Gamatogenesis
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/198
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:41 PM on 2/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
1
New cards
Embryology
* studies the prenatal development of gametes, fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses
2
New cards
What does the human development process include (3)…
* gene regulation
* differentiation
* morphogenesis
* differentiation
* morphogenesis
3
New cards
Cellular events associated with developmental processes are (6)
* cell division
* cell migration
* cell rearrangement
* differentiation
* programmed cell death
* growth
* cell migration
* cell rearrangement
* differentiation
* programmed cell death
* growth
4
New cards
Stages in ontogenetic development (5)
1. Gametogenesis
2. Fertilization
3. Cleavage
4. Morphogenesis
a. Cell and tissue differentiation
b. Pattern and polarity
5. Growth and maturation
5
New cards
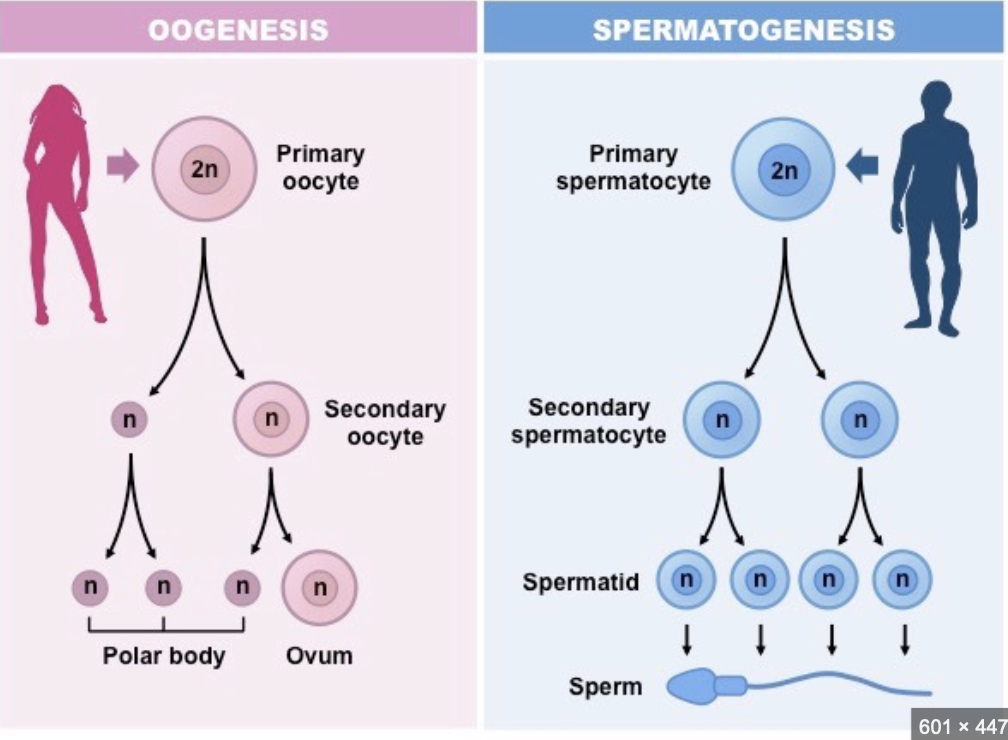
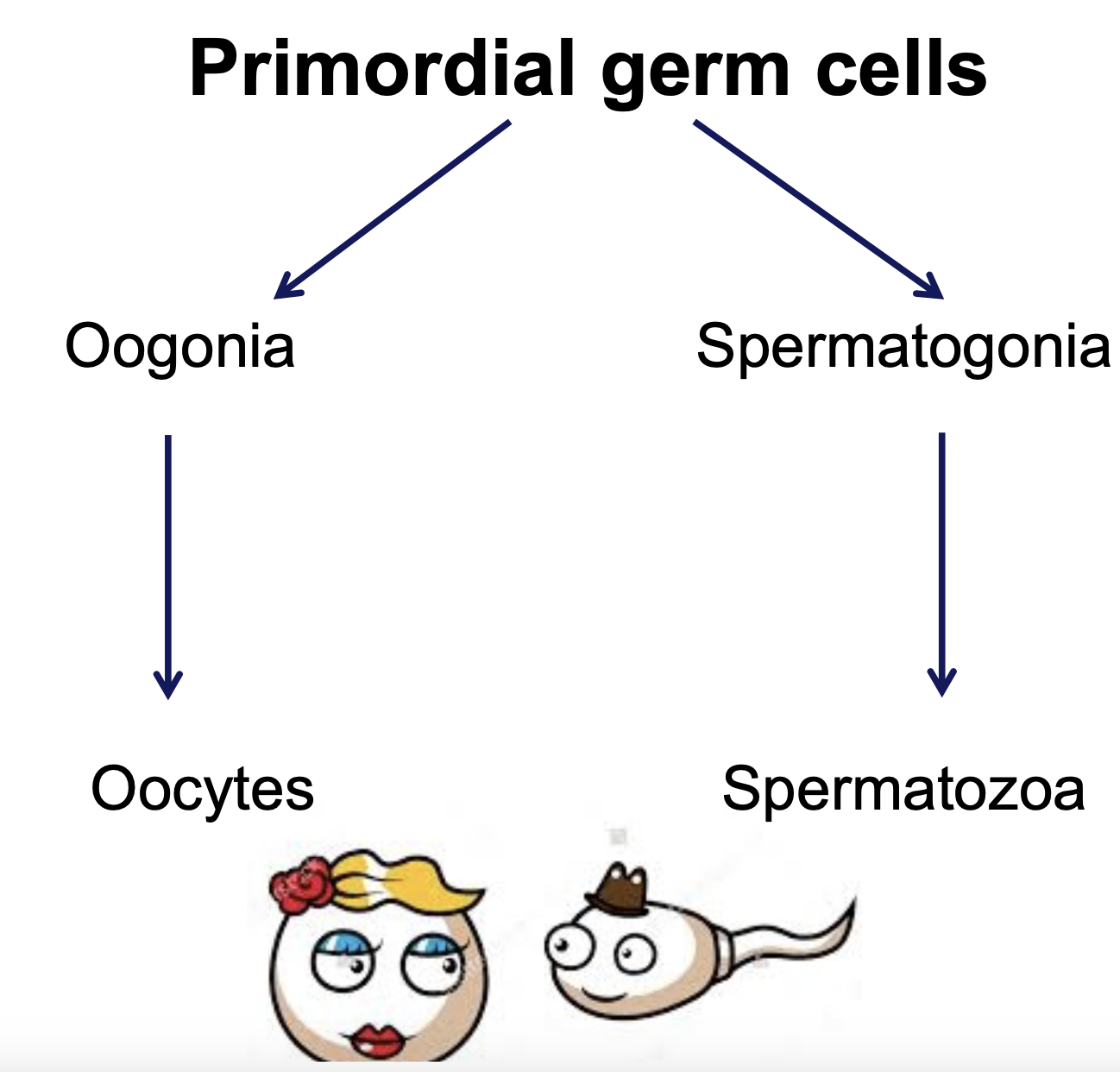
Gametogenesis
* The formation of mature eggs and sperm (aka gametes)
* 1N = haploid
* 1N = haploid
6
New cards
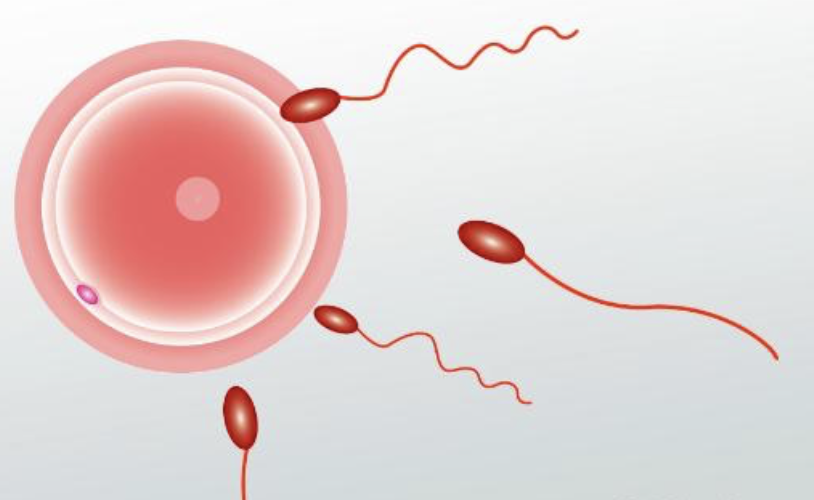
Fertilization
* Fusing of sperm and egg to for a zygote
* 2N = diploid
* 2N = diploid
7
New cards
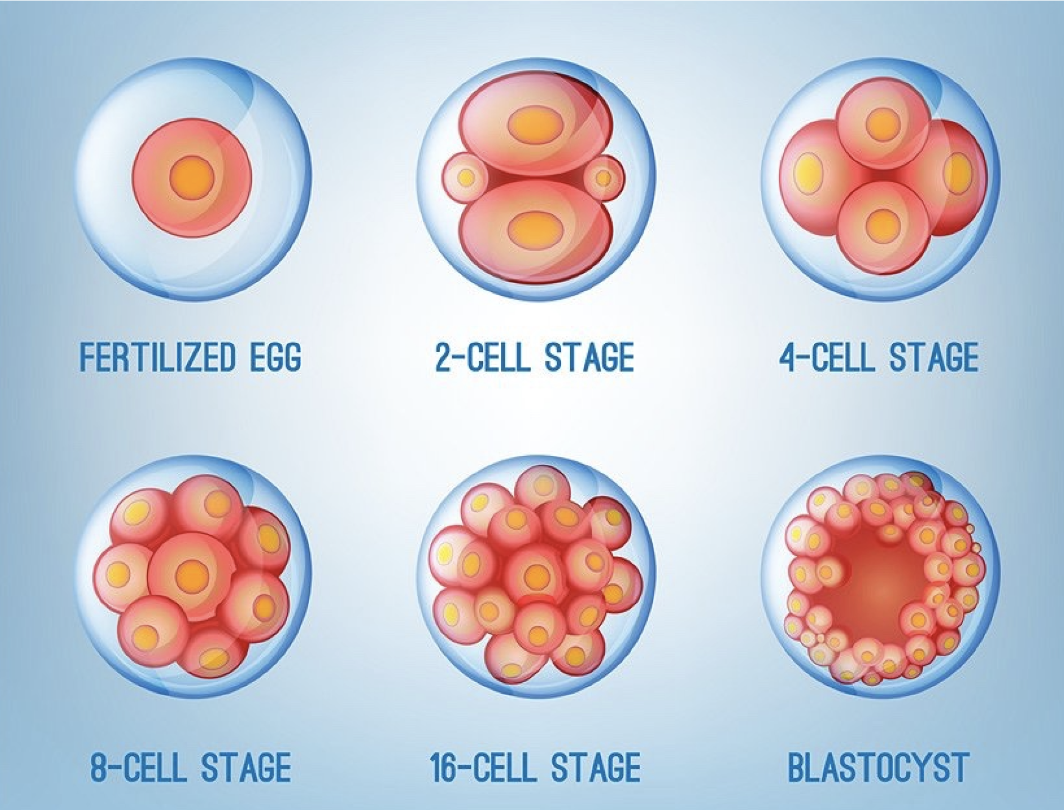
Cleavage
* Rapid mitotic cell division divisions of zygote (early embryo) to form the multicellular embryo (blastula)
8
New cards
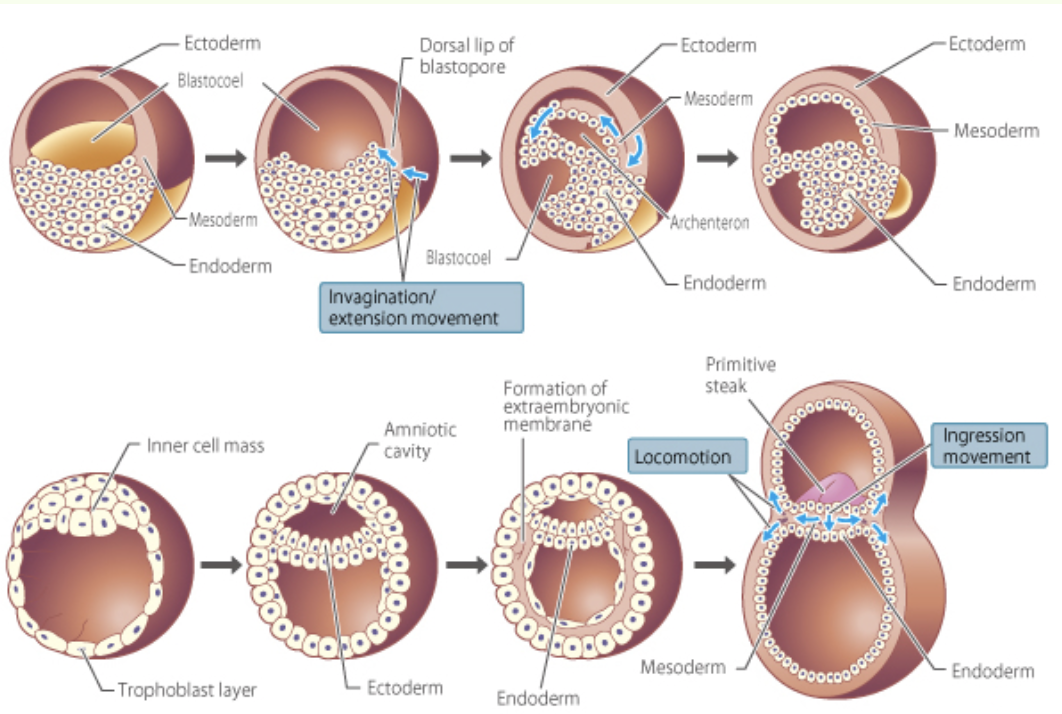
Morphogenesis
* ‘genesis of shape’
* gastrulation and neurulation that form initial primary germ layers + organogenesis
* gastrulation and neurulation that form initial primary germ layers + organogenesis
9
New cards
Cell and Tissue Diifferentiation
* Cellular interactions that regulate gene activity and lead to specialized cell types
10
New cards
Pattern and Polarity
* The development of tissues and organs is a reflection of having symmetry
11
New cards
Growth and maturation
* The fetus grows as development continues, which persists throught the life process
12
New cards
The most critical stage of development occurs during the __ trimester
1st
13
New cards
PGC translates to
primordial germ cells
14
New cards
What are the 4 phases of gametogenesis
1. __origin__ outside the embryo of PGCs and their __migration__ to the gonads
2. increase in # of PGCs by __mitosis__
3. a reduction of chromosomal material by __meiosis__
