PSY 250 Lecture 10 Perceive Edges & Color Perception
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Define Edge.
Rapid change in image intensity within a small region
What is Perception of an Edge?
Perception of a contrast between two adjacent areas of the visual field
Define Contrast Enhancement.
A mechanism in the visual system that enhances the perception of contrast between two areas
What are examples of Contrast Enhancement?
Mach bands & Hermann Grid
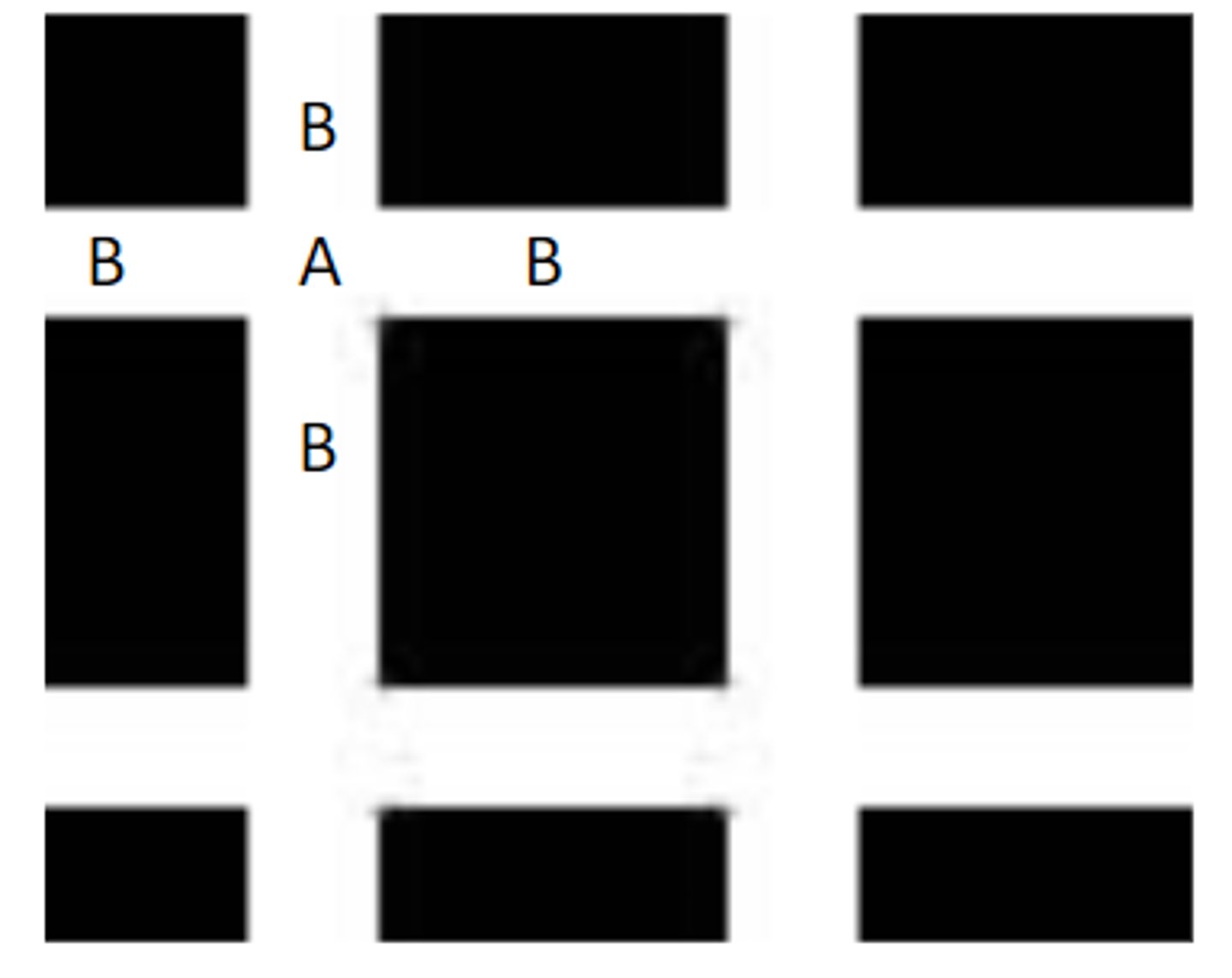
___________:
• B: brightness enhanced due to surrounding low-intensity black boxes
• A: brightness does not change; looks gray because B appears even lighter
Hermann Grid
Neural basis of contrast enhancement:
Lateral Inhibition
What is Lateral Inhibition?
