Unit 5: Evolution and Biodiversity
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5.3 Classification, 5.4 Cladistics, 1.1 origin of cells, 1.2 cell structure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Binomial System
first name is “Genus”, second name is “species”; italicised. Earliest published name is correct, may be abbreviated to “G. species”.
Classification conventions for eukaryota
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → class → order → family → genus → species
Eukaryota
One of the three domains: cells with a membrane-bound nucleus
Prokaryota (Eubacteria)
One of the three domains: unicellular without a membrane-bound nucleus. High degrees of organisation. Bacterias.
Prokaryota (Archaea)
One of the three domains: unicellular without a membrane-bound nucleus. Can survive in harsh conditions. Oldest form of life.
Kingdoms
plants, animals, fungi, protocista
Natural Classification
Classified based on evolving from the same ancestor. Advantages:
systematic identification of species
prediction of characteristics in future
DNA/amino acid sequencing > morphology (physical traits)
Unnatural Classification
based on shared characteristics. However, two genetically unrelated species may share the same trait (eg flight) through Convergent Evolution.
Convergent Evolution
genetically unrelated organisms evolve similar “analogous” structures, traits or habits.
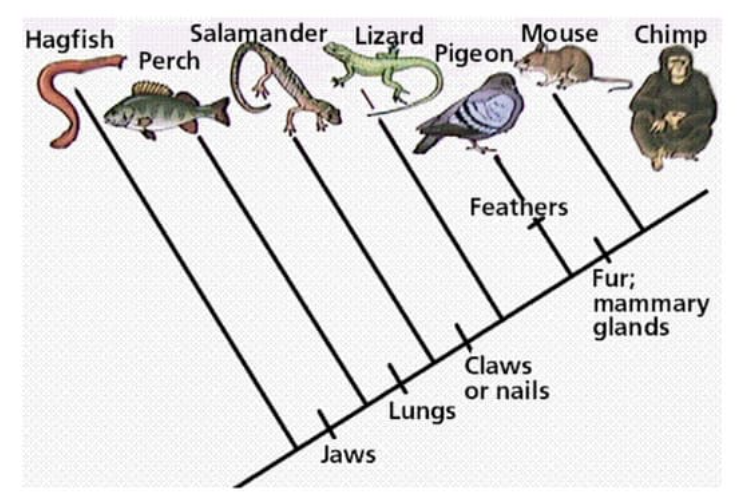
Clade
group of organisms that have evolved from a common ancestor
“Molecular Clocks”
as mutations occur at a relatively consistent rate, the number of mutations can serve as a timer as to when two species diverged.
Homologous traits
similar due to linked ancestry
Analogous traits
similar because of convergent evolution and not ancestry
Cladograms
tree diagram that indicates species in a clade
principle of parsimony: computer programs map evolution through DNA/Amino acid changes
Nodes: branching points in diagram
Characteristics of life
MR H. GREN
Metabolism, Response, Homeostasis, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition
Electron microscopes
scanning: 2d photo
transmission: 3d video
Cell theory
cells only arise from preexisting cells
all living things have 1 or more cells
cell is the smallest unit of life
Exceptions to cell theory
striated muscle cells, giant algae, aseptate hypha, the first life
Paramecium
Example of life: cell blob
M: enzymes in cytoplasm
R: cilia moves cell
H: contractile vacuoles
G: grows
R: asexual and sexual
E: membrane diffusion
N: ingest and digest
c. elegans
Example of life: worm
M: diffusion and gas exchange
R: moves on touch
H: intestine
G: during larval stage
R: asexual and sexual
E: secretary gland
N: eat bacteria
Abiogenesis
1950s Miller-Urey experiment replicated conditions of early atmosphere with heat and lightning. first lifeforms which arose from the primordial soup were simple organisms that gradually became more complex throughout aeons. Life didn’t just spawn in.
Panspermia Hypothesis
first biomolecules arrived on an asteroid from space.
Ecological locations for life
Hydrothermal vents provide heat and nutrients for first tidal pool life to form.
Magnification
degree to which size of image is larger than og thing eg zoom
Resolution
Degree to which one can distinguish between two very close objects eg pixels
Conversion
metres (x/1000) millimetres (x/1000) micrometers (x/1000) nanometres
image size = actual size x magnification

Cell differentiation
all cells contain all instructions to make any cell. triggered on and off through supercoiling (DNA cant replicate if it is coiled). acetylation uncoils DNA while removing acetyl groups supercoils it around histone proteins.
