Options in Small Animal Fracture Repair
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
to determine fracture repair option, what must do
-two orthogonal high quality radiographs
-on occasions (pelvic fracture needs ct)
-fracture score
-equipment and expertise
referred if too difficult or complication rate too high
fracture options
-intermedullary pin and cerclage wire
-plating (+/- compression)
-intermedullary nail
-external fixator
-pin and tension band
-various combos of pin and plate and IM pin with tied in external fixator
choice for fracture repair determined by
fracture type and forces that will be applied
forces that act on bone
axial compression
tension
Bending (when weight bearing, when the leg is placed at an angle to ground or as a result of asymmetrical muscle contraction)
Torsion (when body changes direction with leg planted on ground)
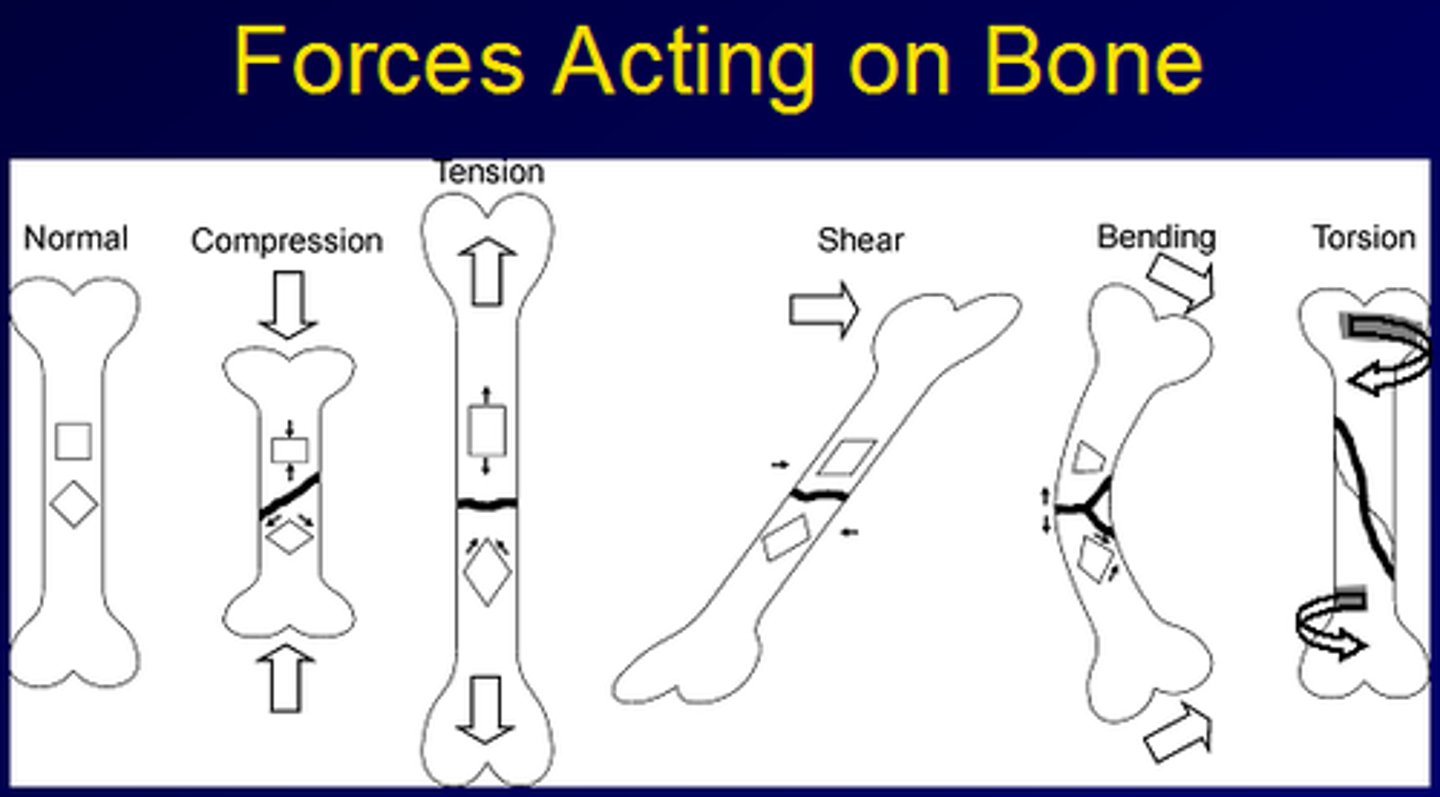
forces on limbs arise from
-weight bearing
-muscle contraction
intramedullary pin advantages
-counteract bending forces as lies in centre of bone
