Chemistry - amount of a substance
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
what is the ‘amount of substance’?
a quantity to count the number of particles in a substance
what is amount of substance measured in?
moles
one mole =?
the amount of substance that contains 6.02×10²³ particles
what is the avogadro constant?
6.02×10²³ mol-1, the umber of particles in each mole of carbon-12
what is 6.02×10²³ particles per mole linked to?
the mass of carbon-12. 12g of carbon-12 contains 6.02×10²³ atoms
how do you find the mass of one mole of atoms of any element?
its its relative atomic mass in grams
why does formula matter for moles?
eg.
1 mol of H; 1 mol of hydrogen atoms
1 mol of H2; 1 mol of hydrogen molecules
what is molar mass, M?
the mass per mole of a substance
what are the units of molar mass?
gmol-1
moles =?
mass / molar mass
eg. M(NO2) =?
14 + (16 ×2) = 46gmol-1
whats a molecule?
2 or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
what is molecular formula?
the number of atoms of each element in a molecule
what is empirical formula?
the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
what is empirical formula important for?
substances that dont exist as molecules, like metals, non metals and ionic compounds, as they form giant structures that would be impossible to formulate
what is relative molecular mass, Mr?
compares the mass of a molecule with the mass of an atom of carbon-12
how do you calculate relative molecular mass?
add together the relative atomic masses of the elements making up a molecule
what is relative molecular mass used for?
small molecules, eg. water
what is relative formula mass?
compares the mass of a formula unit with the mass of an atom of carbon-12
how do you calculate relative formula mass?
add together the relative atomic masses of the elements in the empirical formula
what is relative formula mass used for?
giant structures, eg. NaCl
what is analysis?
investigating the chemical composition of a substance
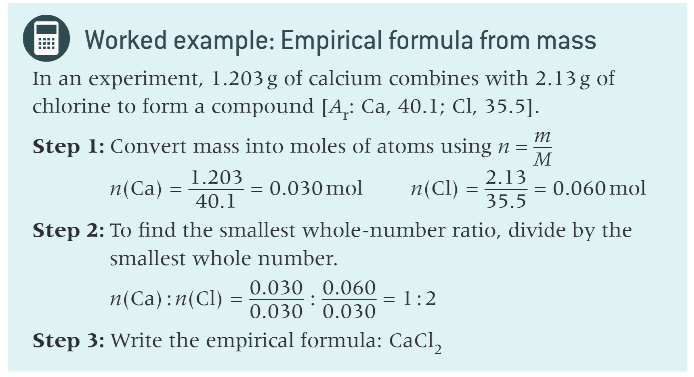
how do you work out empirical formula from mass with example?
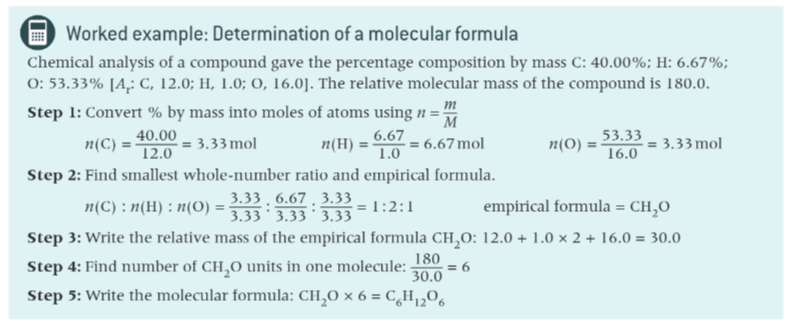
how to work out molecular formula with example?
why are many coloured crystals hydrated?
water molecules are part of their crystalline structure
what is this water known as?
water of crystallisation
eg. what happens when blue crystals of hydrated copper 2 sulfate are heated?
bonds holding the water within the crystal are broken and the water is driven off, leaving behind white anhydrous copper 2 sulfate
equation for this?

