Biochem MCAT
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
what stereochemistry are amino acids in eukaryotes?
L
What configuration do most chiral ammino acids have? what is the exception?
S ; except cystein (glycine is not chiral)
what amino acid interrupts 2ndary structure?
proline
what bonds are involved in primary structure?
peptide bonds
what bonds are involved in 2dry structure?
peptide, hydrogen
what bonds are involved in 3ry structure?
disulfide bonds, hydrophobic interactions, peptide, hydrogen
what are conjugated peptides?
addition of prosthetic group
what are the water soluble enzymes?
B complex & C (asorbic acid). Examples of B vitamins:
thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxial phosphate, biotin, folic acid, cyanocbalamin
what are the fat soluble vitamins?
A,D, E, K
what is km?
enzymes affinity for substrate; the concentration of substate at half v max
How to calculate weight of amino acid? Ex: franeshift mutation from 591 to 626 bp
626-591 = 35 amino acid × (110 Da/amino acid) = 38500 Da = 3.85 kDa
110 Da/amino acid is avg weight of an amino aicd
What two amino acids disrupt 2ndry structure?
Glycine and proline.
What are histones and their functions?
DNA wraps around histones for support.
Strong interactions with histones means tighter wrapping, meaning it inhibits DNAs accessibility and prevents transcription
What is native page gels used for?
To preserve natural structure. Protein structure is preserved and binding interactions can occur
meant to analyize interactions with other molecules
differing net charges andd protein shapes impact migration
what is SDS Page used for ? features?
proteins are denatured and coated with negative charge
binding interactions CANNOT occur
separates proteins on the basis of mass only
can gel electrophorsesis (PAGE) separate protein domains?
No only subunits
what is protein cooperativity?
when binding affinity for one ligand increases or decreases uponf binding to another ligand. when a ligand binds, how it changes the proteins affinity for other ligands
what is the delta g for protein folding
negative since folding is spontaneous
G= - RTlnk
k Is the equilibrium ratio of products to reactants. folding favors products, so k is greater than 1. so ln k is positive, making delta G negative
what is the standard gibbs free energy equation?
G=-RTlnk
a decrease in pH would result in [decrease or increase] of protonation of amino acids?
decrease in pH means more protons floating around (cuz acidic), making it easier for amino acids to be come protonated. So there would be an increase in protonation
what is Kd?
dissociation constant
a low Kd means [high or low] affinity
a low dissociation constant means high affinity
what is Western blot used for?
to detect the presence of a specific protein and compare its relative abundance in one set of conditions compared to other conditions
what are the steps of western blot analysis?
load samples onto gel and undergo electrophoresis
proteins in the gel are transferred to a protein binding membrane where they become emobilized
the portions of the membrane to which protein was not transfered are blocked by protein rich mixtures. This prevents antibodies (proteins) from nonspecifically binding to the membrane (basically it makes sure that only the proteins bound stick and that everything else is empty. IT’S A WASH
the membrane is incubated with antibodies that specifically bind to the protein of interest (they basically mark the protein so it can be seen visually)
antibodies are detected (seen) through fluorescence.
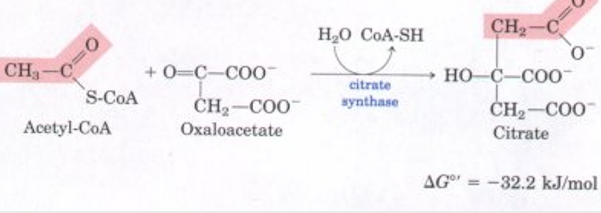
what is the 1st step of citric acid cycle?
oxaoloacetate + acetyl coa → (citrate synthase) citrate
adol condensation followed by hydrolysis
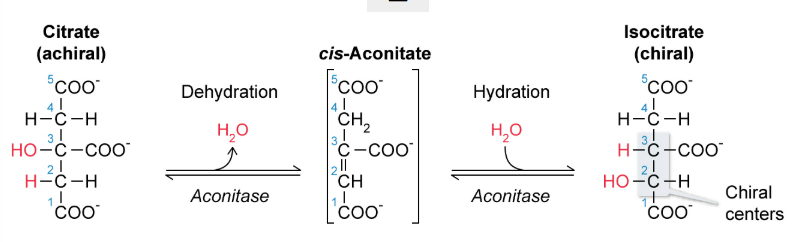
What is the 2nd step of the citric acid cycle?
