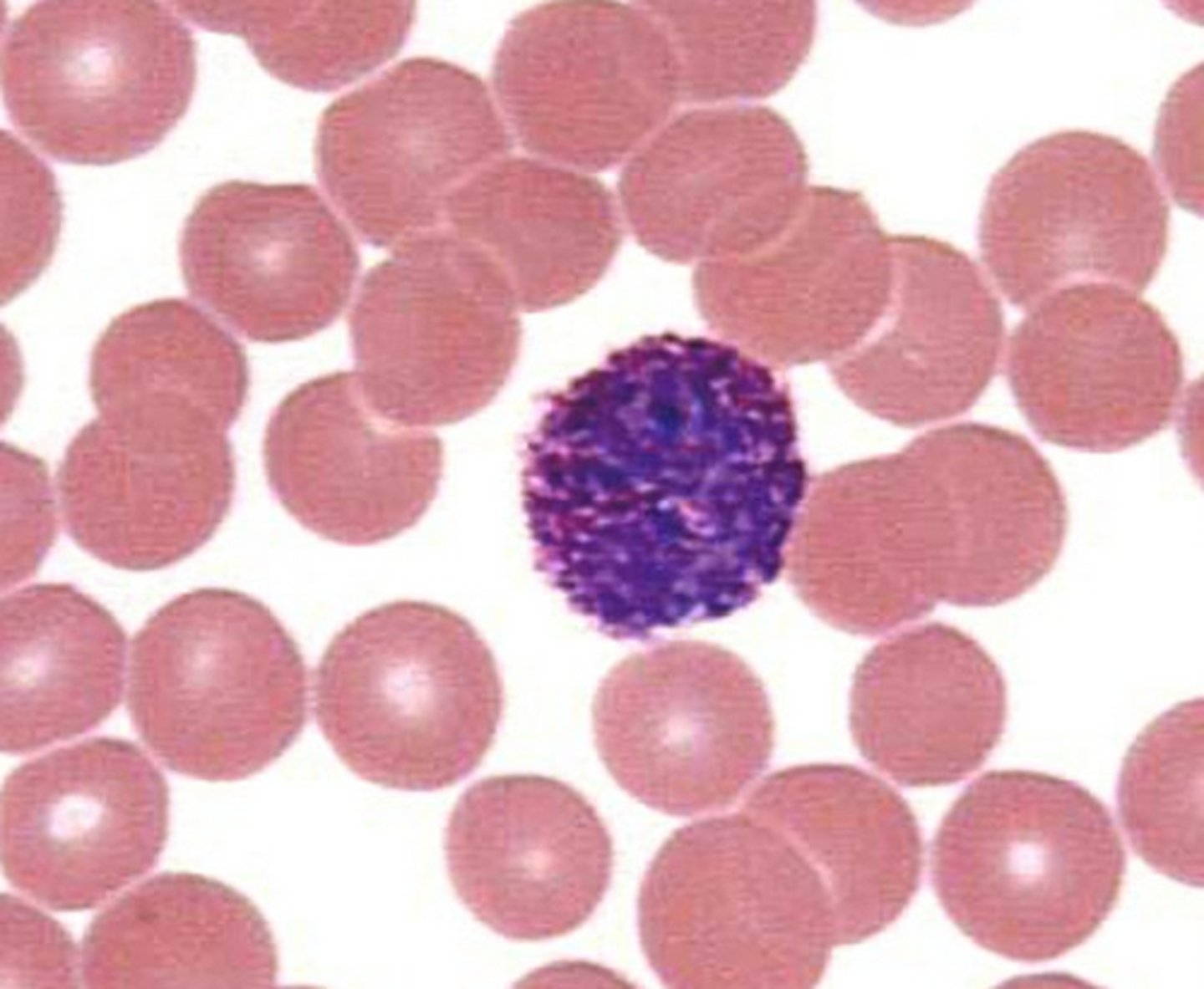
Where does the name basophils come from?
Stain blue with hematoxylin dye
Monocytes
Structure: Largest WBCs, U shaped nucleus
Function: A large WBC that transform into macrophages to fight off viruses and chronic infections
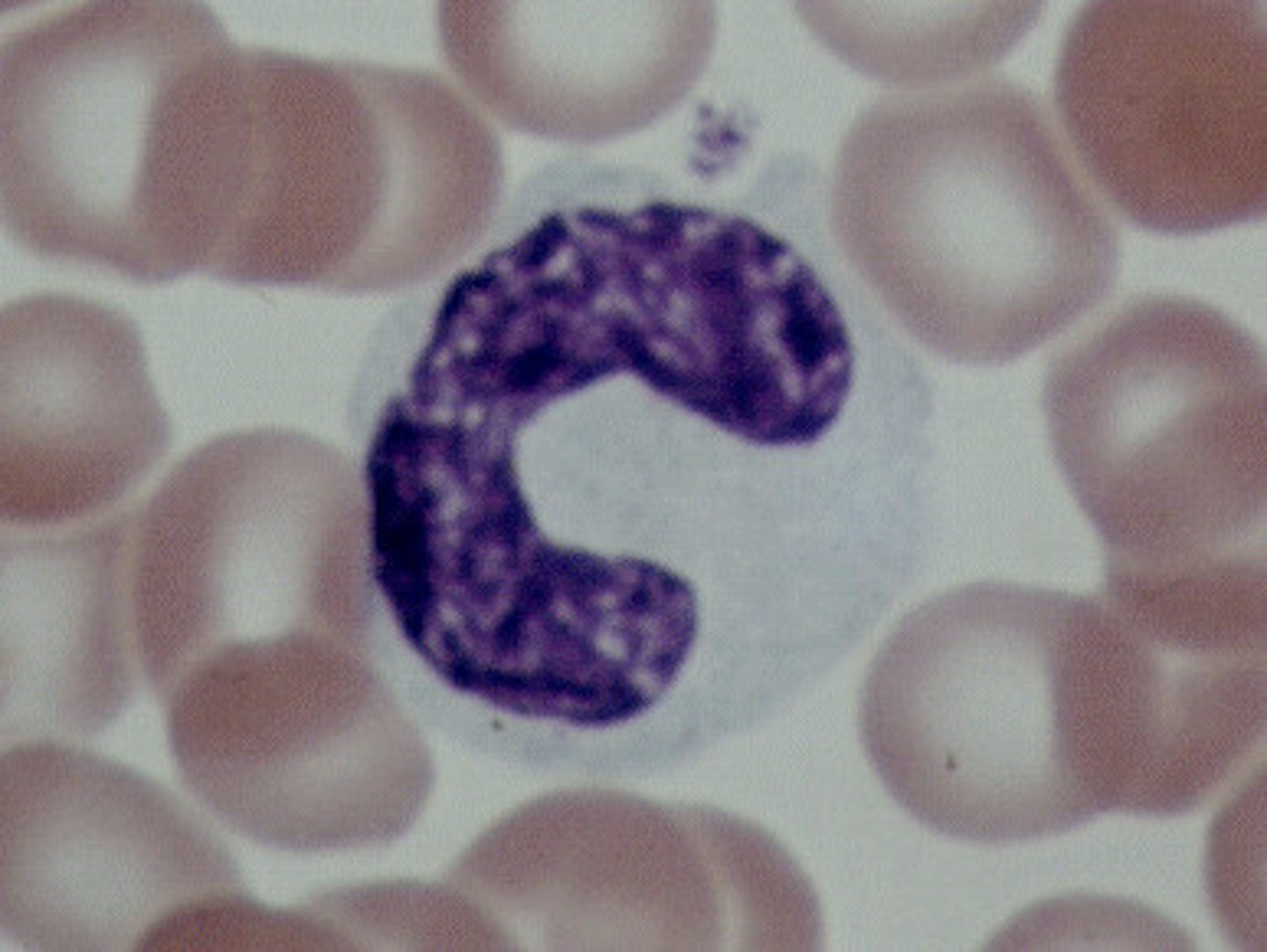
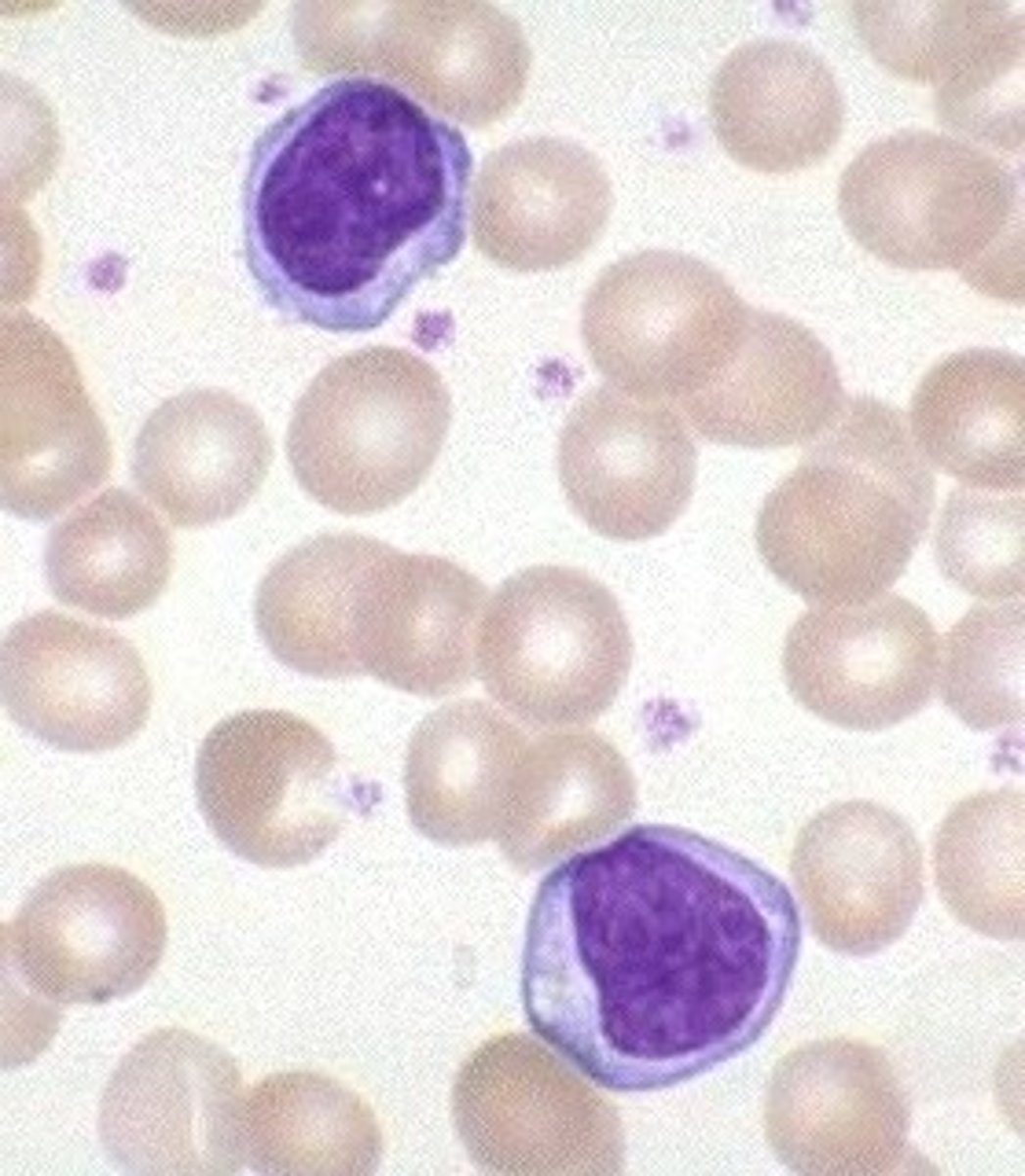
Lymphocytes
Structure: Has a large, dark purple nucleus that takes up most of the cell volume
Function: B cells make antibodies, T cells fight off viral infections, NK cells
B cells