-if fracture oblique
intermedullary pin disadvantages
-poor at axial compression unless bone column reinstated. bone generally reformed with aid of cerclage wires
-increase in pin diameter results in disproportionate increase in strength
-transverse fracture allows rotation so need plate as well or external fixator
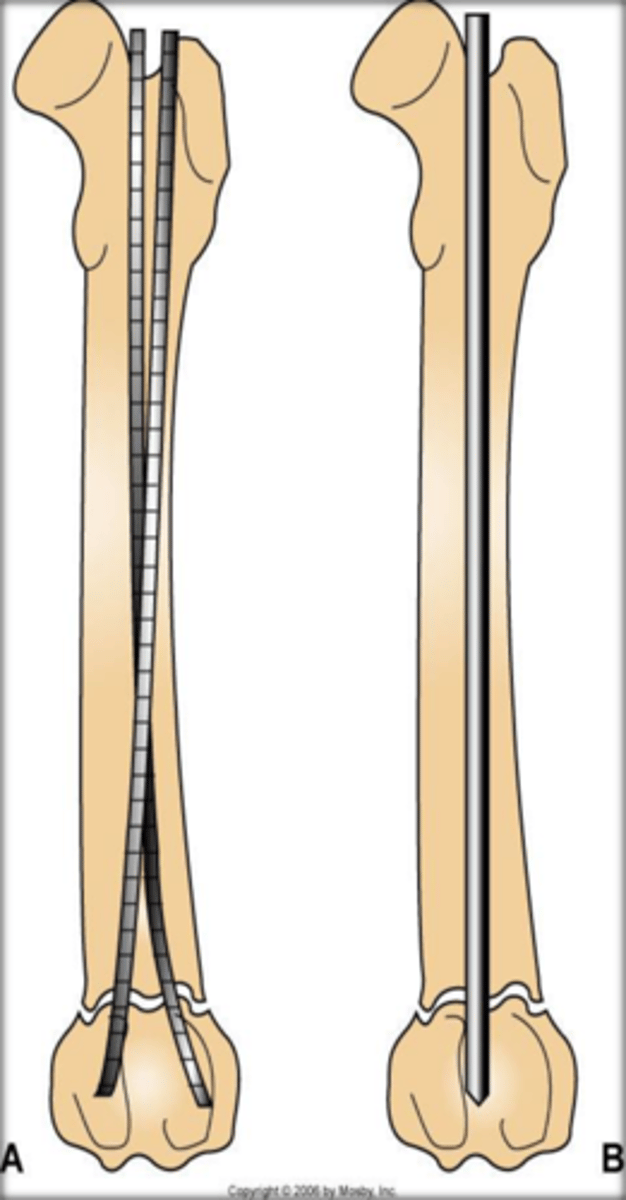
what do cerclage wires do
draw fragments to normal position and fix them relying on circular cross section of bone to produce stability
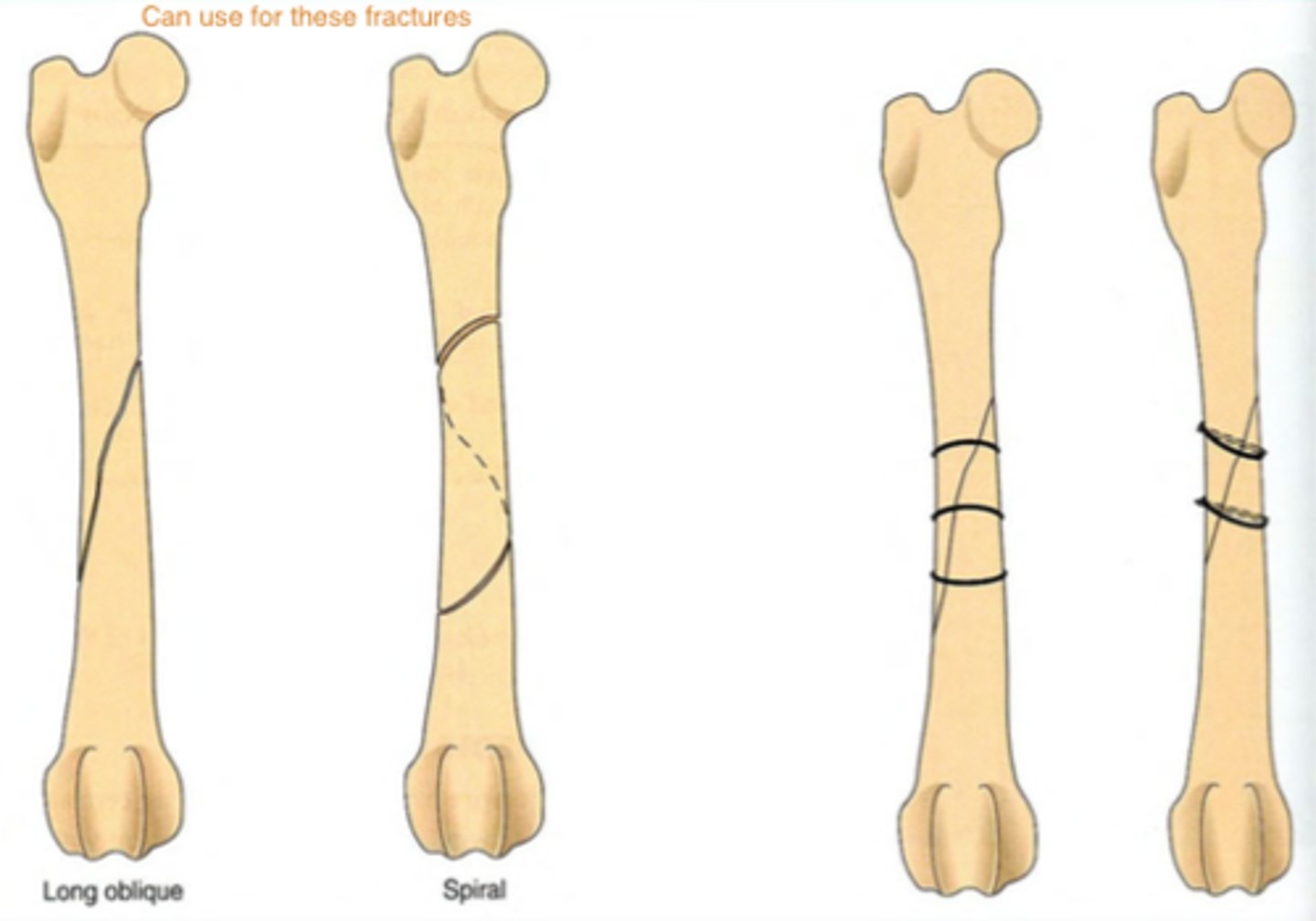
when can a plate be used in addition to a pin
•If a fracture is transverse i.e. at right angles to the long axis of the bone then rotation is possible. This does not occur with an oblique fracture.
•
•To prevent this rotation a plate can be used in addition to the pin (plate rod combination) or an external fixator employed
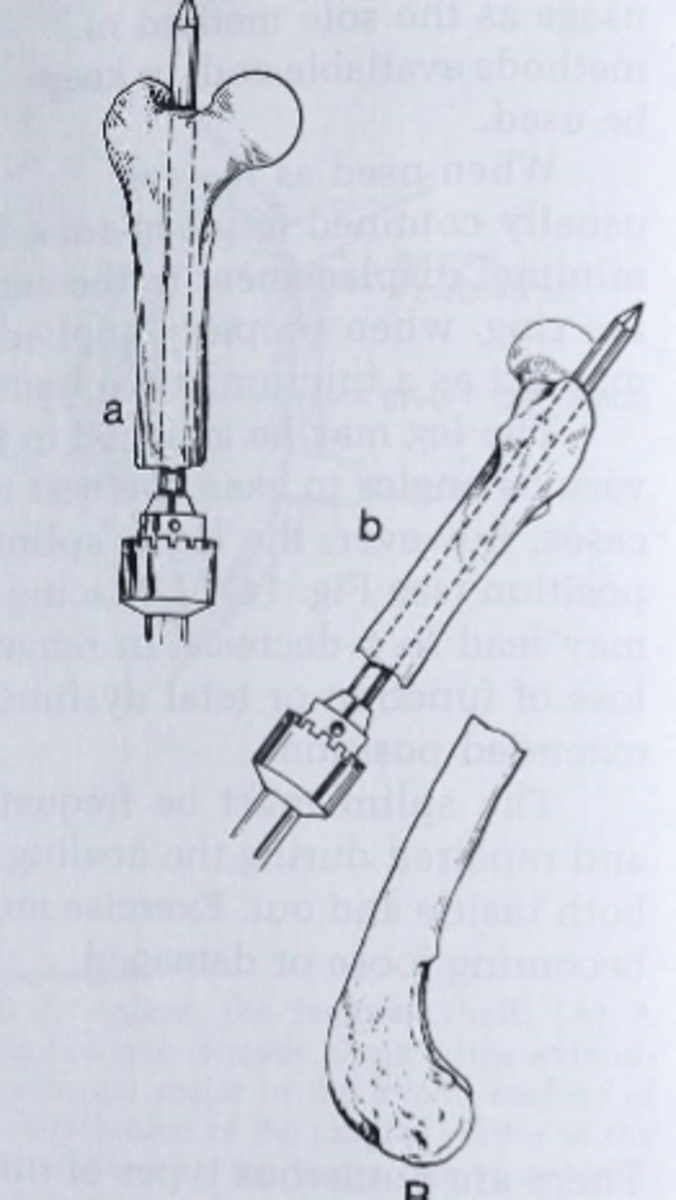
describe normograde placement of IM pin
This is when the pin is placed from proximal end of the proximal fragment.