4. Structural and functional __maturation__ of gametes (oogenesis, spermatogenesis)
15
New cards
Which phase of gametogenesis is identical in males and females
first phase
16
New cards
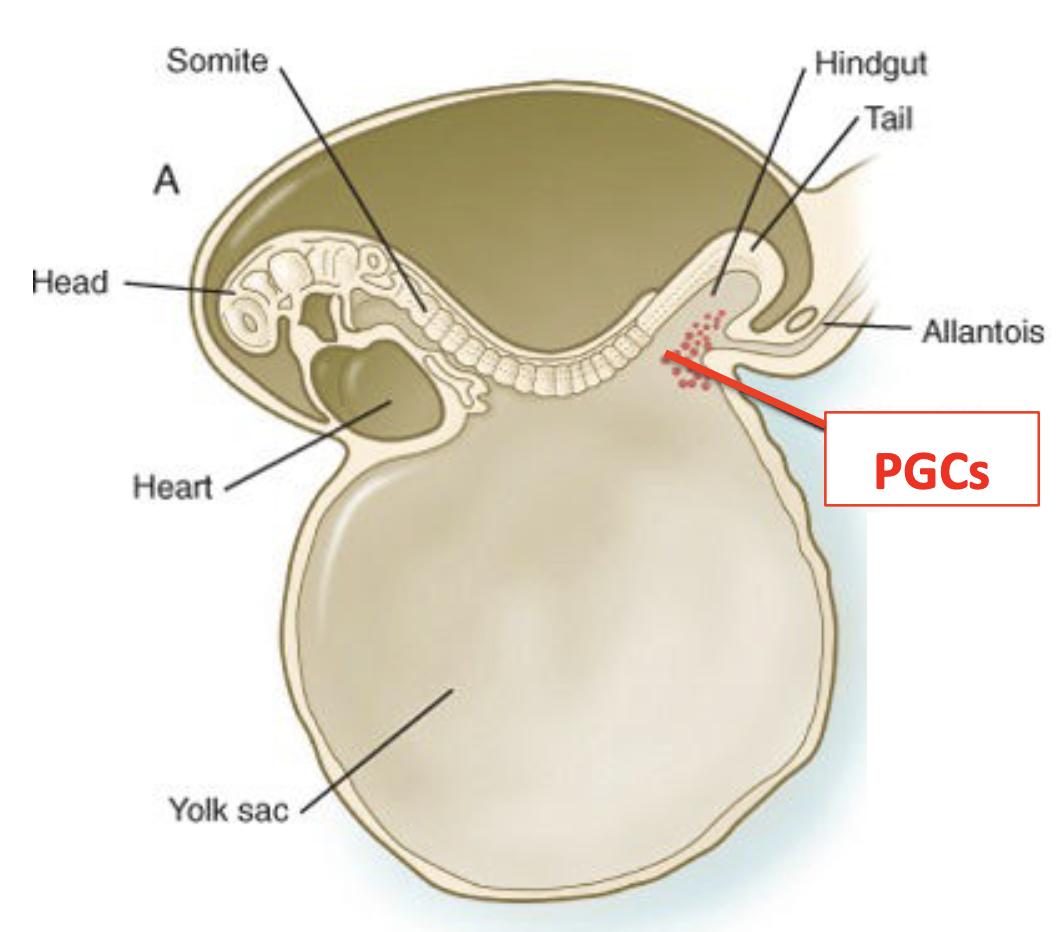
PGCs
* earliest recognizable precursors of gametes
* appears outside the gonads
* migrates to gonads during early embryonic development
* appears outside the gonads
* migrates to gonads during early embryonic development
17
New cards
PGCs are first recognizable how many days after fertilization
24 days
* set aside in the endodermal layer of the yolk sac (high glycogen and alkaline phosphatase content
* set aside in the endodermal layer of the yolk sac (high glycogen and alkaline phosphatase content
18
New cards
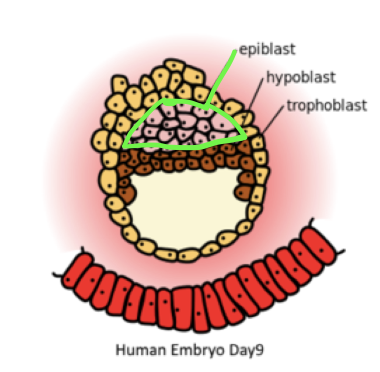
Phase 1 : Origin of PGCs
* in the epiblast prior to gastrulation
* requires inductive signalling
* moved to a yolk sac where they’re determined
* PGCs re-enter the embryo and migrate to the developing gonads
* requires inductive signalling
* moved to a yolk sac where they’re determined
* PGCs re-enter the embryo and migrate to the developing gonads
19
New cards
Genital ridges
* The one way street where PGCs travel to develop into future gonads
20
New cards
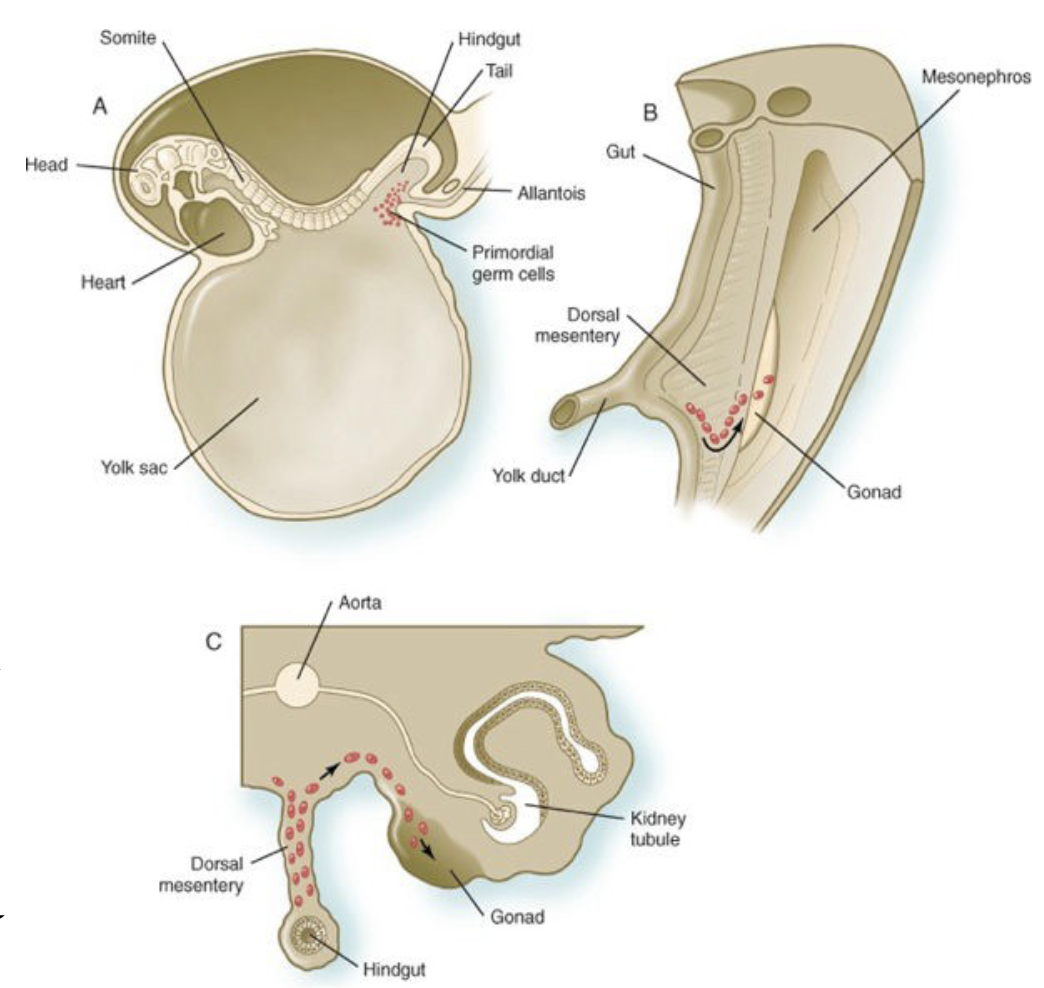
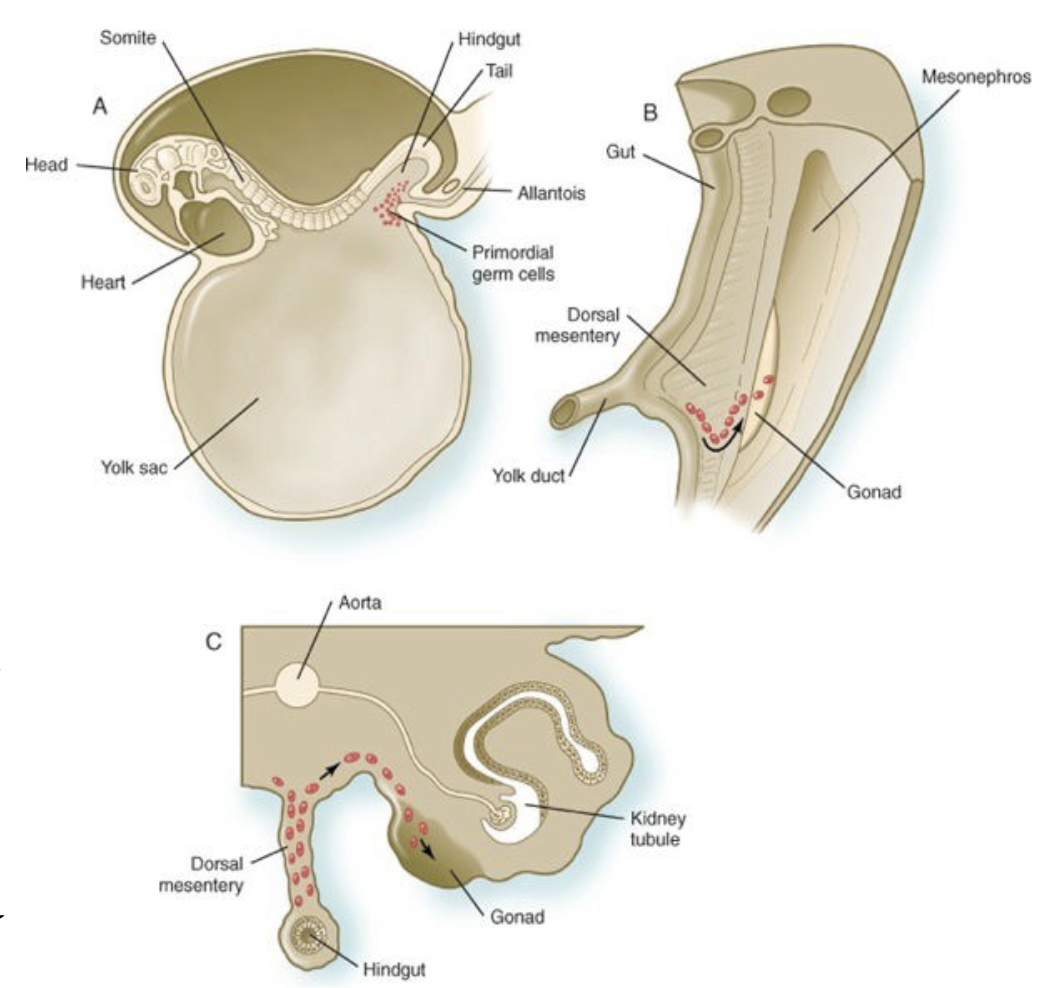
Phase 1: The arduous journey (brief)
* b/w 4-6 weeks in the PGCs
* exit the yolk sac
* enter the hindgut epithelium
* migrate through the dorsal mesentery
* Til they reach the primordial of the gonads
* exit the yolk sac
* enter the hindgut epithelium
* migrate through the dorsal mesentery
* Til they reach the primordial of the gonads
21
New cards
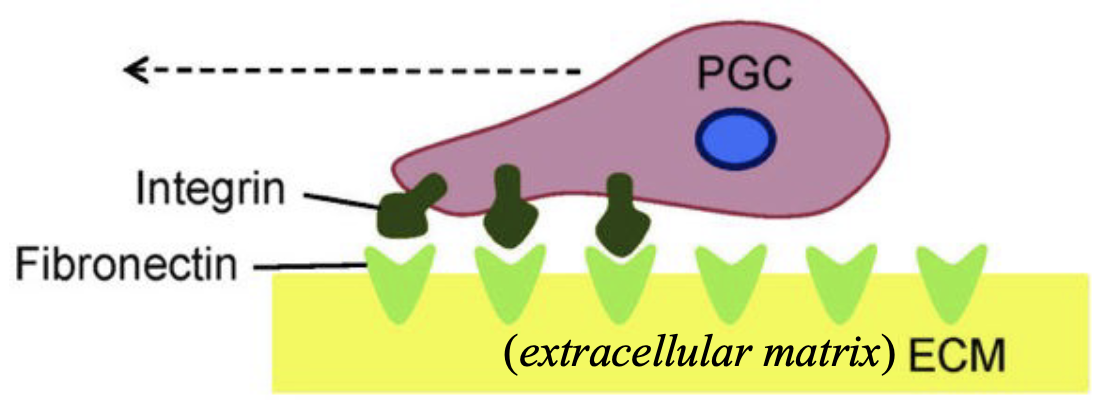
How do PGCs migrate and know where to go?
1. Amoeboid (Amoeba crawl-like) movement during inital migration
2. Cytoplasmic processes link adjacent PGCs
3. Chemoattractants secreted by genital ridges
4. Migration by extending pseudopod (integral-fibronectin interactions)
5. Follow extracellular matrix “roadways lined with fibronectin
22
New cards
What are integrins important for?
PGC movement
23
New cards
Teratoma
* benign tumours/growth
* when PGC don’t reach where they’re supposed to go
* when PGC don’t reach where they’re supposed to go
24
New cards
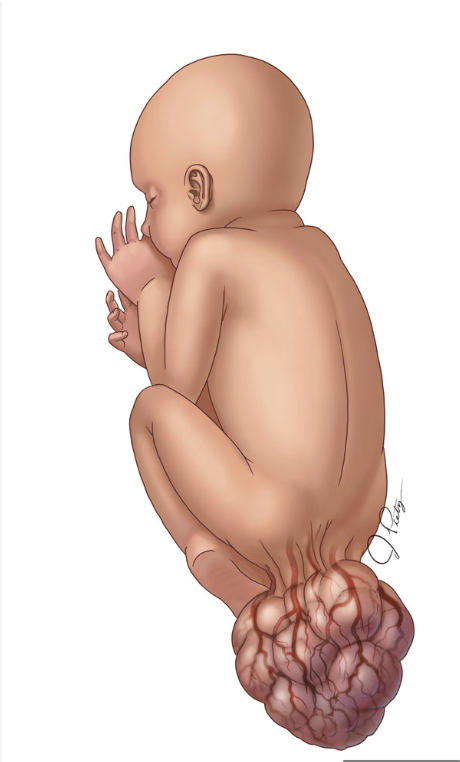
What is a sacrococcygeal teratoma (SCT)
* unusual tumor in the newborn located at the base of the tailbone (coccyx)