A type of lymphocyte that is created in the bone marrow; creates antibodies that isolate and destroy pathogens
Naive B cells
A B cell that has not been exposed to an antigen yet
Effector B cells
Active B cells that have been exposed to antigens
Plasma cells
A type of effector B cells, they produce antibodies
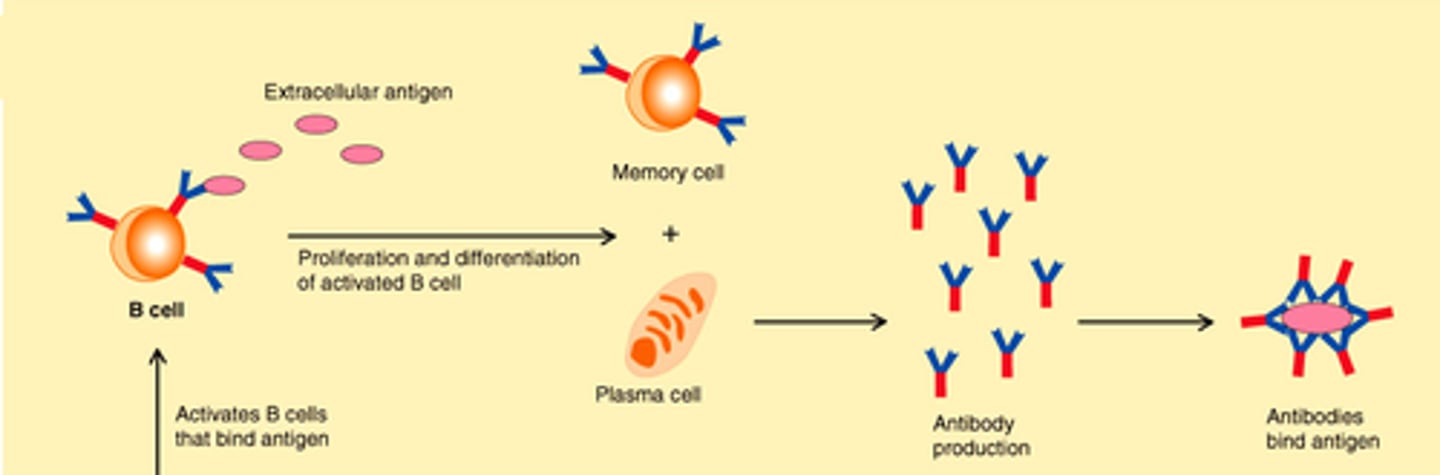
Memory B cells
A type of effector B-cell that memorizes the characteristics of the pathogen antigen; it remains dormant until reactivated by the same antigen
elephant never forgets.