"Enhancing" the effect by inhibiting neighboring cells
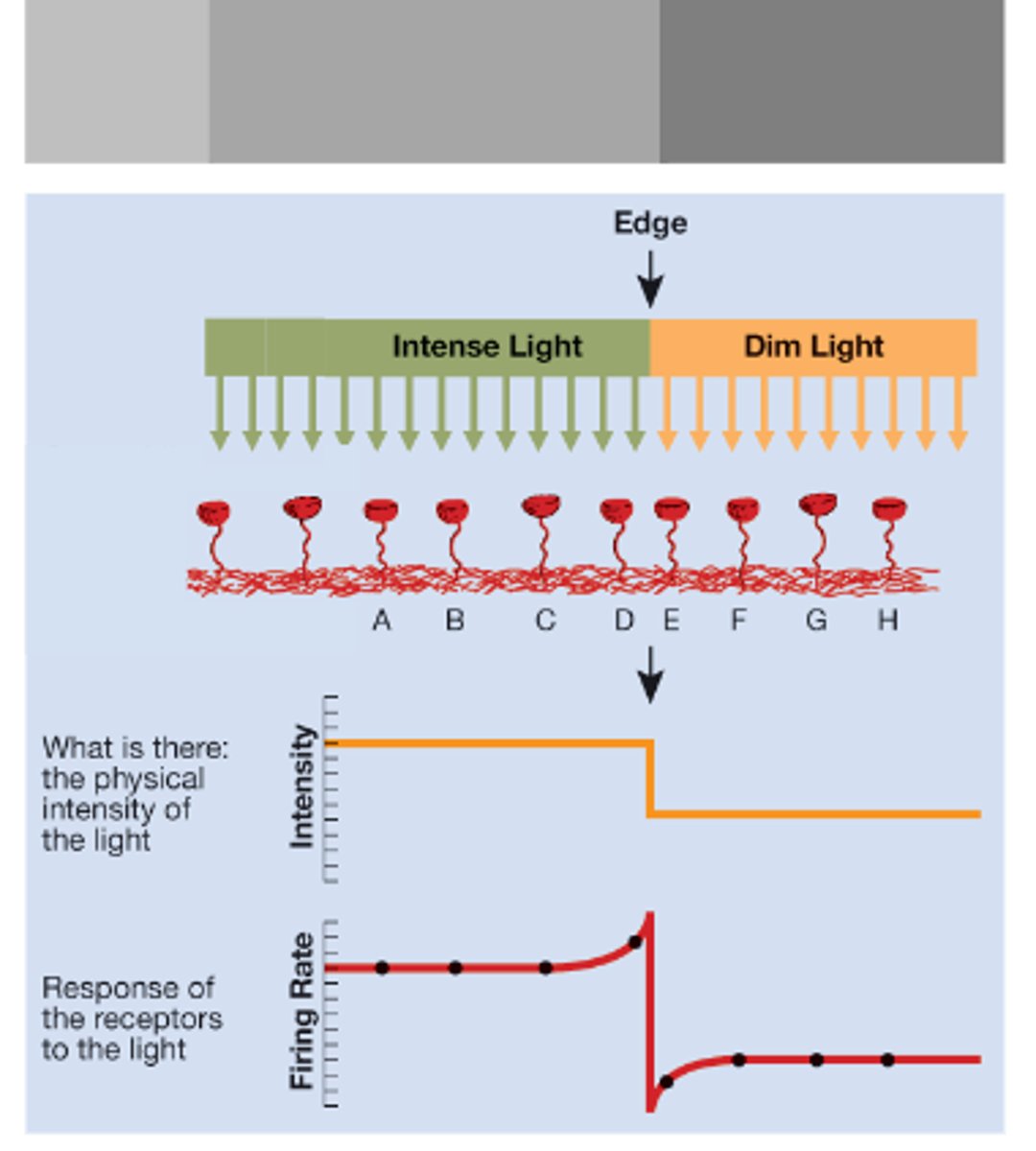
Lateral Inhibition:
1. More intense light = _______firing rate
2. When a cell fires, it inhibits neighboring cells
3. Inhibition is greatest in the closest neighbors
