Emperical finance
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
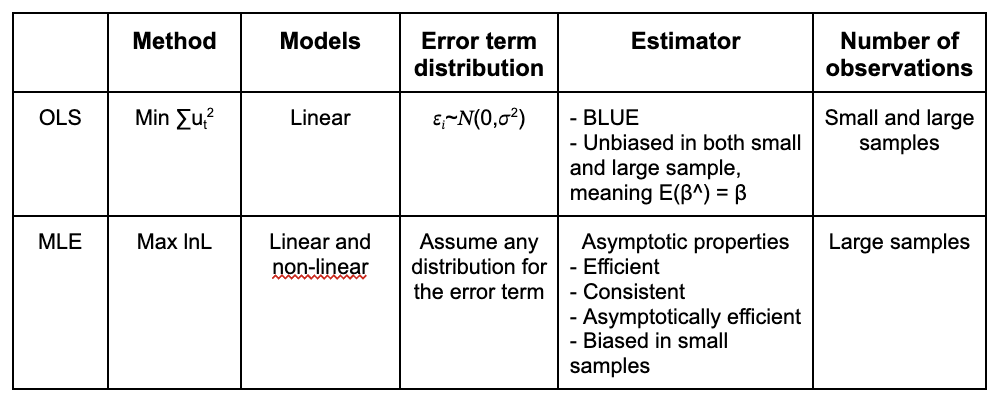
OLS vs MLE
Why do we include a disturbance term in a regression model?
Some determinants of the dependent variable may be omitted or left out.
There may be random influences on the dependent variable which cannot be modeled e.g. a hurricane, a computer failure.
There may be measurement errors of the dependent variables that cannot be modeled.
Error term
In regression analysis, the error term is the vertical distance from the actual data point to the fitted regression line.
Correlation and regression
If we say y and x are correlated, it means that we are treating y and x in a completely symmetrical way.
In regression, we treat the dependent variable (y) and the independent variable(s) (x) very differently.
The y variable is assumed to be random or ‘stochastic’ in some way, i.e. to have a probability distribution.
The x variables are, however, assumed to have fixed (‘non-stochastic’) values in repeated samples. This means that we are given the information on x in order to explain the variations in y.
DF understanding
Suppose that you want to establish an appropriate univariate time series model for your data series, yt. And you want to perform a Dickey Fuller test for your time series.
Which of the following is TRUE in describing the Dickey Fuller test?
If we reject the null hypothesis for the Dickey Fuller test, we conclude that the time series is stationary
Dickey fuller test - unit root test
Dickey Fuller test - unit root test
H0: there is a unit root and the time series is non stationary
H1: there is no unit root and the time series is stationary
When to reject null hypothesis
critical value > t-statistic: reject null
critical value < t-statistic: do not reject
ARMA model
An ARMA (0,0) process is equivalent to a white noise process.

AR(5)
MA(2)

H0: α=0, It means CAPM holds empirically
Wald test statistics in excel
=mmult(mmult(transpose(α);minverse(var matrix));α)
Critical value for the likelihood ratio (LR) test statistic
=CHIINV(significance level;number of assets) ex =CHIINV(0,05;10)
CAPM - true statements
Both Sharpe-Lintner CAPM model and Black's zero-beta CAPM model assumes investors are mean-variance optimizers.
Both Wald test statistics and Likelihood ratio test statistics follow a X2(N) distribution for testing Sharpe-Lintner CAPM.
Both Wals test statistic and Likelihood statistic are always positive
True

It means that issuing new equity has no effects at all on firm values in general.
Purpose of event studies - to measure the effect of economic events on fims’ values (sometimes on other financial variables)
Mergers and acquisitions,
Earning announcements, issues of new debt or equity, or
Announcements of the macroeconomic variables.
Assumptions of event studies
Market is efficient,
The event was unanticipated
There were no confounding effects during the event window
Event studies practical application
A set of theoretical predictions for the consequences of an event will be proposed.
Then a test will be conducted to determine if the data is consistent with the theoretical predictions.
Underlying assumptions of an event study
Event homogeneity, event independence, and event normality.
Wald test - when to reject null hypothesis
H0: The parameter(s) of interest equal specific values (often zero, meaning no effect).
H1: The parameter(s) of interest differ from the specified values.
Wald/LR test statistic > critical value: reject null
Wald/LR test statistic < critical value: do not reject
Event study - when to reject the null hypothesis
H0: CAR = 0, the event has no effect on abnormal returns
test statistic > critical value: reject null
test statistic < critical value: do not reject
Classical linear regression model (CLRM)