T cells
A type of lymphocyte that is created in the thymus; produce substances that attack infected cells in the body
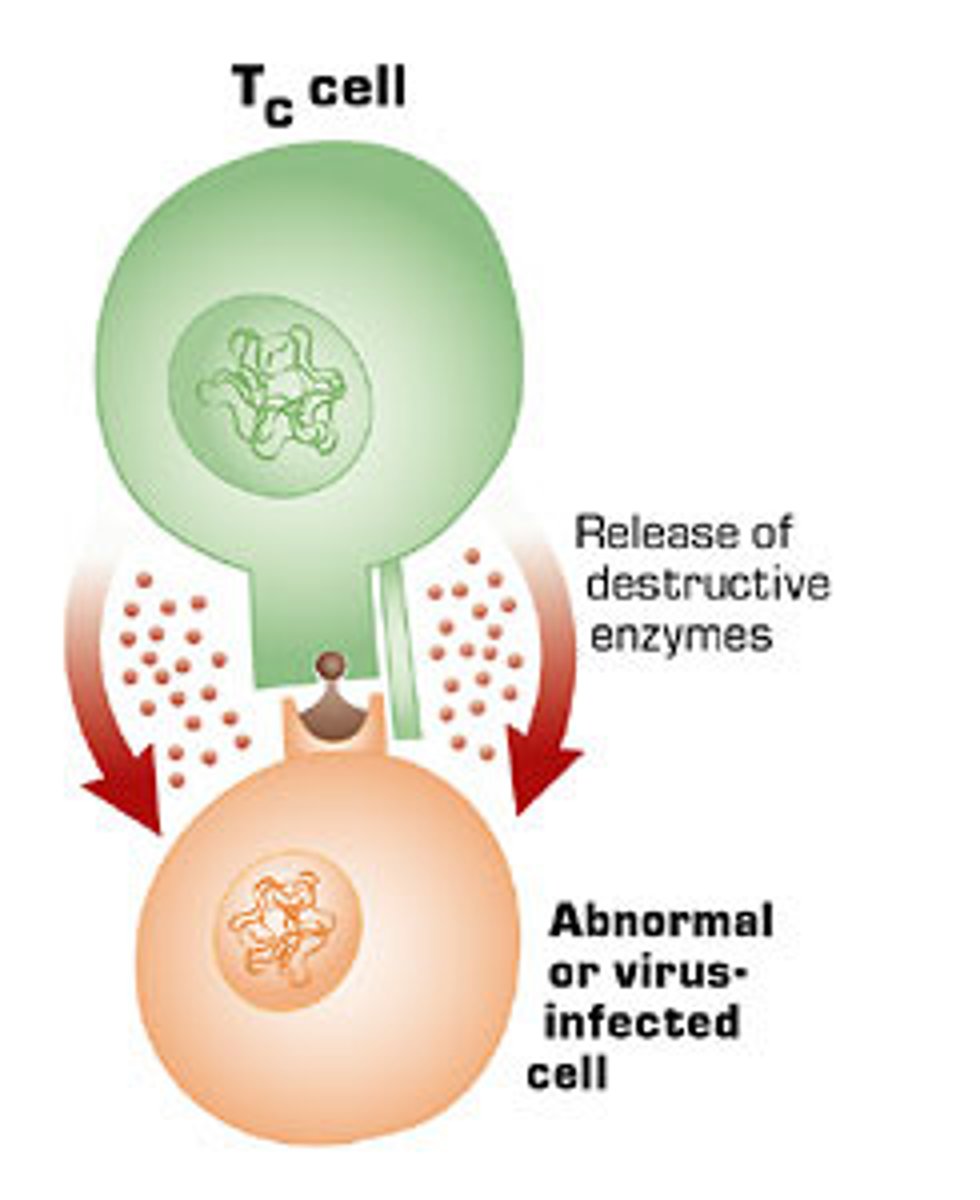
CD8 T cells
Cytotoxic T cells
A type of effector T-cell; they target and kill invading pathogens and cancer cells
CD4 T cells
Helper T cells
A type of effector T-cell that, when activated, stimulates activity of B cells and cytotoxic T cells

Memory T cells
A T cell that remembers antigen and quickly stimulate immune response on re-exposure
crow never forgets.