* more common in females than males
* very large, but not malignant
* cured by surgery after birth
* more common in females than males
* very large, but not malignant
* cured by surgery after birth
25
New cards
What are oropharyngeal teratomas
* Extremely rare
* associated with high neonatal mortality rate due to severe airway obstruction
* associated with high neonatal mortality rate due to severe airway obstruction
26
New cards
Phase 2: Increase in the number of germ cells by mitosis
* after phase 1 they undergo a series of mitotic divisions
* PGC number increases exponentially to millions
* Oogonia: max # reached during gestation
* Spermatogonia: able to divide postnatally
* PGC number increases exponentially to millions
* Oogonia: max # reached during gestation
* Spermatogonia: able to divide postnatally
27
New cards
Gender differences in germ cell mitosis - females
* oogonia undego an intense period(2nd to 5th month) of mitotic activity in embryonic ovary
* germ cell population 1000s → 7 mil
* Atresia of oogonia begins
* germ cell population 1000s → 7 mil
* Atresia of oogonia begins
28
New cards
Atresia
* the __degeneration__ of ovarian __follicles__ which do not __ovulate__ during the menstrual cycle
29
New cards
Gender differences in germ cell mitosis - males
* mitosis begins early in embryonic testes
* seminiferous tubules lined with germ cells
* beginning at puberty, subpopulations of spermatogonia undergo periodic waves of mitosis
* seminiferous tubules lined with germ cells
* beginning at puberty, subpopulations of spermatogonia undergo periodic waves of mitosis
30
New cards
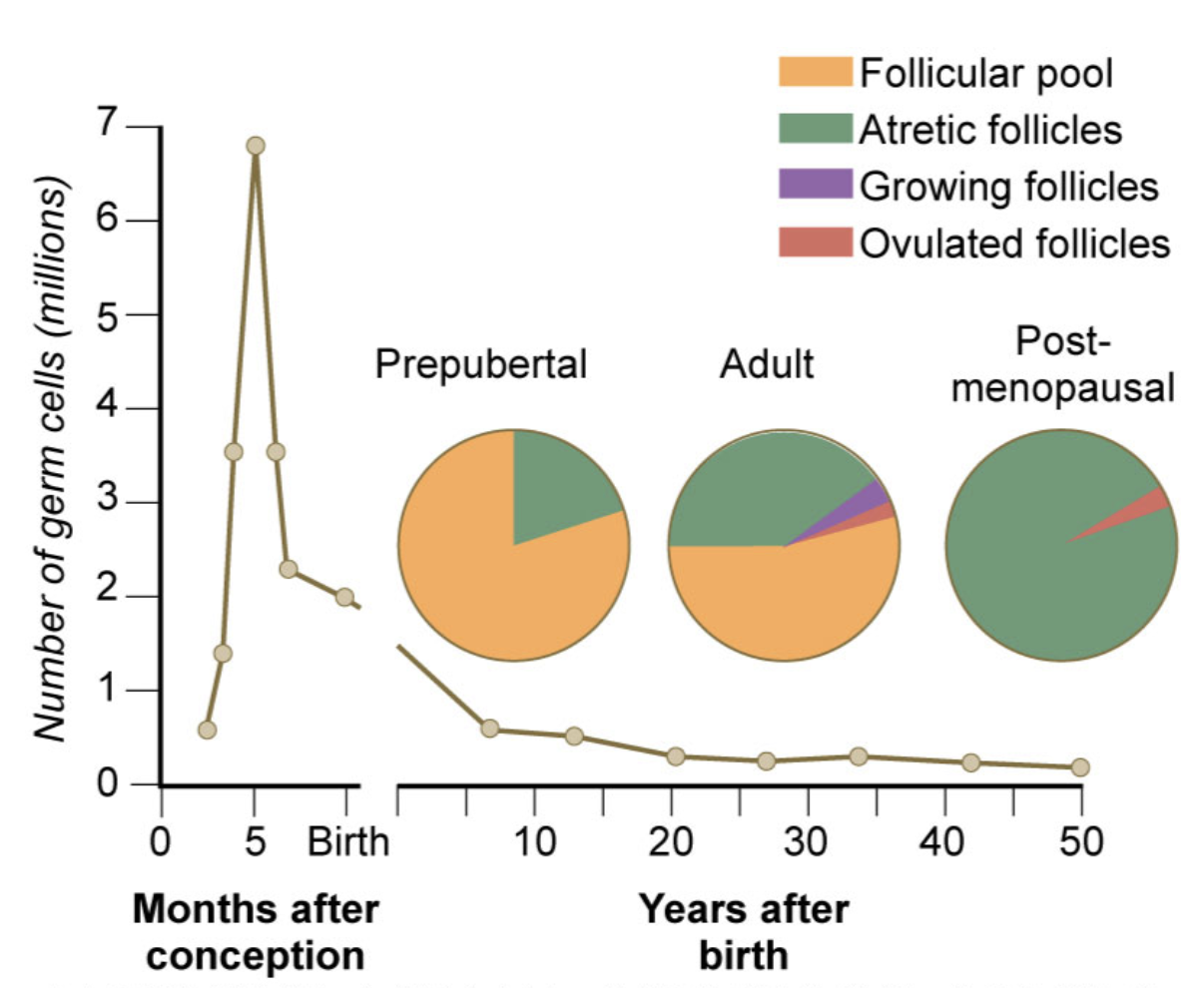
Changes in the number of germ cells in the human ovary with increasing age
\
31
New cards
Phase 3: Reduction in chromosomal number by meiosis
* reduction of number of chromosome from diploid(2N) to haploid (1N)
* independent re-assortment -allows forr better mixing of genetic characteristics
* independent re-assortment -allows forr better mixing of genetic characteristics
32
New cards
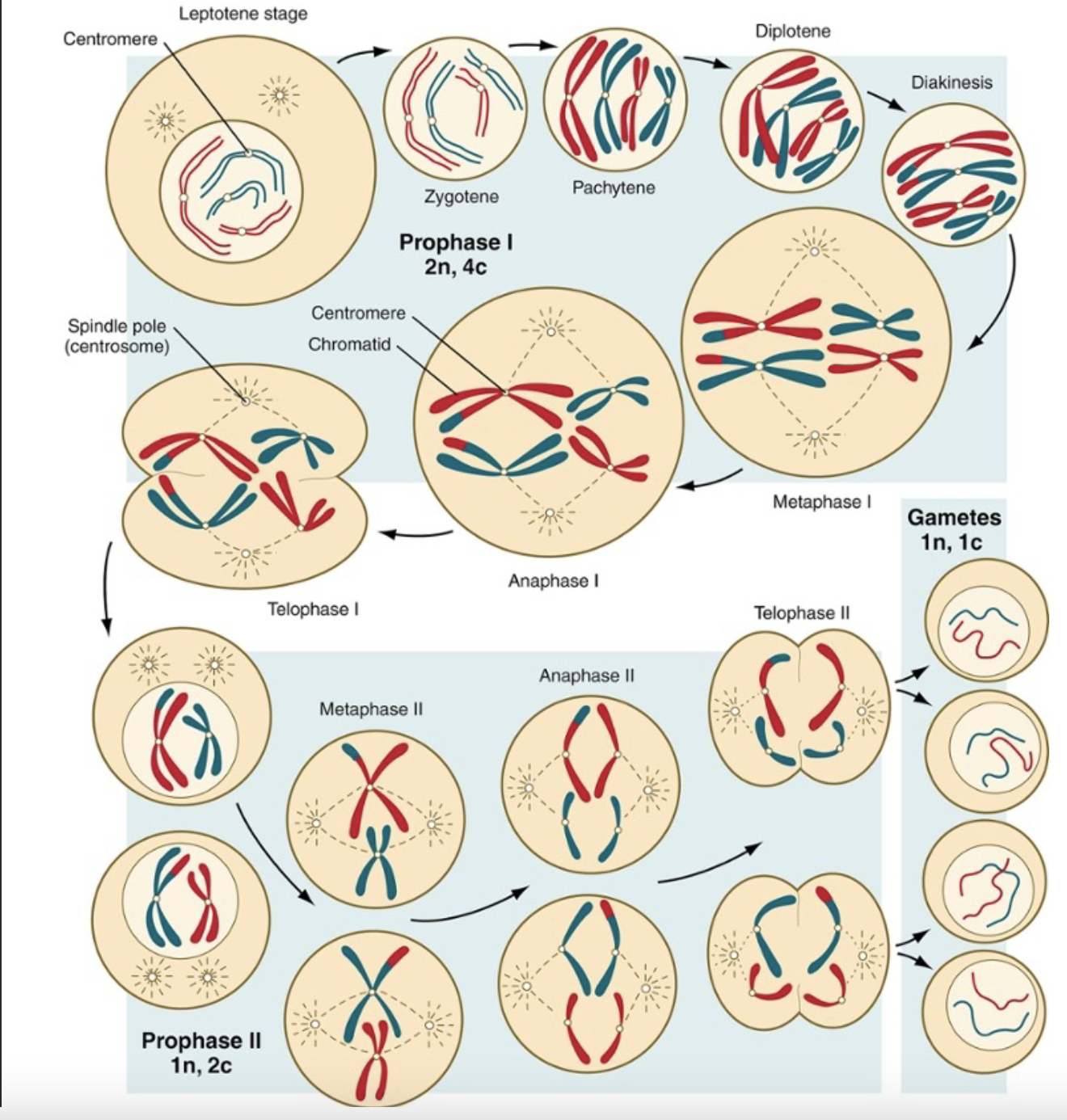
Crossing-Over
* consist of the exchange of segments between the 2 chromosomes during the pachytene stage (3rd stage of the prophase of meiosis)
* occurs also in sex chromosome
* takes place in small region of homology b/w the X and Y chromosomes
* occurs at sites along the chromosomes → hotspots