Error term
In regression analysis, the error term is the vertical distance from the actual data point to the fitted regression line.
The error term follows a normal distribution. This is required for parameter testing.
The error term has a zero mean. This is required for unbiasedness.
Homoskedasticity : Var ( εi ) = σ2 which is constant. So basically, residuals would not have higher variance for higher values of X.
No autocorrelation : εi is independent such that different values of εi are not correlated.
Non-stochastic X : The values of X (i.e, the explanatory variables) are same in repeated samples.
OLS
Linearity, independence, homoscedasticity and normality; Violating these assumptions can lead to biased and inefficient parameter estimates.
Explain why the vertical distance squared is added together in OLS estimation.
To give more weight to larger deviations from the regression line, emphasizing the impact of outliers.
What are the similarities and differences between the ML and OLS estimators?
Both aim to estimate parameters but differ in the method of estimation. ML is more flexible and efficient but requires distributional assumptions, unlike OLS which is simpler but less efficient.
An ARMA (2,4) process is
a stationary process
AR(p) models can be estimated by
OLS
MA(q) models can be estimated by
MLE
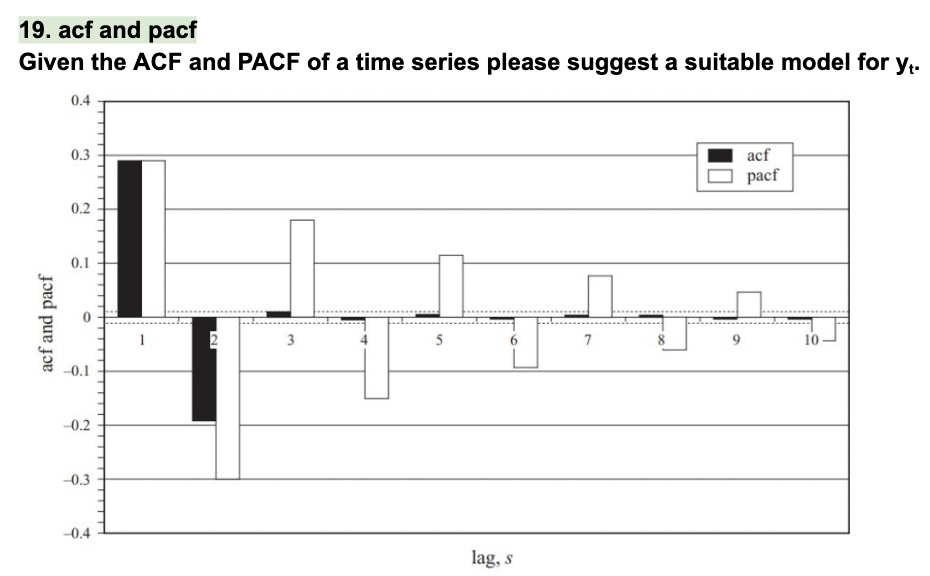
Summary ACF and PACF
AR(p) process is described by:
1. An ACF that is infinite in extent but decays geometrically.
2. An PACF that is (close to) zero for lags larger than p.
For an MA(q) process we have that:
1. An ACF that is (close to) zero for lags larger than q.
2. A PACF that is infinite in extent but decays geometrically.
A combined ARMA model has:
1. A geometrically decaying ACF.
2. A geometrically decaying PACF
Assumptions for the CAPM model
Mean variance efficient portfolio in return and volatility space, risk aversion, greedy customer
Define the major differences between the Sharpe Litner and the Zero beta version of the CAPM model.
Sharpe Litner considers a risk-free asset, while Zero beta CAPM includes a zero-beta portfolio.