Natural Killer (NK) cells
A type of lymphocyte found in the blood/lymph nodes/spleen --> they kill cancer cells and cells infected with viruses

Primary lymphoid tissues
Bone marrow and thymus
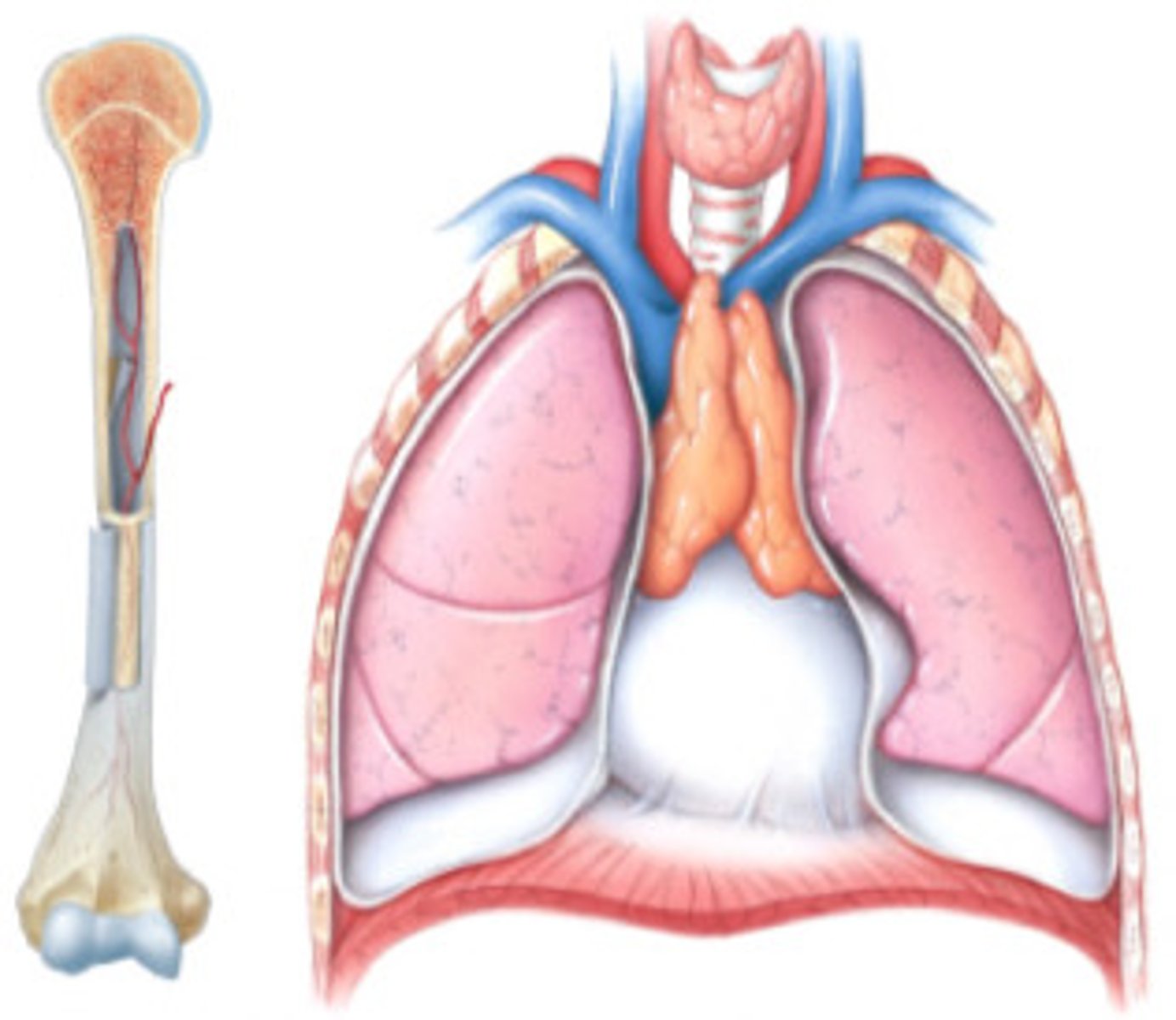
Secondary lymphoid tissues
Lymph nodes, spleen, and mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
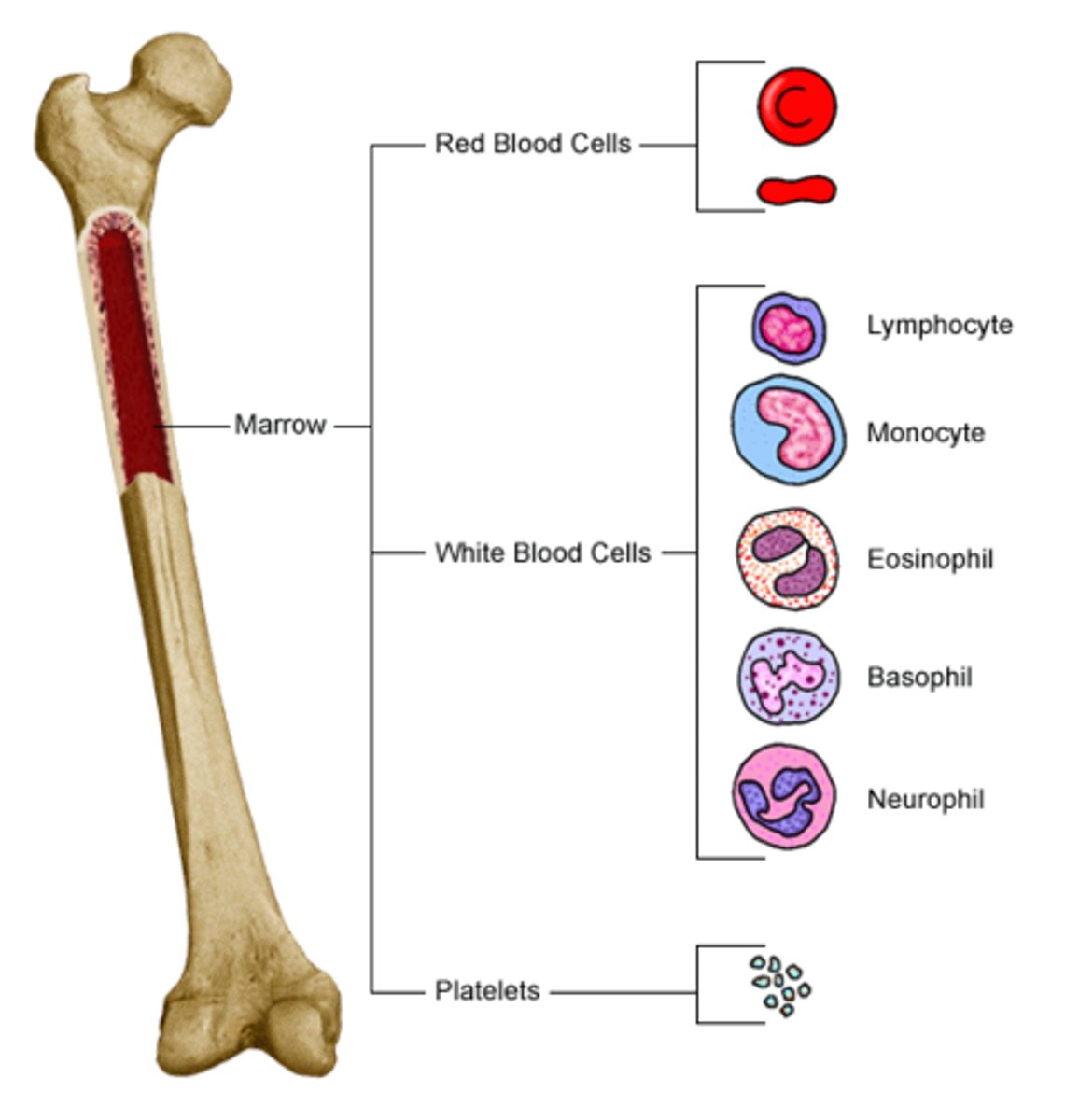
What does the bone marrow do?
