Chapter 17: Short-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Keynesian Cross Model Assumptions
Short-run focussed
AD is the primary driver of economic activity
prices are assumed as fixed
MPC (marginal propensity to consume)
the proportion of any increase in income that is spent on consumption
MPW (marginal propensity to withdraw)
the proportion of any increase in income that is withdrawn from the circular flow
national income will rise
if aggregate expenditure exceeds national income
national income will fall
if national income exceeds aggregate expenditure
Y = E (and W + J)
equilibrium national income
Y (national income)
represents the total income generated in the economy (Cd + W)
AD (aggregate demand)
represents the total demand for goods and services in the economy
Multiplier effect
occurs when an initial injection into the economy causes a bigger final increase in national income
multiplier (K)
Change in real GDP (Y)/ Change in Injections (J)
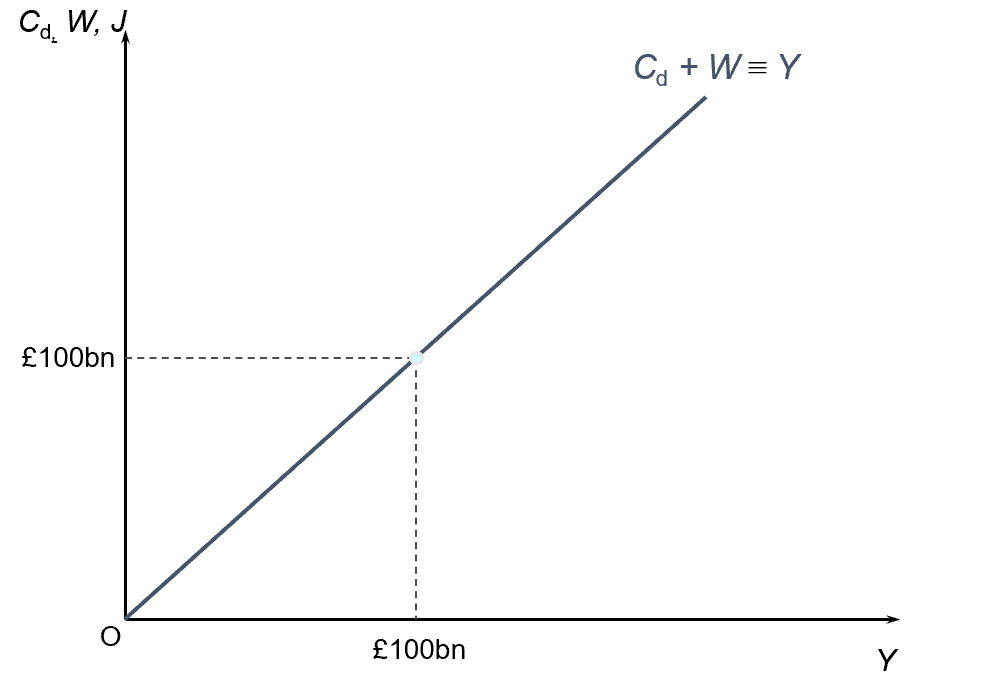
Keynesian Cross Model
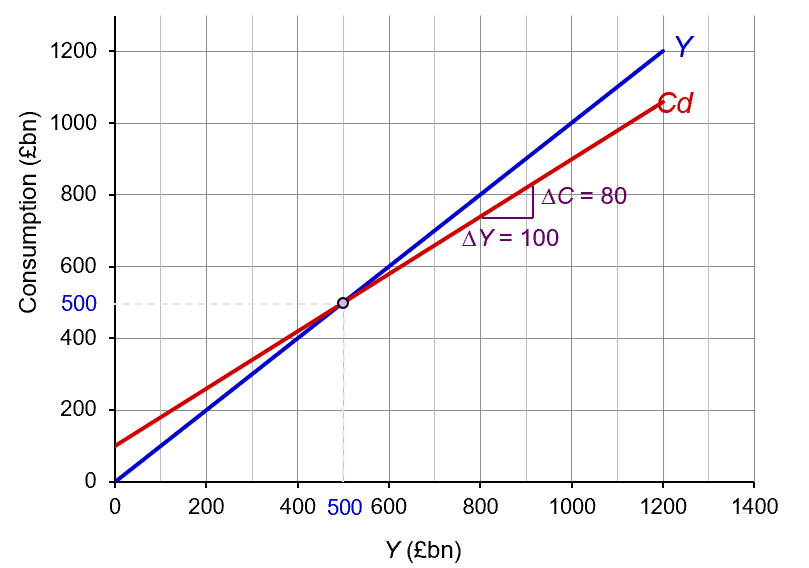
the consumption function
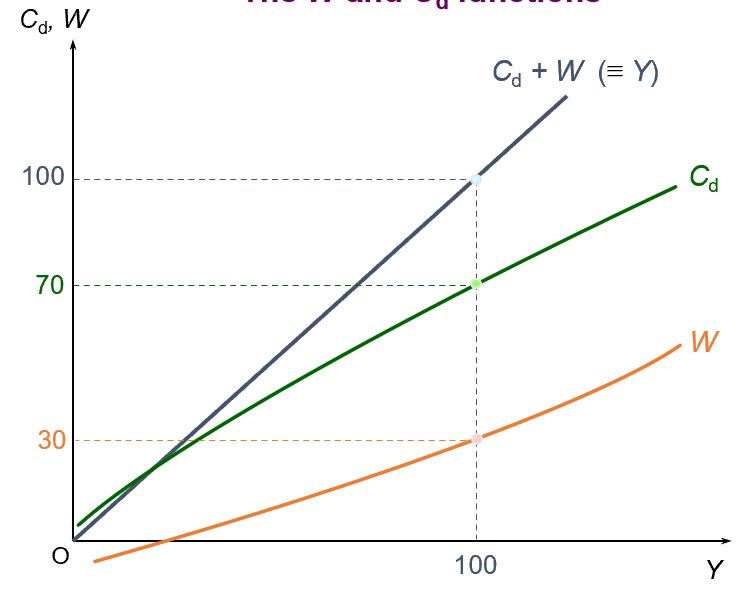
the withdrawals and Domestic Consumption Function
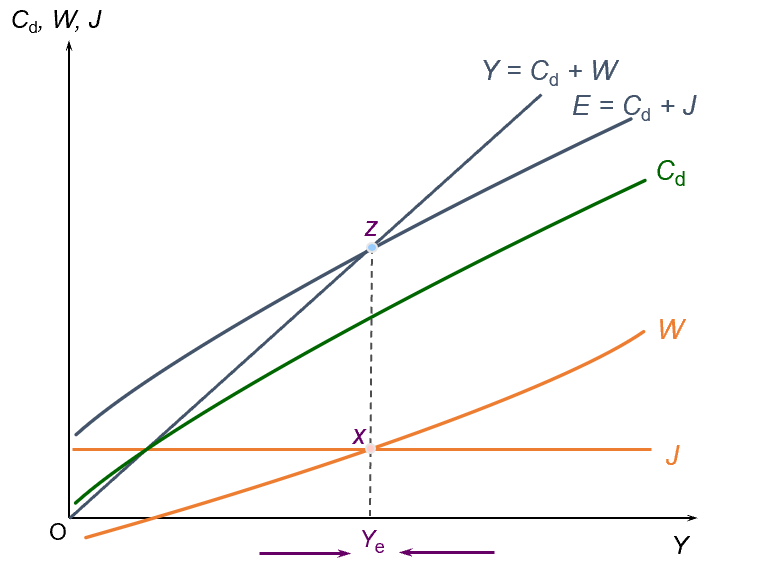
