Week 9 - Policing pt 2
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Where do the powers of police come from?
Legislation
Biased Investigative Boards (e.x. SIU)
Police Powers in the Charter of Rights and Freedoms
Police are governed under:
Information and Privacy Acts
Criminal Code
Charter of Rights and Freedoms
Principle of Accountability
“Actions of policing individuals or agencies are subject to review; individuals can use formal channels to lodge complaints against policing bodies”
(Griffiths, 2025)
Response to police self-investigation
You need an external body to investigate
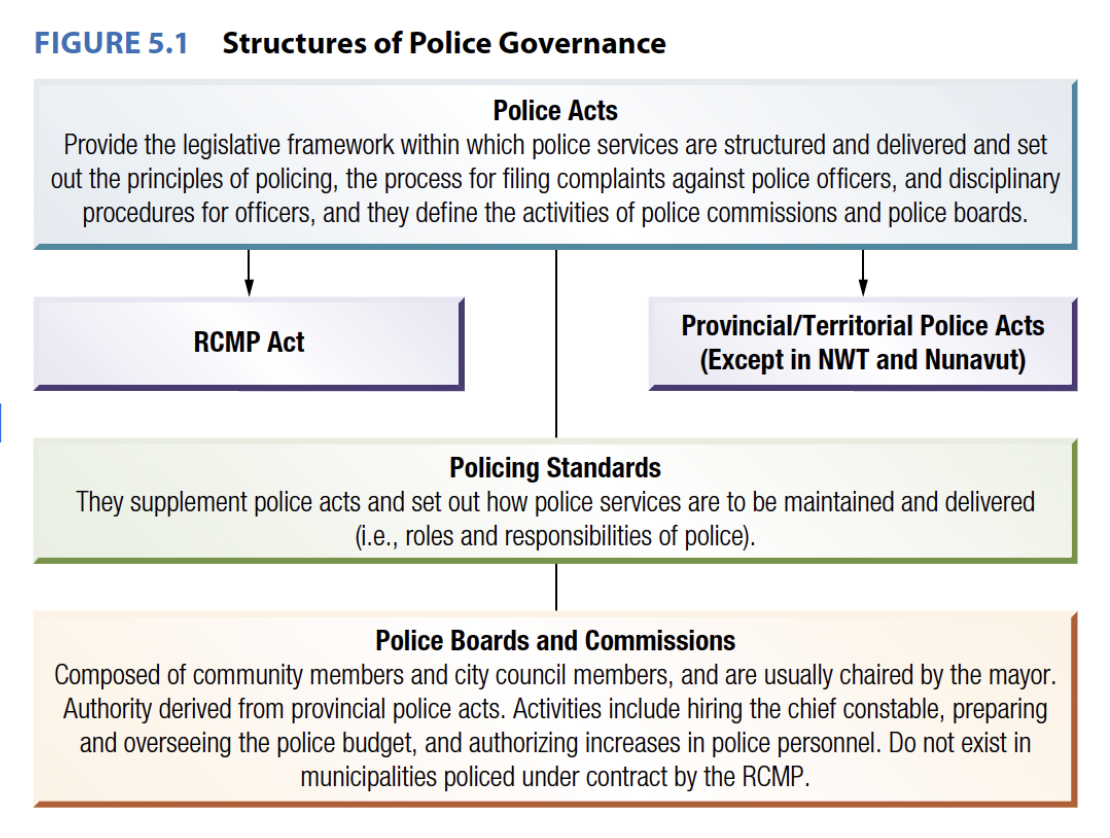
Structures of Police Governance (investigation)
Begins with police acts
Framework for police service (e.x. procedures, how to file a complaint)
Depends on level of policing (rcmp act or provincial/territorial acts)
Policing Standards
Supplements for acts, sets out how police services are to be delivered
e.x. roles, responsibilities
Police Boards and Commissions
Bodies that receive these complaints
Police are the only branch of the CJS with independent oversight
Saskatchewan, PEI, Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut….
