Geography IGCSE - Rivers
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Water cycle
the journey water takes as it moves from the land to the sky and back again
Precipitation
transfer of water from atmosphere to Earth's surface in the form of hail, sleet, rain or snow
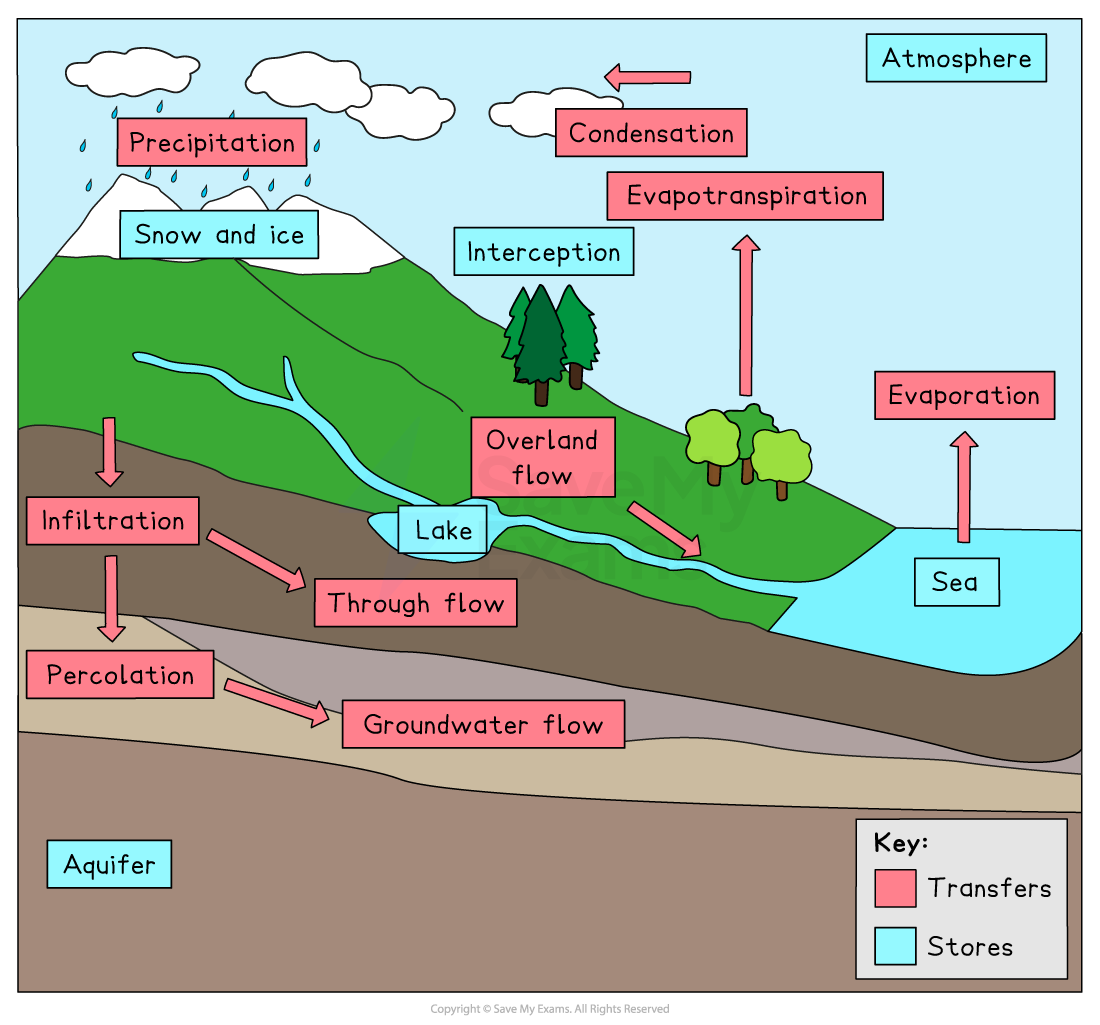
Interception
how precipitation is prevented from reaching the ground → usually by leaves or branches
Infiltration
Process where water enters the ground by seeping through soil or any other surface
Surface runoff
the flow of water that occurs when excess stormwater, meltwater, or other sources flows over the earth's surface
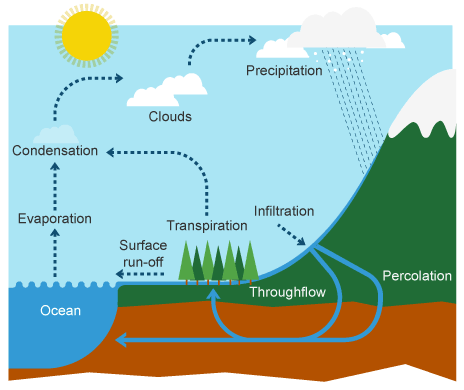
Throughflow
the water moving through the soil below the surface and above the water table
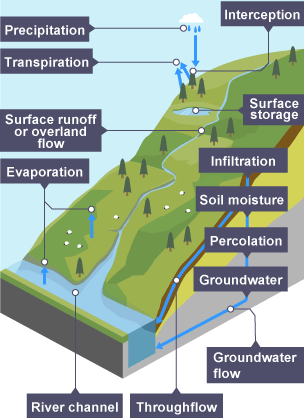