citrate → (aconitase) cis-aconitate →(aconitase) isocitrate
dehydration then hydration
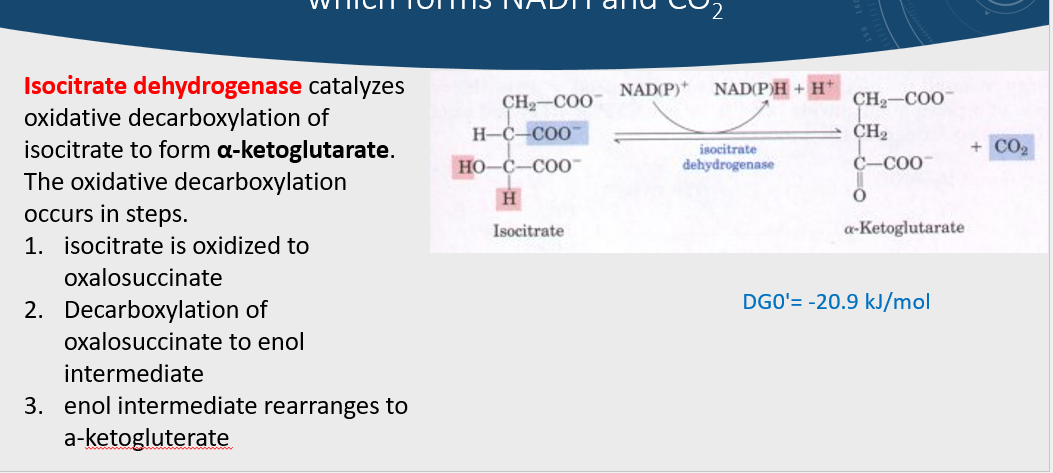
3rd step of citric acid cycle
isocitrate → (isocitrate dehydrogenase) alpha ketoglutarate + NADH & CO2
OXIDATION, enol intermediate, then rearrangement
4th step of citric acid cycle
4. alpha-ketoglutarate →( alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex) succinyl-coA + NADH + CO2
oxidation
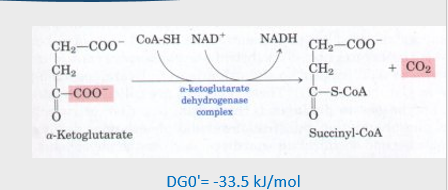
5th step of citric acid cycle
succinyl-coA + GDP → (succinyl-coA synthetase) succinate + GTP/ ATP
CLEAVAGE couple with substrate level phosphorylation
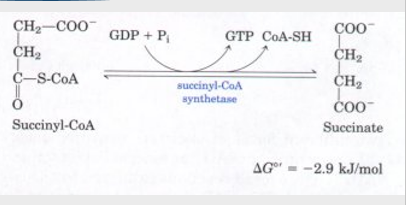
6th step of citric acid cycle
succinate + FAD → (succinate dehydrogenase) Fumarate + FADH2
oxidation
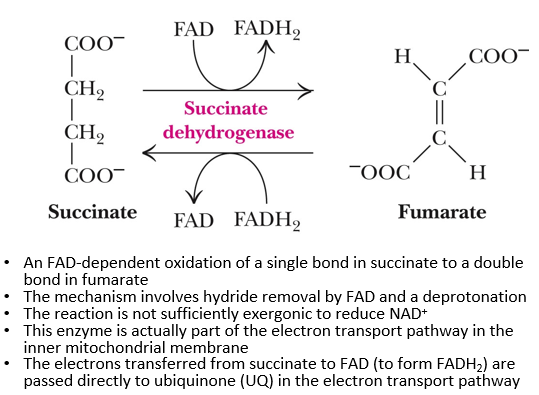
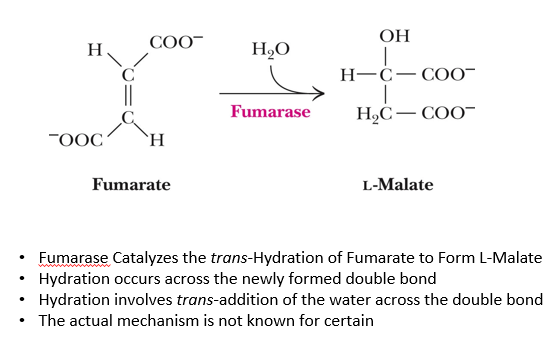
7th step fo citric acid cycle
fumarate +H2O → (fumarase) L-malate
HYDRATION
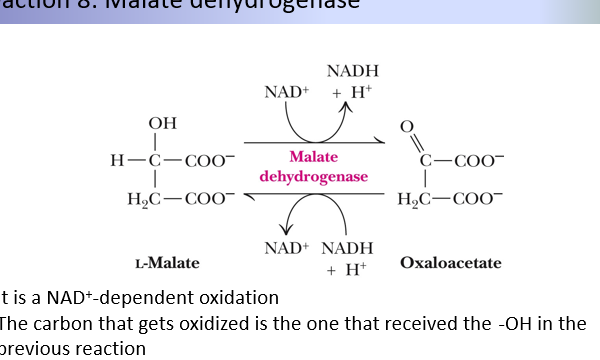
8th step of citric acid cycle
L-malate + NAD → (malate dehydrogenase) Oxaloacetate + NADH
Oxidation
each cycle of TCA produces what?
