Chapter 7: Membranes (Exam 2)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Fluid Mosaic Model
Describes the structure of cell membranes as a dynamic mosaic of phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. These components can move laterally, giving the membrane a fluid and flexible nature
Phospholipid Bilayer
Proteins can travers the membrane; Hydrophobic tail, hydrophillic head
How do things move in the plasma membrane?
Most laterally; Once a month flip flop (switch)
What happens when membrane temps cool off?
Fluid state turns to a solid state
What determines temperature function fo membranes?
Depends on the types of lipids present in membrane
What restrains movement of phospholipids?
Cholesterol
Diffusionq
The natural tendency of particles to move
Proteins:
Determine most of the membranes specific functions
Peripheral proteins
Proteins that are not embedded
Integral proteins
Penetrate the hydrophobic core; span across the membrane.
What are Transmembrane proteins?
Integral proteins that span the membrane
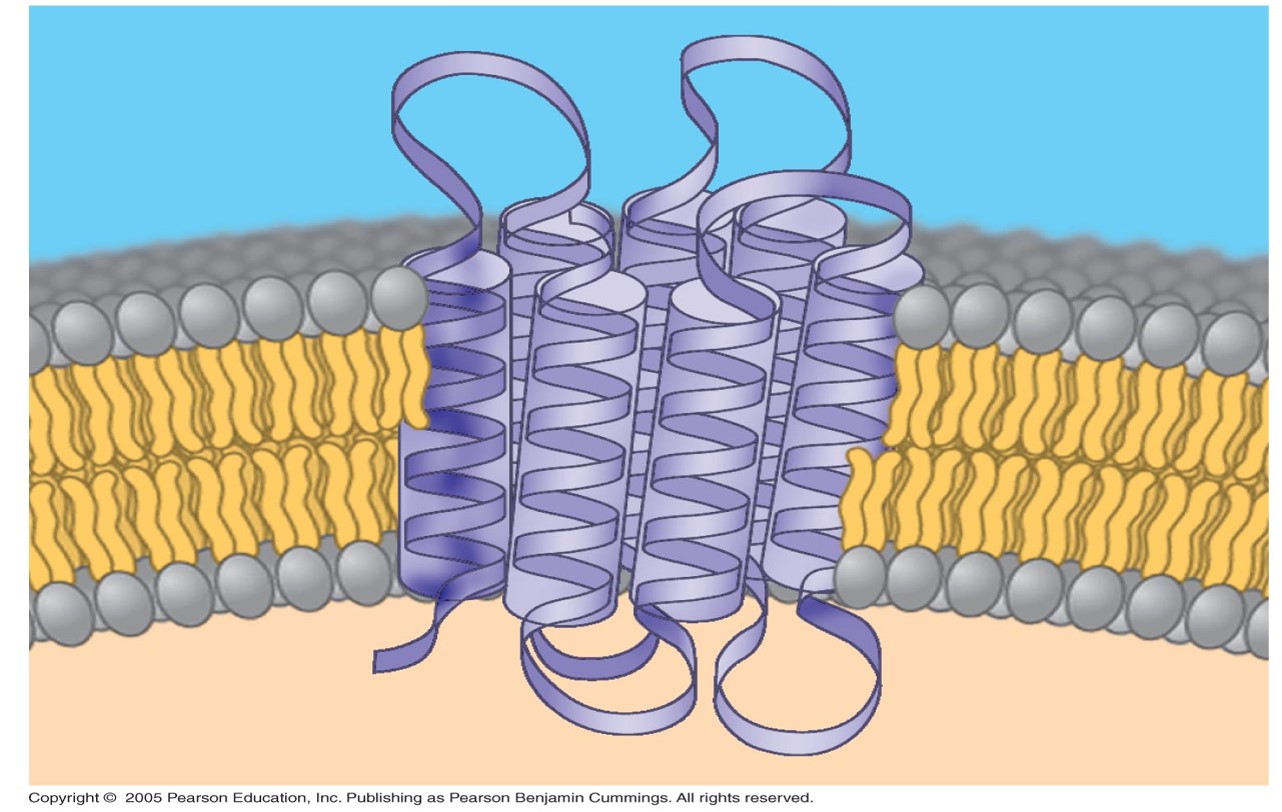
Hydrophobic regions of integral proteins:
Consist of one or more stretches of nonpolar a-acids; coiled into alpha helices
Functions of membrane proteins:
Transport
Enzymatic Activity
Signal Transduction
Cell-cell recognition
Interstellar joining
Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix (ECM)
How do cells recognize each other?
Binding to surface molecules, often carbs, on plasma membrane
Inside Membrane face:
Intracellular
Outside Membrane face
Extracellular
Selective Permeability
regulates what leaves and enters the cell membrane
Hydrophobic Molecules:
Dissolve in the lipid bilayer and pass through the membrane rapidly
Polar Molecules (Sugars):
Do not cross the membrane easily
Transport Proteins
Allow passage of hydrophilic, polar substances across the membrane
Channel Proteins
Hydrophilic channel that certain molecules or ions can use as a tunnel
Carrier Proteins
Bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across membrane
Dynamic Equilibrium
As many molecules cross one way cross in the other direction
Which way do substances diffuse?
Down their concentration gradient
Passive Transport
Requires no energy from cell to make it happen
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane
Direction of osmosis is determined by:
Difference in total solute concentration; goes from lower solute to higher solute.
Tonicity
Ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or lose weight
Isotonic Solution
Solute concentration is the same as that inside the cell
Hypertonic Solution
Solute concetration is greater thatn that inside the cell; cell loses water
Hypotonic Solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
Osmoregulation
The control of water balance
Turgid
Plant cell in hypotonic solution until the wall opposes uptake
Flaccid
Plant cell with 0 net movement
Plasmolysis
contraction of the protoplast of a plant cell as a result of loss of water from the cell.
Facilitated diffusion
Passive transport aided by proteins; Transport proteins speed movement of molecules across membranes