Percolation
The downward movement of water from the soil into the rock beneath
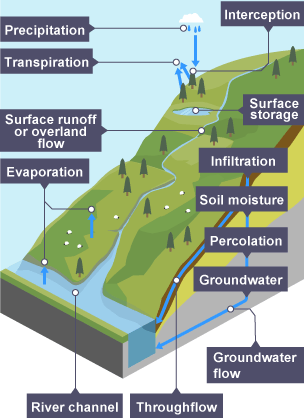
Groundwater flow
Water flows through the rock below the water table towards the river
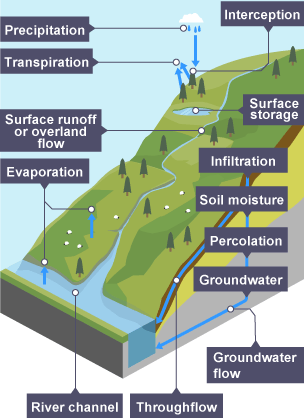
River discharge
the volume of water flowing through a river channel
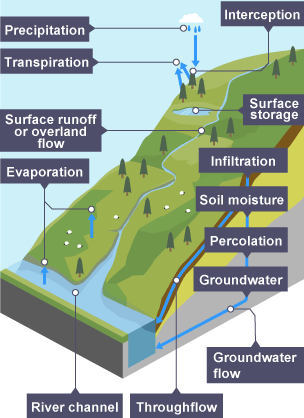
Transpiration
process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers
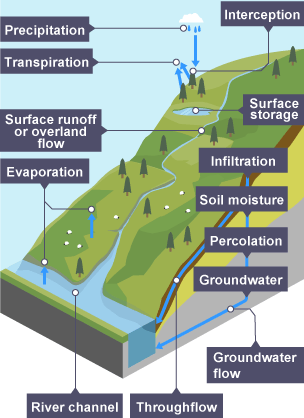
Evapotranspiration
all processes by which water moves from the land surface to the atmosphere via evaporation and transpiration
Confluence
the point where 2 rivers meet
Drainage basin
area of land drained by a major river and its tributaries
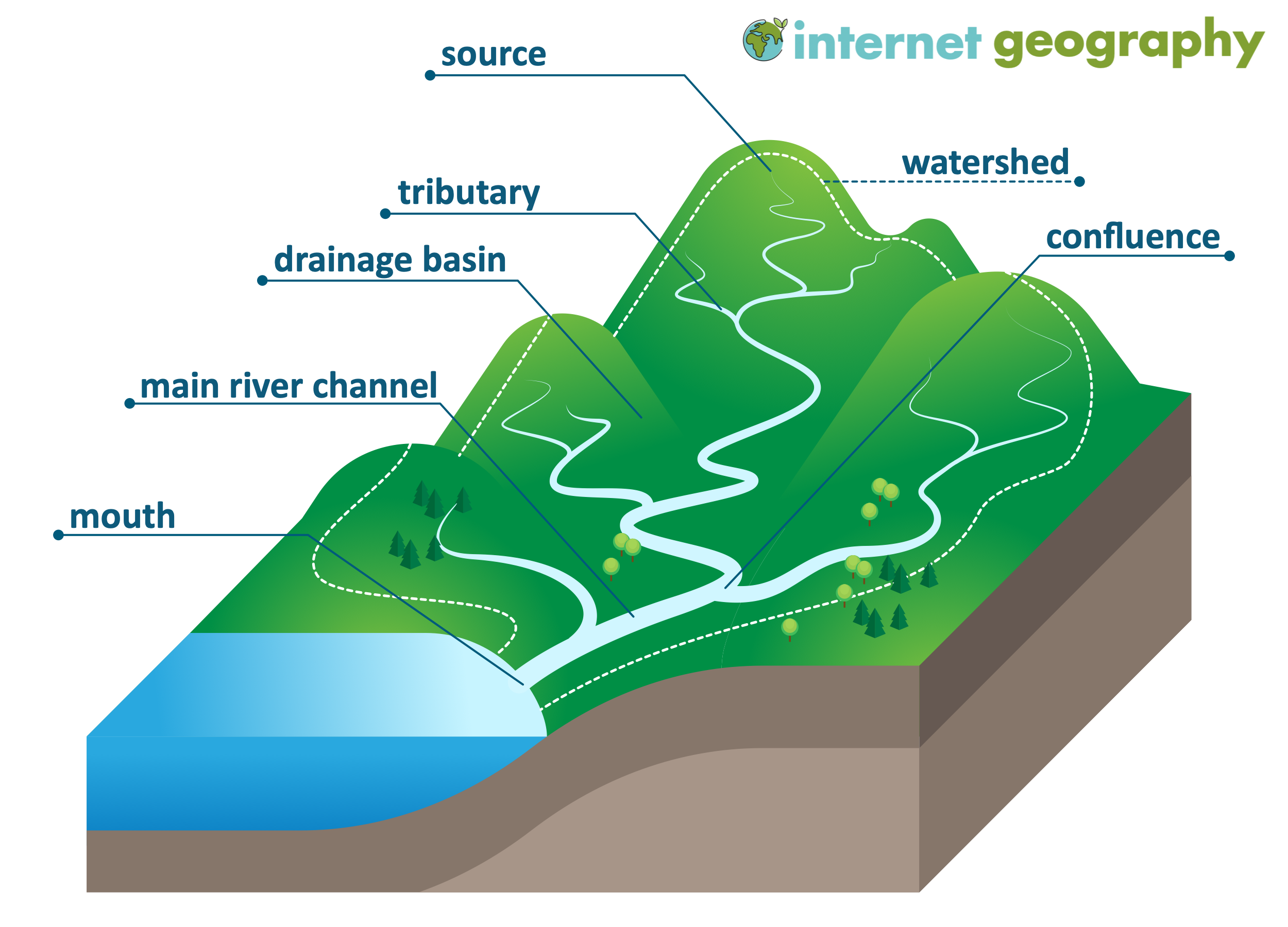
Watershed
area of high land forming the edge of a river basin