Produces blood cells
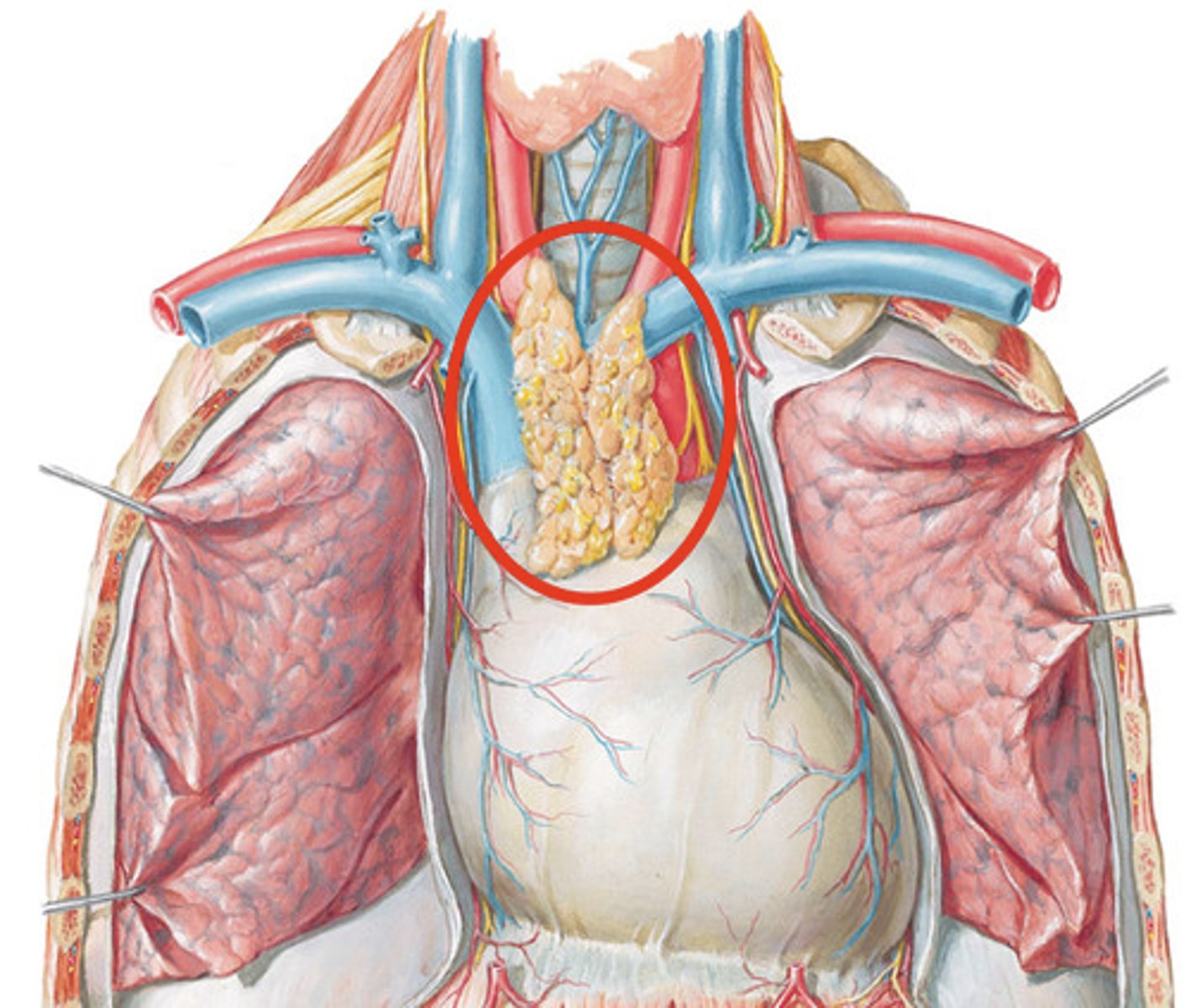
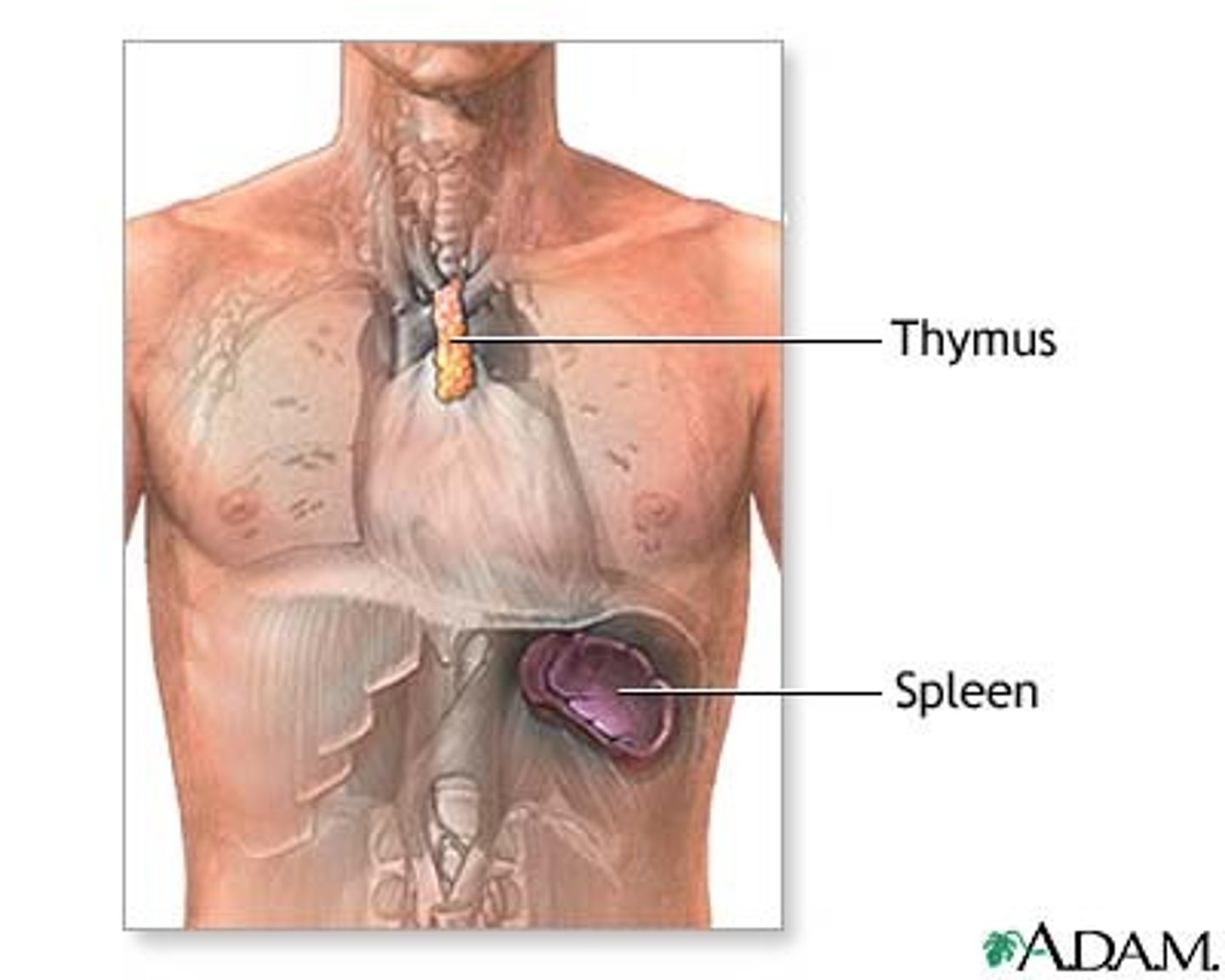
What does the thymus do?
Site of T cell differentiation and maturation
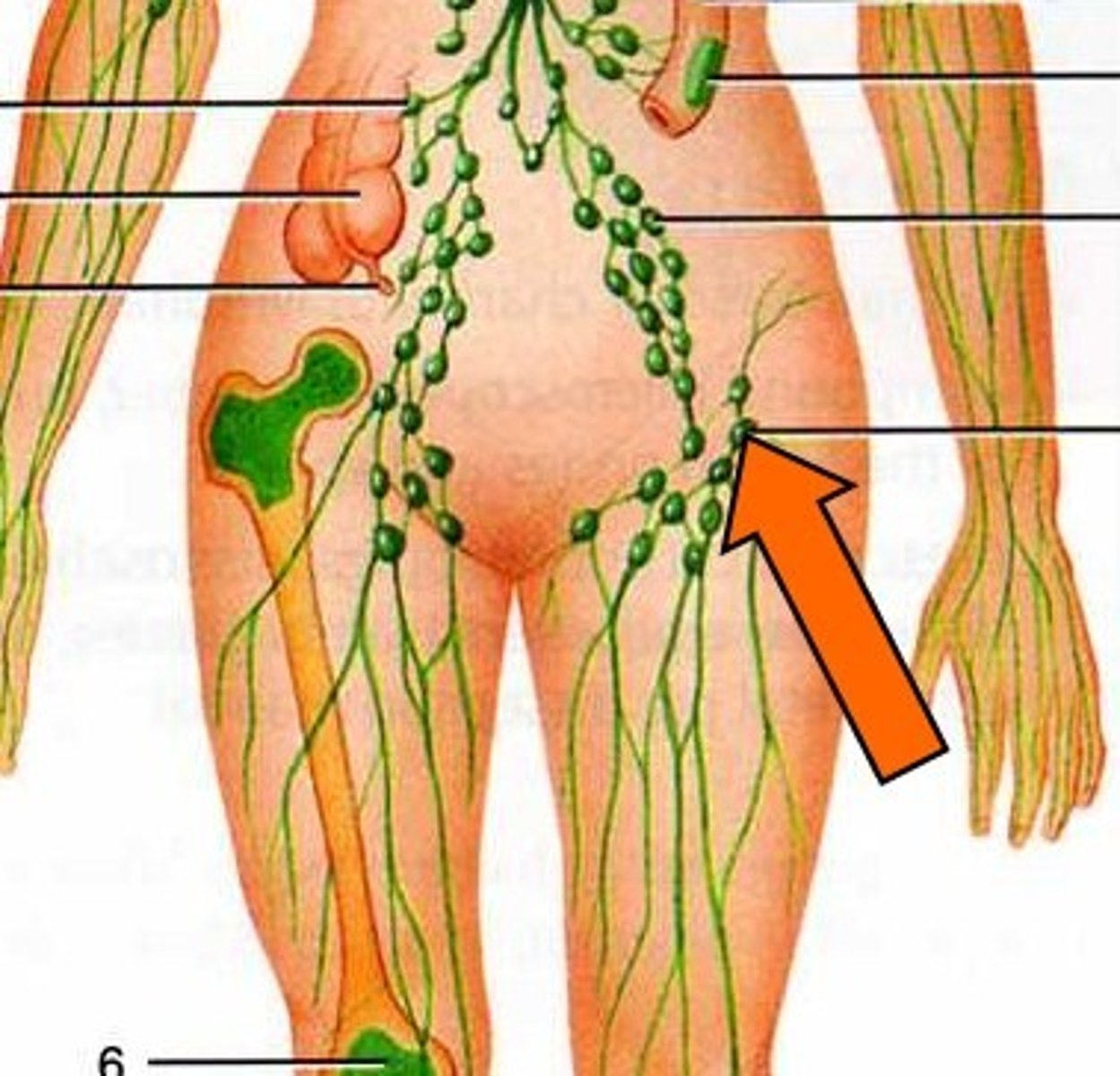
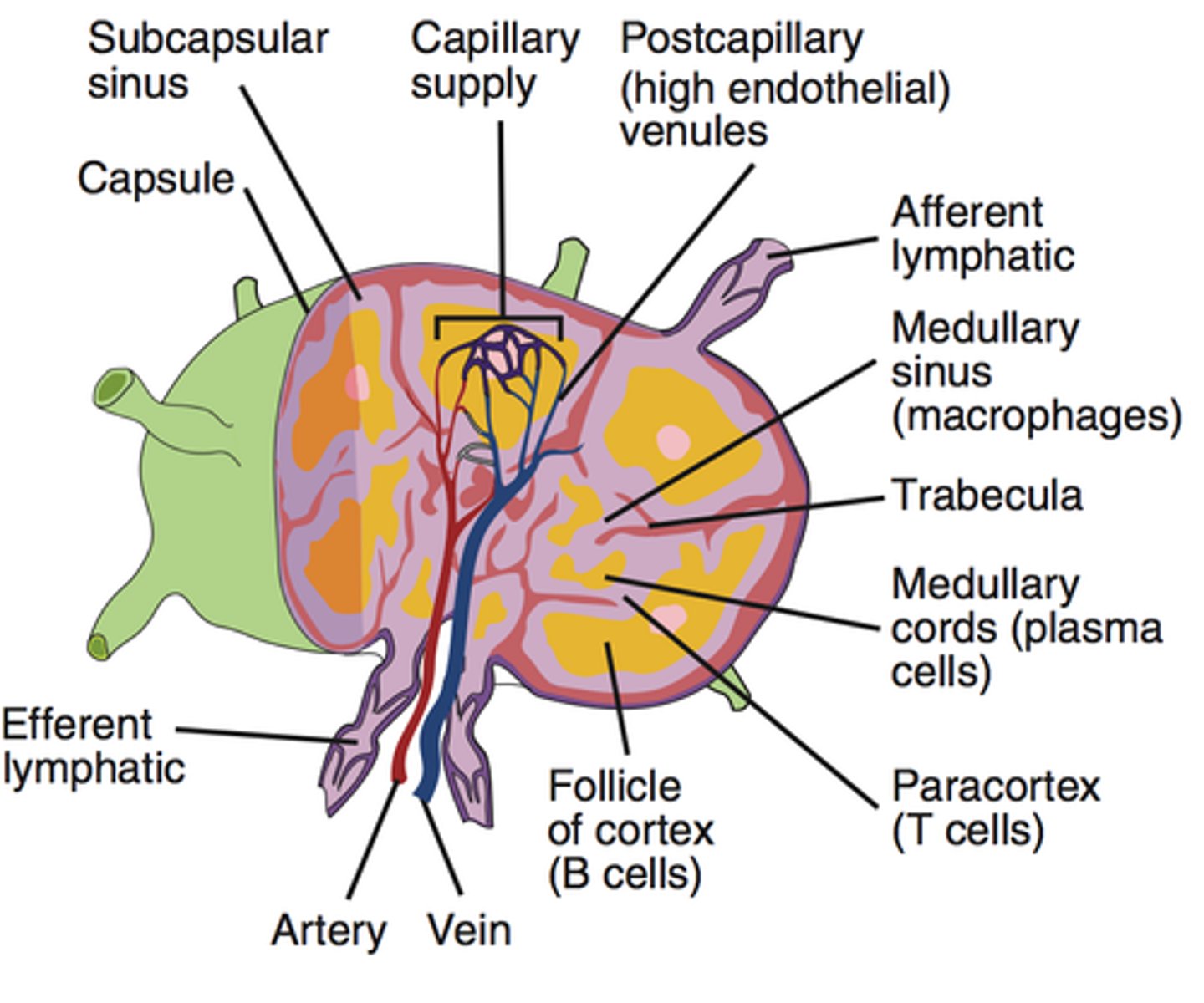
What do the lymph nodes do?
Filter lymph --> trap pathogens for destruction by white blood cells
What does the spleen do?
Filters blood and removes damaged blood cells
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
Lymphatic tissue without a connective tissue capsule (salivary glands, eyes, breast tissue)
Non-neoplastic
Not cancerous
What kind of non-neoplastic disorders are the most common?
Those that involve neutrophils and lymphocytes
What kind of non-neoplastic disorders are the least common?
Those that involve monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils
Neutropenia
Definition: Abnormally low number of neutrophils
Etiology: Chemotherapy, autoimmune disorders, septicemia that uses up neutrophils
S+S: Recurrent infections, absence of pus formation at sites of infection
Treatment: Antimicrobial meds, hematopoietic growth factors
Agranulocytosis
Severe neutropenia (appears that you have no granulocytes)
Neutrophilic Leukocytosis
Definition: Abnormally high number of neutrophils
Etiology: Normal immune response to infection, autoimmune disorders
S+S: N/A
Treatment: Solve underlying cause of infection/injury
Lymphocytopenia
Definition: Abnormally low number of lymphocytes
Etiology: Chemotherapy, autoimmune disorders, HIV or TB
S+S: Recurrent infections, decreases in B, T, or NK cells
