OB Exam 1 Study Guide (Labor and Delievery)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Station
Relationship of presenting part to the ischial spines of the maternal pelvis
+ or - number to describe how high or low the baby is to the pelvis
Level is “station ZERO”
"-” means above
“+” means below
Cervix
The cervix plays a significant role during pregnancy. It is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina and undergoes various changes throughout pregnancy.
How do you note a cervical exam
dilation/effacement/engagement
Dilation
The opening and widening of the cervix
0-10 dilated
Effacement
Thickness or thinning of the cervix
0% - 100%
Attitude
Degree of flexion or extension
Leopold’s
A four-step process aids the nurse or provider in identifying the fetal lie, attitude, and position of the fetus to determine the best fetal monitor location
Best done before starting FHR assessment
BOW
Bag of water
What does the BOW do?
protect the baby
maintain baby's temperature
allow for the baby to move
nutrient exchange
infection barrier
When do you expect the BOW to break?
ANY TIME
it can break before or during birth, either naturally or by the MD
AROM
artificial rupture of membrane
*when the women's water breaks artificially, by the MD
*the baby's head must be engaged in order for the MD to break her membrane
*can be done to stimulate labor
*known as a amniotomy
How can AROM stimulate labor?
because when the women's water breaks, oxytocin is naturally released, which helps with uterine contractions
SROM
spontaneous rupture of membrane
*when the women's water breaks naturally, not from the MD
Amniotic fluid
A clear (or slightly yellowish) fluid that surrounds and protects the fetus during pregnancy
Presentation
cephalic/vertex = head first
*the most common
transverse lie = acromion first
*laying sideways
*cannot deliver vaginally, needs C-section
complete breech = butt first, legs crossed
frank breech = butt first, body doubled
footling breech = foot/feet first
Position (Passenger)
relationship of the presenting part to the pelvis
*1st letter = maternal body (R or L)
*2nd letter = presenting part (O = occiput, S = sacrum, A = acromium/shoulder, B = brow)
*3rd letter = position of the presenting part (A = anterior, P = posterior, T = transverse)
2 stages of the first stage
latent phase
active phase
latent phase of 1st stage of labor
from onset to 5cm of dilation
UCs mild and infrequent but increasing to every 5-30 mins and lasting 30-45 seconds
menstrual cramp like feeling
women tend to be sociable excited and cooperative
active phase of 1st stage of labor
6-10 cms dilation
75% effacement
fetal station often "0"
duration of UCs 45-60 seconds
women begin less sociable and begin to turn inward, still cooperative, request analgesia
stage 1 of labor
dilation
*onset of true labor
*ends with complete dilation (10cm) and 100% effacement