Tributary
a small river or stream that joins a larger river
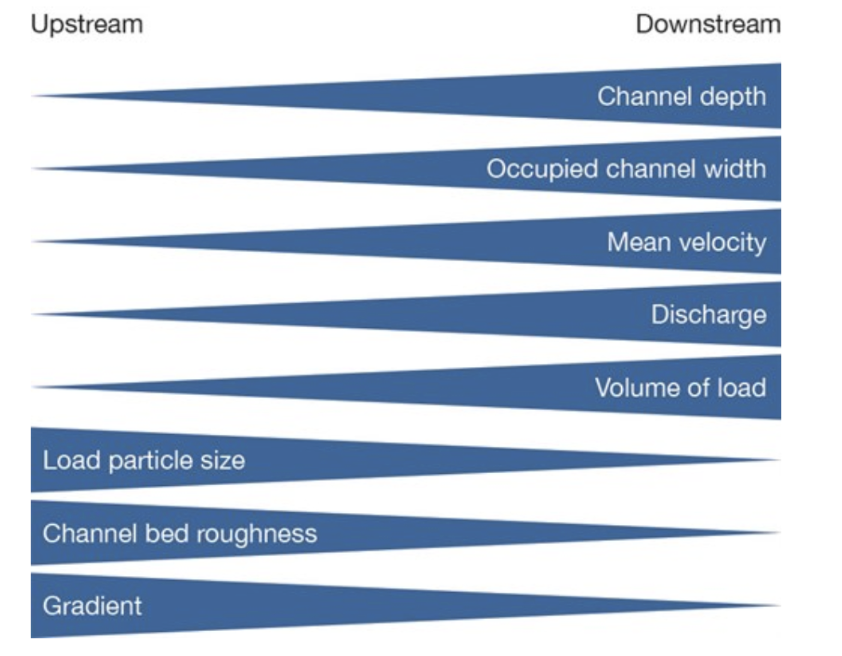
Bradshaw model
River erosion
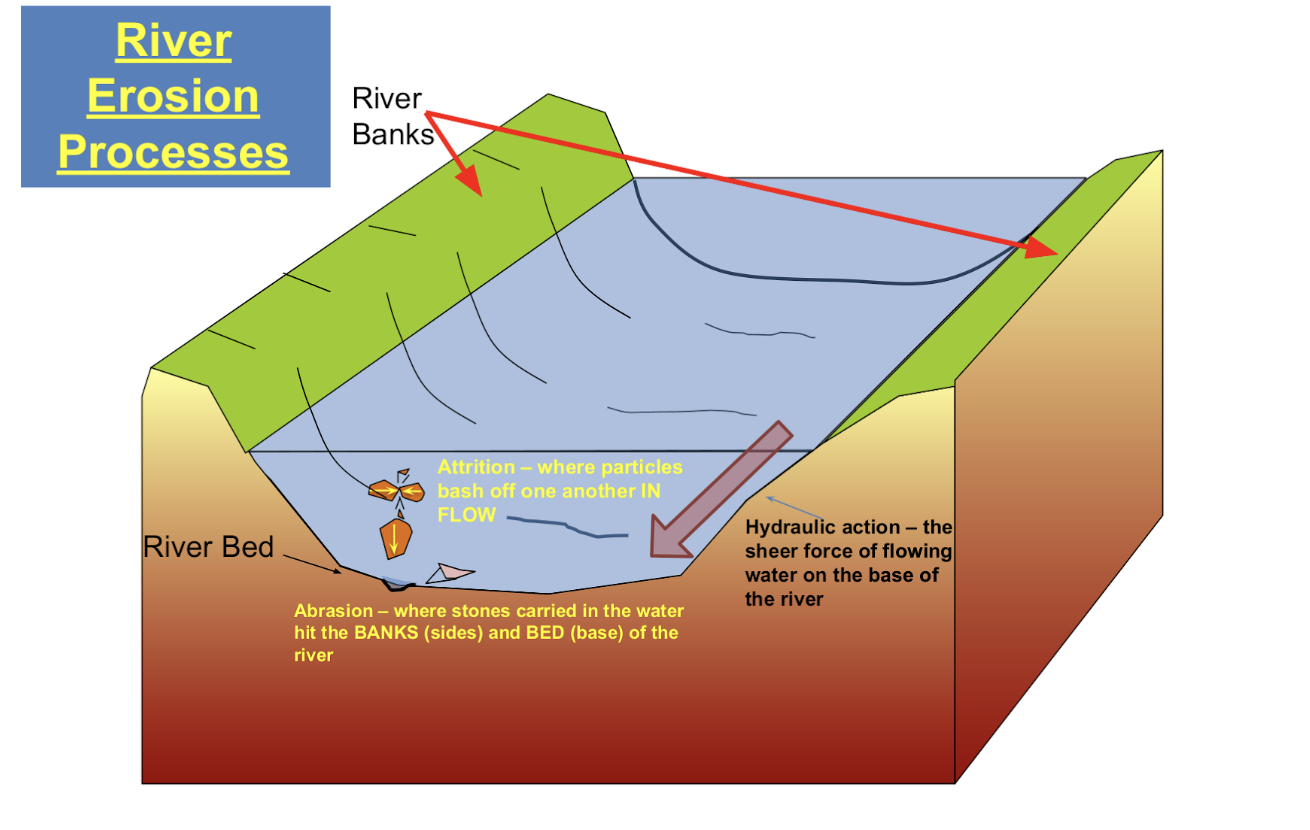
River transportation
Solution: Minerals dissolve in water and move in solution
Suspension: Fine particles are carried within the water flow
Saltation: Small pebbles and stones bounce along the riverbed
Traction: Larger boulders and rocks roll along the bottom
River deposition
Decreasing velocity: Slower water flow reduces river’s capacity to carry material
Reduced gradient: Flatter riverbeds slow water flow → leads to sediment deposition
Increased width: Wider sections of a river have slower flow
Landforms of erosion
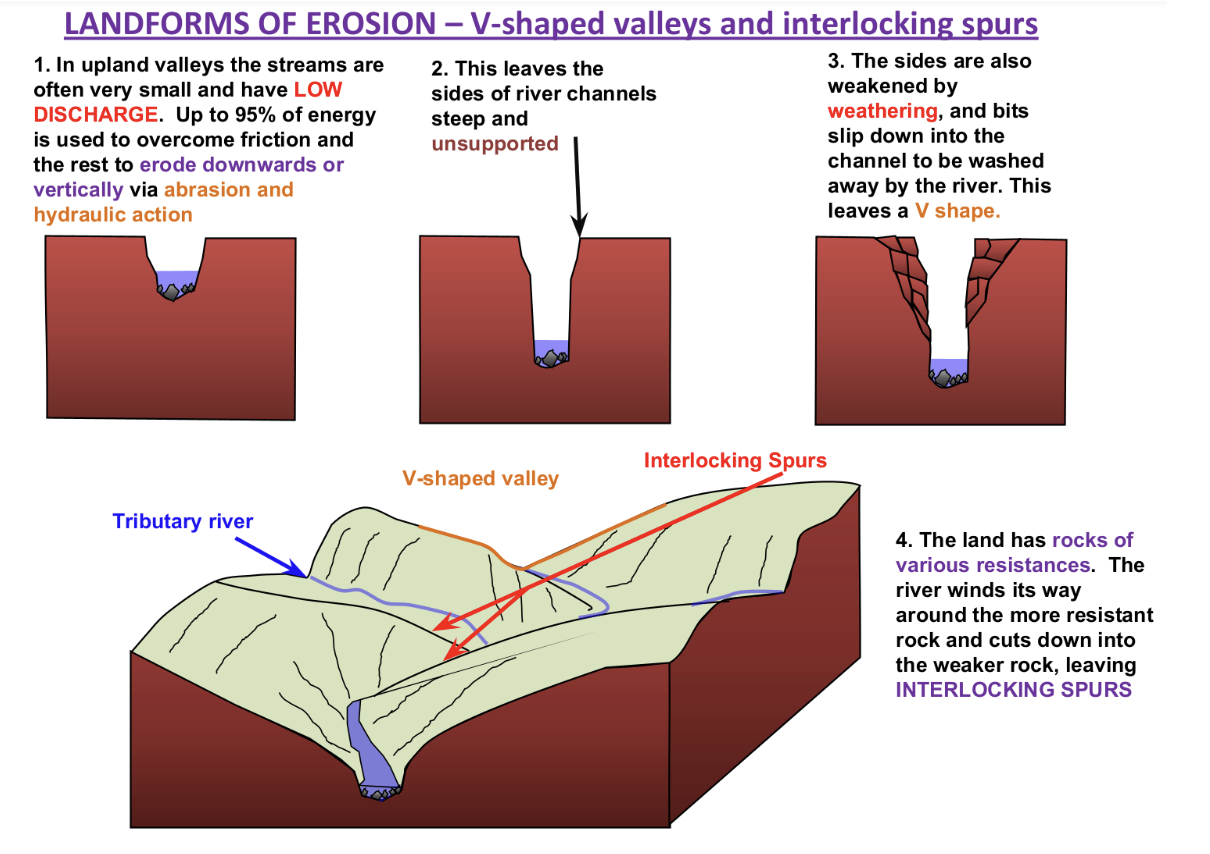
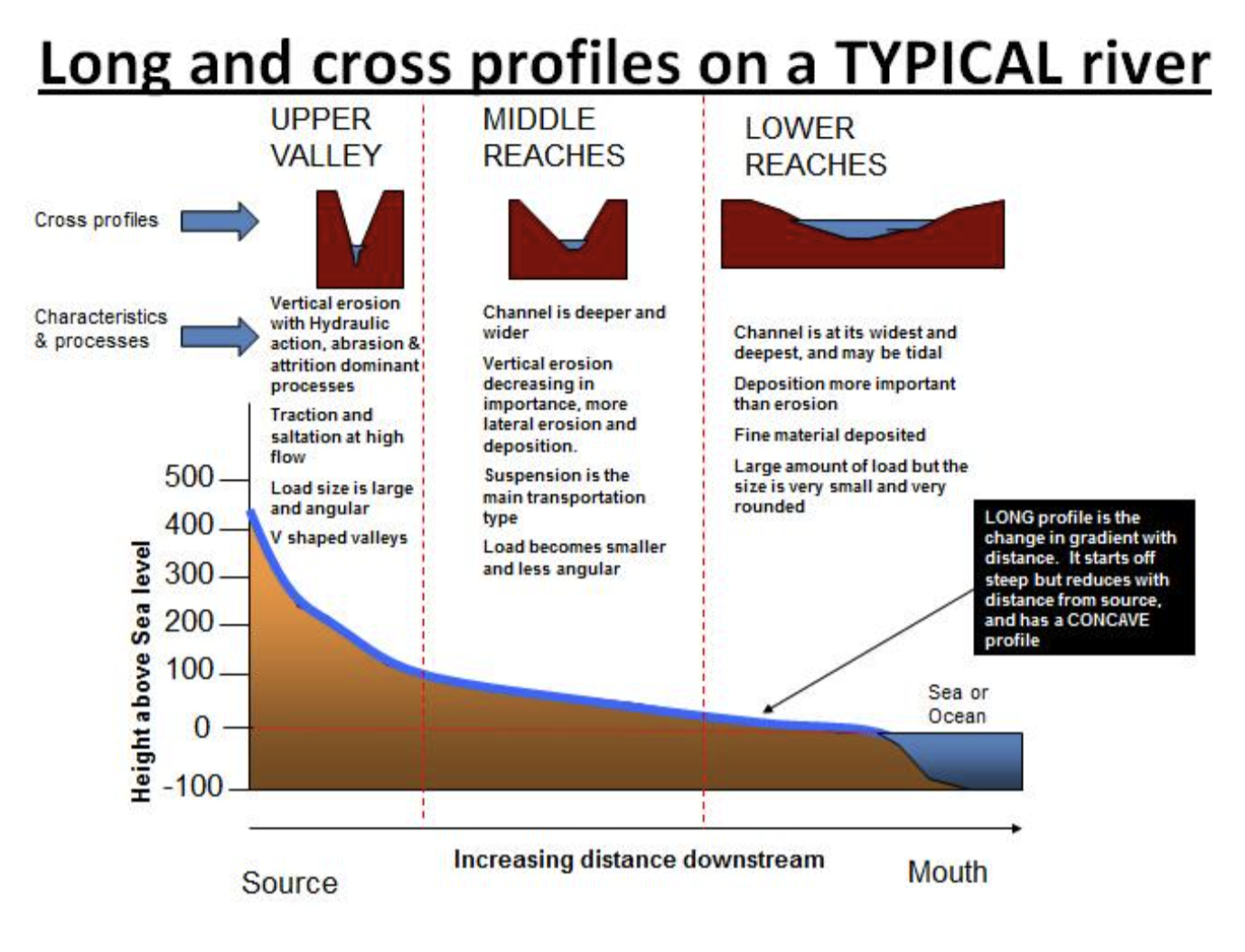