* occurs also in sex chromosome
* takes place in small region of homology b/w the X and Y chromosomes
* occurs at sites along the chromosomes → hotspots
33
New cards
Cohesin
* holds sister chromatids together during division
34
New cards
Condensin
* Is important in compaction of the chromosomes, necessary for mitotic and meiotic division
35
New cards
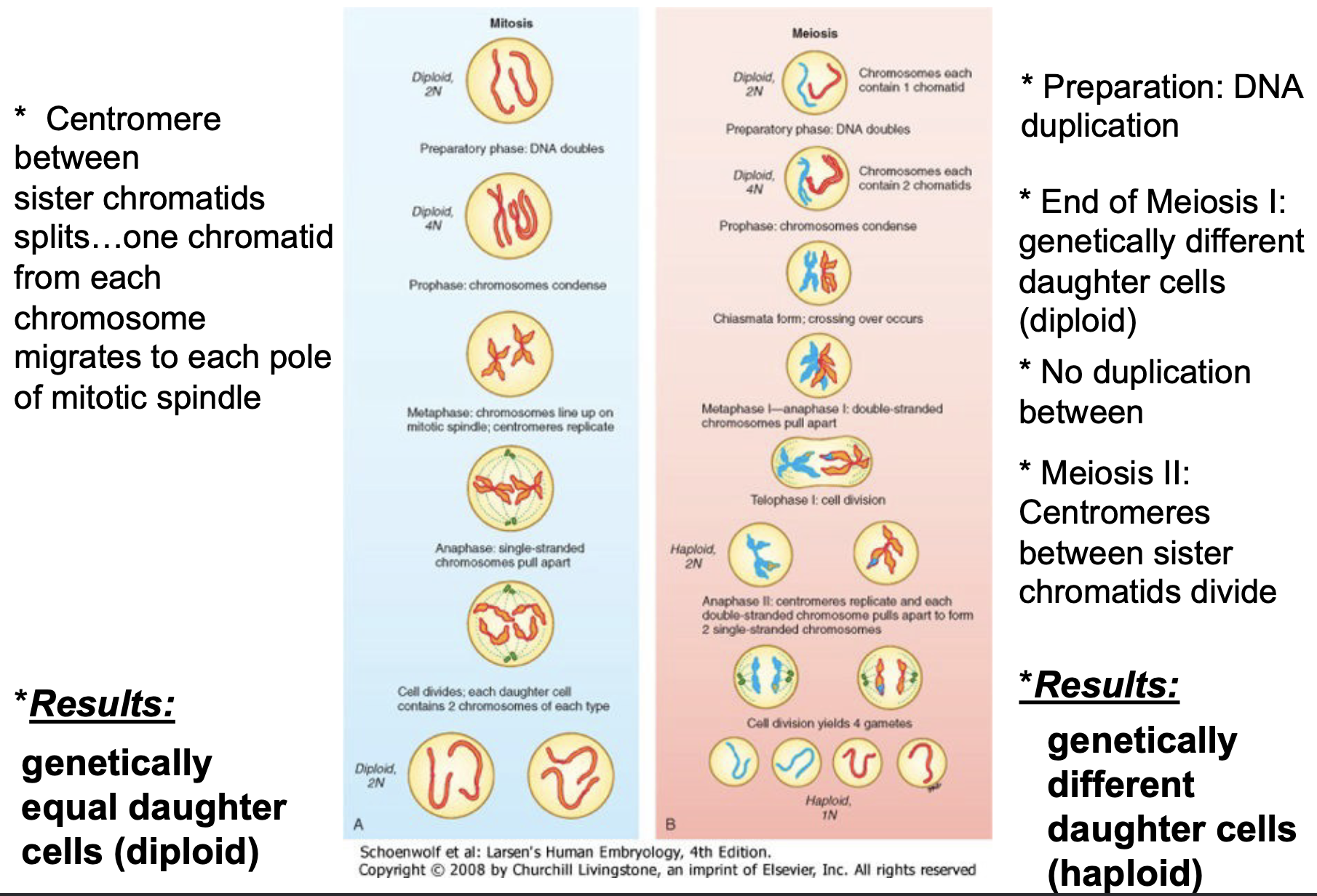
Compare mitosis and meiosis
36
New cards
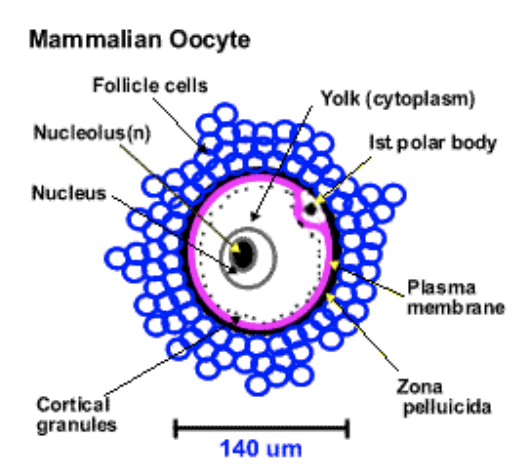
Female Mature Gametes
oocyte or egg or ovum
37
New cards
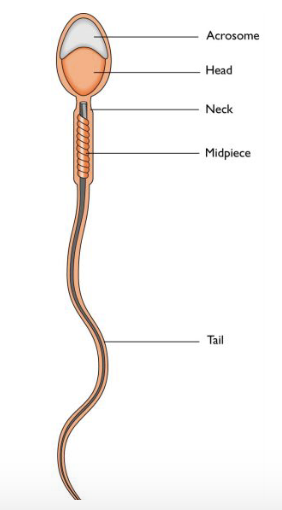
Male Mature Gametes
Spermatozoon (sperm)
38
New cards
Oogenesis Overview
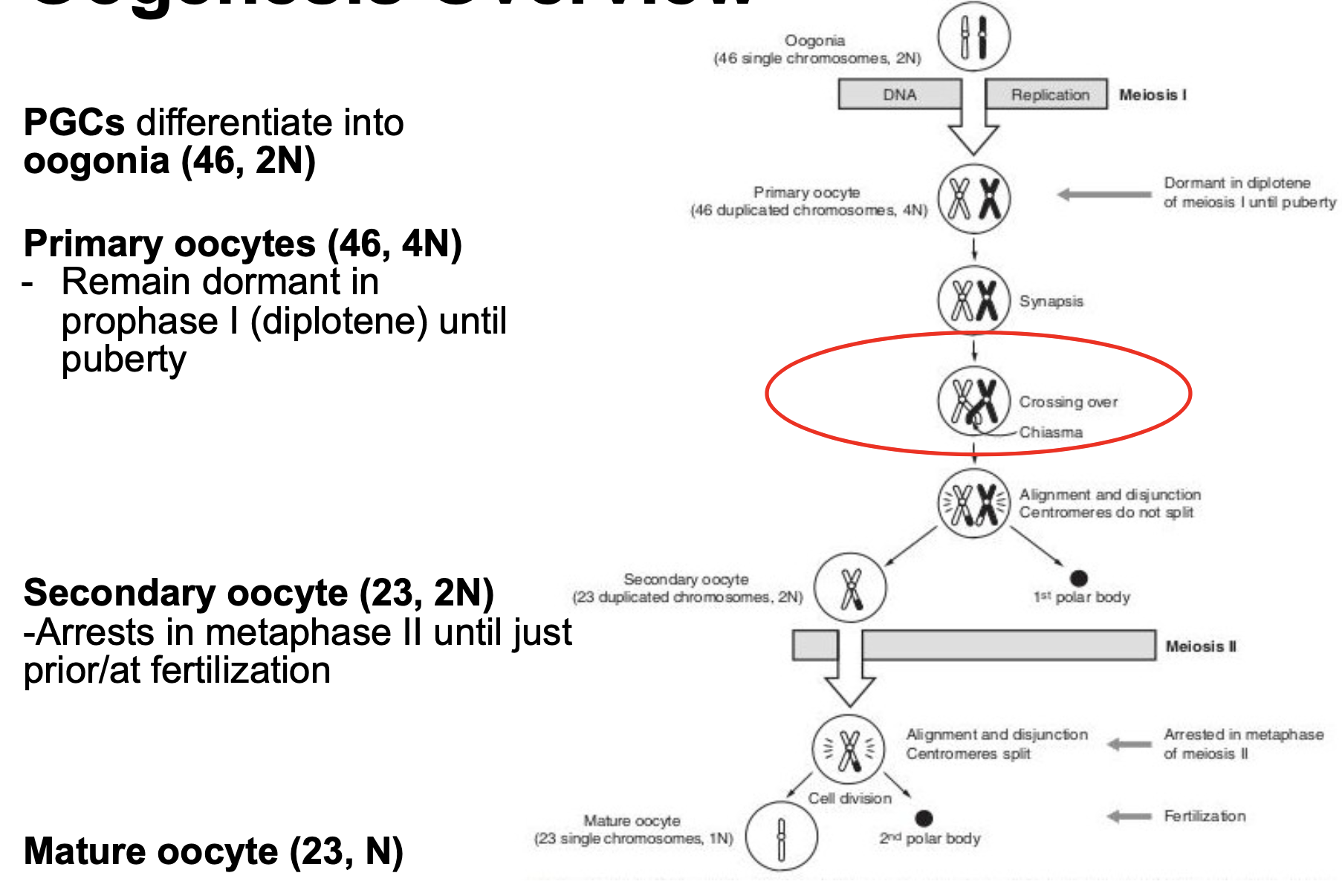
39
New cards
Female Reporductive System (Human) Diagram
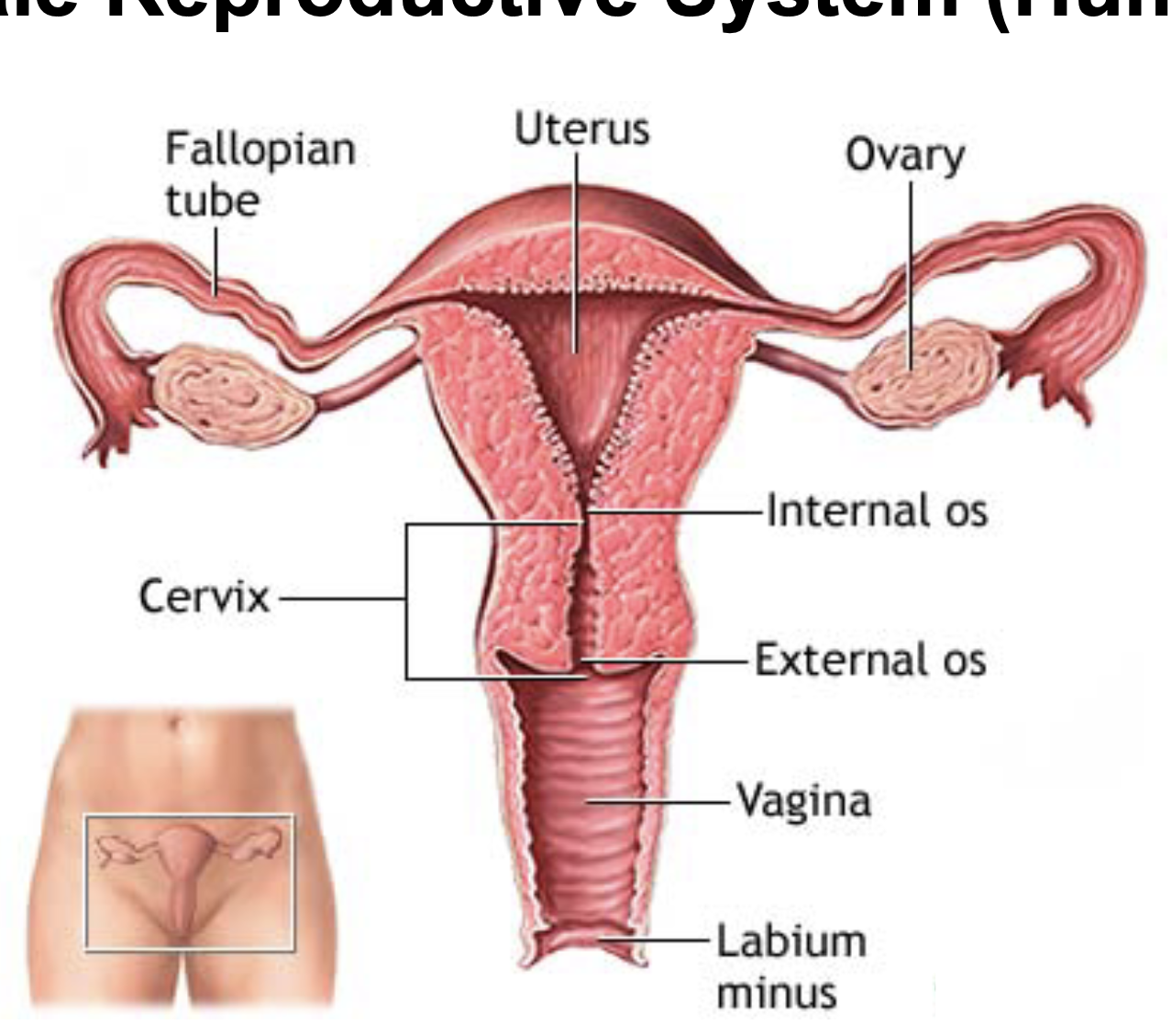
40
New cards
Female Reporductive System Diagram
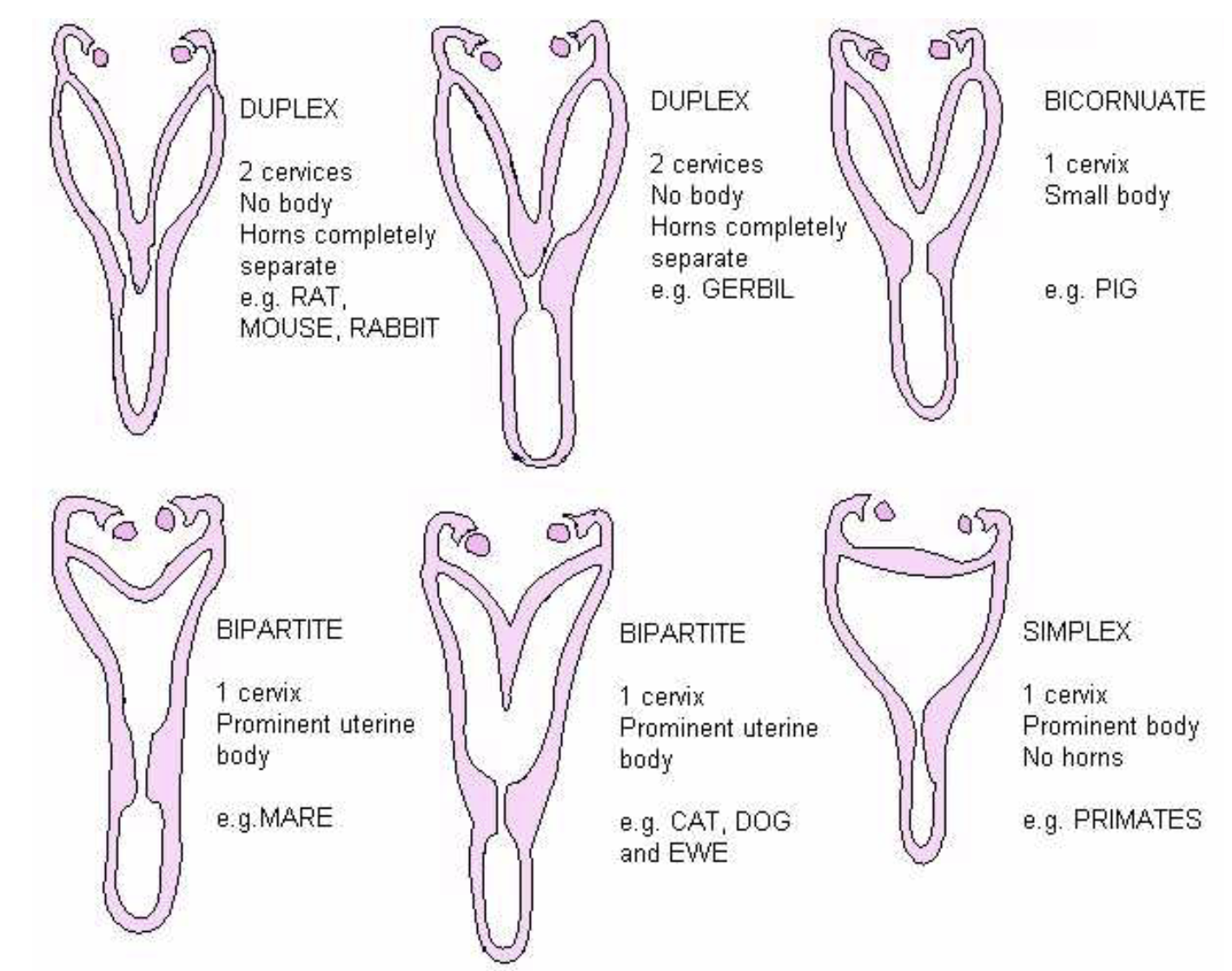
41
New cards
Structure of an Ovary
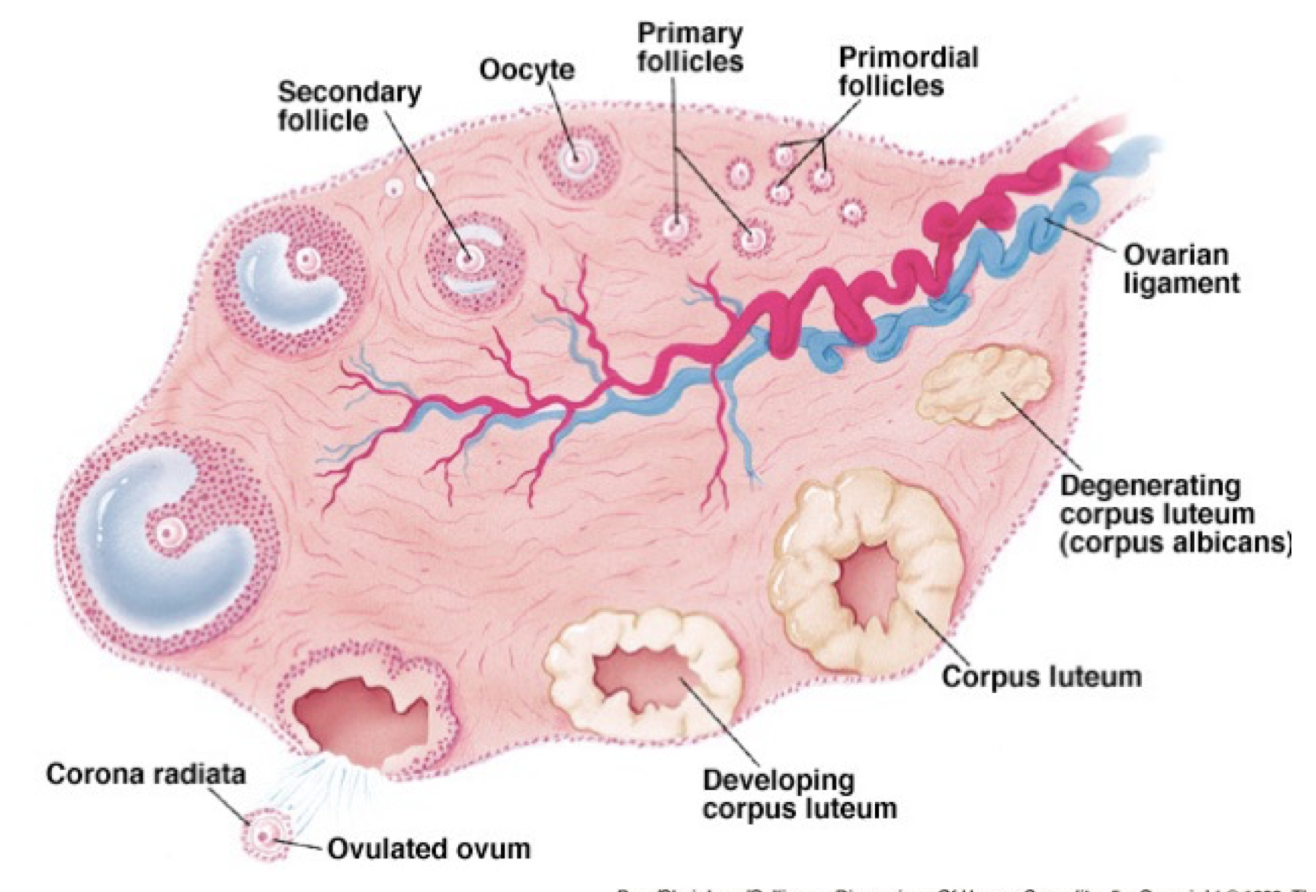
42
New cards
Ovarian Follicles (4)
* Basic unit of female reproductive biology
* contains a single oocyte
* initiated to grow and develop
* consists of granulosa cells and theca cells
* contains a single oocyte
* initiated to grow and develop
* consists of granulosa cells and theca cells
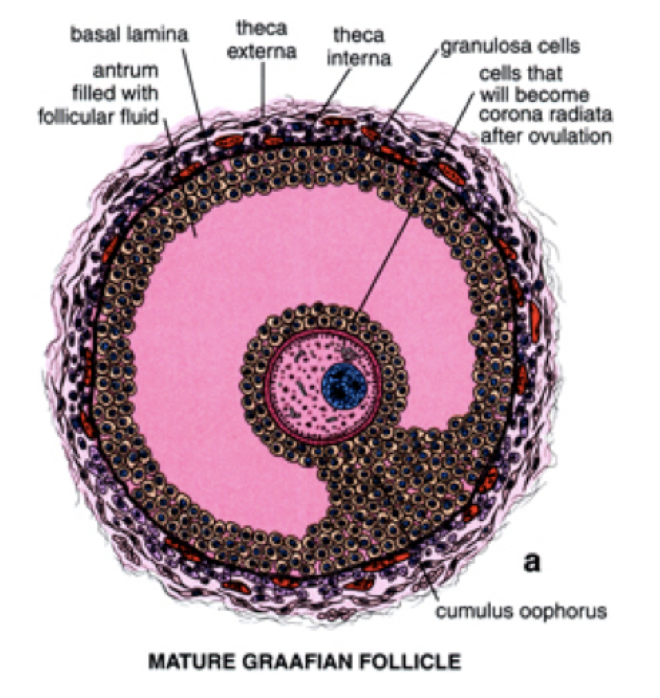
43
New cards
What stimulates a gradual rise in the level of FSH in a primordial follicle
* A rise in GnRH
* Thus turning stimulates 5 to 20 primordial follicles to begin to develop
* Thus turning stimulates 5 to 20 primordial follicles to begin to develop
44
New cards
Folliculogenesis - Primordial Follicle step 1
* one cell thick: squamous
* cells from the ovary surround the arrested primary oocyte
* A rise in GnRH stimulates a gradual rise in the level of FSH.
* cells from the ovary surround the arrested primary oocyte
* A rise in GnRH stimulates a gradual rise in the level of FSH.
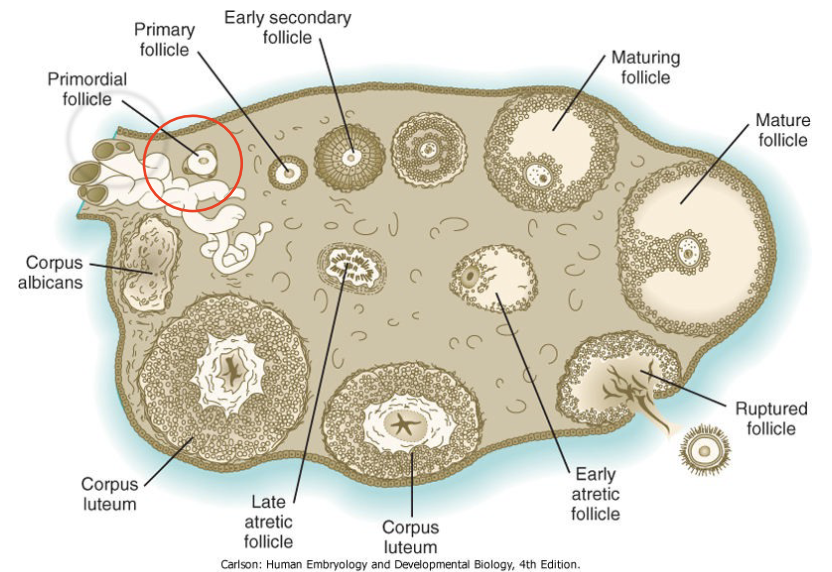
45
New cards
Folliculogenesis - Primordial Follicle step 2
* one cell thick: cuboidal
* by birth, primary oocytes have a complete layer of follicular cells
* Zona pellucida begins to form but may not be visible
* by birth, primary oocytes have a complete layer of follicular cells
* Zona pellucida begins to form but may not be visible
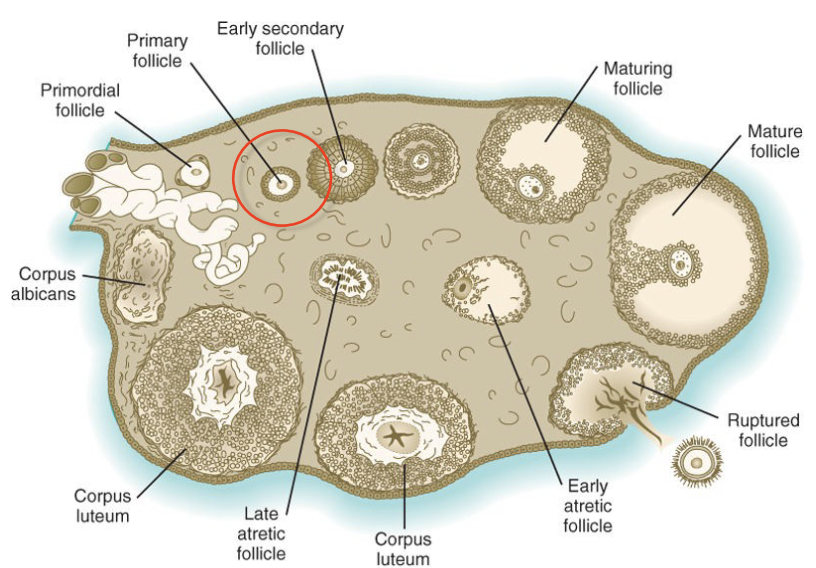
46
New cards
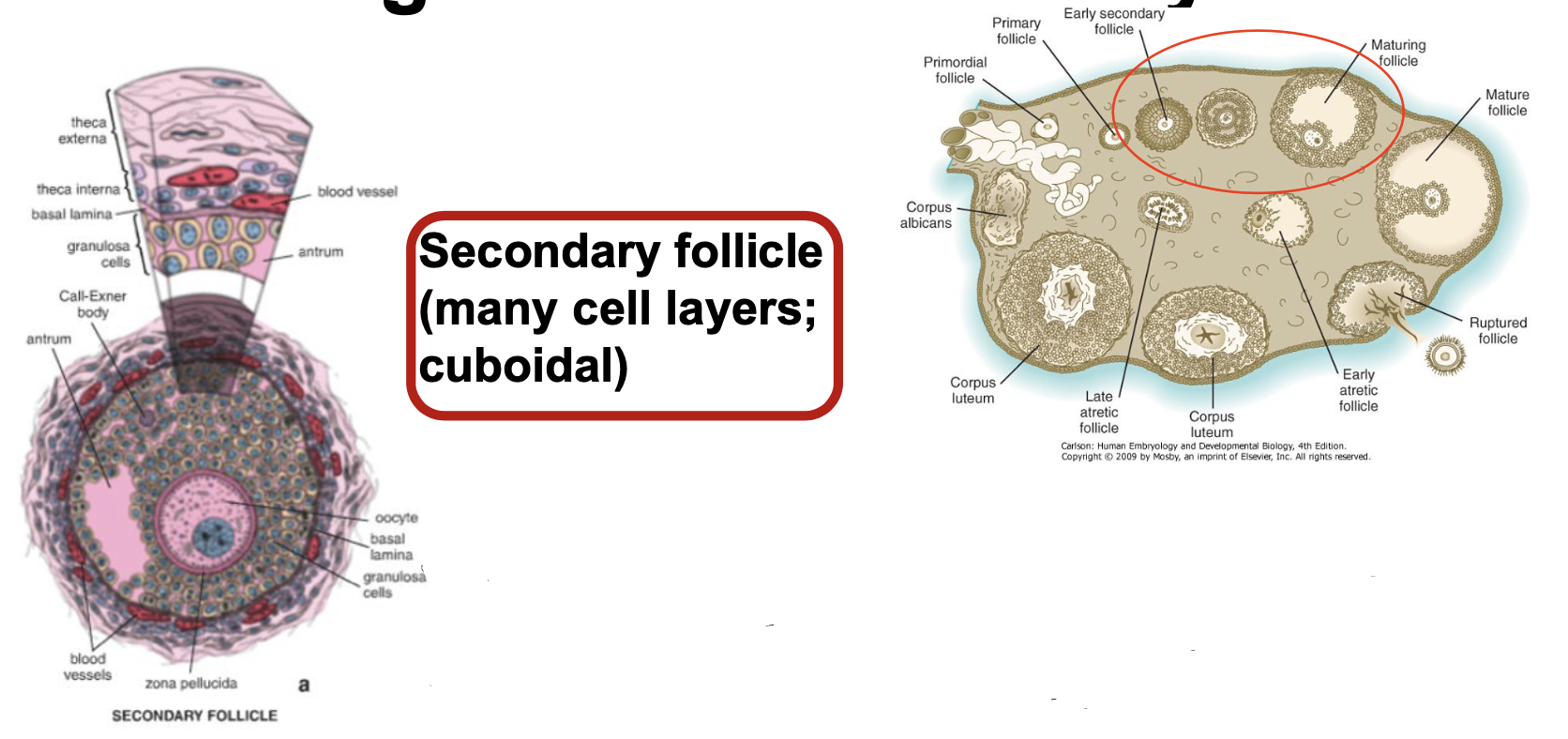
Folliculogenesis - Secondary Follicle step 1
* many cell layers; cuboidal
