muscular system notes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:33 AM on 11/7/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
skeletal, smooth, cardiac
3 types of muscle tissue
2
New cards
excitable, contractile, extensible, elastic
4 characteristics of muscles
3
New cards
hypertrophy
muscle fiber diameter expands (lifting) or gets stretchier (stretching)
4
New cards
atrophy
muscle fiber diameter shrinks, moves faster than hypertrophy
5
New cards
origin
attachment of a muscle that remains relatively fixed during muscular contraction
6
New cards
insertion
The attachment of a muscle tendon to a moveable bone or the end opposite the origin
7
New cards
opposite
muscles usually end on the __ side of the joint
8
New cards
fascia/epimysium
outside muscle covering, where tendon attaches
9
New cards
tendon/aponeurosis
anchors the muscle to the connective tissue covering of a skeletal element or to the fascia of other muscles
10
New cards
fascicles
Bundles of muscle fibers wrapped in perimysium
11
New cards
perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
12
New cards
endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
13
New cards
muscle fiber
muscle cell
14
New cards
sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
15
New cards
sarcoplasmic reticulum
specialized endoplasmic reticulum of muscle cells, stores calcium
16
New cards
sarcoplasm
cytoplasm of a muscle cell
17
New cards
myosin
The contractile protein that makes up the thick filaments of muscle fibers, has heads
18
New cards
actin
Thin filament of protein found in muscles, has binding site
19
New cards
tropomyosin
covers myosin binding sites on the actin molecules
20
New cards
troponin
regulatory protein that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium
21
New cards
i band
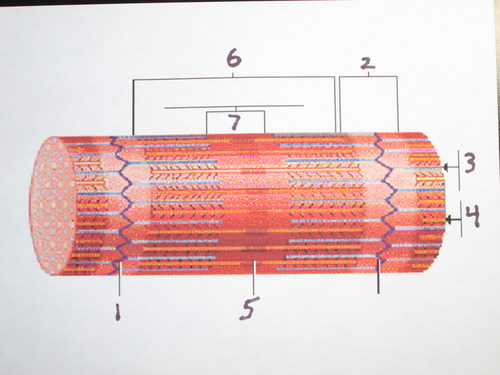
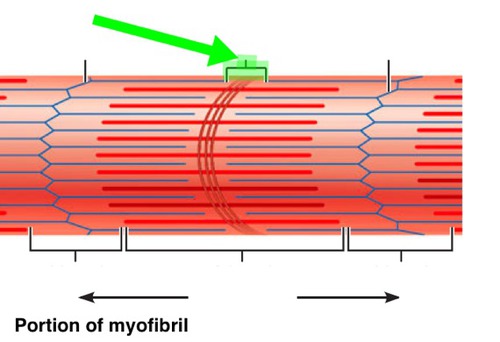
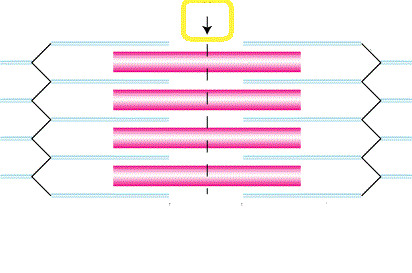
light band, end of myosin to end of myosin, contains actin and Z line (2)
22
New cards
a band
dark area; extends length of the thick filaments (7)
23
New cards
h zone
The region at the center of an A band of a sarcomere that is made up of myosin only. It gets shorter (and may disappear) during muscle contraction.
24
New cards
m line
center of sarcomere
25
New cards
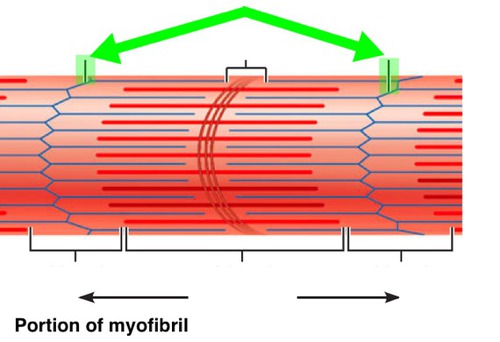
z line
A dark thin protein band to which actin filaments are attached in a striated muscle fiber, marking the boundaries between adjacent sarcomeres.
26
New cards
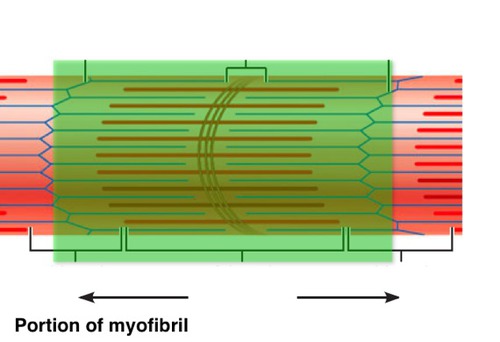
sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle
27
New cards
crossbridge
this forms when the myosin heads attach to actin during muscle contraction
28
New cards
powerstroke
the myosin pulls on the actin and the actin slides toward the middle of the sarcomere
29
New cards
cocking
muscle goes back to normal
30
New cards
ATP
__ binds to myosin and causes relaxation
31
New cards
rigor mortis
muscle stays contracted without ATP during death
32
New cards
isotonic
contraction that moves a load (bicep curl)
33
New cards
concentric
muscle shortens
34
New cards
eccentric
muscle lengthens
35
New cards
isometric
contraction without movement (wall sit, plank)
36
New cards
tone
state of partial contraction that allows for easier contraction/reaction
37
New cards
creatine phosphate
An energy storage molecule used by muscle tissue. Can phosphorylate ATP to generate energy quickly (lasts about 10s)
38
New cards
anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen. This produces lactic acid. (lasts about 40s)
39
New cards
aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen (lasts hours)
40
New cards
mental fatigue
brain tells body that it's tired, protective mechanism
41
New cards
ion imbalance
calcium, sodium, potassium imbalance, follows mental fatigue
42
New cards
longitudinal, circular
2 layers of smooth muscle
43
New cards
overload principle
increasing the intensity (resistance), frequency, or duration of the training above the levels normally expected
44
New cards
peristalsis
Involuntary waves of muscle contraction that keep food moving along in one direction through the digestive system.
45
New cards
stress-relaxation response
Responds to stretch only briefly, then adapts to new length; Retains ability to contract on demand;
Enables organs such as the stomach and bladder to temporarily store contents
Enables organs such as the stomach and bladder to temporarily store contents
46
New cards
all
smooth muscle can contract at __ lengths
47
New cards
hyperplasia
the enlargement of an organ or tissue because of an abnormal increase in the number of cells in the tissues, possible in smooth muscle
48
New cards
18
age of peak muscle control
49
New cards
same
males have more muscle mass, but __ number of fibers
50
New cards
fibers
skeletal and cardiac can't make more __ past adolescence, but smooth muscle can
51
New cards
30
muscle mass rapidly declines after age __ without exercise
52
New cards
prime mover
muscle with the major responsibility for a certain movement
53
New cards
antagonist
muscle that opposes the prime mover
54
New cards
synergist
muscle that aids a prime mover in a movement and helps prevent rotation
55
New cards
fixator
stabilizes the origin of a prime mover
56
New cards
location, shape, relative size, direction of fibers, number of origins, location of attachments, action
7 ways to name a muscle