Treatment: Antimicrobial meds, gamma globulins (artificial antibodies)
Lymphocytic leukocytosis
Definition: Abnormally high number of lymphocytes (B cells, T cells, or NK cells)
Etiology: Viral infections, autoimmune disorders
S+S:
Treatment: Solve underlying cause of infection/injury
Infectious mononucleosis
Definition: Kissing disease
Etiology: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
S+S: Sore throat, fatigue, fever, enlarged spleen, large number of BIG lymphocytes
Treatment: Rest + no exercise

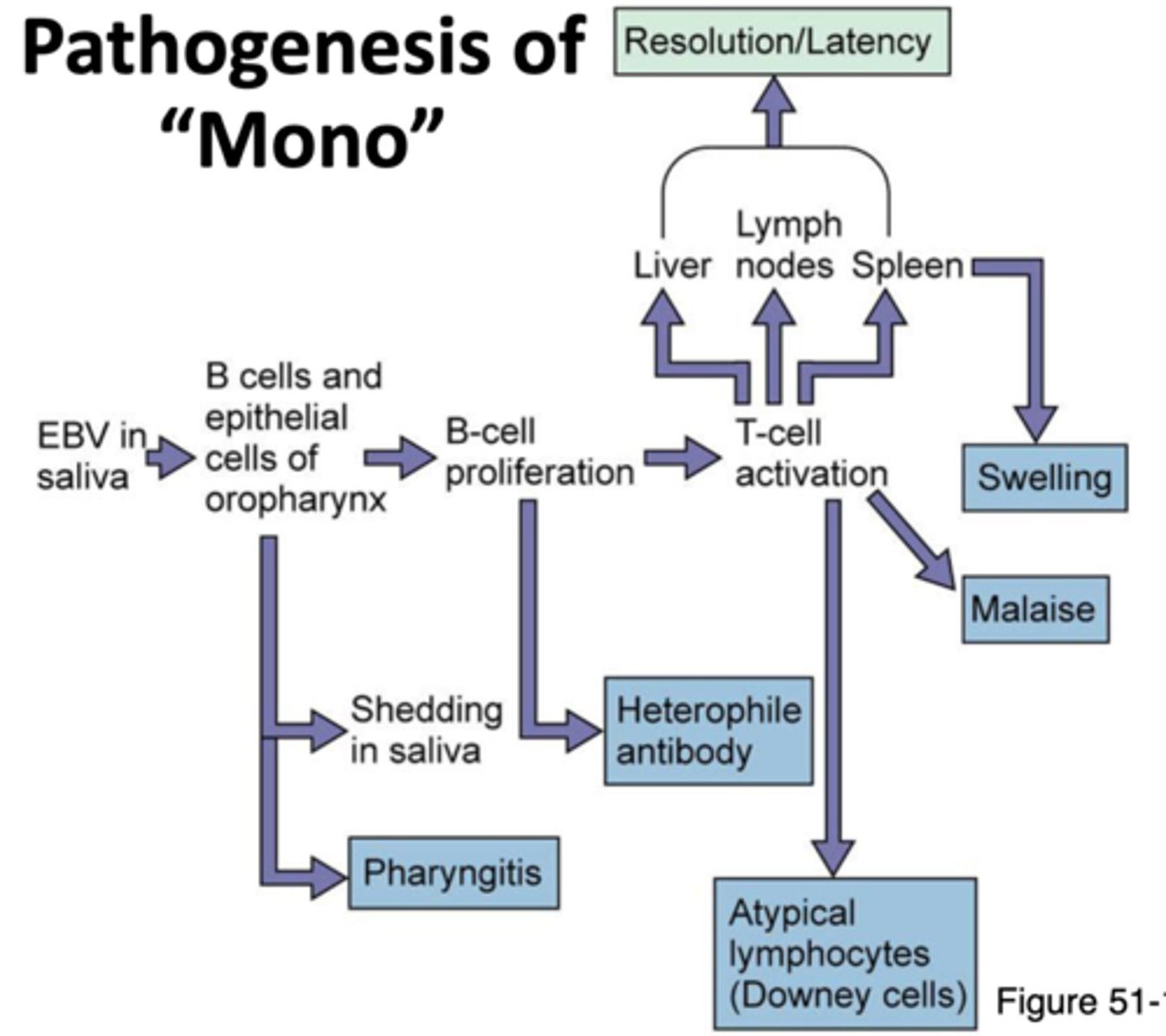
Pathogenesis of mono
EBV enters and multiplies in epithelial cells in mouth --> Spreads to B cells in the throat --> Infected B cells multiply --> Signs and symptoms --> Cytotoxic T cells and NK cells destroy infected B cells --> Recovery
Leukemias
Cancers of the hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow
Where does the name leukemia come from?
There is a reversal of the normal RBC to WBC ratio --> now more WBCS than RBCS --> "white blood"
What 2 factors are used to classify leukemias?
Based on
1. Whether they are acute or chronic
2. Affected cell type (lymphoid or myeloid)
Lymphocytic leukemia
Leukemia involving cells that originate from lymphoid stem cells
Myelocytic leukemia
Leukemia involving cells that originate from myeloid stem cells
Acute Leukemias
Large numbers of immature BLAST leukocytes in the blood and bone marrow (rapid onset and progression)

Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
Acute leukemia of lymphoid stem cells that occurs in children and adolescents
Acute myelocytic leukemia (AML)