A small skin incision is made and pin seated into the bone
Once the pin is positioned in the medullary cavity and advanced to just proximal to the fracture site, the fracture is reduced
Then the pin is pushed into the distal fragment.
This is more difficult than retrograde pinning but allows accurate placement of the pin proximally avoiding the sciatic nerve in the femur or entering the stifle in the tibial repair.
inserting IM pin
-small skin incision made and pin seated into bone
-pin positioned in medullary cavity and advanced to just proximal to fracture site, fracture reduced
-pin pushed into distal fragment
normograde IM pin placement more difficult why
-than retrograde pinning
-allows accurate placement of pin proximally avoiding sciatic nerve in femur or entering stifle in tibial repair
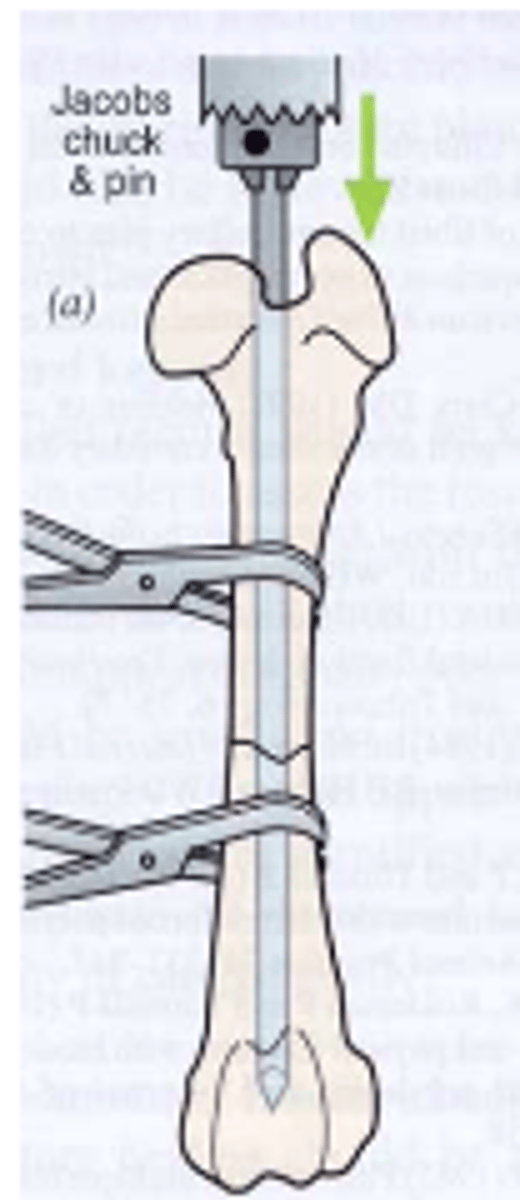
retrograde placement of IM pin
the pin enters the proximal fragment distally i.e. from the fracture site
It leaves the proximal bone fragment and a small wound is made in the skin
and the pin pushed through.