higher
In Lateral Inhibition, Cell D fires more than _______ because of less inhibition from E-H
A - C
In Lateral Inhibition, Cell E fires _______ than F-H because of more inhibition from A-D
less
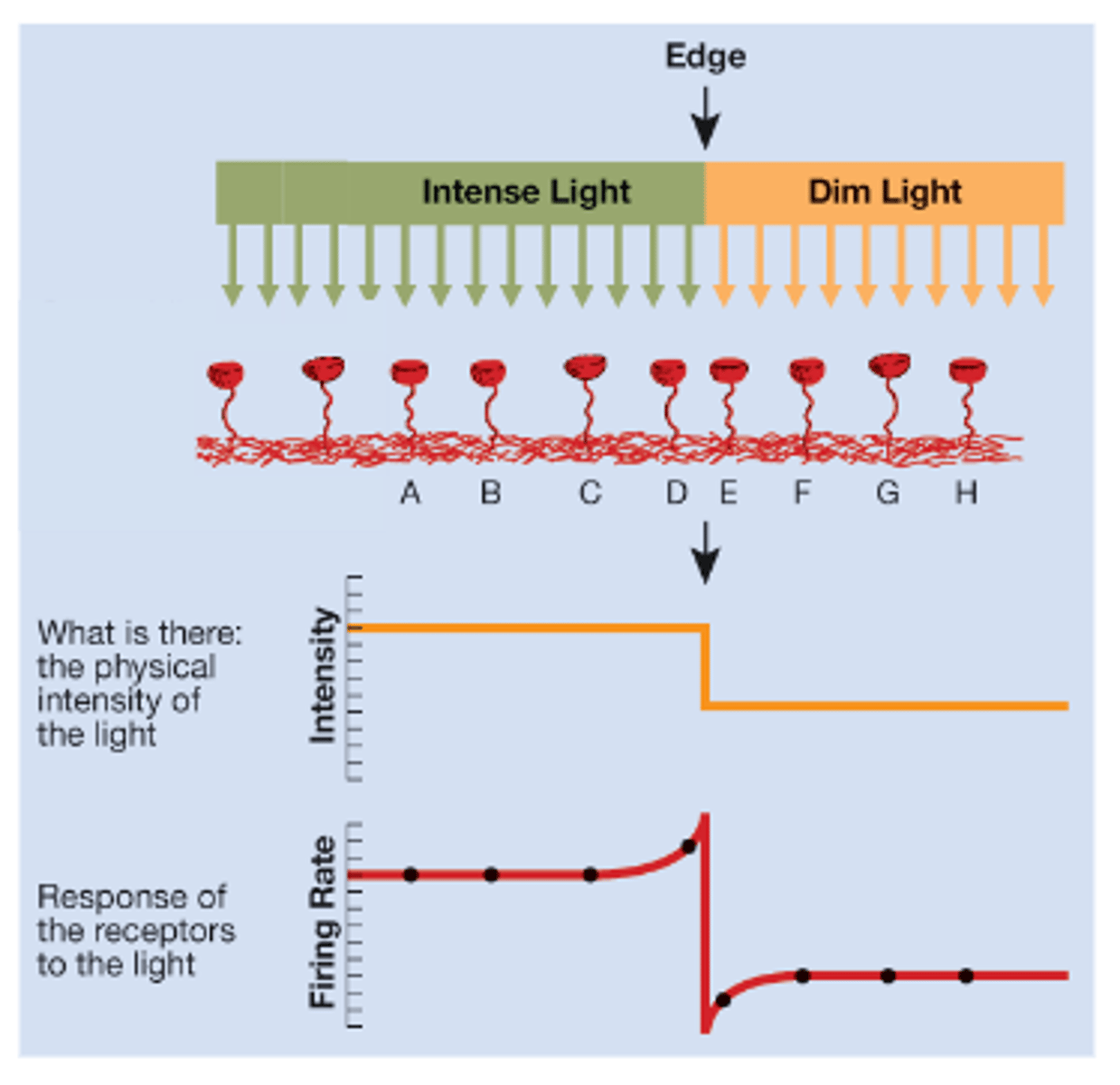
In human, lateral inhibition occurs through the activity of
horizontal cells
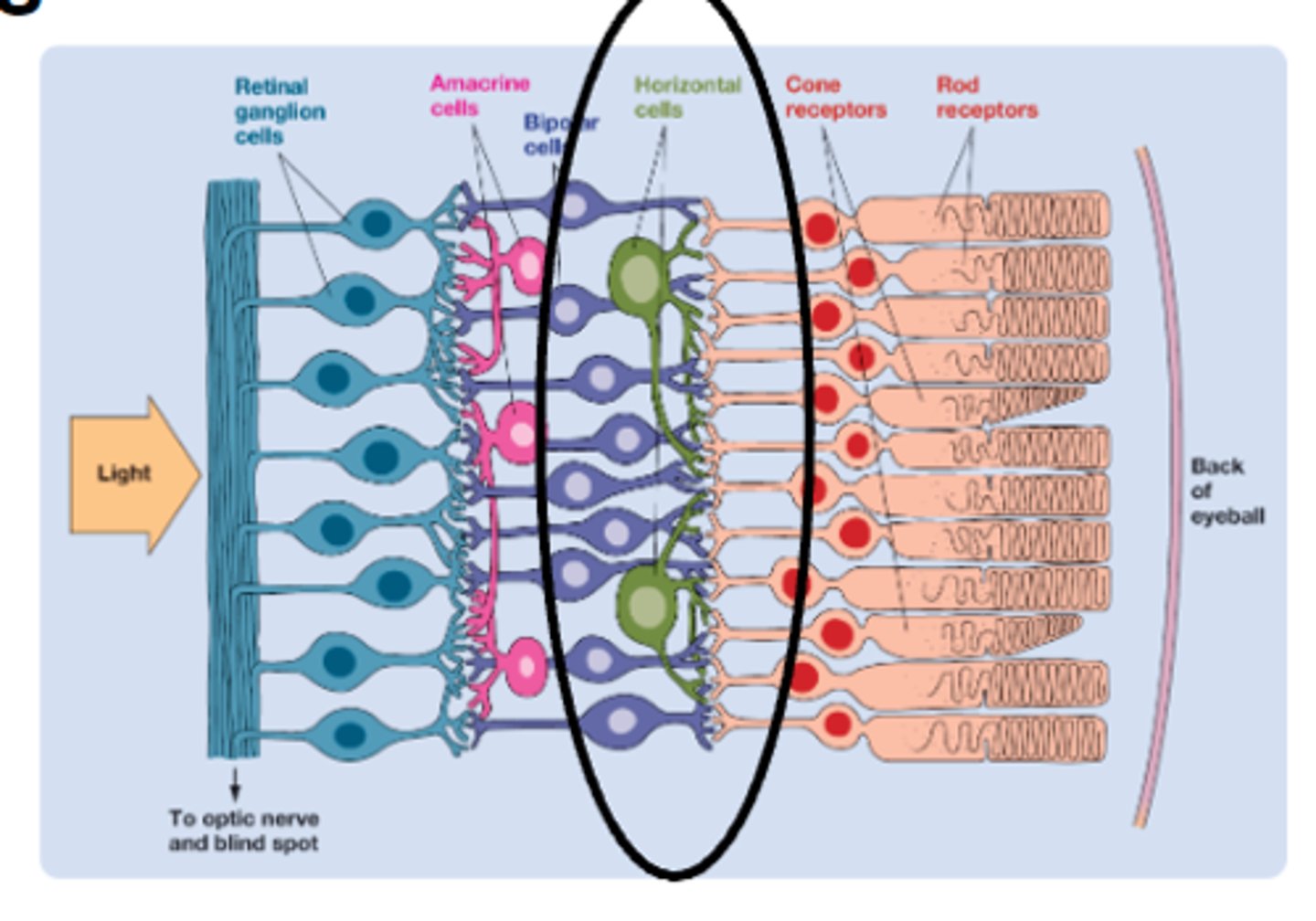
Perception of Color
Cones come in three types, each sensitive to different wavelengths of light.