Long and cross profiles
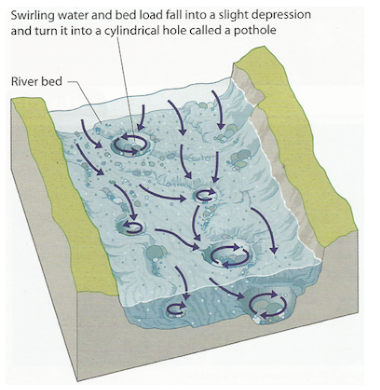
Potholes
Stones that have been broken by waterfalls and banks by hydraulic action have been transported down the river
These rocks get rounded by the process of attrition
When they reach small depressions they get stuck → force of the river water is not great enough to lift it out of the depression
But if there is enough energy in the river flow, currents circulate around the depression and form eddies
The rocks circulate, causing abrasion → drills down into the bedrock forming potholes
They vary in size depending on the force of the river
Different sizes of potholes will eventually join → the rock in between these potholes will be eroded away
Over long periods of time, potholes erode through the rock
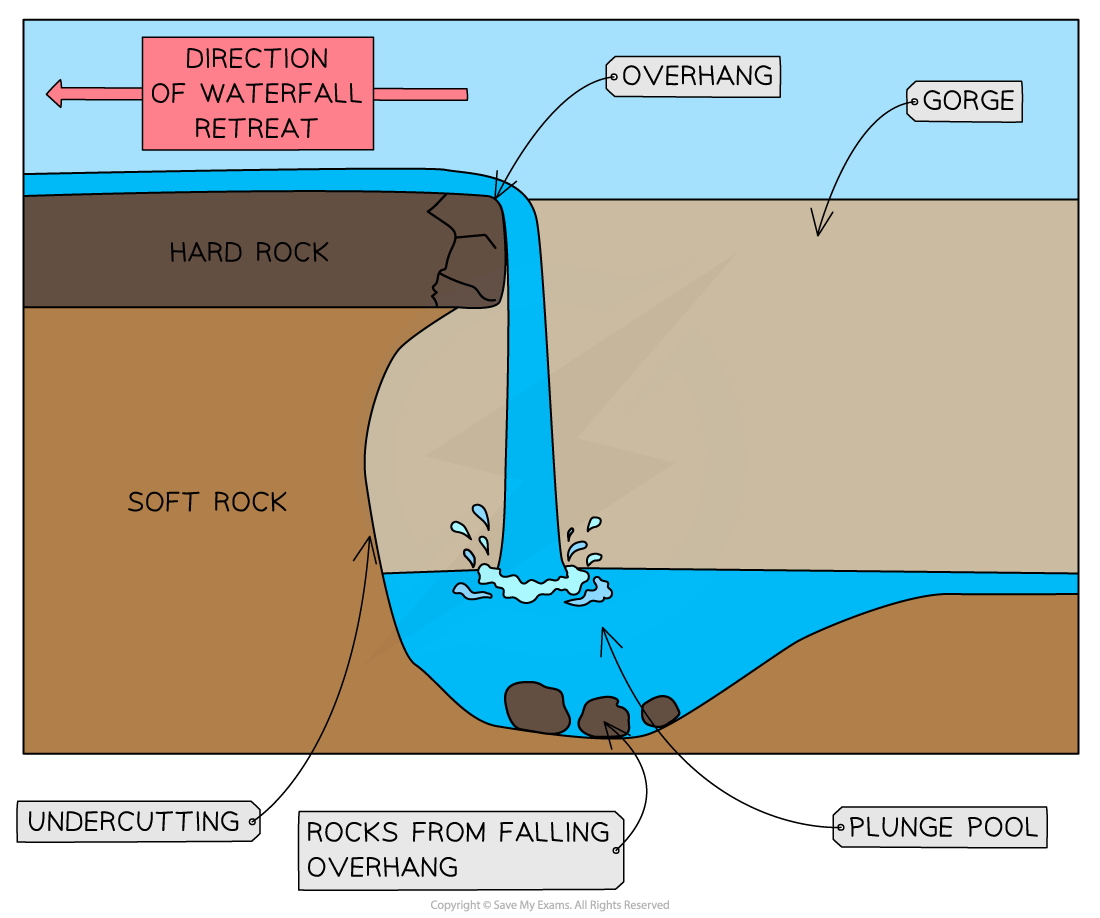