The pin is grasped by the Jacob’s chick pulled proximally till it is positioned just proximal to the fracture site
The fracture is reduced and pin driven into the distal fragment
This is easier than normograde pinning but suffers from loss of control as
to where the proximal part of the pin lies
why retrograde to place IM pin
-easier
-suffers loss of control as to where proximal part of pin lies
what does the external fixator prevent
rotation as well as offering resistance to axial compression both of which the IM pin achieves poorly
issue with intramedullary interlocking nail
-need special jigs to ensure screws enter nail
why intramedullary interlocking nail
-strong
-excellent at preventing rotation and bending
when to use intramedullary interlocking nail
straight bones like tibia and femur
-not really used in vetmed
what is external fixator
-repair fracture with series of pins placed through skin and connected to connecting bar
-pins attached to bar with clamps or epoxyresin
-pins threaded or triangulation of pins to prevent pulling out
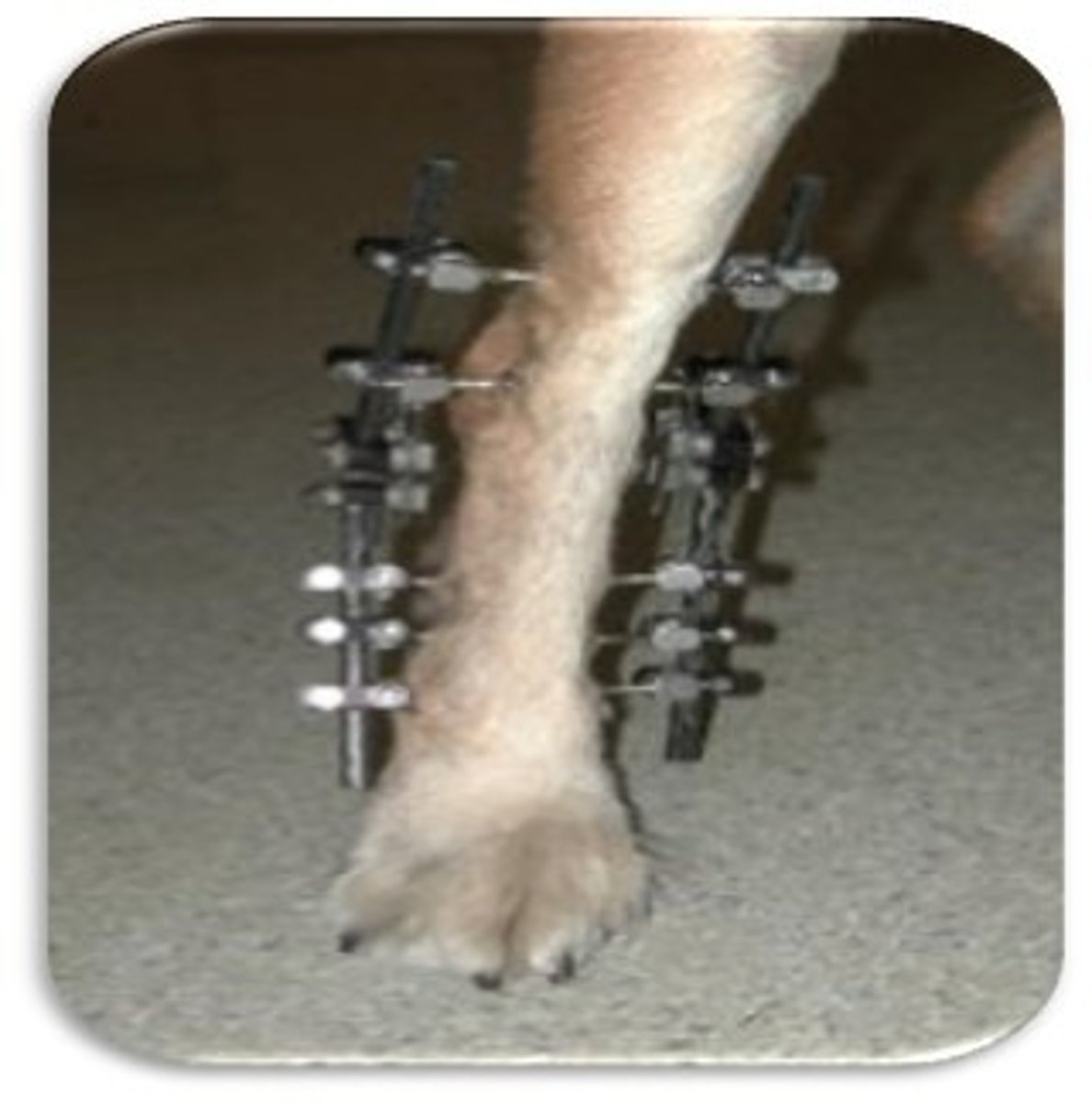
why choose external fixator
-versatile
-counteracts all forces especially if with intramedullary pin
when to use external fixator
-open fractures when open wound management required
application of external fixator to radio-ulnar fracture
-uniplanar or biplanar
-unilateral or bilateral
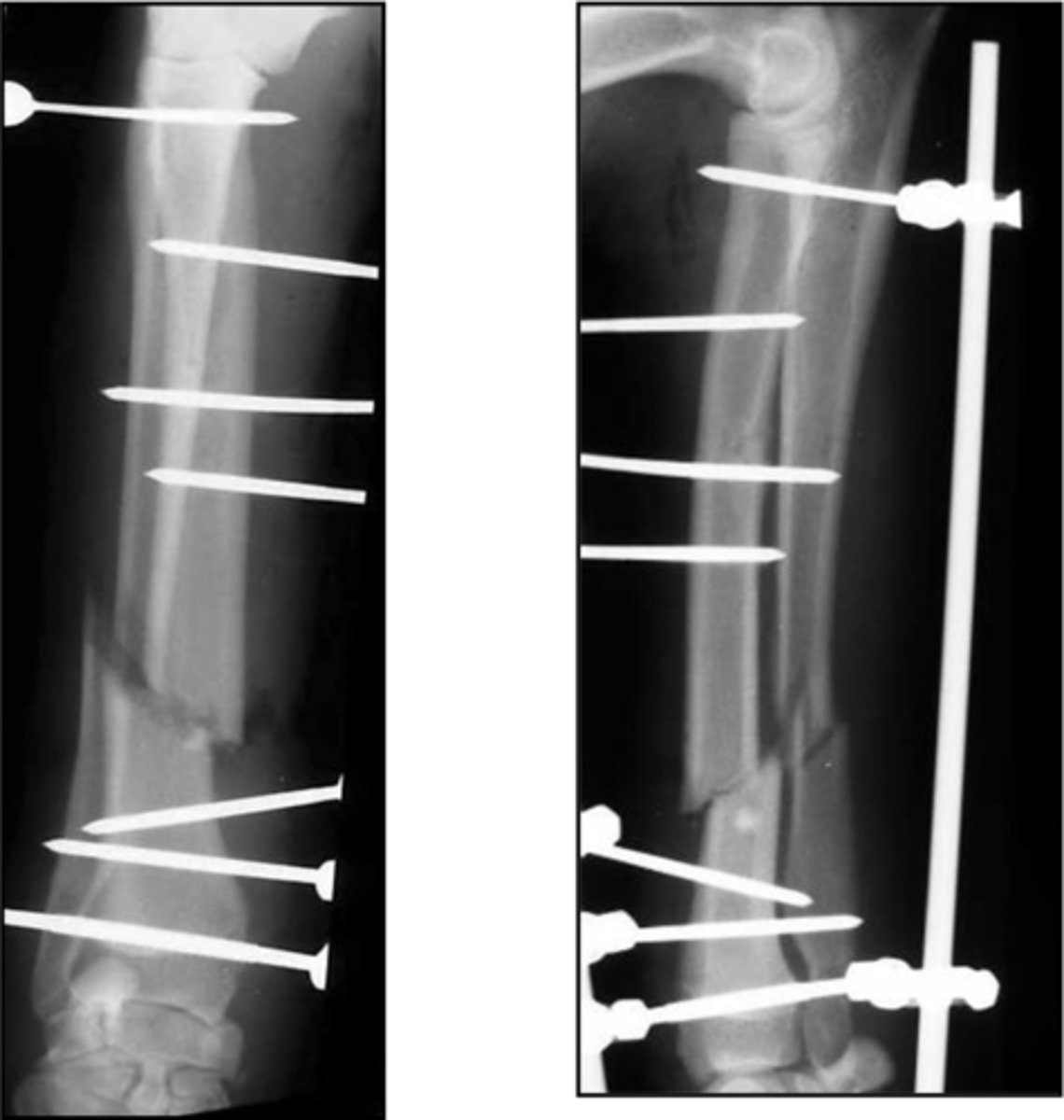
complications of external fixators
-pins prone to infection
-may be discharge esp where pins pass through large muscle masses
-need frequent exams and may require re application of loose pins
-require down staging (remove few pins to change load bearing from fixator to bone)
-need several radiographs after
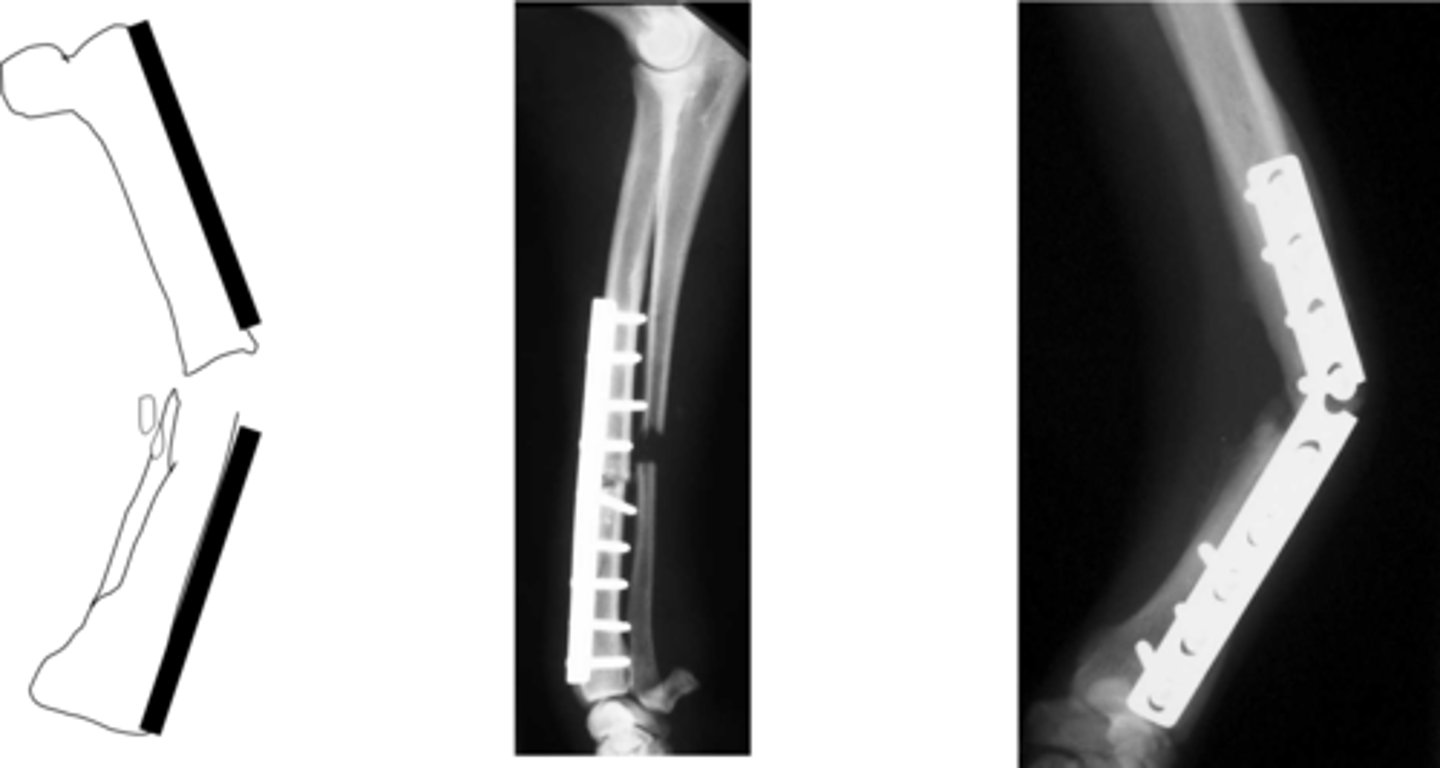
when to use plate fixation
-reconstruction of comminuted fractures
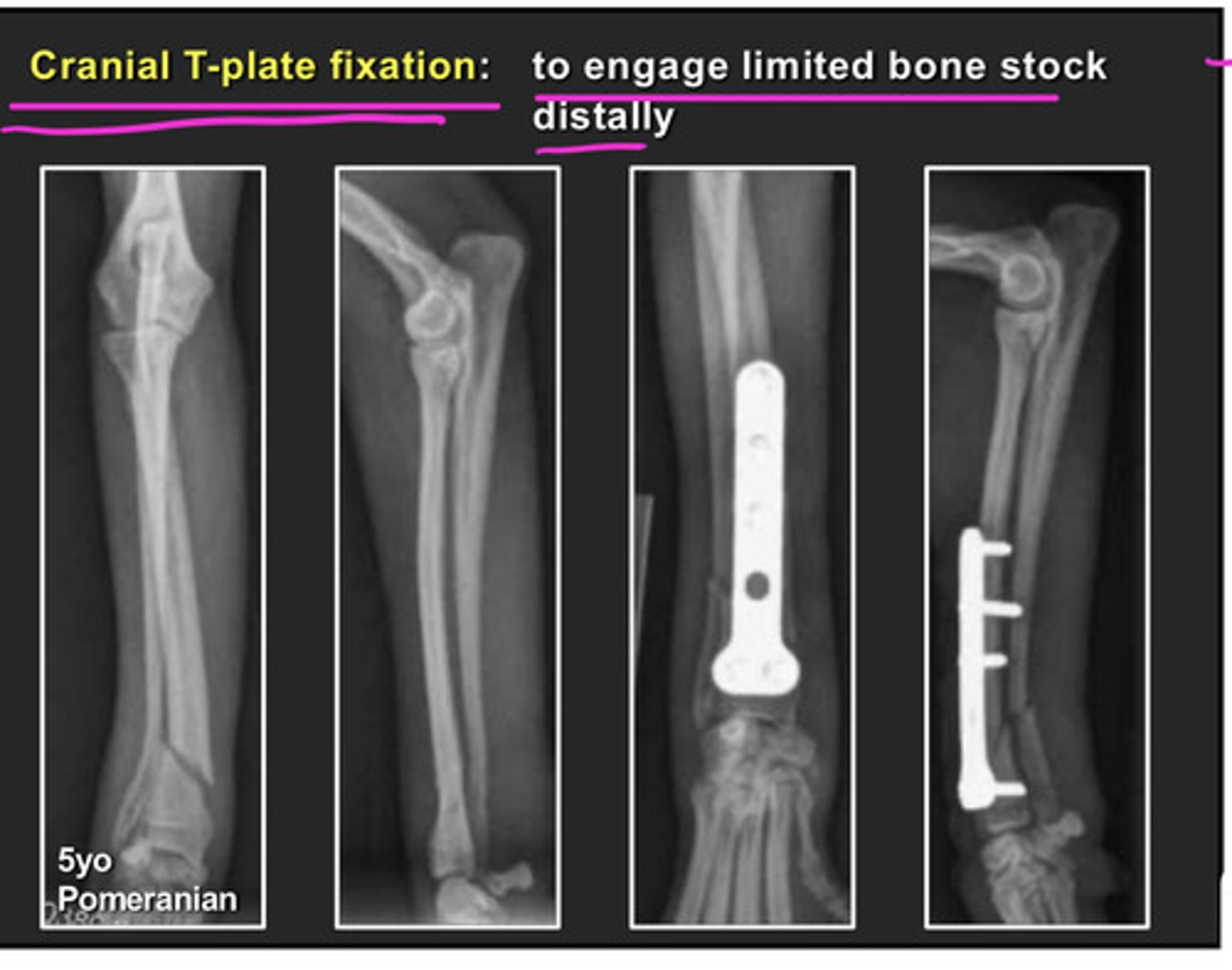
why use plate fixation
-protect against axial and rotational forces
disadvantages of plate fixation
-not good at preventing bending as not positioned along central axis of bone
how to fix plates