2 CO2, 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, and 1 ATP each cycle. 2 cycles cuz u have two pyruvate (which turn into acetyl coa)
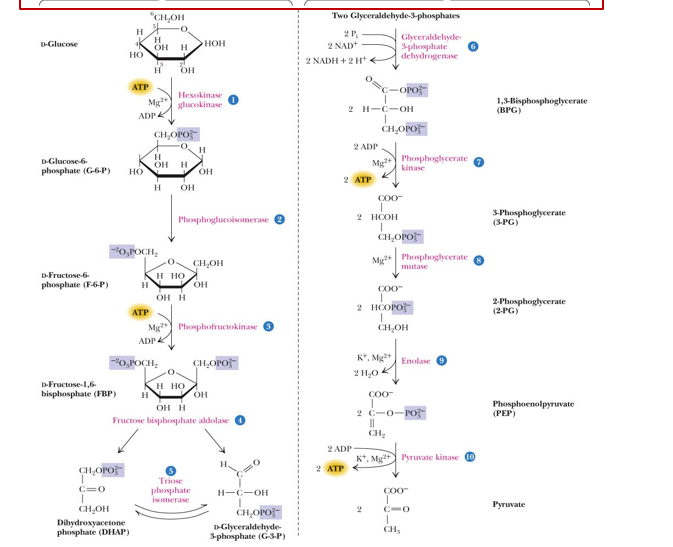
STEPS OF GLYCOLYSIS
Produces 2 pyruvate, 2 atp, and 2 NADH
where are fatty acid chains activated and oxidized in the cell?
they are broken down in the mitochondria. Fatty acids are synthesized in the cytosol
what is the difference btwn ligand gated channels and g-protein coupled receptors
g-protein coupled receptors once bound to a ligand, activated 2nd messengers.
ligand gated ion channels once bound to ligand are immediately activated
what value of gibbs free energy is spontaneous?
negative delta G
features of enzymes
-stabilize transition state
-lower activation energy
-do NOT change the equilibrium of the rxn (Keq)
-saturation of enzyme actives sites by substrate molecules limits the maximum rxn velocity V max
-enzymes can be activated or deactivated by posttranslational modifications
true or false: substrates can covalently modify the enzyme to cause a permanent decrease in the enzymes turnover number k cat.
FALSE - they cannot be permanently changed when an enzyme acts on its substrate. kcat is not expected to permenantly change
which part of the cell does gluconeogenesis mainly occur?
cytosol
which part of the cell does the krebs cycle (citric acid cycle)
mitochondria
what are the steps of glycolysis?