stem cells
can self replicated, not fully differentiated (embryonic, adult bone marrow). totipotent > pluripotent > multipotent > unipotent
Sources of stem cells (pros and cons)
embryonic
many stem cells, toti/pluripotent, regulated
rejection for transplants, embryo destroyed
umbilical cord
embryo unharmed,
limited doses, hereditary disorders, storage, slow to graft
adult
less likely to be rejected for transplants, regulated, differentiation
rarely pluri/totipotent, harvest from live human
induced pluripotent stem cells
adult stem cells genetically reprogrammed into embryonic stem cell, unlimited
very new untested technology
binary fission
cellular division for prokaryotes
prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
prokaryotes: 1x circular DNA, no histones, no organelles, smaller
eukaryotes: linear chromosomes, histone-bound proteins, organelles, bigger
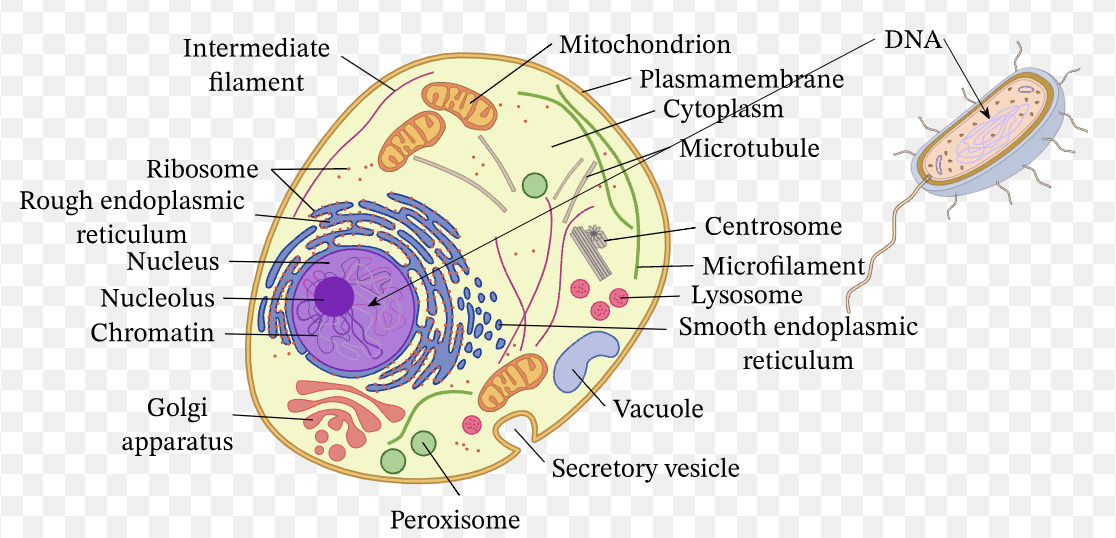
Eukaryotic cell
membrane, nucleus (double membrane), nucleolus, ribosomes, mitochondria, golgi apparatus, vesicles, cytoplasm, rough/smooth endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, vacuole, centriole, lysosomes
plants vs animals
plants: cell wall + membrane, chlorophyll + chloroplasts, large vacuole, form a grid in mitosis
animals: cell membrane, no chlorophyll, small vacuole, completely separate in mitosis.
Plant phyla
angiophyta- flowering
coniferophyta- pines/ cones
bryophyta- mosses/ liverworts
filocinophyta- ferns
Animal Phyla
chordata- vertebrates, bilateral symmetry
arthropoda- exoskeletons, many legs
porifera- sponges, no symmetry
annelida- round worms, segments
mollusca- shell, muscle foot, no segments
platyhelminthes- flat worms
cnaidaria- jellyfish, radial symmetry
echinodermata- sea star, invertebrates with spines
Evolution
a change in the frequencies of alleles within a gene pool over time. heritable characteristics = coded for by DNA
Theory of Natural Selection
individuals best adapted to an environment survive to reproduce a greater number of offspring. thus, favourable heritable characteristics are passed on in higher proportion.
variation
caused by mutation, meiosis (crossing over possibilities) and sexual reproduction
overproduction
Producing more offspring than is viable to ensure that all available resources are used- any leftover offspring die off. Fosters competition, variation, probability of survival. [ex: nazca boobies 2 offspring kane and abel]
mutations
silent- no change in amino acids
missense- change in amino acids
nonsense- change in base DNA codes for a stop (partial translation, often fatal)
variations cannot be passed on if acquired during lifetime.
adaptations
physical, physiological, behavioural
linear VS adaptive radiation
change from one trait to another VS multiple variations of a trait from a base one
Process of Natural Selection
heritable variation
overpopulation
selective pressures
favourable alleles survive to reproduce
over time favourable alleles more common
Evidence for evolution
fossils
embryology
homologous structures
artificial selection as a proxy
biogeography
biochemistry
Stabilising selection
selection gravitates towards one “average” better trait
directional selection
selection moves in one direction favouring one kind of trait
disruptive selection
selection favours two extremes and average is phased out
Process of speciation
natural selection → divergent evolution → speciation → species
Species
organisms that can interbreed to produce viable offspring
hybrid
an infertile mixture between two species