* Oocyte secretes active; stimulates granuloma cells to proliferate (cells secrete estrogen)
* Shortly after birth, follicular sells secrete a meiotic inhibitory factor (MIF)
* Oocyte secretes active; stimulates granuloma cells to proliferate (cells secrete estrogen)
* Shortly after birth, follicular sells secrete a meiotic inhibitory factor (MIF)
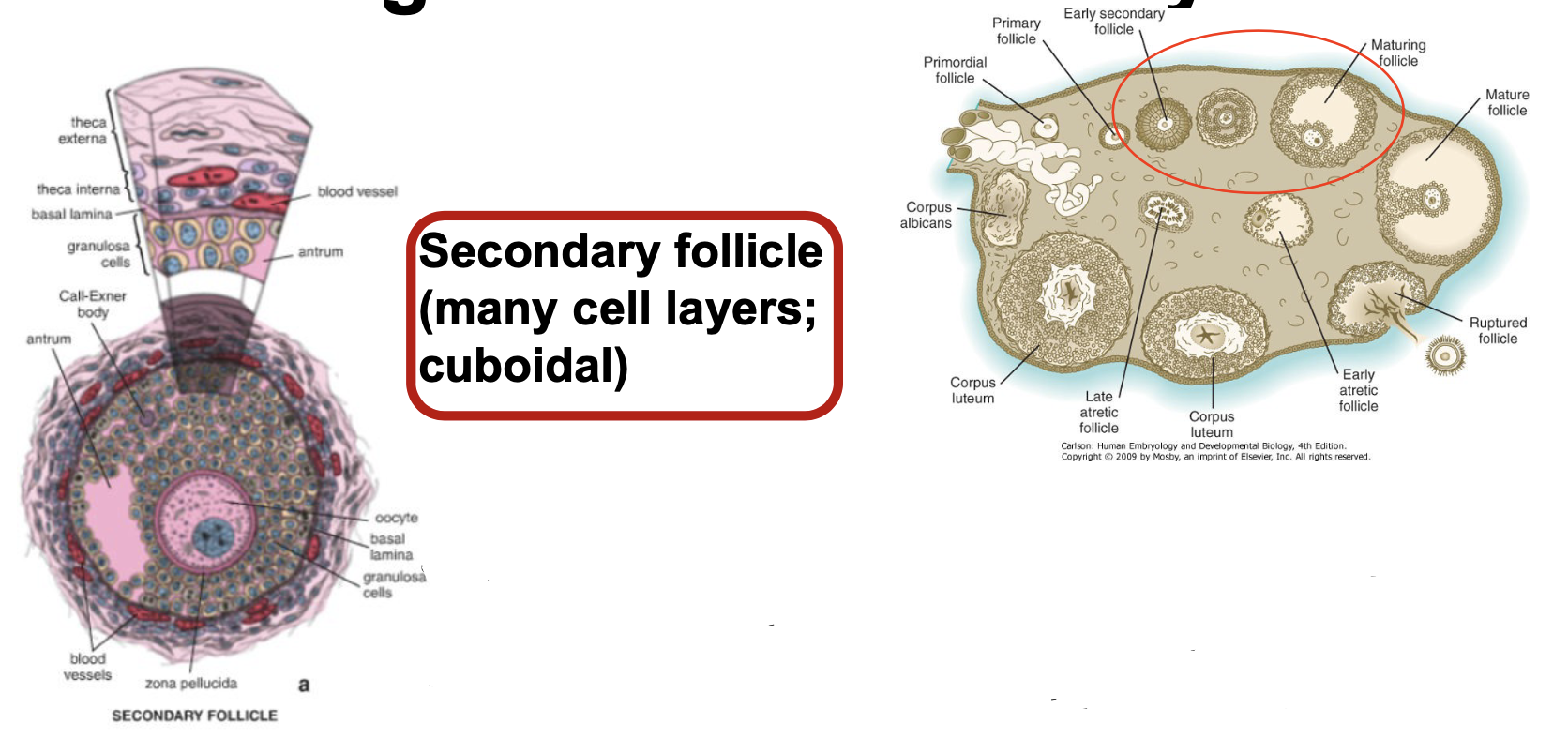
47
New cards
What is Meiotic inhibitory factor (MIF)
* causes first meiotic arrest in diplotene of prophase I until puberty
48
New cards
Folliculogenesis - Secondary Follicle step 2
* FSH actis on granulosa cells; enhances active action
* Zona pellucida well developed
* Antrum visible
* Thea forming
* Zona pellucida well developed
* Antrum visible
* Thea forming
49
New cards
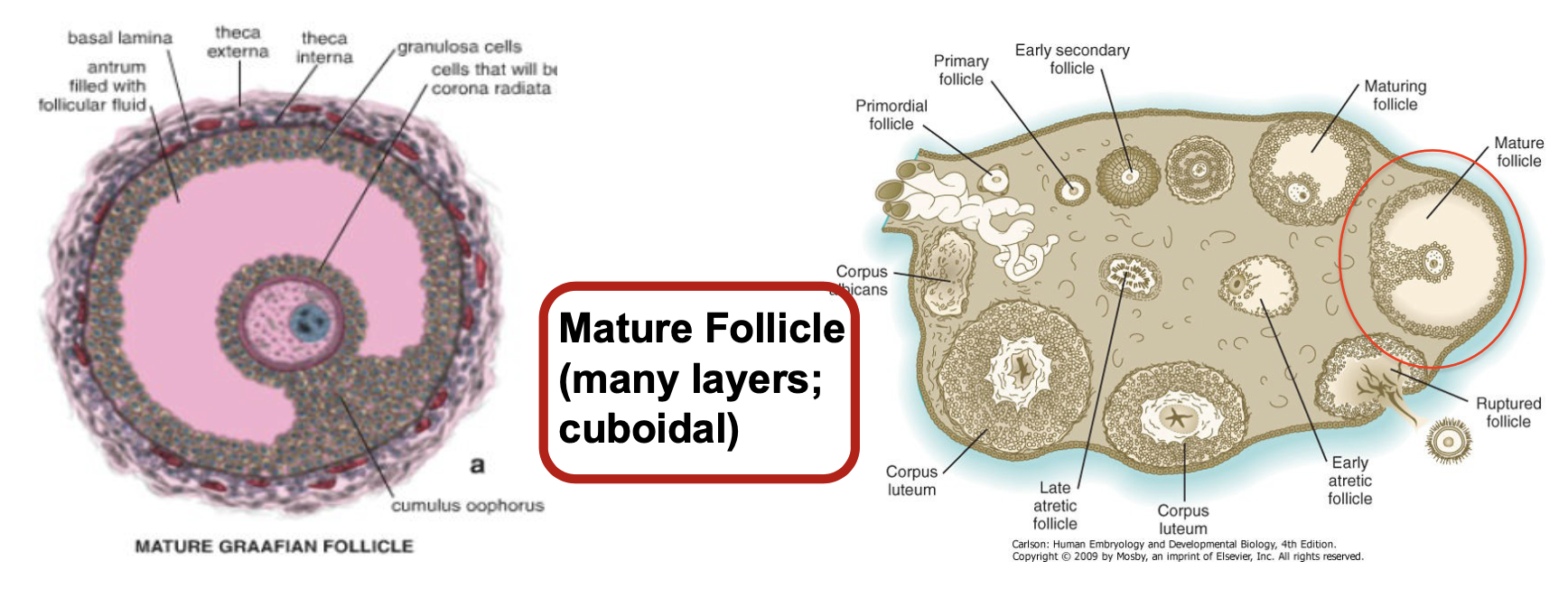
Folliculogenesis - Mature Follicle
* many layers; cuboidal
* @ puberty, follicle enlarges
* Secondary oocyte arrested in Metaphase II until fertilization
* Antrumm very large
* Cumulus oophorus evident
* Corona radiata surrounds the mature secondary oocyte
* Thecal layers aare prominent
* @ puberty, follicle enlarges
* Secondary oocyte arrested in Metaphase II until fertilization
* Antrumm very large
* Cumulus oophorus evident
* Corona radiata surrounds the mature secondary oocyte
* Thecal layers aare prominent
50
New cards
Luteinizing hormone (LH) surge results in
* MPF production
* Release from MI arrest
* Progesterone production
* Release from MI arrest
* Progesterone production
51
New cards
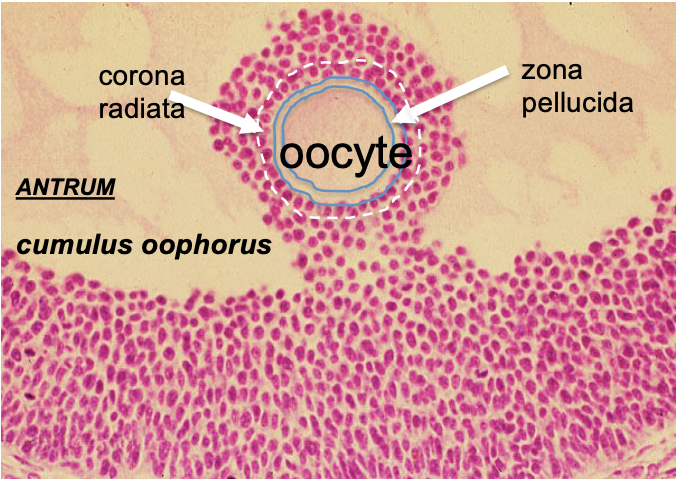
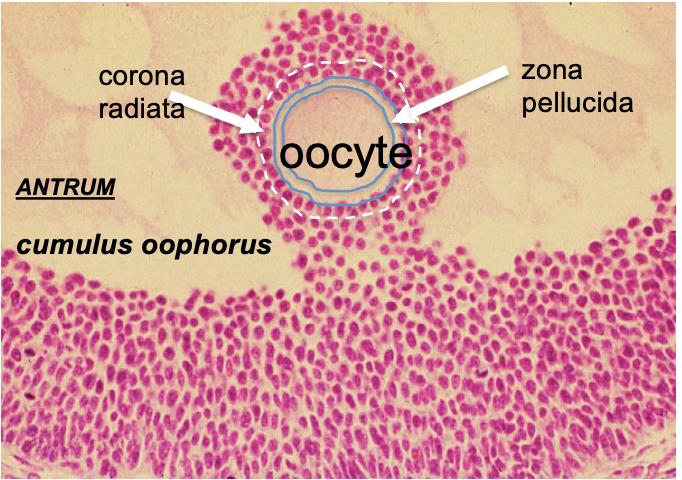
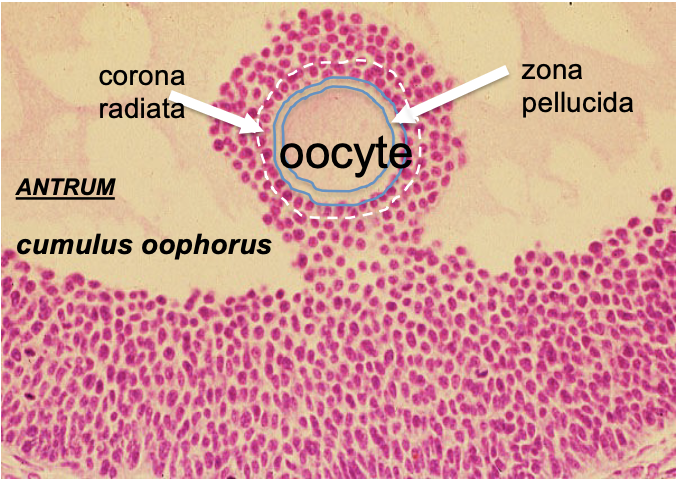
What is cumulus oophorus?
Surround oocyte in follicle and after ovulation
* Roles are: protection, development, during fertilization too
* Roles are: protection, development, during fertilization too
52
New cards
What is corona radiata?
Part of the cumulus oophorus; innermost layer closet to the ZP
53
New cards
What is zona pellucida
Surrounds secondary oocyte and polar body
* Roles are: binds spermatozoa, species-specific barriers
* Roles are: binds spermatozoa, species-specific barriers
54
New cards
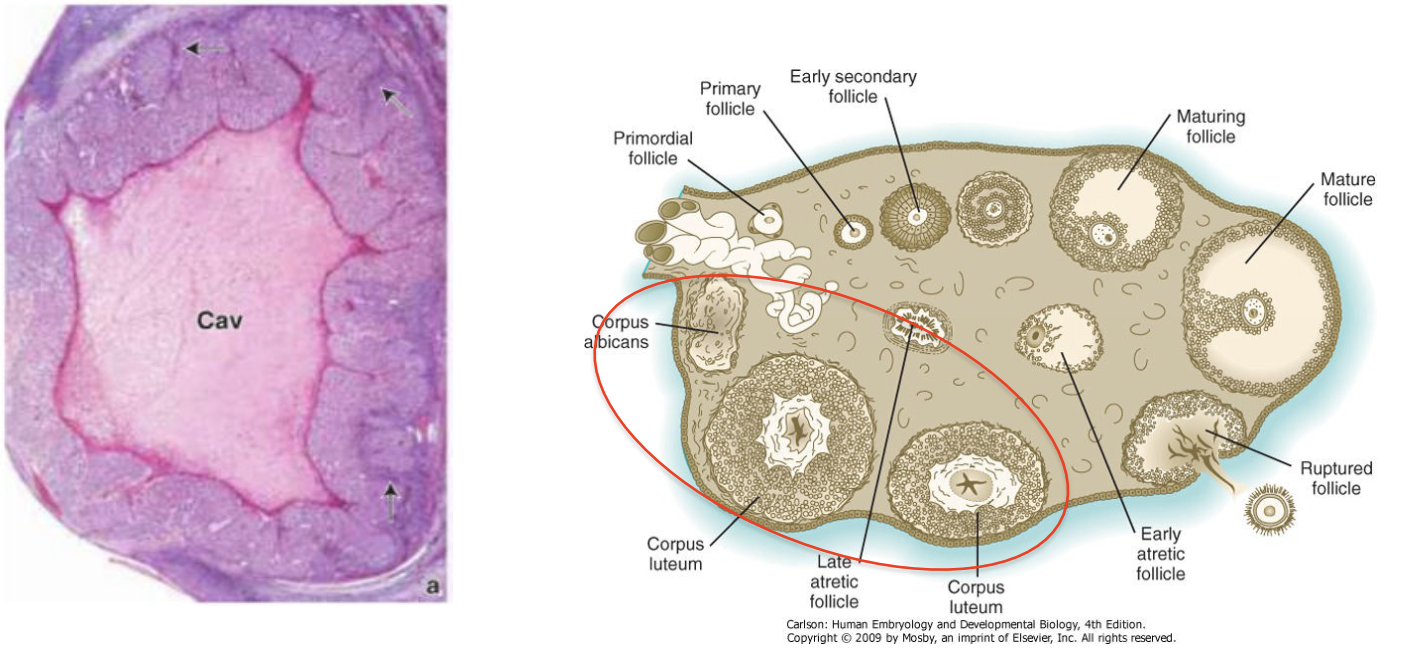
Folliculogenesis - Corpus luteum
* Ruptured and empty follicle (granulosa cells) left behind after ovulation
* Lutein reaction converts cells to progesterone-producing cells
* Lutein reaction converts cells to progesterone-producing cells