Waterfalls
Develop where river flows over layer of hard rock followed by layer of softer rock → softer rock erodes more quickly through hydraulic action and abrasion → leads to undercutting of hard rock layer → unsupported hard rock collapses due to gravity → form steep drop that is characteristic of waterfalls
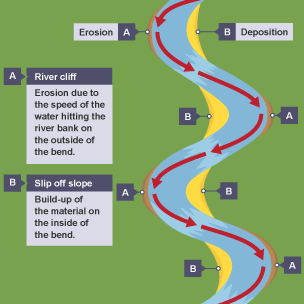
Meanders
Formed by erosion (outer bends) and deposition (inner bends) within river channel → process of hydraulic action and abrasion erodes outer banks → deposition of sediments on inner banks occurs where water flow has less energy → leads to formation of these sinuous curves in the river channel
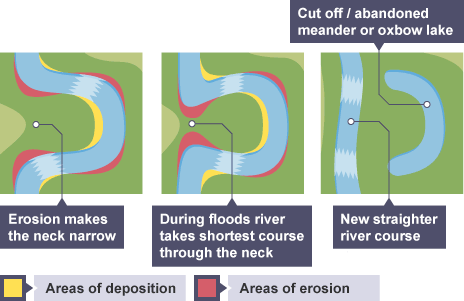
Oxbow lake