nursing interventions for stage 1 labor
encourage frequent urination or urinary catheter
* Full bladder prevents fetal descent into birth canal
* Filled bladder is at risk for trauma/injury from fetal descent
monitor vaginal exams Q2h or PRN
monitor FHR and UC pattern
monitor fetal station and presentation
encourage deep breathing and relaxation
second stage of labor
complete dilation and effacement to delivery
can last 5 mins - 2 hours
average 20 mins for multip and 50 minutes for primip
mom feels urge to push with UCs
women regain control
tired but excited
nursing interventions for 2nd stage of labor
monitor FHR Q5-15 mins
monitor BP, pulse, and RR Q5-30 mins
monitor frequency and strength of UCs
evaluate pushing eefforts
assist in positioning
assist support person in being involved
provide ice chips
promote rest between UCs
note for shakiness or quivering
*from adrenaline, not coldness
delivery cares for stage 2 of labor
suction mouth and nose after baby's head is delivered
baby's face wiped with sterile gauze
deliver body by pulling down then up
keep baby at level of mom's heart
cord is cut when pulsating stops
*delayed cord clamping
APGAR score at 1 and 5 minutes after delivery
signs of placenta separation
uterus rises anteriorly and abdomen takes on an oval (globular) shape
small gush of blood precedes expulsion
cord lengthens
*This is bad if it happens during pregnancy
stage 4 of labor
fundus can be felt as a round ball the size of a grapefruit - midline initially half-way between symphysis pubis and umbilicus
*if uterus is deviated = bladder is full
placenta is delivered
monitor blood loss closely
cleanse perineum and apply pads
clean, dry gown and linens
initiate skin to skin and breastfeeding ASAP
provide privacy for hour of bonding
how often do you do VS and final massage after birth
Q15 mins x 8
Q30 mins x 2
Q1 hr x 2
MD order
what do you do if the fundus is boggy
administer oxytocin as ordered
*mom may be hemorhaging
APGAR
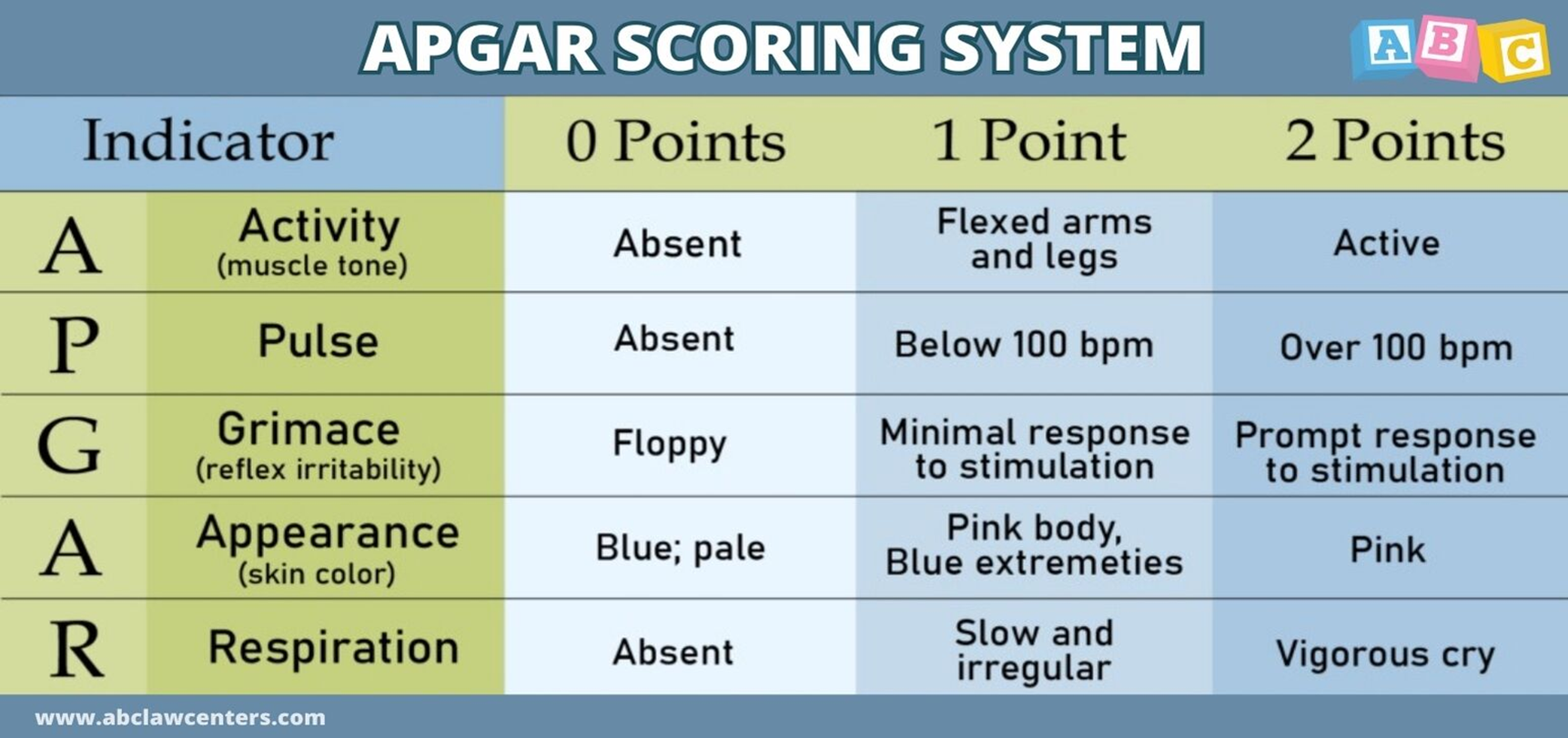
Must score a 7 or higher
APGAR: Activity
Muscle tone
Active - 2 points
Flexed arms and legs - 1 point
Absent - 0 points
APGAR: Pulse
Heart pulse
Over 100 bpm - 2 points
Below 100 bpm - 1 point
Absent - 0 points
APGAR: Grimace
Reflex irritability
Prompt to respond to stimulation - 2 points
Minimal response to stimulation - 1 point
Floppy - 0 points
APGAR: Appearance
Color of skin
Pink - 2 points
Pink with blue extremities - 1 point
Blue and pale - 0 points
APGAR: Respiration
Breathing
Vigorous cry - 2 points
Slow and irregular - 1 point
Absent - 0 points
true labor signs
regular rhythmic UCs
UCs become closer together and stronger
usually start in lower back and radiate to abdomen
UCs don't stop with walking/relaxation
* UCs do not stop no matter what
cervix thins and dilates
blood show
fetus moves downward and engages in pelvis
false labor