55
New cards
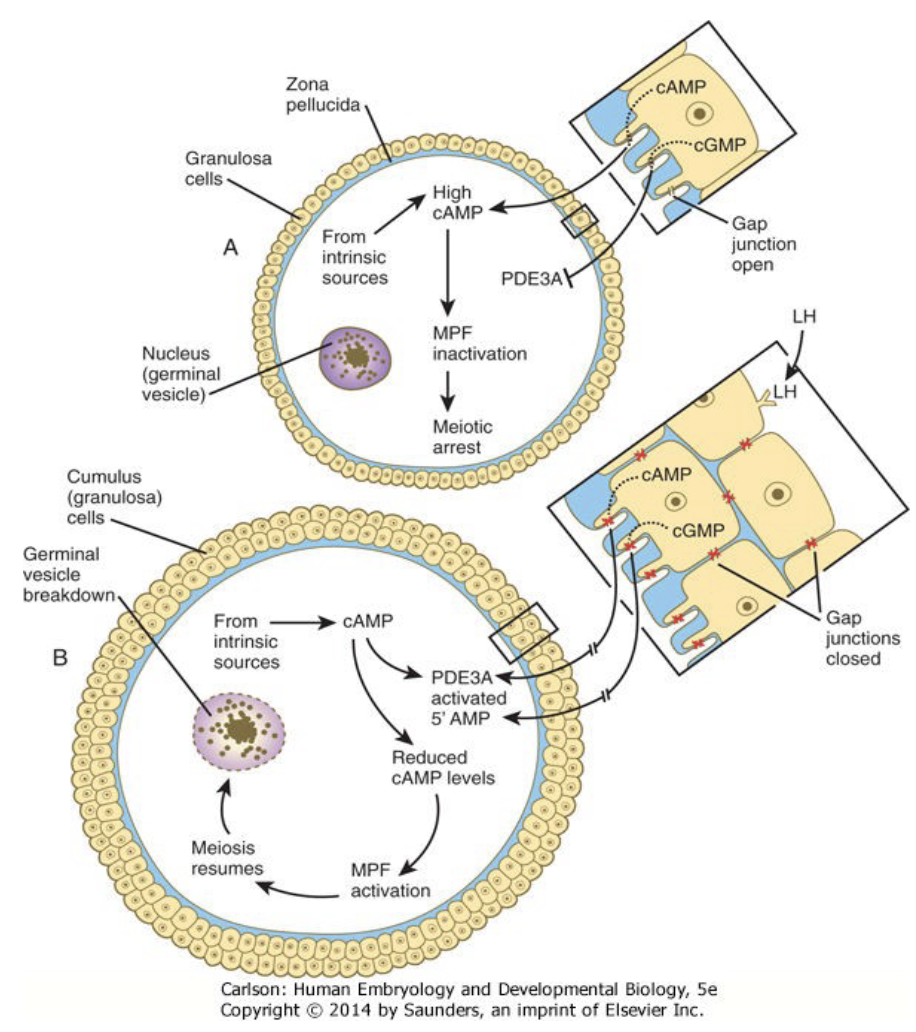
Meiotic arrest involves second messengers and hormones: Arrest-
* ↑cAMP inactivates MPF
* meiosis arrested
* cGMP inhibits PDE3A
* meiosis arrested
* cGMP inhibits PDE3A
56
New cards
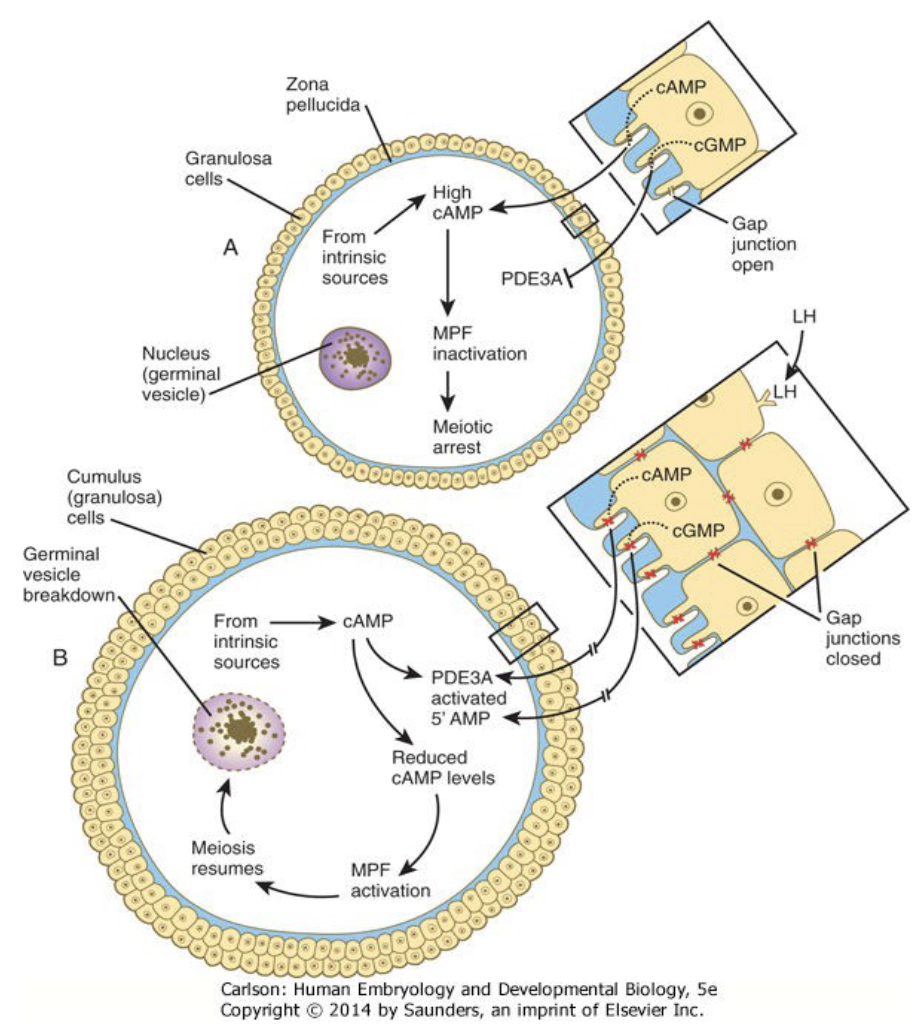
Meiotic resumption involves second messengers and hormones: Resumption of meiosis-
* LH surge
* closes gap junctions
* in effect decreases cAMP
* activates MPF
* closes gap junctions
* in effect decreases cAMP
* activates MPF
57
New cards
MPF stands for
maturation promoting factor
58
New cards
What is the theca
* cellular coverings from the surrounding ovarian storm begins to form around a __developing follicle__
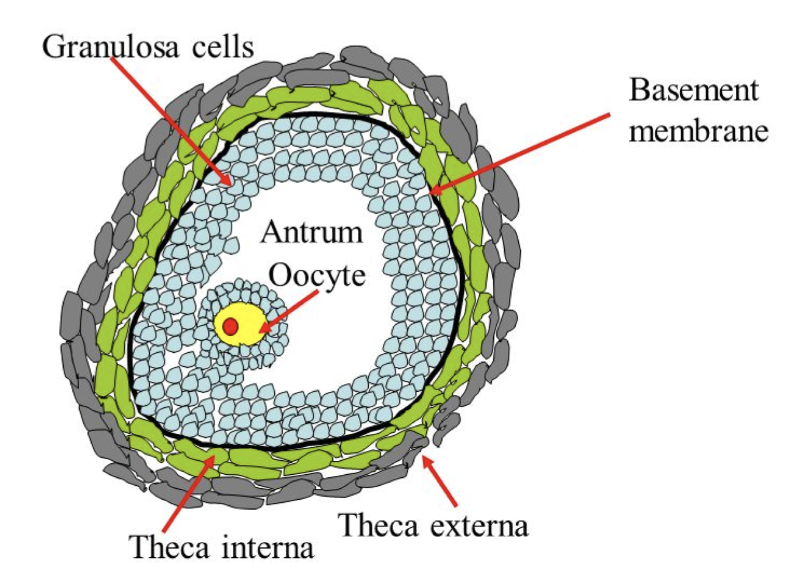
59
New cards
Theca folliculi
* 2 or 3 layers thick
* differentiates into 2 layers: theca interna, and theca external
* differentiates into 2 layers: theca interna, and theca external
60
New cards
What is the theca interna
* inside granulosa cells
* highly vascularized and glandular
* highly vascularized and glandular
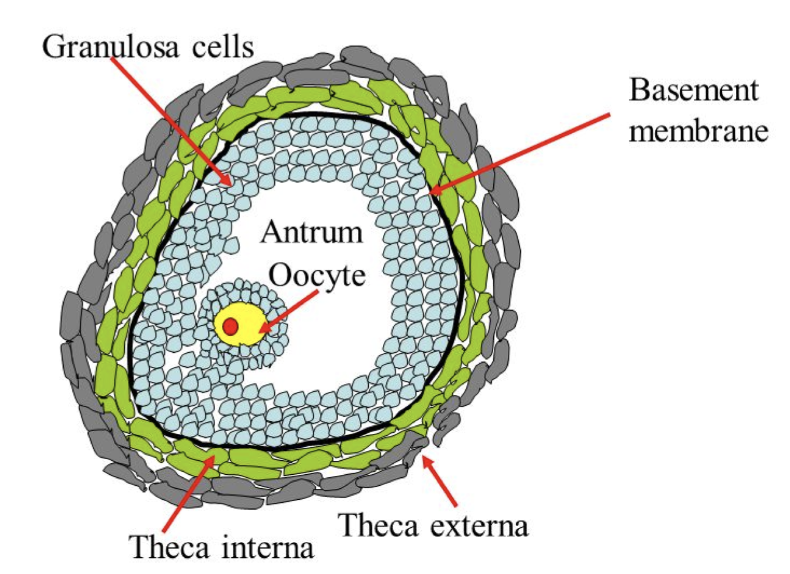
61
New cards
What is the theca externa
* outside granulosa cells
* connective tissue=like outer capsule
* connective tissue=like outer capsule
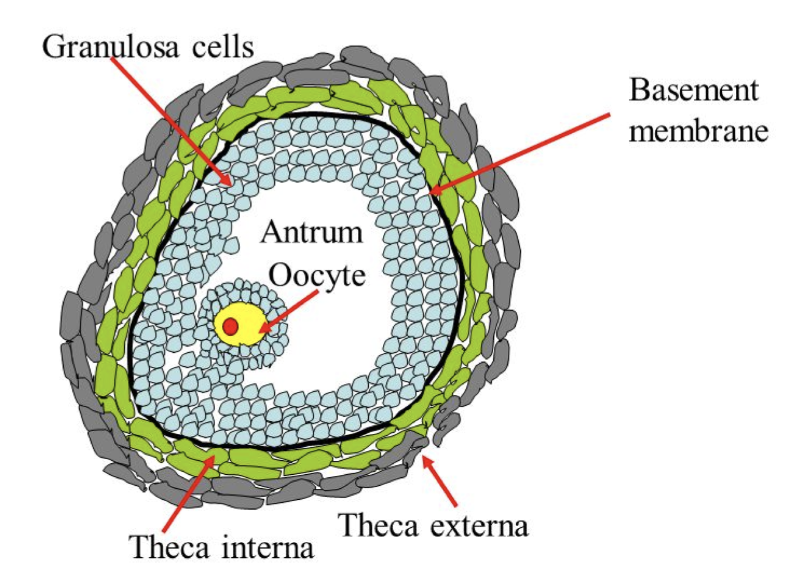
62
New cards
What are the major hormonal interaction in the theca and granulosa cells in follicle development (4)
* FSH
* Estrogen
* Activin
* Inhibin
* Estrogen
* Activin
* Inhibin
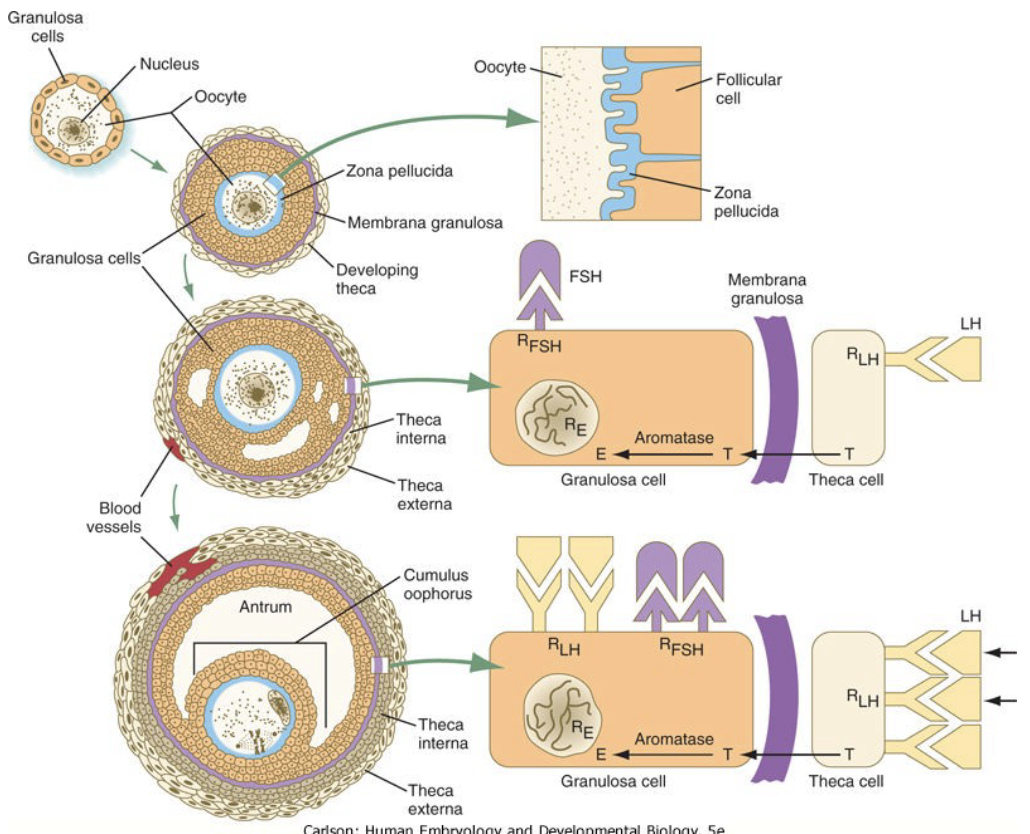
63
New cards
What does FSH do? (3)
* Pituitary gonadotropin
* Acts on granulosa cells
* Stimulates estrogen production
* Acts on granulosa cells
* Stimulates estrogen production
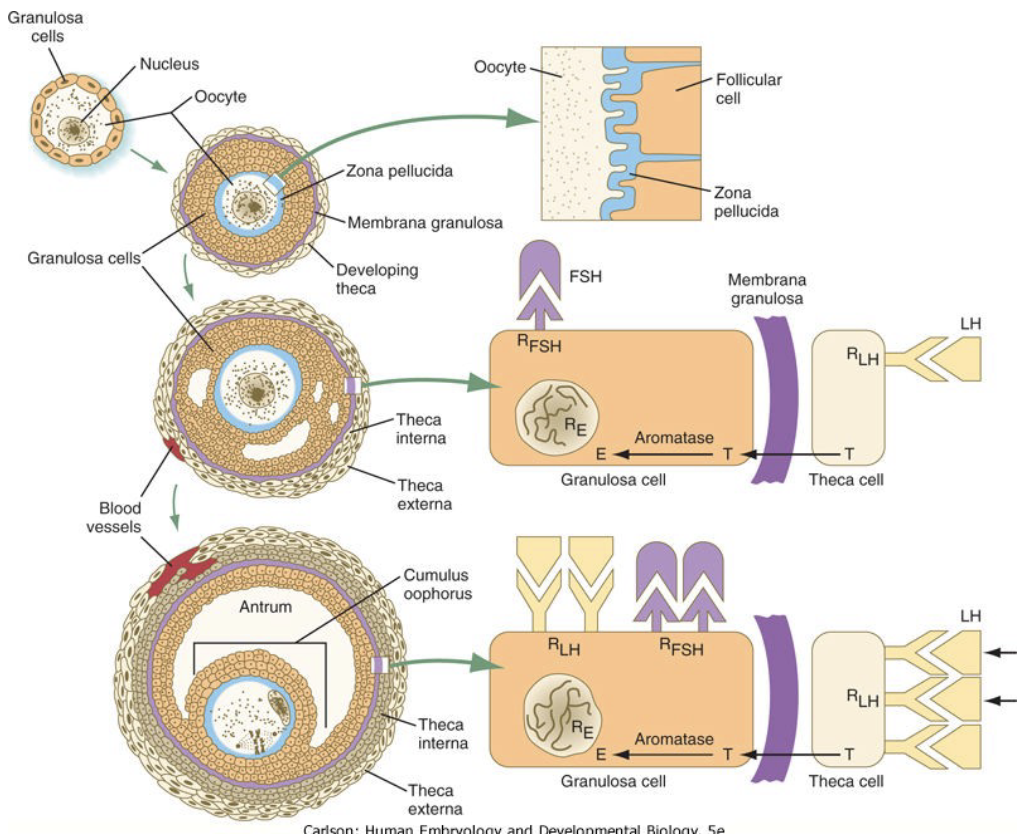
64
New cards
What does Estrogen do?
* stimulate the formation of LH receptors on granulosa cells
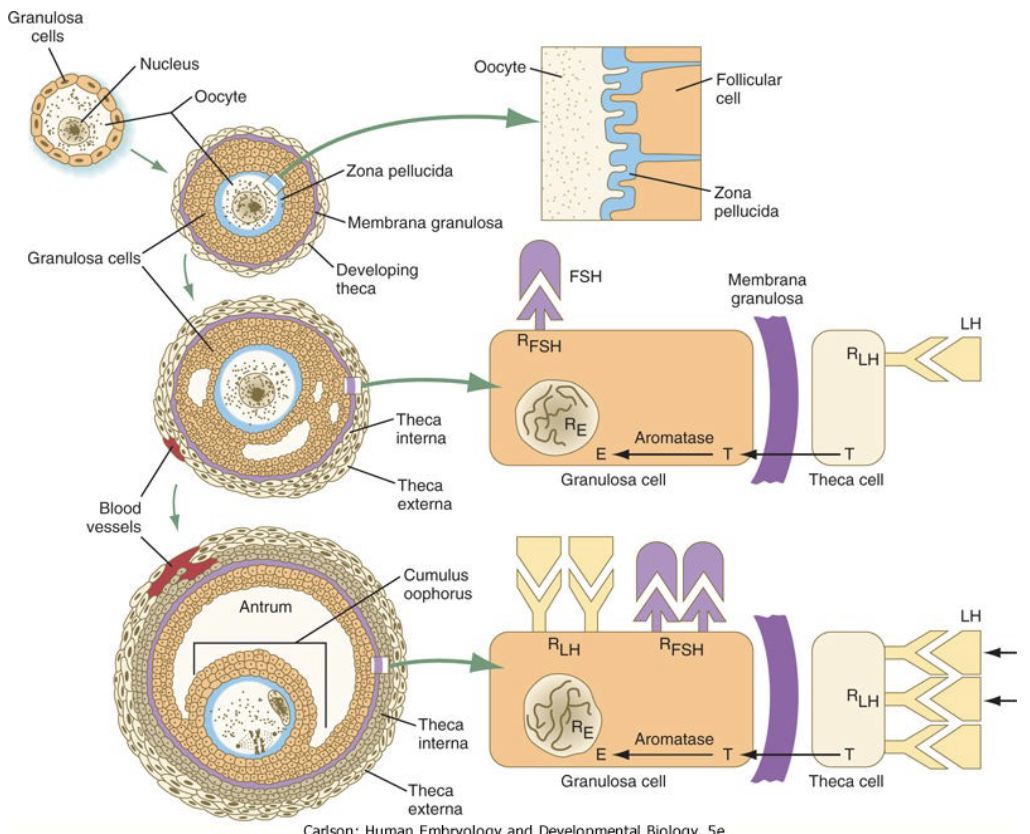
65
New cards
What does activin do?
* Stimulates granulosa cells proliferation (rapid reproduction of a cell)
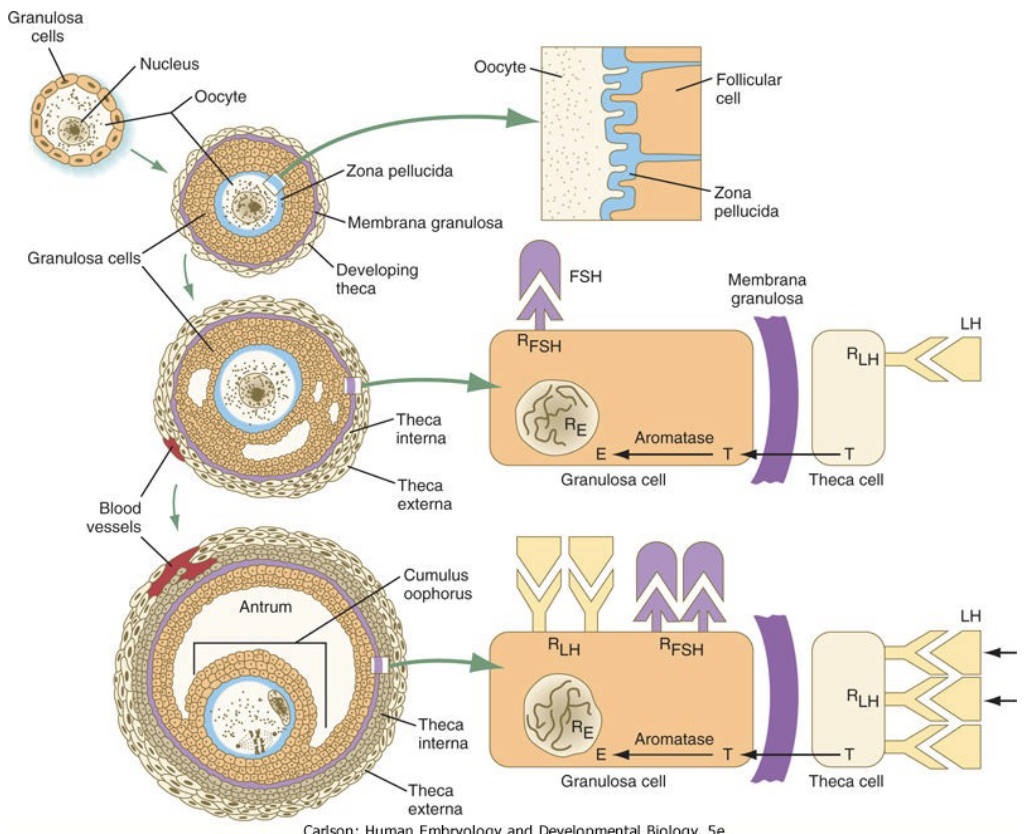
66
New cards
What does Inhibin do?
* secreted by granulosa cells of dominant secondary follicle
* inhibits secretion of FSH (and LH) by negative feedback
* Results in atresia of other follicles
* inhibits secretion of FSH (and LH) by negative feedback
* Results in atresia of other follicles
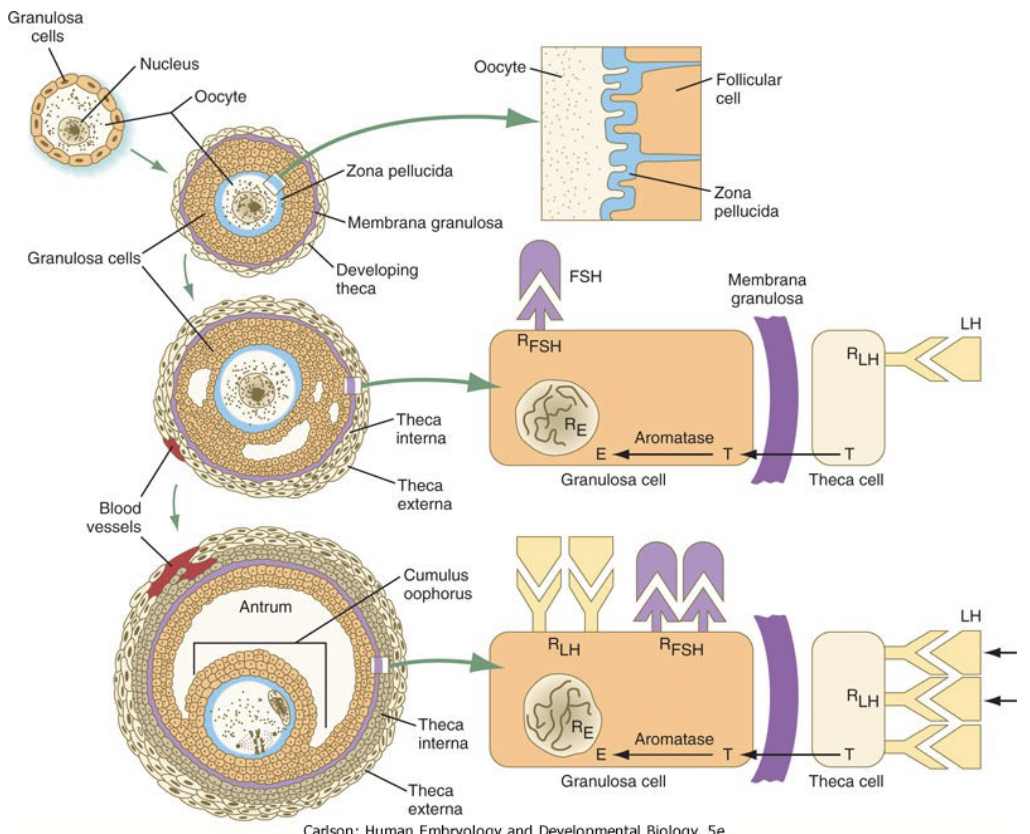
67
New cards
What are the 3 stages of the menstral cycle?