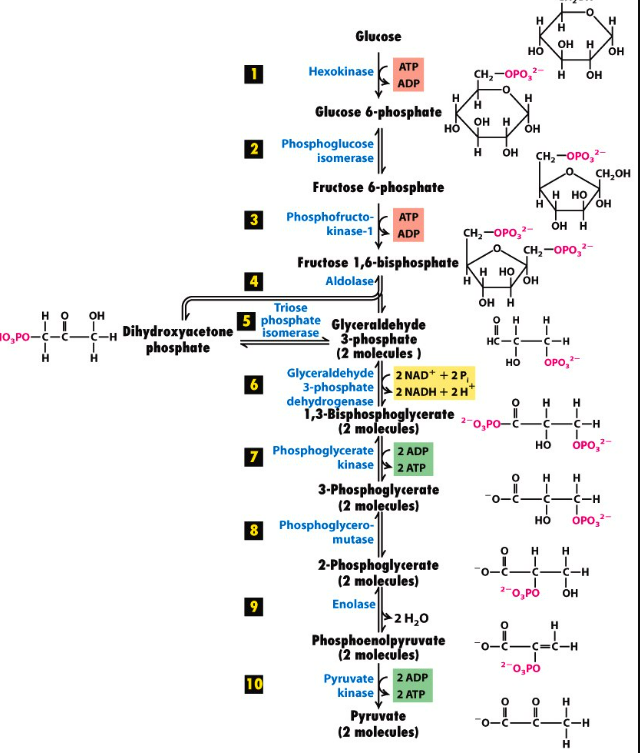
1st step of glycolysis
glucose +ATP → (hexokinase) glucose 6 phosphate +ADP
phosphorylation
step of glycolysis
glucose-6-phosphate → (phosphoglucoisomerase) fructose 6 phosphate
isomerization
3rd step of glycolysis
fructose 6 phosphate + ATP→ (phosphofructokinase) fructose 1,6 bisphosphate +ADP
phosphorylation
4th step of glycolysis
cleavage into g3p and DHAP
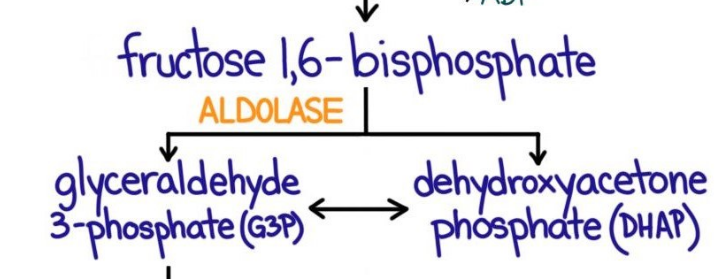
5th step of glycolysis
5. DHAP → ( triosephosphate isomerase) G3P
now we have two glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
6th step of glycolysis
6 . two G3P → (glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate + 2 NADH
oxidation
7th step of glycolysis
1,3 bisphosphoglycerate → (phosphoglyerokinase) 3 phosphoglycerate + 2ATP
dephosphorylation
3-phosphoglycerate → (phosphoglyceromutase) 2-phosphoglycerate
phosphate transfer/ISOMERIZATION
2-phosphoglycerate → (enolase) phosphoenolpyruvate
dehydration +2 H2O
10th step of glycolysis
Phosphophenolpyruvate → (pyruvate kinase) 2 pyruvate + 2 ATP
dephosphorylation
where does glycolysis occur in the cell?
in the cytosol
what enzmes are different in gluconeogensis compared to glycolysis?
2 pyruvate → (pyruvate carboxylase) 2 Oxaloacetate
2 oxaloacetate → (PEP carboxykinase) phosphenolpyruvate
PEP → (enolase) 2-phosphoglycerate
2-phosphoglycerate → (phosphoglycerate mutase) 3-phosphoglycerate
3phosphoglycerate → (phosphoglycerate kinase) 1,2 bisphosphoglycerate
1,2 bisphosphoglycerate → (G3P dehydrogenase)glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate
G3P → (triose phosphate isomerase) DHAP
DHAP → (aldolase) fuctose 1,6 bisphosphate
fructose 1,6 bisphosphate → (fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase) fructose 6 phosphate
fructose 6 phosphate → ( phosphohexose isomerase) glucose 6 phosphate
g6p → (glucose 6 phosphatase) 2 glucose
what assumptions does the Michaelis Menten equation rely on?
to ensure that ES formation does not significantly impact [S], the total concentration of enzyme should be much smaller than any substrate concentration
the concentration of ES remains constant over the course of the reaction, allowing the rate of product formation to remain constant. as [S] becomes significantly depleted, ES levels decrease and rxn slows
rxn proceeds only in the forward direction. product does not get converted back to substrate
what is Km?
the substrate concentration at which ½ vmax occurs.
what is needed for fatty acid synthesis?
