PEU: Decision-making
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
EU decision-making in lens of International Relations
Delegation of power
EU outlier in this case —> Commission negotiates trade deals for all EU states
The power has been delegated but it has to be done on the mandate of the member states (final control)
Right of initiative
Within states: members of Parliament
EU: Commission
Member states stay in control bc they sit in the Council and the Commission has to come to them for approval (change it, kill it)
Pulling of sovereignty
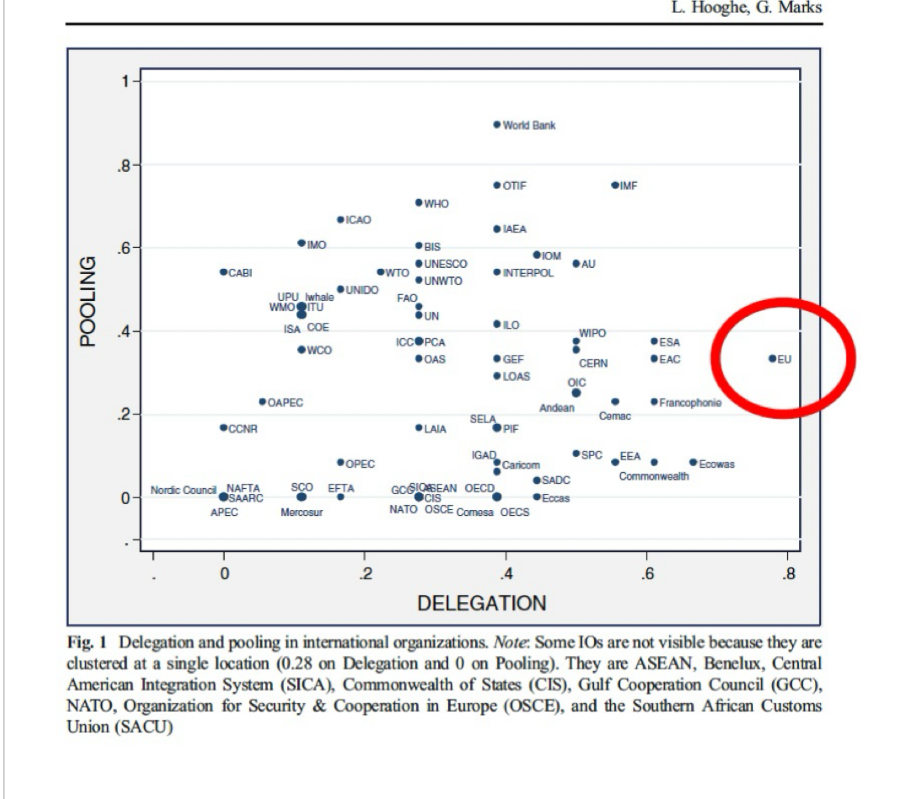
EU decision-making in lens of Comparative Politics
Commission: executive
Right of initiative —> strong
Can’t implement laws —> weak
Decision making
Council: represent member states
National executive
Brussels legislative (with EP)
What type of decision-making is the focus?
Secondary legislation
What is secondary legislation decisions-making
Regulation, Directive Decisions
Ordinary legislative procedure (‘co-decision’) & special legislative procedures
Policy setting
Treaties tell us how secondary legislation is made
What is not within secondary legislation
Implementing legislation
Puts out what comes from secondary legislation into practice
EU competence within decision-making
Exclusive
Shared
Supportive
Exclusive Competences
Can only be taken at the EU level
Ex. Trade (member states can NOT have bilateral agreements with other nations)
Ex. Competition for internal market (common competition)

Shared Competences
Members can agree to have decisions made at EU level BUT in some areas it can take decisions at national level
Ex. Environment, climate change
If EU does not have legislation on it, member states are decide themselves how to deal with it

Supportive Competences
EU commission can gather member states in Brussels and they talk/exchange ideas —> end of the day they go back to their own nations and decide what to do
Commission can support member states in the discussion of ideas, no legislation is coming from it
Learn from each other, discuss ideas with each other
Might be the most effective way to make legislative
Why? Governments take ownership