Form from meanders that become extremely curved over time → during high-flow events → river may cut through a narrow neck of land → through hydraulic action and abrasion → shortens river path and leaving the meander loop cut off from the main flow → forms an oxbow lake
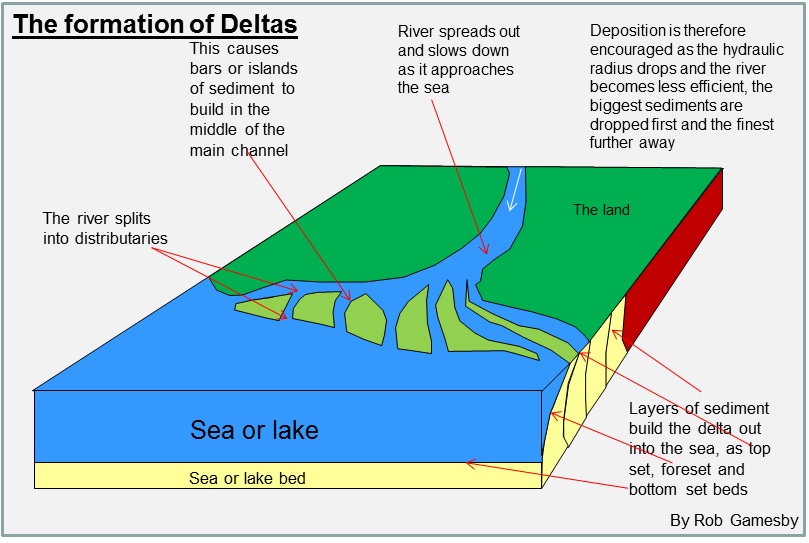
Delta
When rivers deposit sediments as they enter slower-moving or standing bodies of water → reduction in water velocity allows for deposition of sediments → gradually builds up delta over time → process of sedimentation creates these complex landforms characterized by multiple channels known as distributaries
Levees
When river overflows its banks in flood conditions → depositing heavier sediments close to river channel → process of deposition during flood events builds up the levees over time → creates natural embankments along river
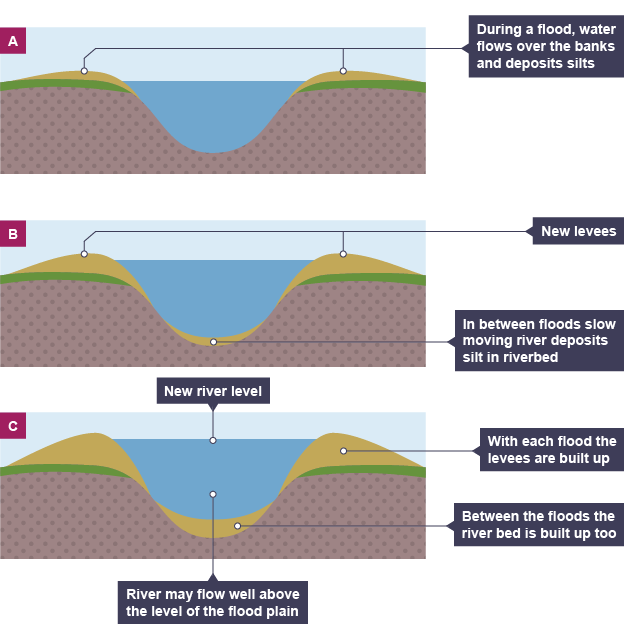