Equilibrium national income
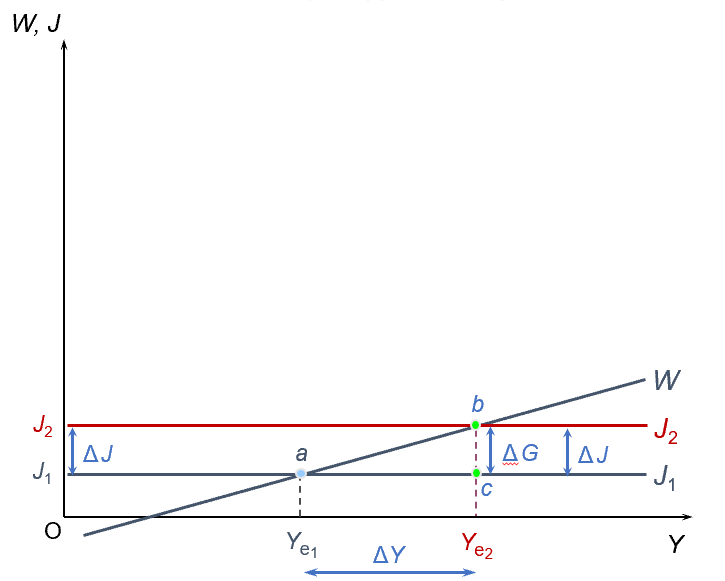
the multiplier; a shift in injections
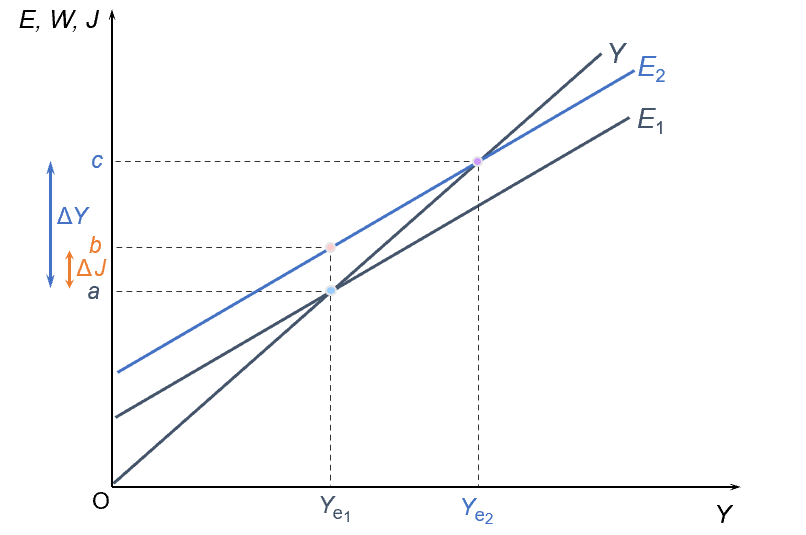
the multiplier; shift in expenditure
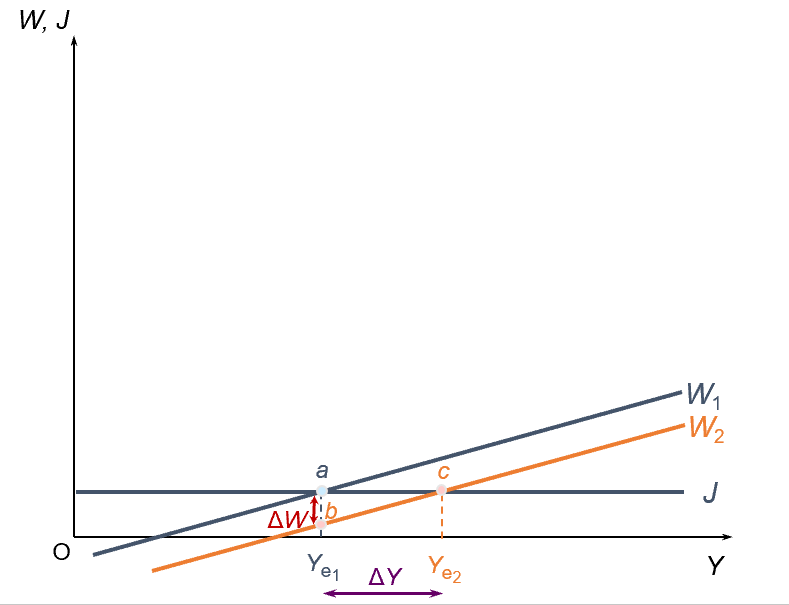
the multiplier; a shift in withdrawal
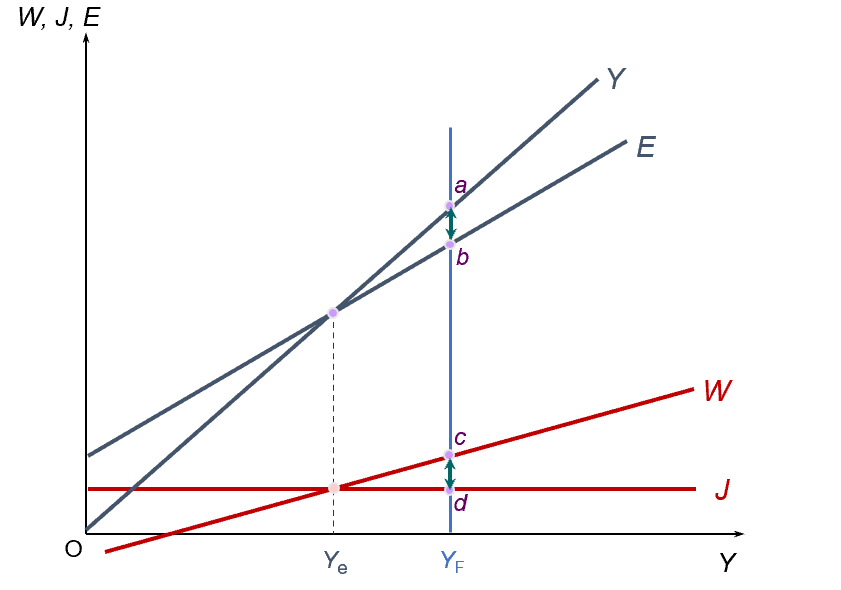
deflationary (recessionary) gap
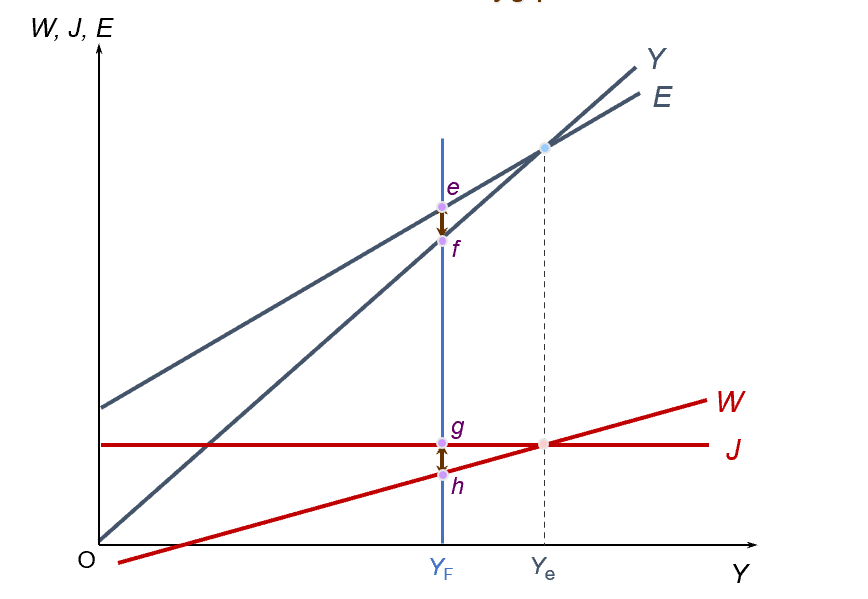
inflationary gap