* Proliferative Phase (day 5 - 14)
* Ovulation
* Secretary Phase (day 14 - 28)
* Ovulation
* Secretary Phase (day 14 - 28)
68
New cards
What happens during the proliferative phase
* GnRH stimulates the release of FSH and LH
* secondary follicles secrete estrogen (acts of reproductive tract)
* LH and FSH surge
* secondary follicles secrete estrogen (acts of reproductive tract)
* LH and FSH surge
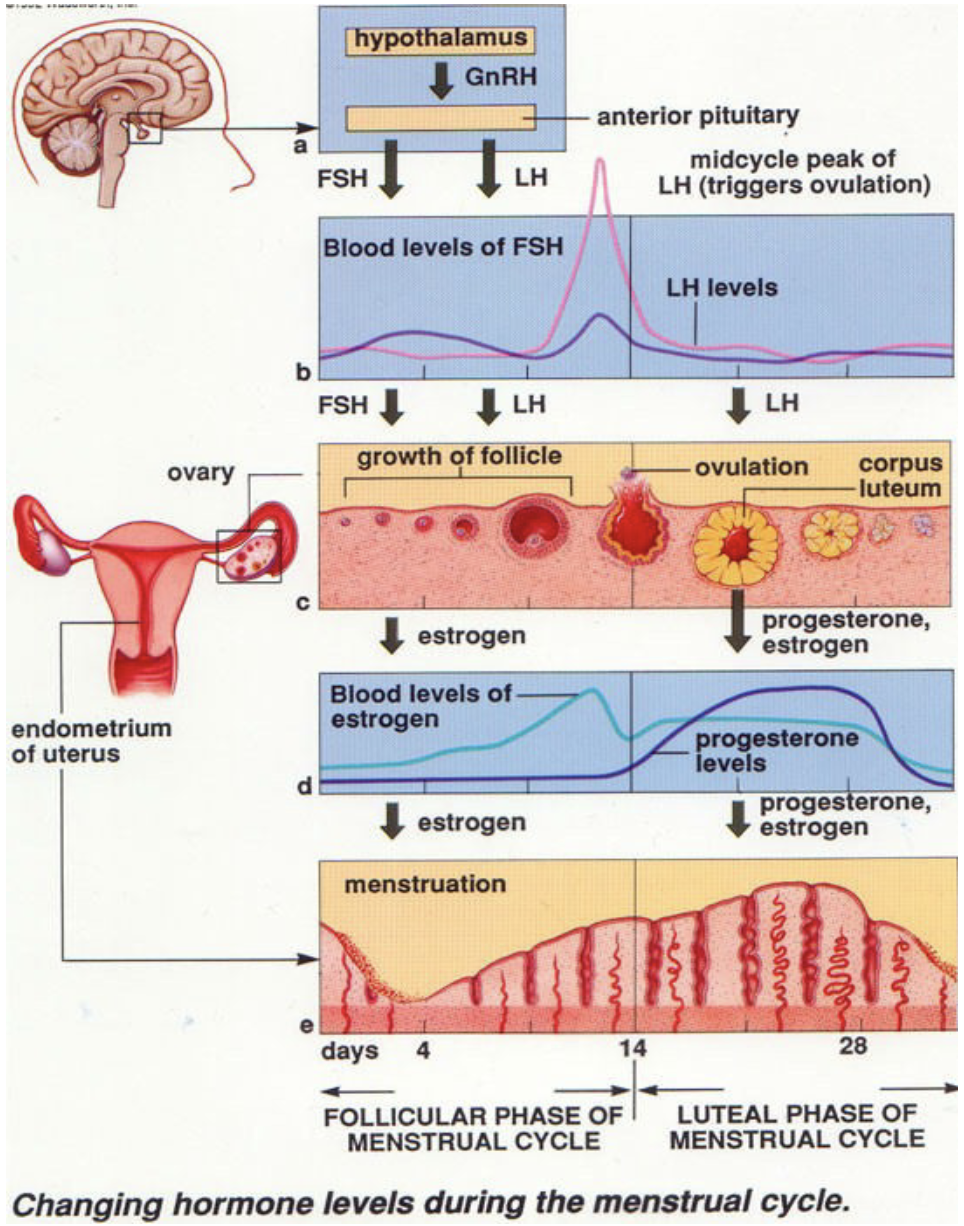
69
New cards
What happens during ovulation?
* Result of LH surge
* Transforms ruptured follicle to corpus luteum (secretes progesterone)
* Transforms ruptured follicle to corpus luteum (secretes progesterone)
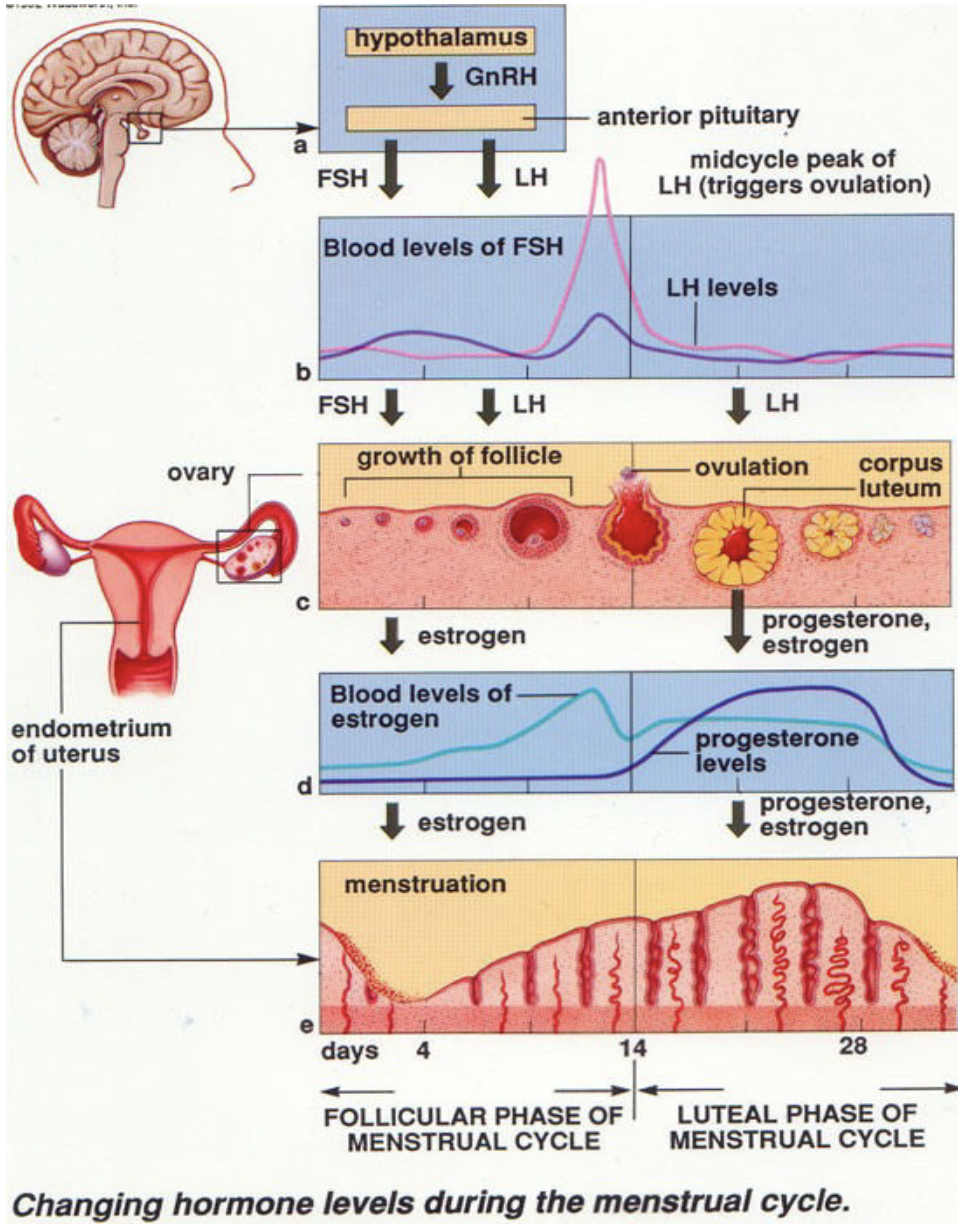
70
New cards
What happens during the secretory phase?
* Progesterone helps ready the repro tract for implantation
* Inhibin production
* Endometrium sheds
* Inhibin production
* Endometrium sheds
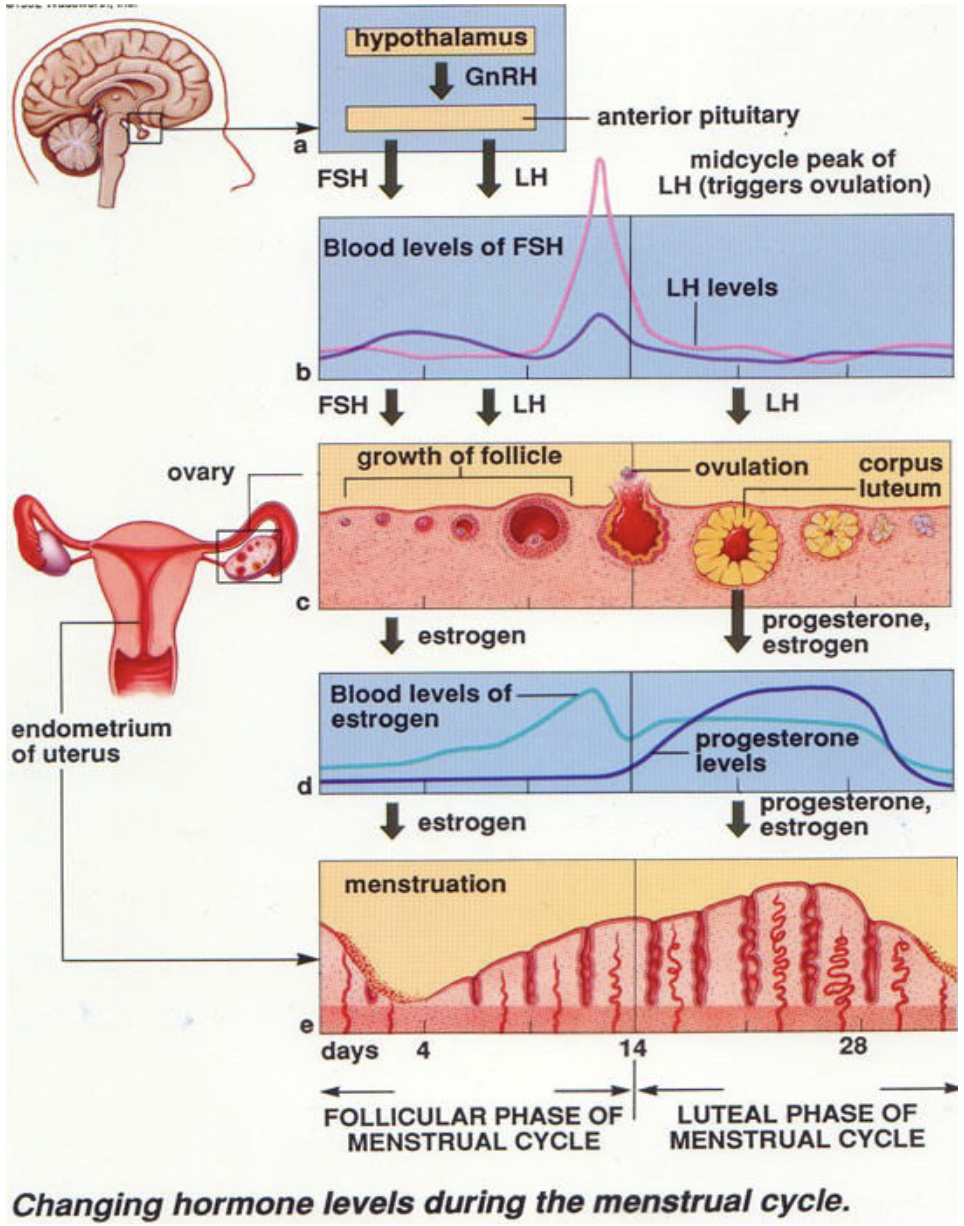
71
New cards
3 stages of oogenesis
* oocytogenesis (oogonia developing into primary oocytes by mitosis)
* ootidogenesis (the primary oocyte turns into an secondary oocyte)
* oogenesis (formation of female gametes)
* ootidogenesis (the primary oocyte turns into an secondary oocyte)
* oogenesis (formation of female gametes)
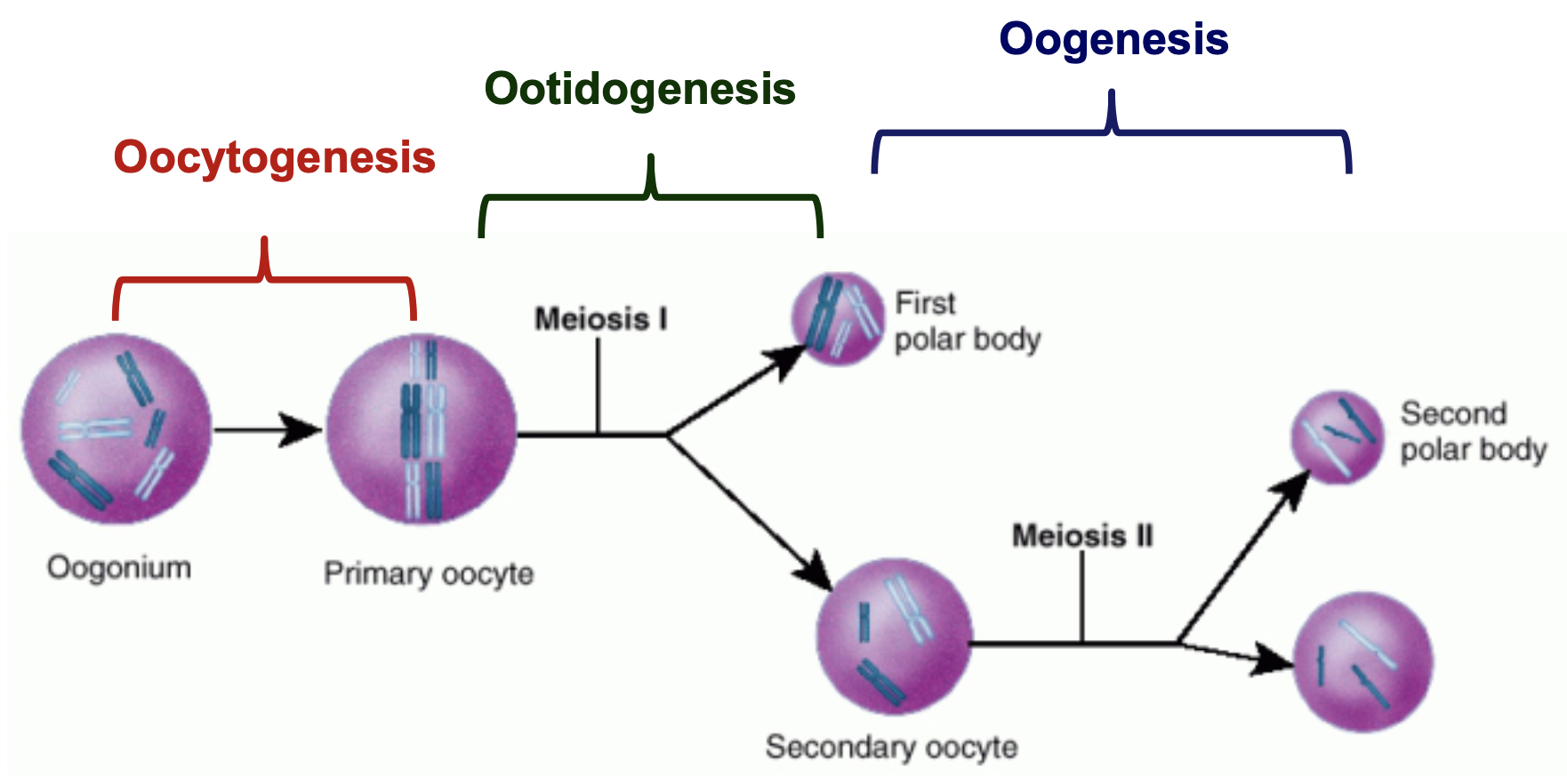
72
New cards
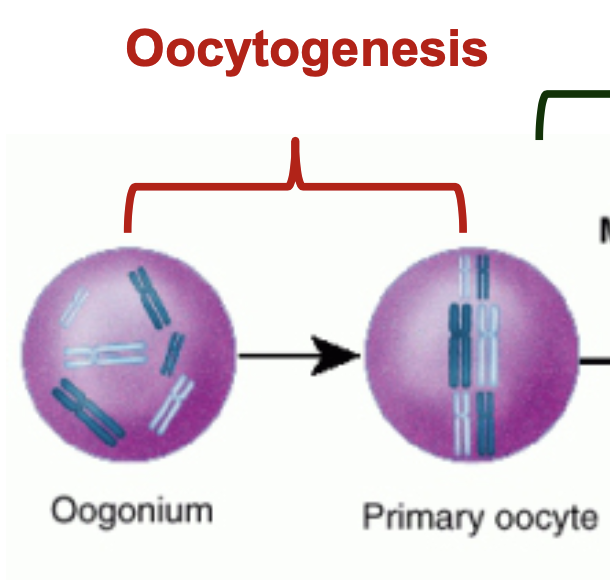
What is ooctyogenesis?
* oogonia developing into primary oocytes by mitosis
* complete either before or after birth
* primary oocytes reach their maximum development at roughly 20 weeks of gestational age
* primary oocytes at birth are approximately 1-2 million
* complete either before or after birth
* primary oocytes reach their maximum development at roughly 20 weeks of gestational age
* primary oocytes at birth are approximately 1-2 million
73
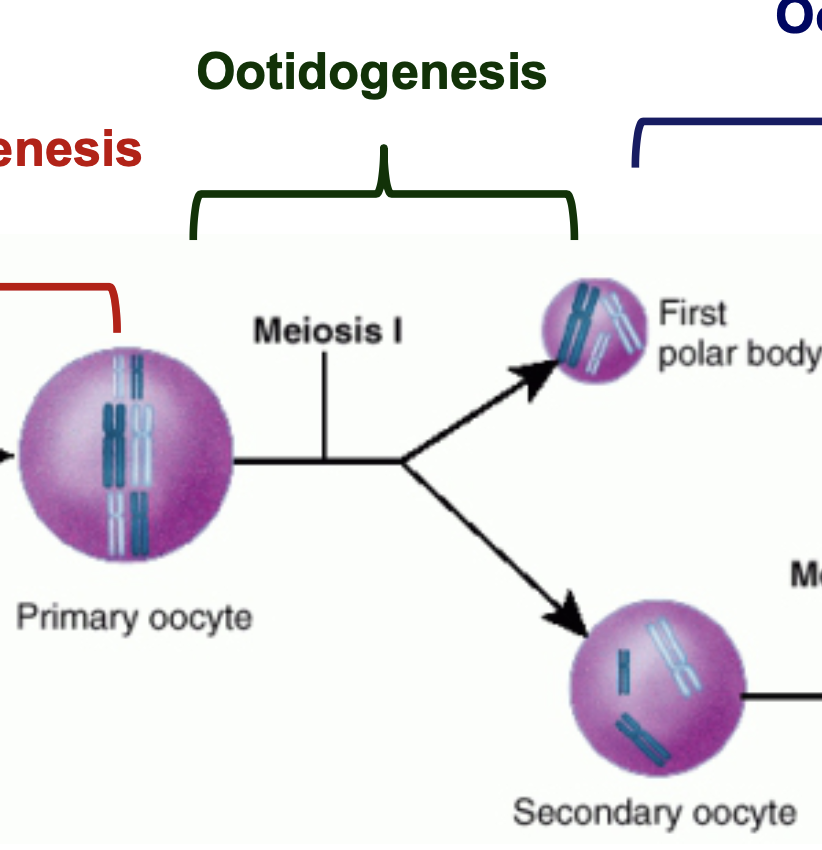
New cards
What is ootidogenesis
* primary oocyte develops into a secondary oocyte
* It begins at prenatal age, stops in the diplotene \n stage of prophase I of the first meiotic division (dictyate) \n until puberty.