Principle of Subsidiarity
Areas that do not fall under its exclusive competence, the Union shall only act as so far as the objectives of the proposed action cannot be sufficiently achieved by the member states, either at central, regional or local level. Those goals can be achieved at the EU level.
Are policy and decision making the same thing
No!
Policy making
Community method
Intensive transgovernmentalism mode
Member states are in charge —> make the most important decisions
Unless money is needed to be given -> commission needed (budget)
Commission is always in the room
Centralized decision-making: member states delegated the task to EU level
Competition policy
Eurozone interest rates
Open-method: similar to supported competences
Community method: policy making
commission proposes, European Parliament and the Council decide, Court adjudicates
Community method: decision-making
Commission proposes, EP and the Council decide, Court adjudicates
Community method: 4 decision-making procedures
Consultation procedure
Consent procedure
Cooperation procedure (not relevant)
Ordinary Legislative Procedure (aka co-decision)
What is the difference between the different procedures in the community method
The role of the EP
Consultation procedure
Within community method
Treaty of Rome
Council can:
Amend (change what is being proposed)
Veto (yes or no)
European Parliament can:
Amend (change what is being proposed)
Consent procedure
Within community method
Single European Act
Council can:
Amend (change what is being proposed)
Veto (yes or no)
European Parliament can:
Veto (yes or no)
Ordinary Legislative Procedure
Aka co-decision
Within community method
Maastricht Treaty (Lisbon Treaty)
Council can:
Amend (change what is being proposed)
Veto (yes or no)
European Parliament can:
Amend (change what is being proposed)
Veto (yes or no)
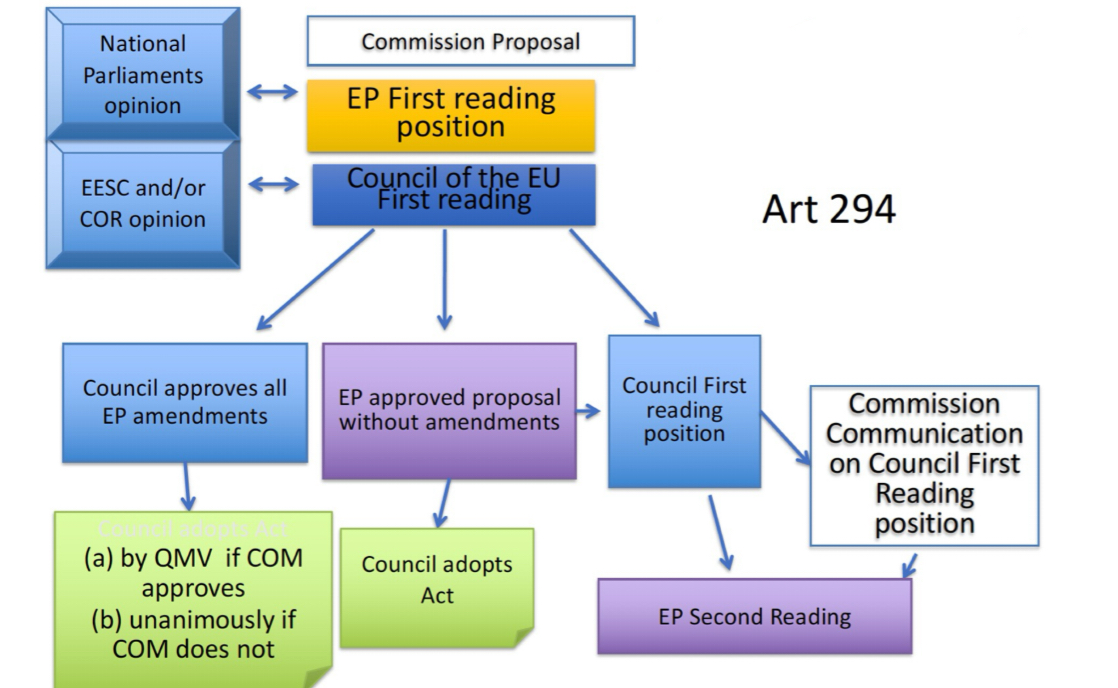
Ordinary Legislative Procedure: First reading
Commission comes up with proposal
Sends proposal to EU parliament and council + national governments for their opinions
First reading of EP - if it likes everything it can approve without amendment but can also add amendments to it if they are not satisfied (the Council then has to approve the amendments)
To approve them there is either QMV (if Commission also agrees with changes) OR with unanimity (if Commission does not agree with changes)
Council can also make amendments
Second reading of EP with Commission present
Ordinary Legislative Procedure: second reading
Second reading:
Do nothing —> act considered adopted
Like what the Council proposes and approves by simple majority
Really not like it —> veto
Not adopted
EP can included further amendments
Commission is asked for their opinion again
Goes to Council second reading
Can approve (QMV with Commission approval/ unanimity without Commission approval) —> act adopted
Doesn’t approve
Moves to third reading (if no agreement made)