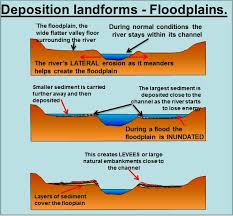
Flood plains
Formed through deposition → when rivers flood and overflow their levees → sediment-laden water spreads out across the wider valley floor → deposits its load of sediments as water slows down → creates flat, fertile areas alongside rivers
Hazards from rivers
Flooding → residential areas near rivers, particularly in floodplains, are vulnerable to floods → lead to loss of life, damage to homes, destruction of infrastructure + economic losses
Erosion and Land Loss → riverbank erosion can threaten properties, agricultural land + infrastructure by washing away soil + ground stability → lead to displacement of communities + loss of arable land
Opportunities living near a river
Water resources → essential for human survival, providing water for drinking, cooking, bathing → also crucial for irrigating crops, supporting agriculture → backbone of many economies
Economy → facilitate various economic activities → fishing (supports livelihoods) transportation + trade (rivers are economical routes for transporting goods) + energy production → particularly hydroelectric power → major electricity source worldwide
Recreational + culture → recreational activities → boating, fishing, + watersports → important for leisure + tourism industries → culturally, rivers have been central to many societies, featured in rituals, festivals + sacred places
Habitat → provide habitats for diverse aquatic + terrestrial species → contributes to ecological health + biodiversity → not only crucial for environmental balance → also supports human life through ecosystem services