irregular UCs
duration and intensity vary
UCs lessen with walking
UCs lessen with relaxation or position changes
minimal cervical change
no change in fetal position
pain usually in groin and abdomen
no bloody show
braxton hicks contractions
when should moms go to the hospital?
regular contractions q5 mins or closer
gush or leakage of bag of water
bright red vaginal bleeding - active bleeding
decreased or zero fetal movement - could be fetal demise
Expected newborn vital signs
Temp: 36.5 to 37.5 C (97.7 to 99.5
Bonding
Unidirectional, rapid, and facilitated or optimized by physical contact
Engrossment
term for dad bonding
look at baby
smile at baby
skin to skin
talk to baby
make positive statements about baby
Positive bonding behaviors
responding to the baby's needs
holding the baby
calling the baby by name
Thermoregulation
To help maintain the body’s stable level of heat despite changes
In pregnancy, the baby is held skin-skin to the mother’s body to keep it warm
4 ways of heat loss for newborns
convection
radiation
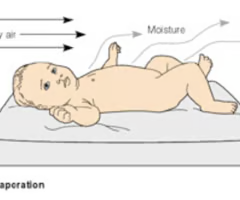
evaporation
conduction
convection
air currents
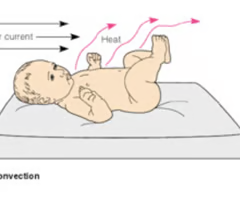
radiation
surfaces near body that are cooler than body
heat radiates out
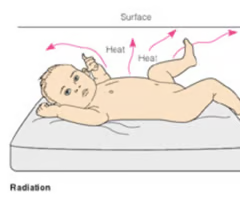
evaporation
moisture is converted to vapor
*this is why we dry them immediately after birth
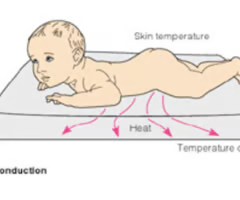
conduction
heat is transferred through touch
*ex: baby is touching cold surface
GTPAL: G
# of times pregnant
GTPAL: T
# of term deliveries (over 37 weeks)
GTPAL: P
# of preterm deliveries (20 - 37 weeks)
GTPAL: A
# of abortions or miscarriages (under 20 weeks)
GTPAL: L
# of living children
Naegel’s Rule
LMP (last menstrual period) minus 3 months plus 7 days
Provides EDD (estimated date of delivery)
Leopold’s Manuvers
determines the baby's position in the mom's uterus
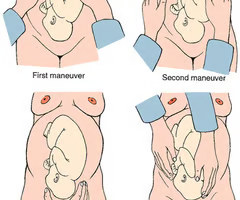
what must you have the mom do before doing the Leopold's maneuver
void then lay on their back with knees slightly flexed
maneuver 1 in Leopold's maneuver
determines shape, size, consistency, and mobility of presenting part
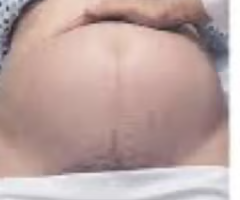
maneuver 2 in Leopold's maneuver
determines fetal back and side
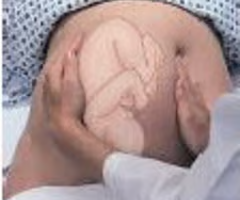
maneuver 3 in Leopold's maneuver
determines what fetal part is lying above the pelvic inlet
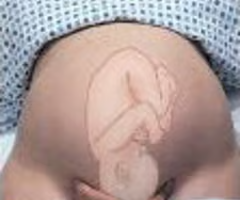
maneuver 4 in Leopold's maneuver
determines the fetal attitude

what are the five P's of labor
power
passageway
passenger
psyche
position
powers of labor
contractions - 1st stage of labor, involuntary
dilation and fetal descent - active phase of 1st stage, involuntary
maternal pushing - 2nd stage, voluntary
contractions
involuntary smooth muscle contractions that efface and dilate the cervix
pushing
voluntary action to propel the fetus down through the pelvis