-either locking or non locking
non locking plate fixation
-old
-require plate to adhere to screws by friction and bone
locking plate
-thread in plate where screw engages as well as in bone
-diameter of screw that engages plate generally greater than that which engages bone
-special guide needed → align the screws
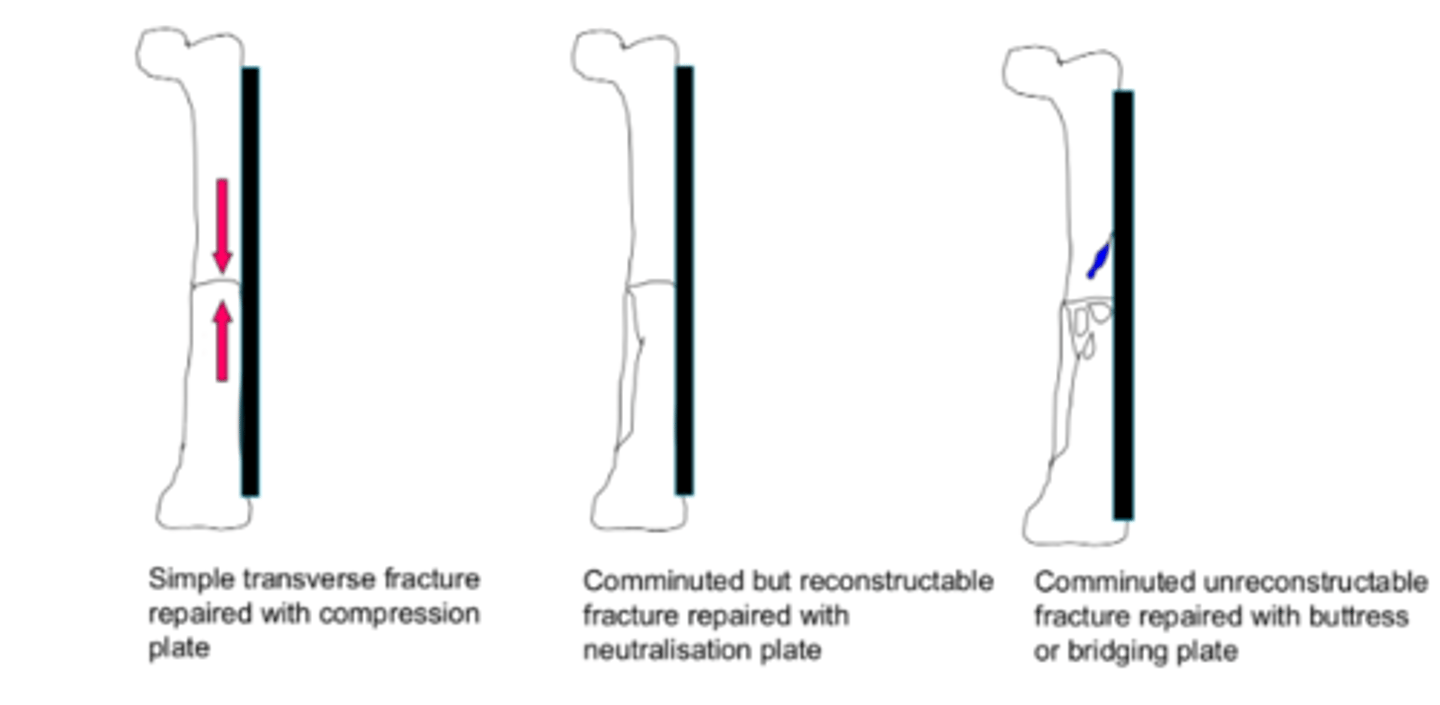
buttress plate
-strong central section that bridges comminuted section of fracture
-plate takes all of load
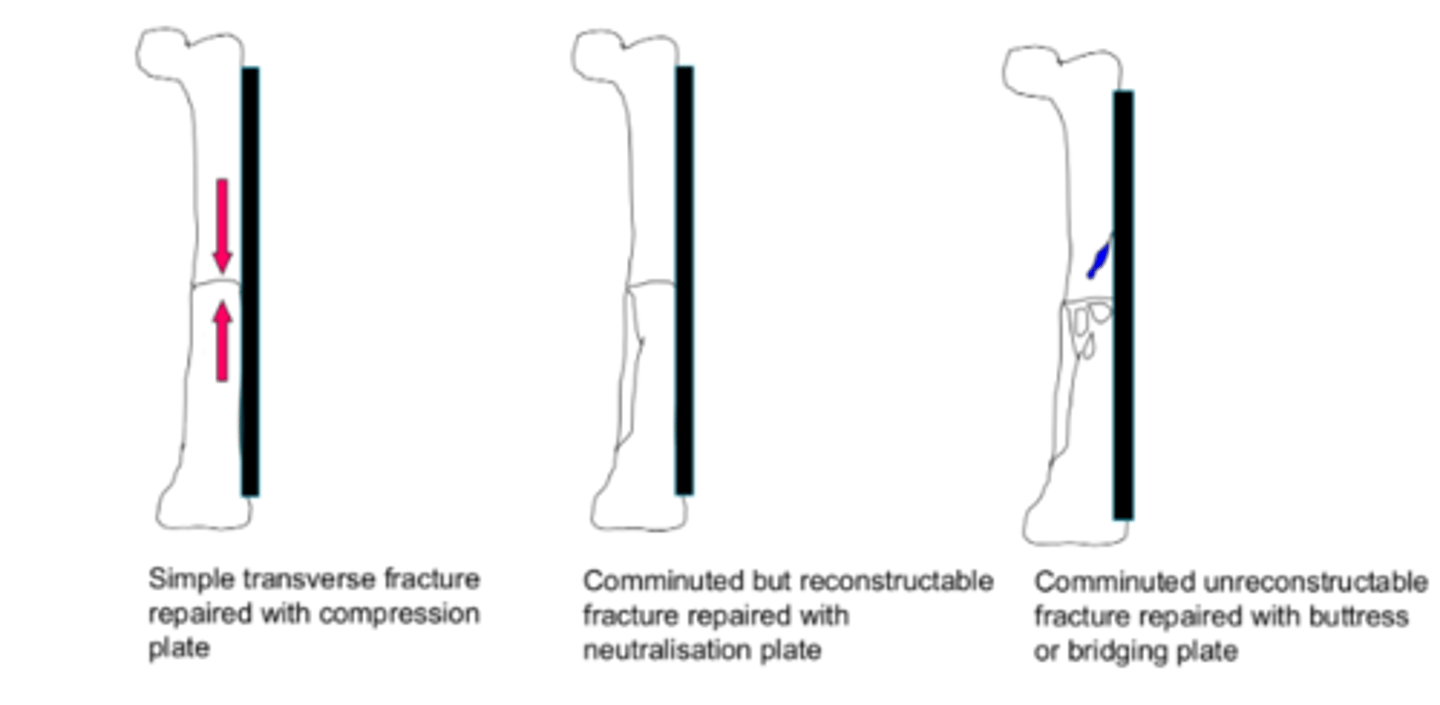
neutralisation plate
-reconstruction of fracture and acts as scaffold
-takes some of load with rest taken by reconstructed bone
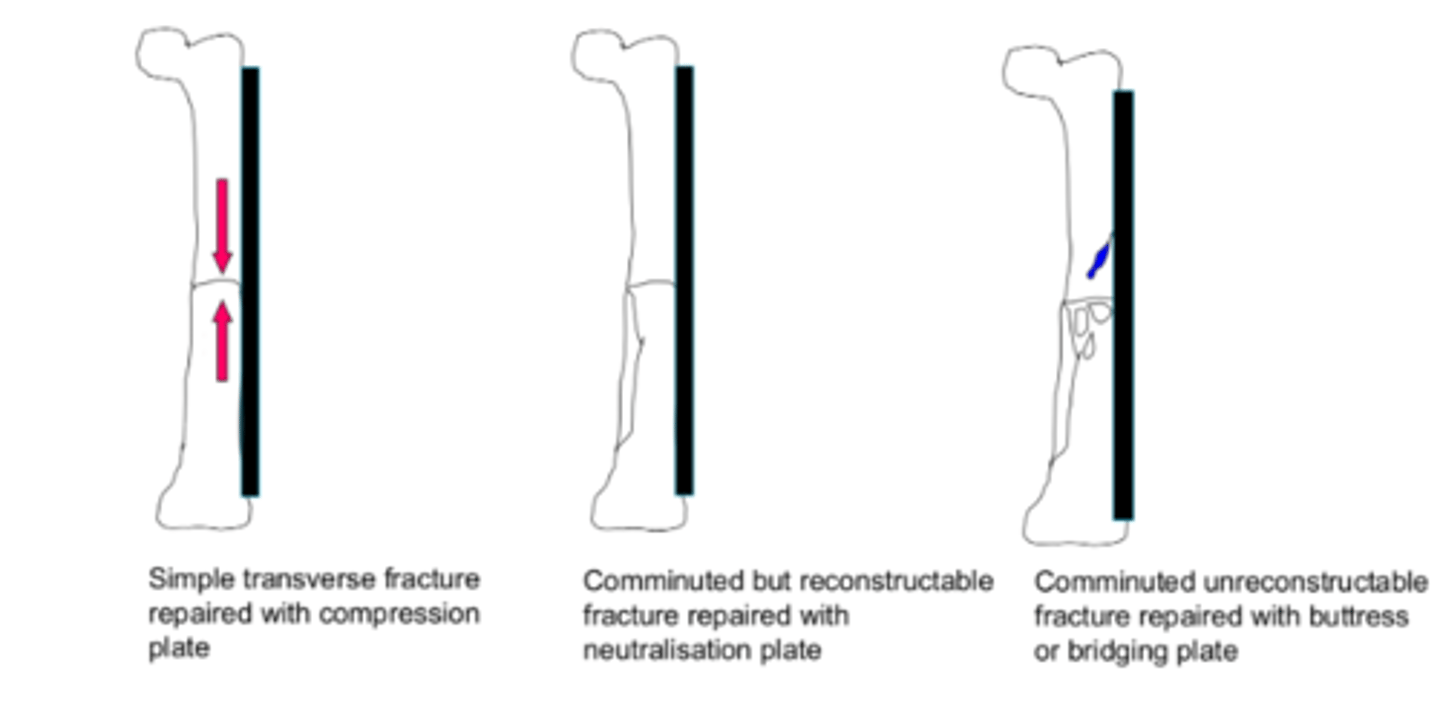
compression plate
-compresses fracture by making use of eccentrically placed screws in oval screw hole
-screw starts at top of slope and when tighted moves down the slope and shifts one fragment towards fracture hence compressing
-bone takes all load
cyclical loading leading to plate failure
-trans cortex and radius incomplete compounded by absence of section of ulna