Ordinary Legislative Procedure: third reading
Third reading = procedural deadlock
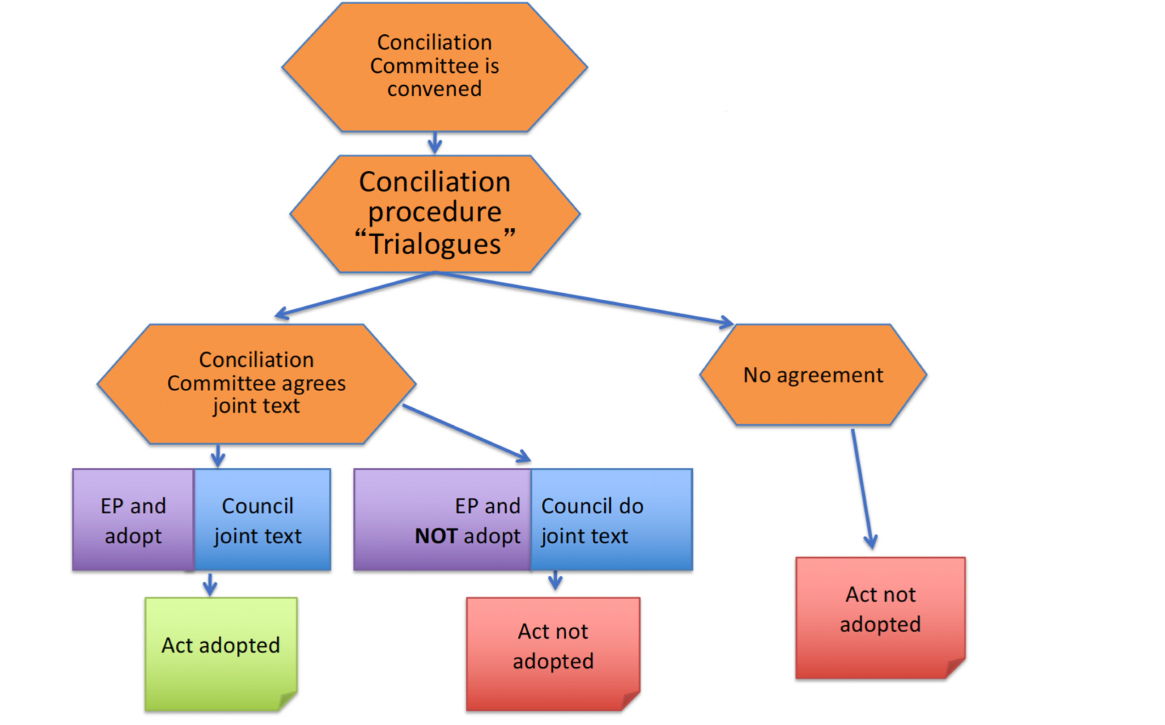
Conciliation committee is convened
There to find consensus
Made up of equal parts EP and the Council (27 each)
Commission is also represented —> the relevant Commissioner
Conciliation committee there to discuss any breakthroughs and find a way to agree on the text - formal procedure
Trialogues (informal): each representative from each delegation meet to clarify things, move things forward
Happens in parallel to conciliation committee
If both EP and Council within the Conciliation committee agree —> act adopted
If one does not agree —> not adopted
If no agreement can be reached at all —> not adopted
EP and the Council are present at every step of decision making
This means that representatives from every member state is present throughout —> can’t say ‘them in Brussels decided this’
Simple majority
14 member states vote in favor
Qualified majority
55% of member states, representing at least 65% of the EU population, vote in favor
Unanimous vote
All votes are in favor
Council voting in reality
Mostly consensus
Even though QMV is the norm and what they are allowed to use 82% of the decisions are made by consensus
Culture of consensus in Council
don’t want to leave anyone behind, everyone on board
How the EP decides in the OLP
“Working parliament” → Committee with a rapporteur and a “shadow” rapporteur
Plenary
Simple majority in the first reading
Absolute majority later on
What is absolute majority in the EP
353 out of 705 votes
Average length of legislative process
Based on 2014 - 2016
First reading: 16 months
Second reading: 37 months
Third reading: -
Total average: 22 months
“Bang Goes the theory”

Problems with “Bang goes the theory ”
Lack transparency
Accountability (who is accountable?)
Odd one out in decision making
Foreign affairs
How are decisions made in foreign affairs
Agenda-setting/ policy proposals
High Representative/ EEAS
Member states - Council or European Council
Decision-making (no “laws”)
Unanimity in Council (“Decision”) & “constructive abstention”
For international agreements: consent of EP
Implementation
Programming decision by Commission/ EEAS
Member States
Trialogues: problematic?
not very transparent
More difficulties to exert democratic accountability
Old dilemma: efficiency vs transparency