method for how to carry out an experiment to determine the waterof crystallisation in hydrated crystals?
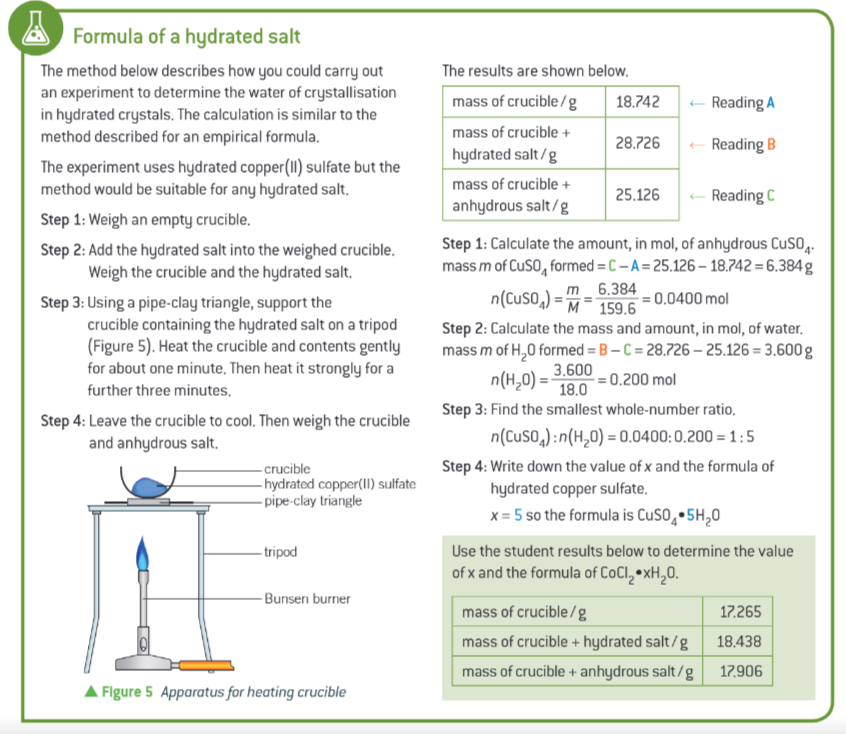
how accurate is an experimental formula?
not very accurate as some assumptions could be made:
all the water has been lost
no further decomposition
all the water has been lost explained
you may think all the water has been removed if the colour changes when heated but it actually hasnt fully, and water could still be there. a good solution is to continue heating until constant mass, suggesting all the water is removed
no further decomposition explained
many salts decompose further when heated, so might change formula. eg. when heated strongly copper sulfate decomposes to form black copper oxide
how are liquids and gases measured?
by volume
how many cm³ are in 1ml?
1cm³
how many cm³ are in 1dm³ and 1l?
1000cm³
what is a solute?
a dissolved compound
what is the concentration of a solution?
the amount of solute in moles dissolved in each 1dm³ of solution
what does a 1moldm-3 solution contain?
1 mol of solute dissolved in each 1dm³ of solution
concentration =?
moles / volume
examples using this equation?