-plate exposed to cyclical loading and failure, are prone to bending
-in humerus, femur and tibia can be managed with IM pin, rod plate combo
what are avulsion or tension fractures
•These are a special set of fractures that are produced by distractive forces generated internally
•As a result they are exposed to distractive forces during healing
reparation of avulsion or tension fractures
-with larger, place screw and compress using lagging technique
-or distractive forces can be converted into compressive forms using a tension band
example of avulsion fracture
-tibial tuberosity distracted by quadriceps
-olecranon distracted by triceps
-greater trochanter by gluteal muscle
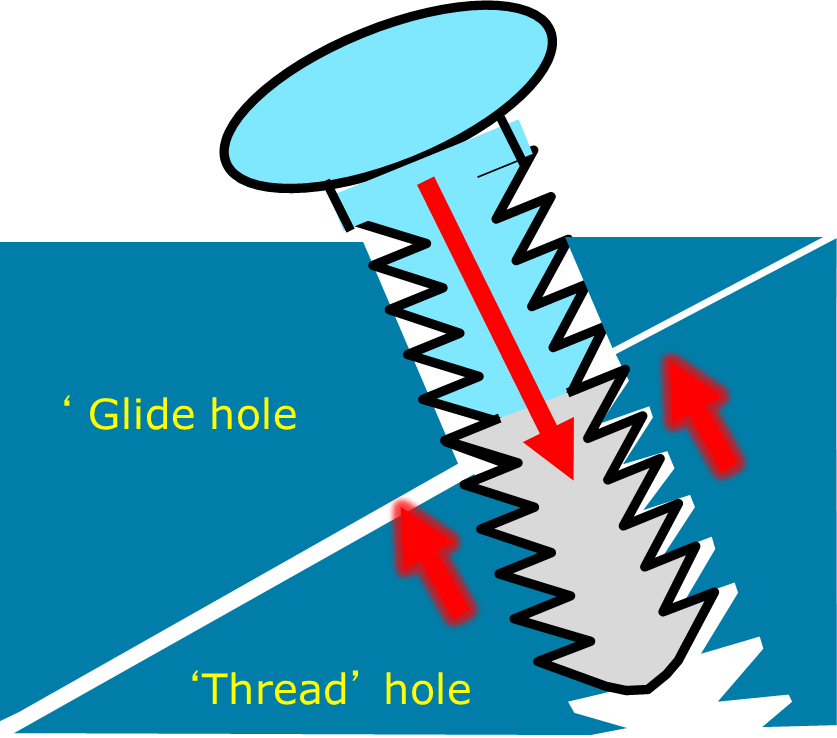
lag screw
-compression applied to fracture
how lag screw carried out
-near hole over drilled to have same diameter as thread so doesn't grip
-when screw tightened, pulls far fragment against near
-used to produce rigid fixation and counteract distractive forces
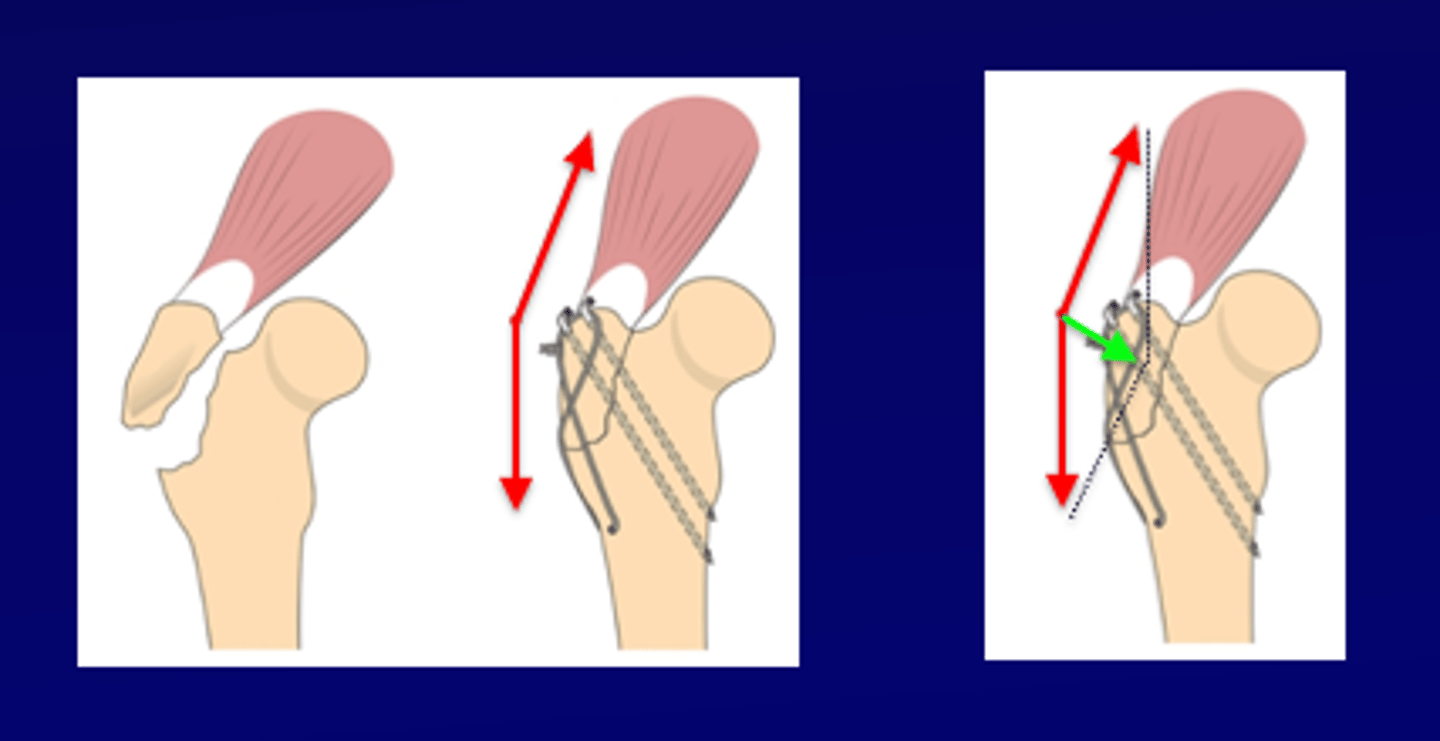
tension band