DO NOT HAVE INDEPENDENT INVESTIGATIVE UNITS
MUST RELY ON ANOTHER POLICE SERVICE TO INVESTIGATE THEMSELVES
Problems with police investigative units
Independent investigative units almost always comprise of former police officers
Police culture is tight-knit
Hard to blame other officers of their actions
95% of cases by the SIU cleared any police wrongdoing
Typifications
Constructs based on an officer’s experience that describes what typical about people or places
e.x. a Cop being keen on watching a group of hooded teens standing at a corner store late at night
How officers categorize people, places, or situations based on prior experiences
Usage of heuristics
Recipes for Actions
Standardized Actions taken by officers in certain stuations
e.x. an officer questioning a typified “suspicious youth group” applies a recipe for action (stop, questioning, record their names)
Three Challenges in Policing
Police Use of Force
Mental Health Calls
Use of Technology
Types of Force
Physical
Chemical
Electronic
Impact
Firearm
PCEIF - range of severity from higher to lower
Recommendation of physical force over other methods of compelling compliance (NO TALK)
In Canada, all law enforcement agencies employ this continuum of
Apply minimal force to the use of force
No set definition of police use of force in the legislation
Sammy Yatim Example
18 year old in Toronto who was shot for wielding a small knife
Sparked debate about police force, mental health, and accountability
Appeared distressed, but not physically threatening
Officer James Fortillo shot him 3 times, and shot him another 3 times when he was on the ground
Tased him right after
Which Criminal Code Sections outline use of force
s.25 - outlines authority of police officers to use force on reasonable grounds
s.26 - outlines excessive use of force, which is not allowed
National use of Force Model (Training Model)
Training model used to prepare officers during times where they need to use force
Trained not to use force unless needed
Potential for issues, such as when the onus pressures police officers to use force

Police use of Force in Calgary outlines…..
Police use of force isn’t as prevalent of an issue as we think
# of firearm incidents vs. # of force incidents vs. # of persons charged
Majority of police interactions are resolved without force
Use of Force in Canada
Cases that involve use of force involve patterns of:
Mental health, poverty, social class
Intersectional grounds apply
Deadly use of force has not declined in the past 20 years
Use of force rates increase as we move from East to West
Implies heavier usage of RCMP contracts in rural communities
Conductive Energy Weapons (tasers) has increased in Canada
2010-19 taser deployments increased by 140%
31% increase in officers pointing these weapons
Policing & Mental Health (THE PODCAST)
Podcast argues that police don’t resolve 80% of criminal happenings for mental health
Often rely on use of force
Researchers argue a 1-30% increase for calls to mental health in certain jurisdictions
People who experience mental health crises work through substance issues
3x more likely to be arrested
Intersecting issues such as mental health, poverty, racism, etc
Mental health calls related to substance abuse are only referred to as “substance abuse calls”
We don’t have a good mental health system, but we have an established police system unequipped to deal with these issues
Mental Health Act, RSO 1990 (Ontario)
When an officer has reasonable grounds to believe someone:
Is threatening to hurt themselves
Behaving violently towards another person
Shows a lack of care for themselves
They may take the person in custody for examination by a physician
Usage of Technology
Videos of police interactions
Includes
Bodycams
Citizen Journalism
Citizen Journalism (Usage of Technology Issue)
Bystander videos of police-citizen interactions
Police are pushed back on their use of force
Cops don’t have control over citizen journalism
“Produces a new visibility”
Public participates in the creation of the encounter
Before, they visibility was limited to a police perspective
Bodycams
Worn by cops as a response to public outcry to use these technologies
Adds a record of accountability
Vancouver in 2008 was the first to use them
Gives both sides of the story
Calgary recommends that Canadian policies force police not to hide these cameras
Civilizing effects (bodycams)
Idea that police wearing a bodycam means people are more likely to be compliant with police
Police are also less likely to commit wrongdoing
Decreased # of complaints made since bodycams were introduced
Hawthorne effect?
R. V Duarte (SCC 1990) - Bodycams & Tech
Precedent set that police can’t secretly record the public unless they have authorization
S.8 and S.7
Apple Tree Analogy
Apple - individual cop
Tree - police service
Orchard - the system of policing as a whole
Does the issue stem from bad values, or the system itself?