ATP, NADPH, and acetly coa
if fatty acid synthesis is inhibited, what will build up?
NADPH will build up
when blood sugar is high, what hormone is used for homeostasis?
insulin reduces blood sugar level by increasing glucose uptake and storage
pyruvate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate into what?
to acetyl coa
CHECK OCHEM DECK FOR DYNEINS, KINESINS, CAMS (Integrins, Selectins, Cadherins)
what are the three types of G protein-coupled receptors?
Gs -(stimulate) stimulates adenylate cyclase → increases level of cAMP
Gi- (inihibit) → inhibits adenylate cyckase → decreasing levels of cAMP
Gq (activates phospholipase C), opening calcium channels in the ER → increases calcium levels in the cell
what is Native PAGE used for?
(Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis)
Used to compare molecular size or the charge of SIMILAR size proteins
what is SDS PAGE used for?
Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
SDS binds to the proteins and creates large chains with net negative charges → NEUTRALIZES the protein’s original charge and DENATURES.
Used to find MASS without interference of charges
what charge are anodes and cathodes?
andoes are positively charged (oxidation) so anions are attracted to it
cathodes are negatively charged (reduction) so cations are attracted to it
What is chromatography?
use a solid medium (stationary phase) and run mobile phase through stationary phase. Sample runs (elutes) through the stationary phase. components with a high affinity for the stationary phase will barely migrate (long retention time), while those with high affinity for mobile phase will migrate fast (short retention time)
used to separate charge, pore size, and specific affinities of proteins
what is column chromatography used
USED TO SEPARATE POLARITY
the less polar the compound, the faster is can elute through the column (short retention time)
what is ion-exchange chromatography used for
beads in the column are coated with charged substances to bind compounds with an opposite charge. a salt gradient is then used to elute the charged molecules bound to column. Good for separating specific charged molecules
what is size-exclusion chromatography
beads in the column contain tiny pores of varying sizes. small compounds enter the beads and are slowed down. Large molecules pass through.
LARGE MOLECULES ELUTE FIRST, SMALL MOLECULES ARE SLOWED
How can protein structure be determined?
X-ray crytallography and NMR
What is Edman degradation used for?
Edman degradation removes N-terminal of amino acid of the protein, to cleave proteins and sequence them
what are some enzyme that cleave large proteins?
chymotrypsin, trypsin, cyanogen bromide
how to determine concentration of proteins
UV Spectroscopy, BCA assay, Lowry reagent assay, and BRADFORD PROTEIN ASSAY
Bradford protein assay- uses a color change from brownish green to blue. increased protein concentrations = larger concentration of blue dye
true or false: centrioles are involved in cell migration
false. centrioles (composed of microtubules) are only involved in mitosis
what type of receptors use a second messenger cascade system to amplify the signal by a lot?
g-protein coupled receptors and enzyme-linked receptors
true or false: calcium is usually protein bound
true - calcium is protein bound since it is used so much in the body
what type of channels provide MAINTENANCE of the resting membrane potential. Which channels causes DEVIATION from resting membrane potential?
maintenance : ungated “leak” channels permit limited free flow of ions
deviation: ligand-gated and voltage gated channels
what does the gel in isoelectric focusing use to separate by charge?
gel in isoelectric uses pH gradient. when a protein is in a region with a pH above its pI, it is negatively charged and moves to anode. when pH region is below its pI, it is positively charged and move to cathode
what does UV spec use to find protein concentration?
uses conjugated systems of double bonds (aka aromatic systems)
what is an aromatic compound?
alternating double bonds
What is most basic structural unit of carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
what does the simplest monosaccharid contain?
three carbon atoms. called trioses
what are aldoses and ketoses?
aldoses: carbohydrates with an aldehyde group as their most oxidized functional group
ketoses: with ketone
an aldohexose is a 6 carbon sugar with an aldehyde
what are stereoisomers?
compounds with same chemical formula but different arrangement
what is an enantiomer?
same chemical formula, mirror image of each other for spacial arrangement
ex: L and D ribose
how do u determine how many possible stereoisomers?