-fracture reduced (aligned and two pins used to fix in position
-figure of 8 wire applied opposite distractive force and two arms tightened
-with wire tightened and pulling in opposite direction to distractive force the end result is compressive force
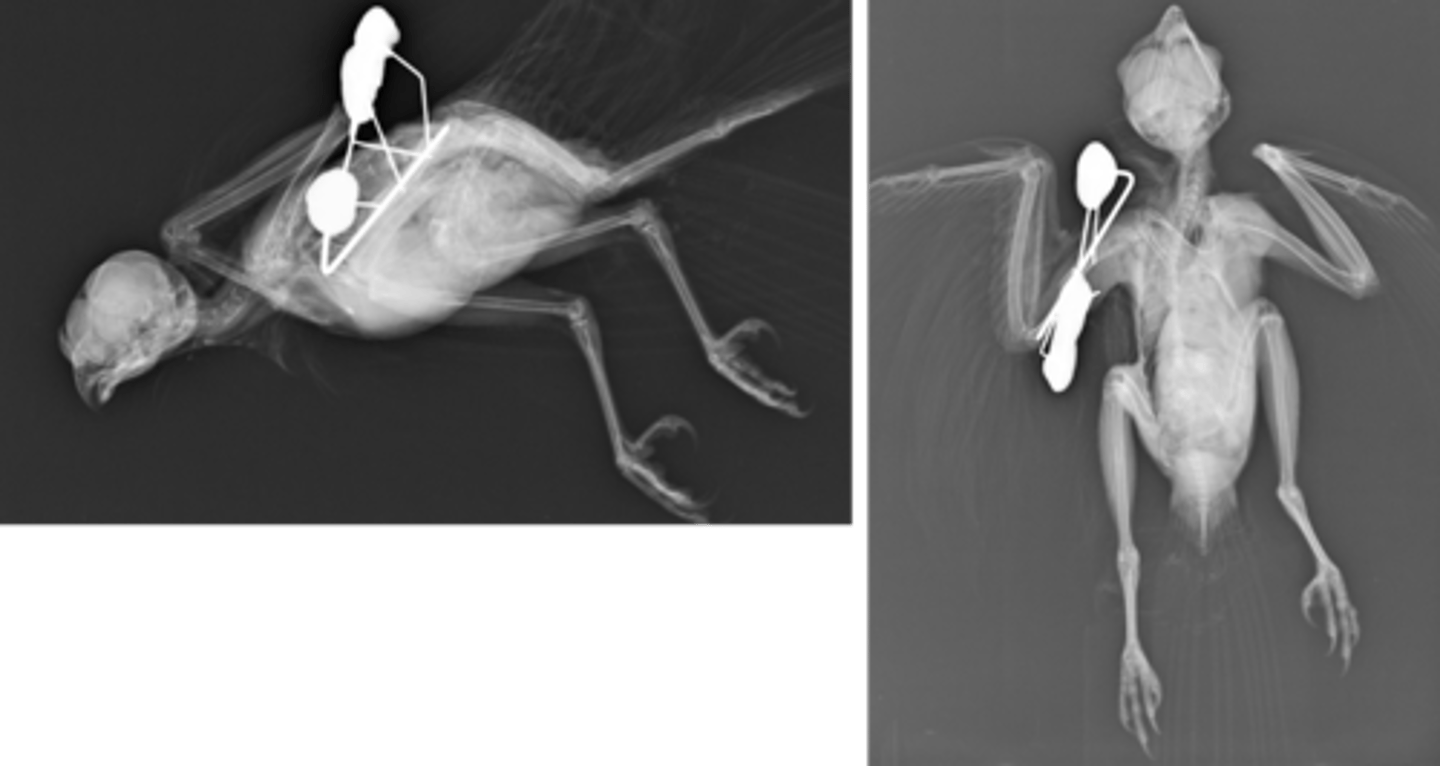
What type of bone structure do avian fractures have?
Pneumatised bone with periosteal blood supply
How do avian bones compare in terms of brittleness?
They are brittle and more splintering
From where do avian bones heal?
Heals from endosteum
What is the healing rate of avian fractures?
Rapid healing
Where do primary wing feathers originate in birds?
From the periosteum of the ulna
Where do tail feathers originate in birds?
From the pygostyle
What is the prognosis for fractures involving a joint or within 10mm?
Poor prognosis
What types of fixation are used for avian fractures?
IM pins and external fixators instead of plates bc thin and brittle bones
avian humeral fracture
-IM pin tied into uniplanar external fixator
-clamps replaced with epoxyresin to reduce weight of device