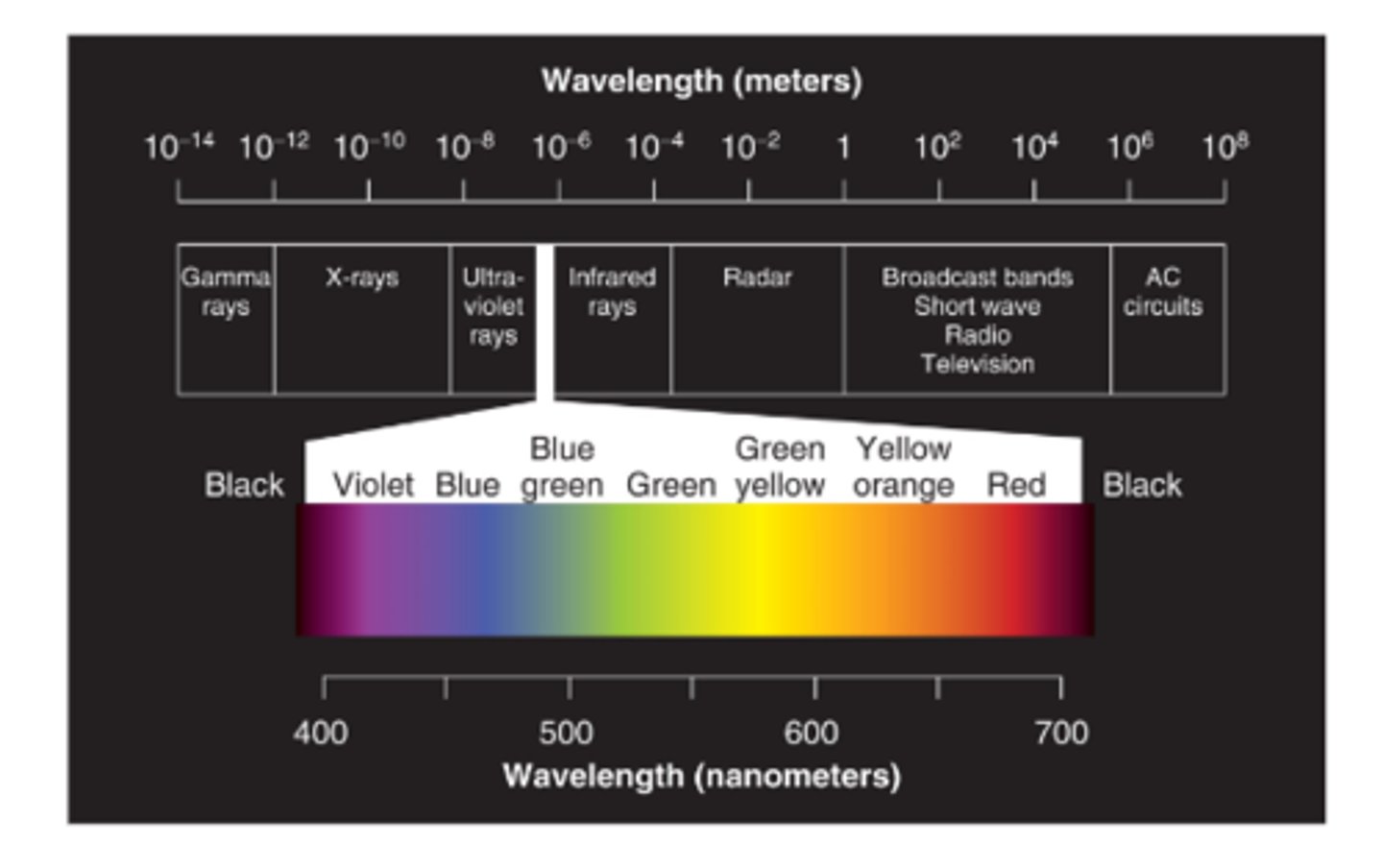
__________________________:
• We perceive color through the response of three types of cones
• Three kinds of cones -- S, M, L
• Wavelength: short, medium, long
• The absorption spectra of the three classes of cones
• Evidence: colorblindness S M L
Component (trichromatic) Theory
___________________:
• 3 sets of cells that perceive colors in opposing pairs (red/green; blue/yellow; black/white)
• If one color is activated, its pair is inhibited
• Evidence: complimentary afterimage
• Complementary after image
Opponent Process Theory
Define Sensory Adaptation.
Sensitivity decreases upon constant stimulation
Sensory systems show adaptation –
change their sensitivity to a stimulus upon constant stimulation
• Example: Dark adaptation
In Opponent Process Theory, E.g., green receptors adapting =>
less activity responding to green. Then when we then see white, it appears more red.
Opponent Process Theory occurs...
at all levels of the visual system after photoreceptors
What is Color Consistency?
The tendency of object to be perceived as the same color despite large changes in the wavelength it reflects
Color Consistency helps us ___________ objects
identify
What is Retinex Theory?
Perception of color is determined by its reflectance -- the proportion of light of different wavelengths a surface reflects
Retinex Theory:
• The visual system calculates the reflectance of the surface by comparing the light reflected by adjacent surfaces with indifferent wavelength
• The relative reflectance does or does not change, so the color perception is constant?
does not