2^n n= number of chiral carbons
on a fisher projection, where are the wedges?
horizontal lines
how do you determine if sugars are L or D?
depends on where the highest numbered chiral center is
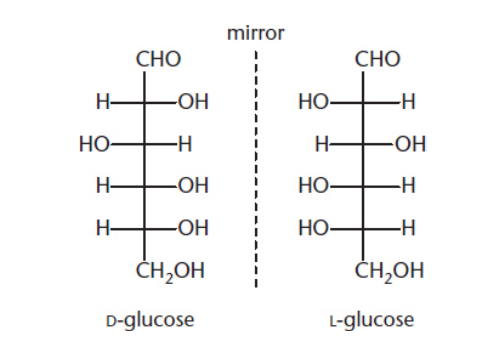
what are diastereomers?
same chemical formula, not mirror image
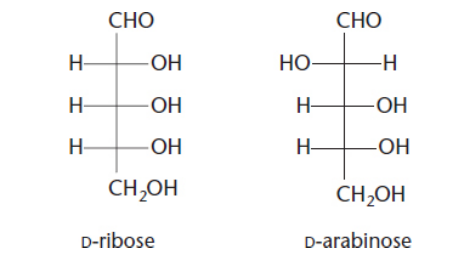
what are epimers?
diastereomer where the sugar only differs at on chiral center
how many carbons do pyranose and furanose rings have?
pyranose - 6
furanose - 5 Furanose Five
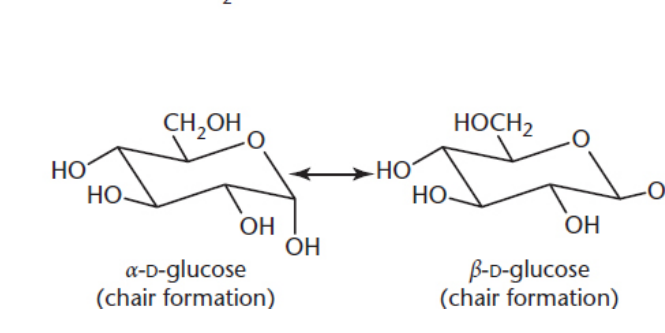
what are anomers?
sugars that differ by configuration on the anomeric carbon (carbon that’s attached to two Oxygens. one O, one OH)
makes alpha or beta
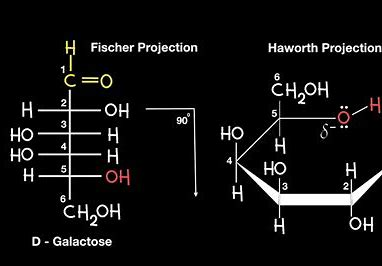
the Haworth projection vs fischer projection
haworth projection - 3D
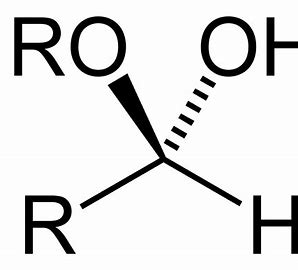
what does hemiacetal look like?
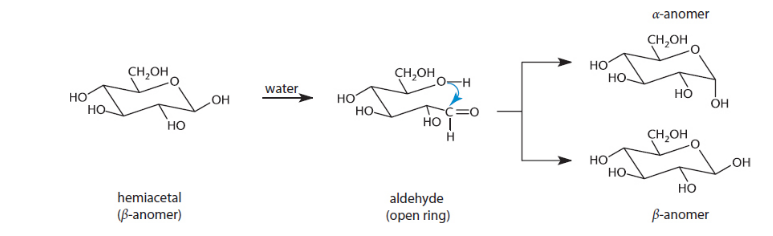
when a hemiacetal ring is exposed to water, what is the name when they spontaneously cycle between the open and closed configuration?
they undergo mutarotation -? causes mixture to have both alpha and beta anomers
true or false: all monosaccharides are a reducing sugar
true
what to reagents are used to detect the presence of reducing sugars?