passageway of labor
bony pelvis
soft tissue - cervix vagina, vaginal opening, muscles, ligaments, & fascia
passenger of labor
the baby and the placenta
psyche of labor
anxiety
culture
great expectations
can increase pain perception and activate stress hormones which inhibit blood flow to the placenta
stress, tension, and anxiety can produce physiological changes that impair the progression of labor
what is rupture of membrane (ROM)?
when the membrane containing amniotic fluid and the baby ruptures
*aka their water breaks
tests to assess for rupture of membrane
1. nitrazine
2. ferning
3. amnisure
nitrazine test
pH paper that will turn blue if it comes in contact with amniotic fluid
*blood can also turn the paper blue
*if paper is blue = positive result
ferning test
A noninvasive test diagnostic test that analyzes vaginal secretions to identify the presence of amniotic fluid. When amniotic fluid dries on a microscope slide, it forms a distinctive fern-like crystalline pattern due to the crystallization of sodium chloride and proteins. This pattern is unique to amniotic fluid and helps differentiate it from other bodily fluids.
when you collect vaginal liquid then put it under the microscope, it should crystalize
*DO NOT use lubricant when collecting the vaginal fluid because the lubricant from the sample can ALSO crystalize, creating a false positive
*crystalizing = positive result
amnisure test
when you collect vaginal fluid and place it on a stick that detects amniotic fluid
* 2 pink lines = positive result
* 1 pink like = negative result
when a women's water breaks what complications should you look for?
cord prolapse
infection
what is a cord prolapse
when the baby's umbilical cord comes through the birth canal before the baby does
why would ROM cause infection?
if a women's water is broken for a long time, bacteria from the vaginal canal can travel up to the uterus, which was previously protected by the amniotic fluid's antibacterial characteristics
what is usually done for mothers with ROM and an increased risk of infection?
they are given broad spectrum antibiotics
PROM
ROM occurs prematurely - before uterine contractions begin
what is at risk with PROM?
Infection, if over 24 hours before delivery
cord prolapse and cord compression (because baby can compress cord due to gravity, etc)
PPROM
preterm premature rupture of membrane
ROM before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy
what are signs that mom is infected due to ROM?
abdominal tenderness
bad odor
how often should the nurse assess fetal heart rate after ROM
immediately after ROM and again 5 minutes later
what should the nurse note after ROM
the color and odor of the fluid
*notify MD or CNM if meconium present
how often should the nurse monitor temperature after ROM
Q 1-2 hours / per hospital protocol
vaginal exams after ROM
should be LIMITED
Q2H