what is a standard solution?
a solution of known concentration, prepared by dissolving an exact mass of the solute in a solvent and making up the solution to an exact volume
example of working out the mass required to prepare a standard solution?
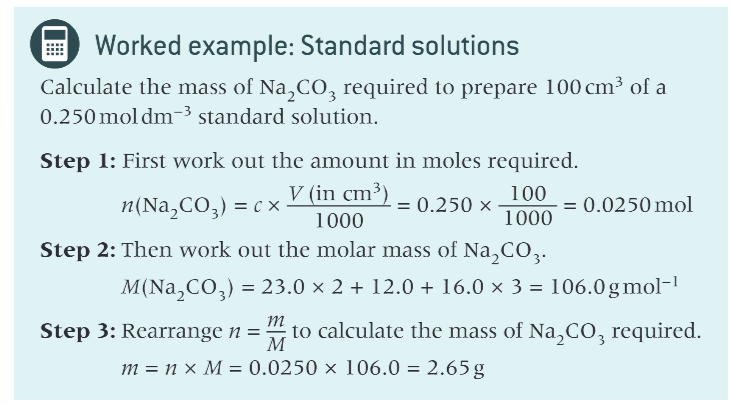
what are some other units that can be used for concentration?
gdm-3
how do you convert moldm-3 to gdm-3?
convert between moles and grams using the equation : moles =mass/Mr
at the same temp and pressure…
equal volumes of different gases contain the same number of molecules
what is molar gas volume? (Vm)
the volume per mole of gas molecules at a stated temp and pressure
what does the volume of a gas depend on?
the pressure and temp, but many experiments are carried out at RTP
what is RTP?
20 degrees C and 101kPa (1atm)
at RTP…
1 mole of gas molecules has a volume of 24dm³
at RTP, molar gas volume =?
24dmmol-1
volume of gas =?
moles x molar gas volume (24dm³)
worked example for this equation?
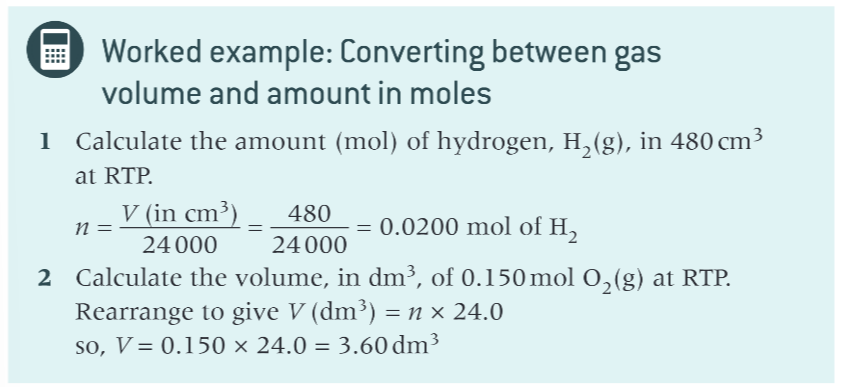
what is the ideal gas equation?
an equation when you are using diff temps and pressures of gases
what assumptions will you come across for the molecules making up an ideal gas?
random motion
elastic collisions
negligible size
no intermolecular forces
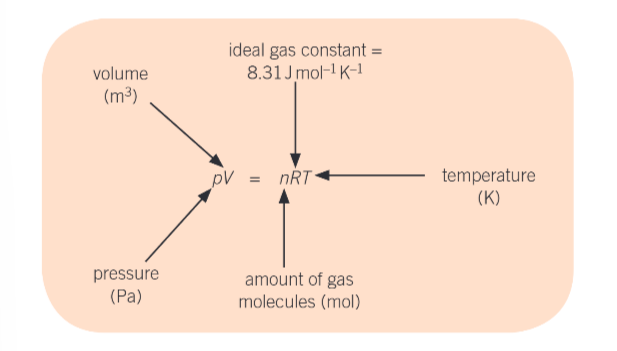
what is the ideal gas equation?
pV = nRT
what is R?
constant
what value is R always?
8.314Jmol-1K-1
what is temp measured in?
Kelvin
how do you convert degrees C to kelvin?
+273
each rise in 1K is…
the same as 1degree rise
units for all of the gas equation?
how to convert cm³ to m³
x 10-6
how to convert from dm³ to m³
x10-3
how to convert from kPa to Pa
x 1000
worked example using equation?
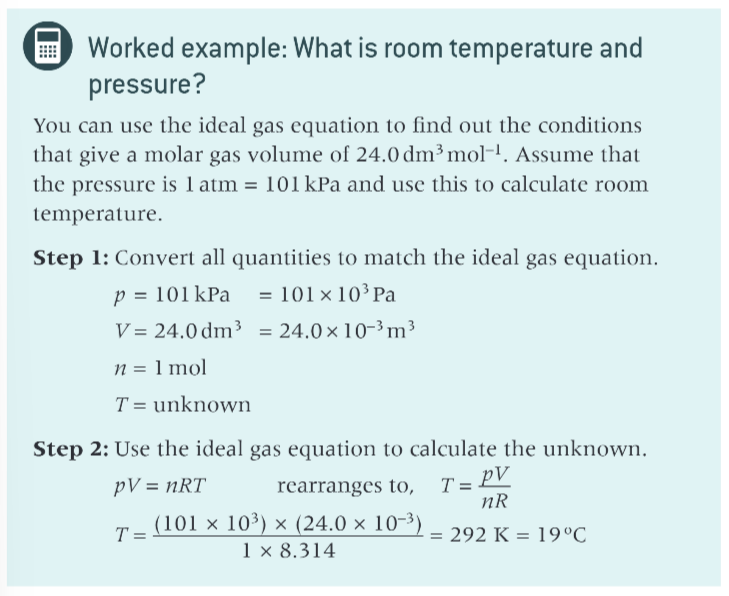
what is the incorrect assumption?
that 25 degrees C is room temp
how to do the method to get the results needed to find relative molecular mass?
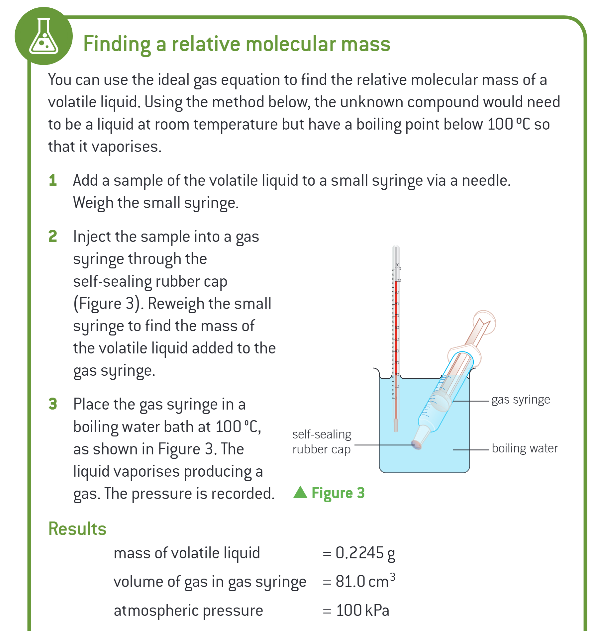
how to use the results to find relative molecular mass?