Tollens reagent- Produces silvery mirror AgNH3 when aldehydes are present
Benedicts reagent- precipitates red Cu2O when aldoses are present
what is a lactone?
a cyclic ester with a carbonyl (c=o) on anomeric carbon
vitamin C is a lactone
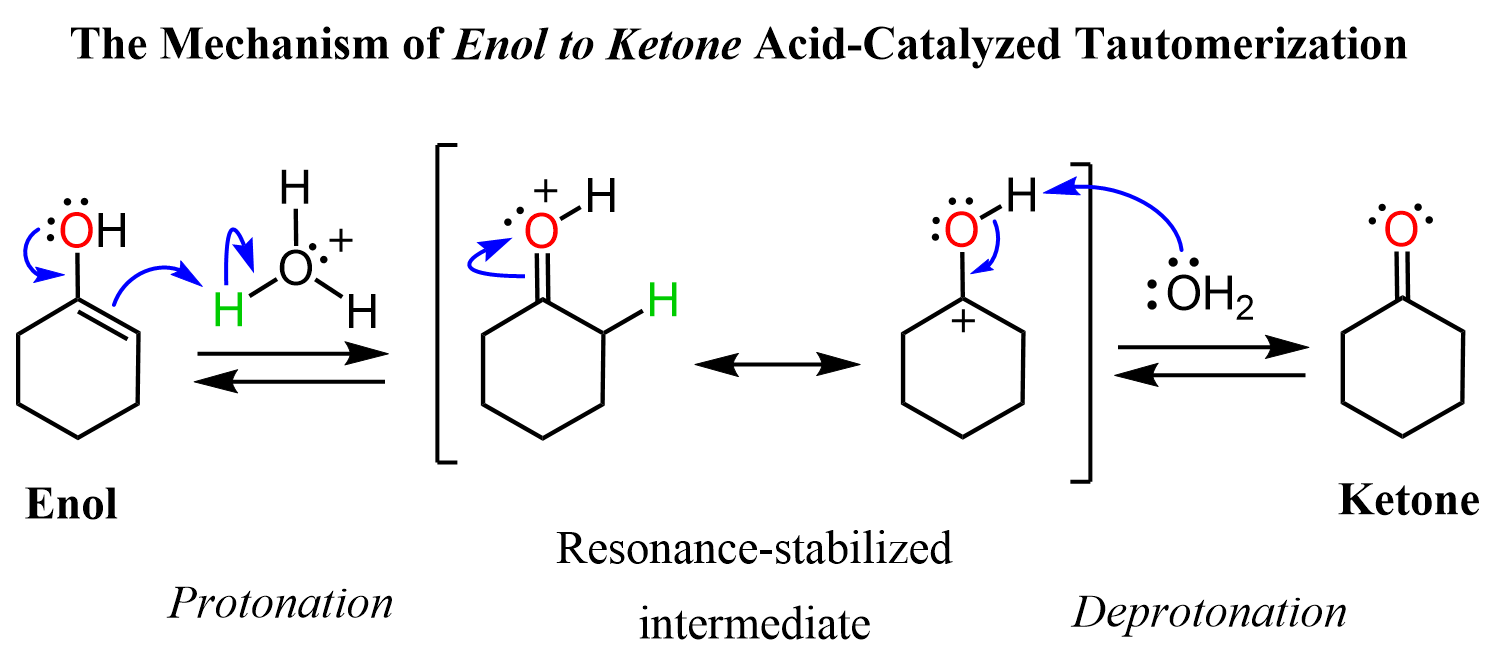
what is tautomerization?
rearrangement of bonds in a compound by moving a hydrogen and forming a double bond
resonance is just movement of electrons
what is the name when an alcohol and an acid (carboxylic acid) form an ester and water?
esterification
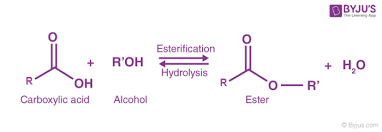
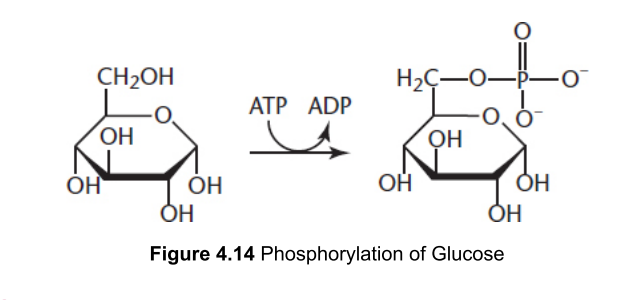
which enzyme catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose (Glucose to G6P)
Hexokinase - forms a phosphate ester