Introduction to Immunohematology
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Blood group system
Group of antigens determined by a single gene or two closely linked genes
Phenotype vs genotype (define + testing style)
Phenotype: physical expression → determined by serological testing (heme-agglutination)
Genotype: genetic makeup → DNA/molecular testing
Clinically significant vs clinically insignificant RBC antibodies
Clinically significant: abs that cause immune destruction of transfused RBCs
React at 37 °C; mostly IgG
Clinically insignificant: abs that usually do not destroy transfused RBCs
React at 4 °C; mostly IgM
**except ABO abs
Allogeneic
Autologous
Allogeneic: transplants that are genetically different
Autologous: transplants originate from self
In Vivo
alloantibody production + re-exposure
Extravascular vs intravascular RBC destruction
Alloantibody production - exposure to foreign (allo)antigens
Transfusion
Transplantation
Pregnancy
Re-exposure leads to hemolysis
Complement
Ab/Ag complex clearance
Extravascular
IgG
Phagocytes in liver and spleen destroy RBCs
Intravascular
IgM
Activation of complement in vessels destroys RBCs
In Vitro
testing principles
Agglutination (hemagglutination)
Sensitization + lattice formation
Hemolysis
Dosage effect
Antithetical
Dosage effect: phenomenon where Ab reacts with RBC carrying double dose (homozygous) of ag over RBC carrying single dose (heterozygous)
Antithetical: antigens that are products of allelic genes
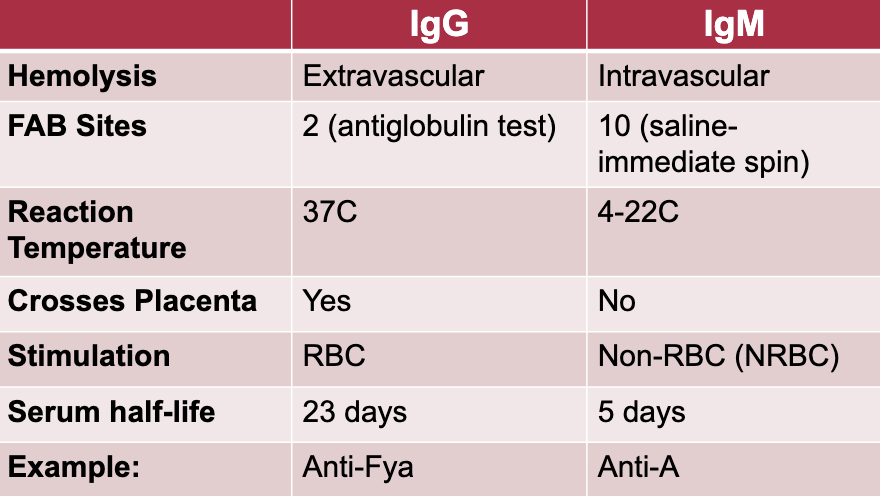
IgG vs IgM
Hemolysis, FAB sites, reaction temp, crosses placenta?, stimulation, serum half-life
Aggluation factors
zeta potential:
significance?
pH
best for testing?
hemolyzed plasma pH?
length of incubation
why?
agglutination
methods
Zeta potential: what is it?
Reduce electrical repulsion to get RBC together for agglutination via enhancement media/potentiators (usually IgG in IAT)
pH
Best for testing: 6.5 to 7.0
Hemolyzed plasma has pH 7.4
Some abs react better at lower pH
Centrifugation
Facilitates lattice formation
Length of incubation
Time for ab-ag complex formation
Agglutination
Tube (common)
Column agglutination (gel)
Solid phase