what 2 assumptions does the ideal gas equation rely on?
forces between molecules are negligible
gas molecules have negligible size compared to the size of their container
when are these assumptions right?
when there are low pressures and high temps when the gas molecules are far apart and moving fast
what is the case when gas molecules are close together?
the volume of the molecules compared with the volume of the container start to become significant
what is the case if the gas molecules are moving slower?
they has less energy and intermolecular forces may become significant
what has then happened?
there have been improvements of the ideal gas equation for real gases
what is this equation?
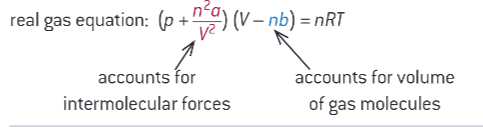
what is stoichiometry?
the ratio of the amount, in moles, of each substance in a balanced equation
what do chemists use balanced equations to find?
the quantities of reactants required to prepare a required quantity of a product
the quantities of products that should be formed from certain quantities of reactants
what is the basic method for working out unknown information about a substance?
work out the amount in moles of whatever possible
use the equation to work out the amount in moles of the unknown chemical
work out the unknown info required
worked example with this method: reacting masses

worked example with this method: reacting mass, gas volumes, and concentration

steps for an experiment that can be carried out to identify an unknown metal (group 2 metal X)
set up apparatus as shown
weigh a sample of the metal and add to the flask
using a measuring cylinder, add 25cm³ of 1moldm-3 HCl to flask and replace bung
measure the max volume of gas in the syringe
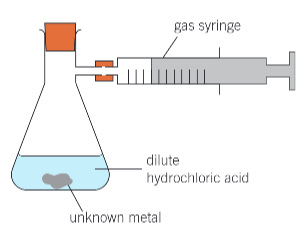
how to identify unknown metal from results?

what is the maximum possible amount of product called?
the theoretical yield
why is the theoretical yield difficult to achieve?
the reaction may not have gone to completion
other reactions may have taken place alongside the main reaction
purification of the product may result in loss of some product
what is the actual yield?
what you actually obtain from a reaction
percentage yield =?
(actual yield/ theoretical yield) x 100
worked example to calculate percentage yield?

what is the limiting reagent?
the reactant that isnt in excess and will be completely used up first and stop the reaction
how can you find out which reaction is in excess?
work out the amount in moles of each reactant and compare with the equation
example using limiting reagents

what is atom economy?
a measure of how well atoms have been utilised
reactions with high atom economies:
produce a large proportion of desired products and few unwanted waste products
are important for sustainability as they make the best use of natural resources
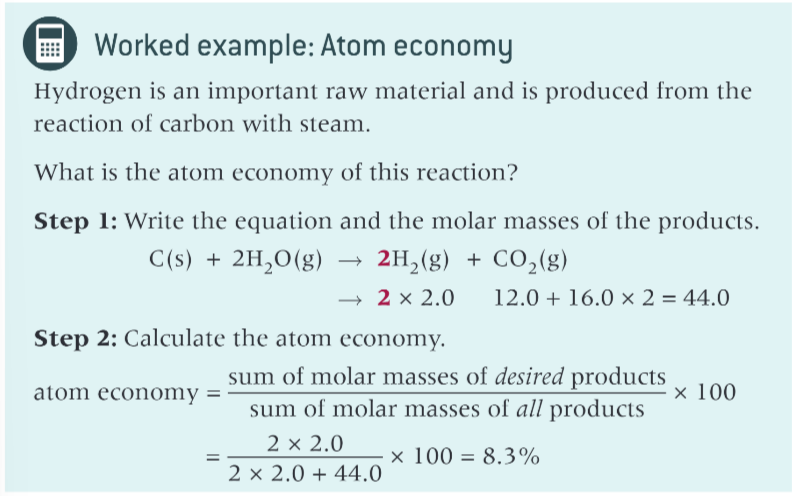
atom economy = ?
(sum of the molar masses of desired products/ sum of molar masses of all products) x 100
what has atom economy been developed from?
awareness of finite resources and environmental concerns
what is good about improving atom economy?
makes industrial processes more efficient, preserves raw materials, and reduces waste
what would ideal atom economy be?
100% (all products are desired)
worked example with atom economy?
what makes a reaction more sustainable?
using reactants that are readily available. energy may be needed to produce some, but costs for obtaining starting materials are low
what does efficiency and sustainability depend on?
both atom economy and % yield
can one be high and one low?
yes