Acute leukemia of myeloid stem cells that occurs in older adults
Chronic Leukemias
Large numbers of mature, differentiated leukocytes in the blood and bone marrow (slow onset and progression)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Chronic leukemia of lymphoid stem cells that occurs in older adults
Chronic myelocytic leukemia (CML)
Chronic leukemia of myeloid stem cells that occurs in older adults
S+S of leukemias
Fever, chills and night sweats, loss of appetite, weight loss, bone pain, enlarged lymph nodes, spleen, and liver
Why is fatigue a symptom of leukemia?
Anemia
Why is bleeding a symptom of leukemia?
Decreased platelet count
Why is recurrent infections a symptom of leukemia?
Neutropenia
Leukostasis
Complication of acute leukemia; a severely elevated circulating immature WBC count --> blood is more viscous --> clot development
Pulmonary leukostasis
Sudden shortness of breath and progressive dyspnea; caused by a WBC clot
Cerebral leukostasis
Severe headache which can progress to confusion and coma; caused by a WBC clot
Genetic factors that increase the likelihood of leukemia
Down Syndrome --> high risk of acute leukemias
Family history --> high risk of CLL
Philadelphia chromosome --> high risk of CML
Environmental factors that increase the likelihood of leukemia
Exposure to chemicals, chemotherapy
How are leukemias diagnosed?
Leukocyte count, bone marrow biopsy, genetic tests
How are leukemias treated?
Chemo, radiation, bone marrow transplants, antimicrobial meds
Malignant Lymphomas
Solid neoplastic tumors that originate in the peripheral lymphoid tissues
Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL)
Definition: Tumor that originates in ONE single lymph nodes --> spread to other nodes
Pathogenesis: B cells transform into large, abnormal cells (Reed-Sternberg cells)
S+S: Painless enlargement of lymph nodes above the diaphragm, fever, weight loss
Treatment: Chemo and radiation
What ages are most affected by Hodgkin's lymphomas?
Common in young adults (20-30 yrs) and older adults (over 55 yrs)
Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas (NHLs)
Definition: Tumor that originates in multiple lymph nodes --> spread to other body tissues
Pathogenesis: B cells OR T cells become malignant
Etiology: Infections, immunosuppression, chemicals
S+S: Painless enlargement of lymph nodes in neck, axilla, or groin, fever, weight loss
Treatment: Chemo, radiation
What ages are most affected by Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma?
Common in the elderly (over 65 yrs)
Multiple Myeloma
Definition: Malignancy of plasma cells
Pathogenesis: Terminally differentiated plasma (B) cells secrete a TON of antibodies
Etiology: N/A
S+S: Bone pain, fractures, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, kidney failure
Treatment: Chemo + palliative care :(
Defining characteristics of Multiple Myeloma
High antibody level, osteolytic lesions in bones
What demographic groups are most affected my multiple myeloma?
More common in elderly, men, and African-Americans
How is multiple myeloma detected?
Blood test will detect M proteins (abnormal IgG)
Urine test will detect Bence-Jones proteins (fragment of antibody)