* At puberty, some primary oocytes develop in each \n menstrual cycle, chromosomal crossover occurs, \n meiosis I is completed, first polar body extruded and \n oocyte secondary oocyte
* It begins at prenatal age, stops in the diplotene \n stage of prophase I of the first meiotic division (dictyate) \n until puberty.
* At puberty, some primary oocytes develop in each \n menstrual cycle, chromosomal crossover occurs, \n meiosis I is completed, first polar body extruded and \n oocyte secondary oocyte
74
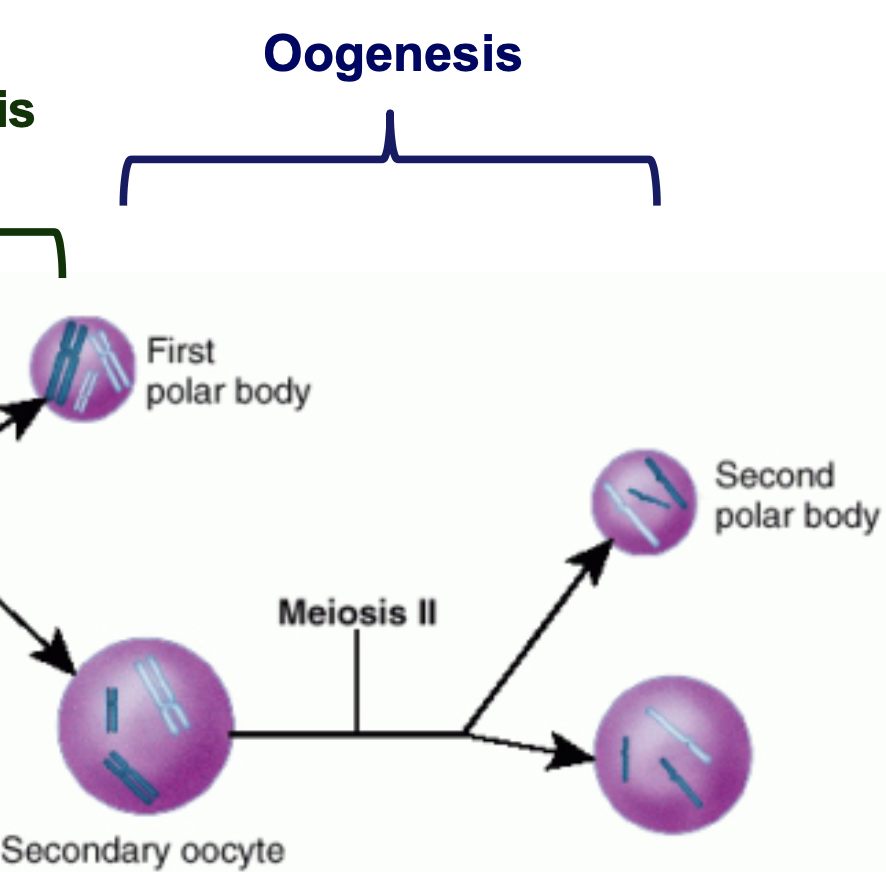
New cards
What is oogenesis?
* the haploid secondary oocyte initiates meiosis II and stops at the metaphase II stage until fertilization
75
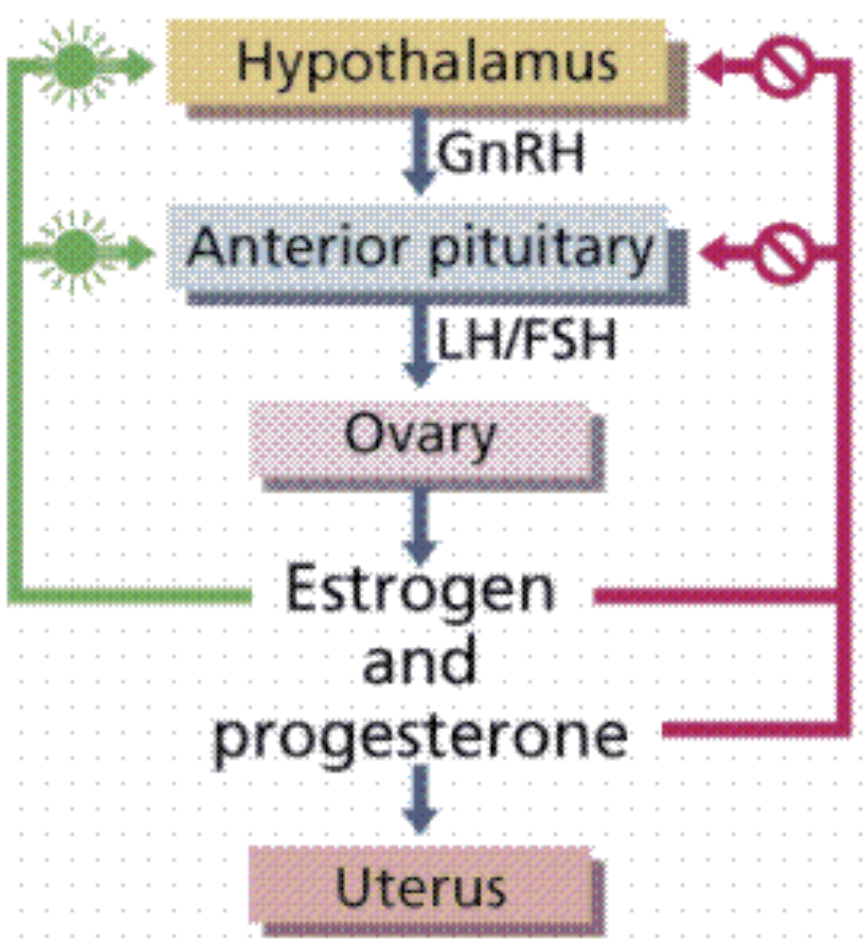
New cards
Hormonal control of oogenesis/folliculogenesis
* estrogen and progesterone can be either a negative and positive regulator
76
New cards
What is oocyte cytoplasmic maturation?
* the accumulation of mRNA, proteins, substrates, and nutrients required to achieve the oocyte developmental competence that fosters embryonic developmental competence
77
New cards
Parts of oocyte cytoplasmic maturation
* Mitochondria → redistribution
* Golgi apparatus → fragmentation
* Endoplasmic reticulum → redistribution and structural changes
* Cytoskeleton→ reorganization
* Golgi apparatus → fragmentation
* Endoplasmic reticulum → redistribution and structural changes
* Cytoskeleton→ reorganization
78
New cards
Spermatogenesis
* process in which spermatozoa are produced from male primordial germ cells by way of mitosis and meiosis
79
New cards
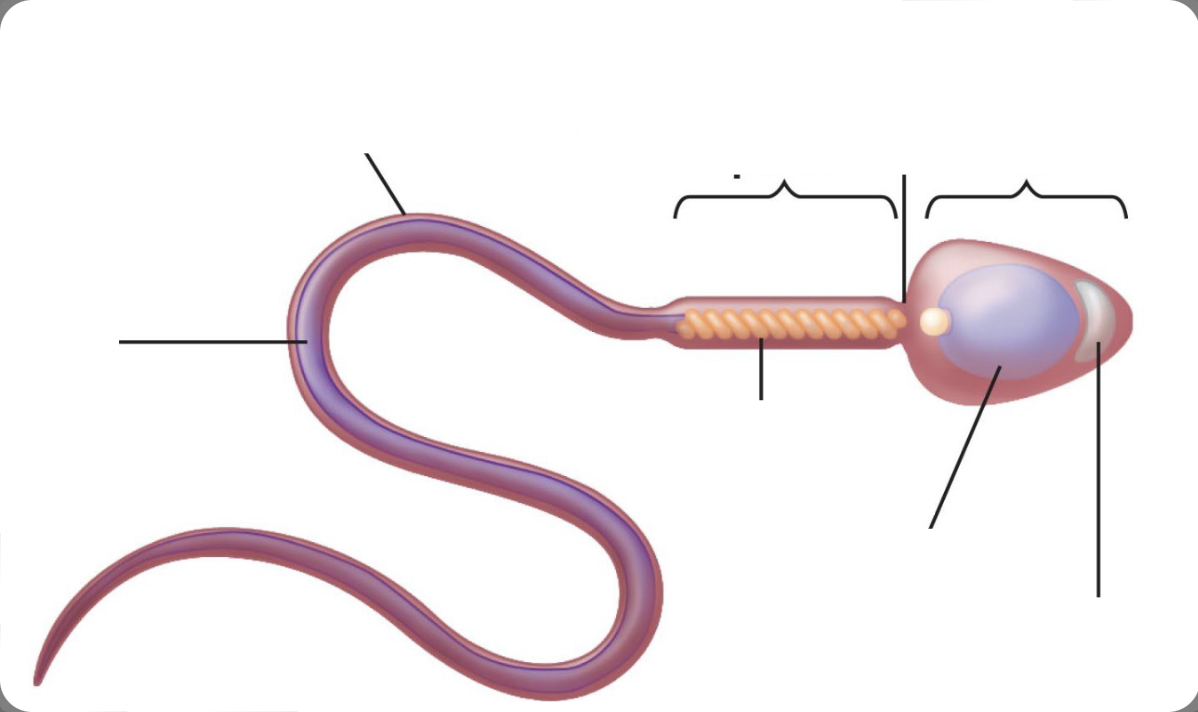
Mature Spermatozoon
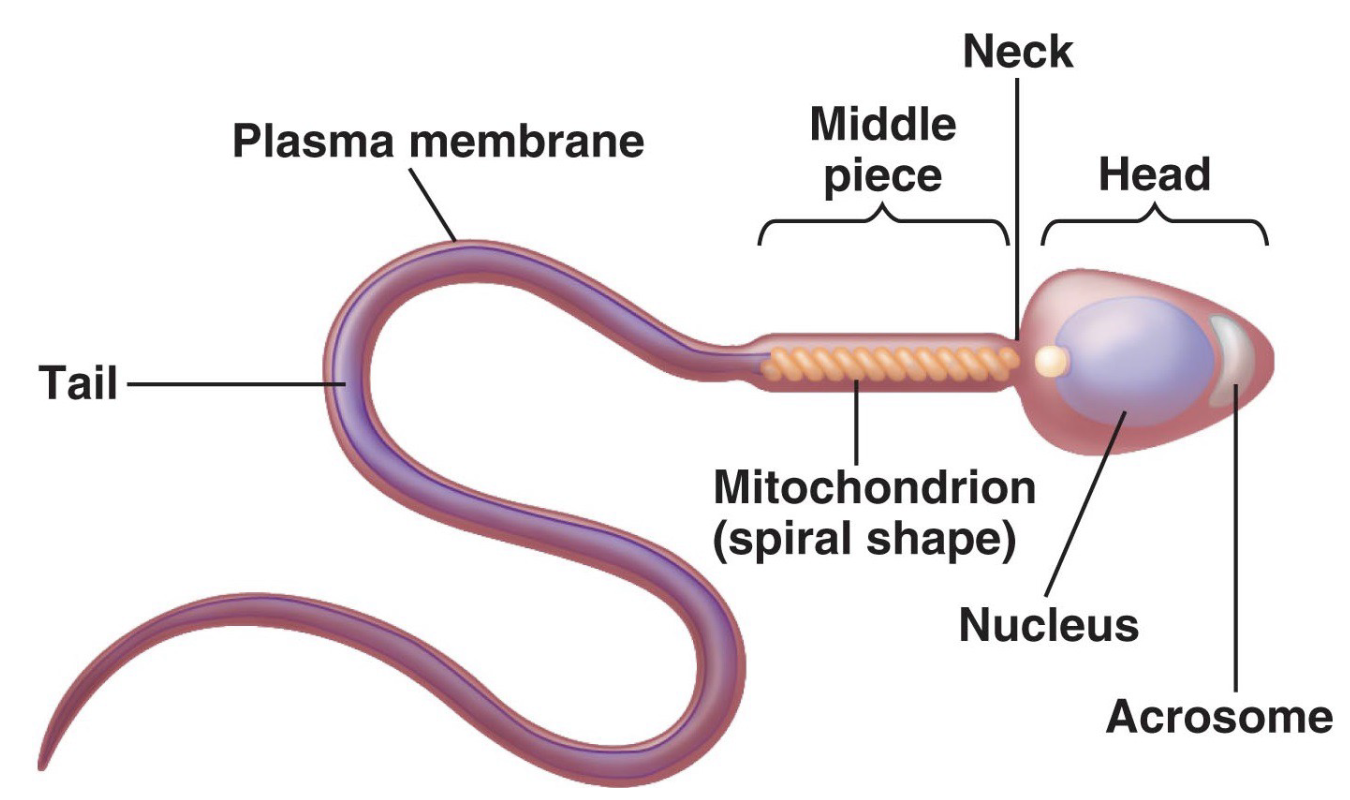
80
New cards
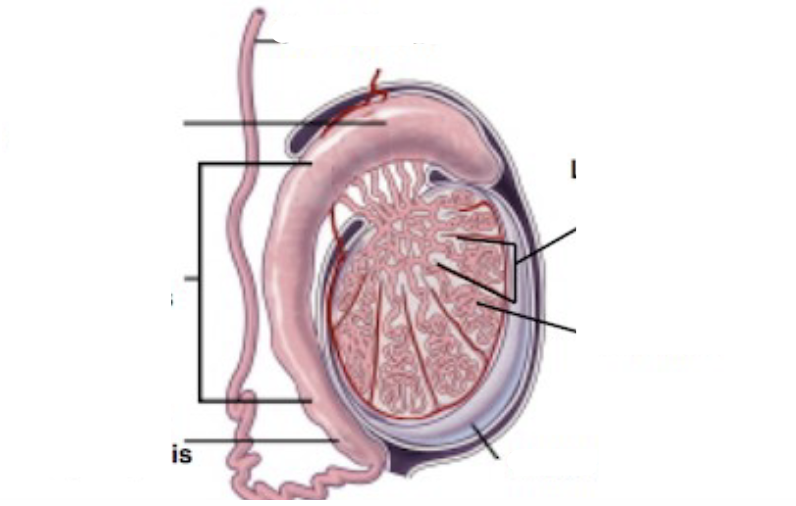
Male Reproductive Tract
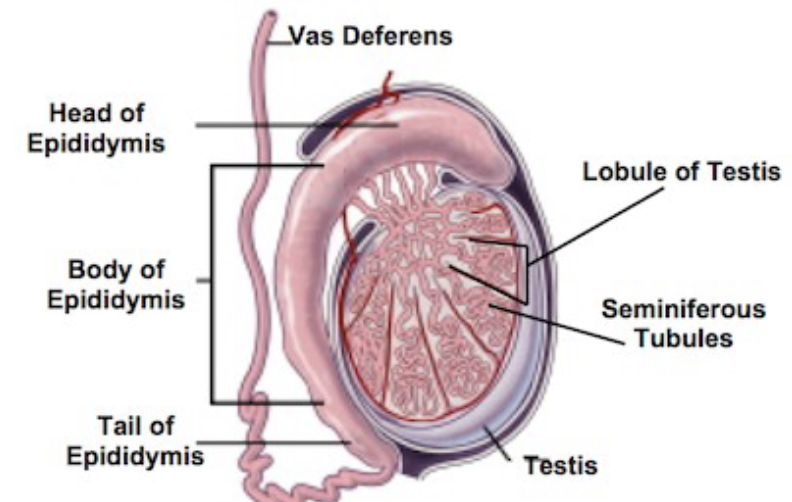
81
New cards
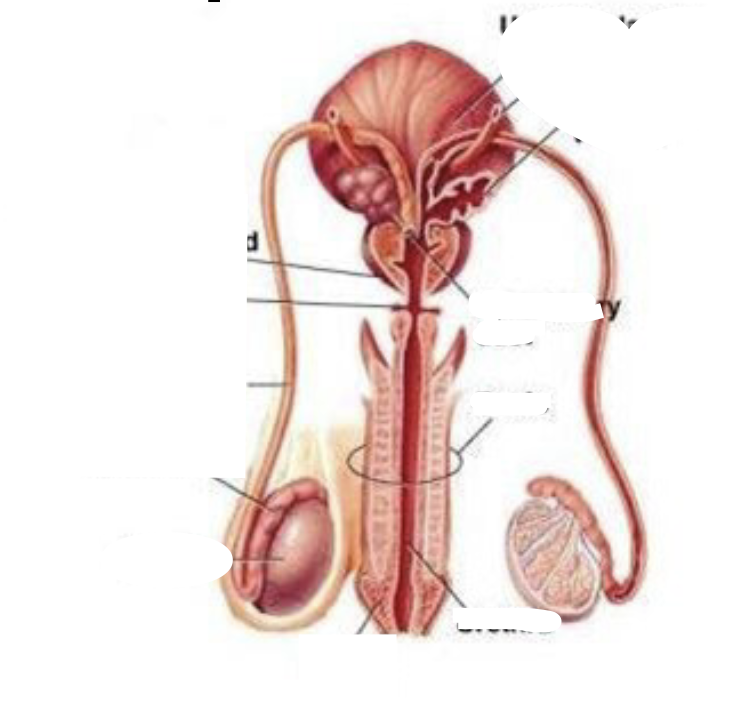
Male Reproductive
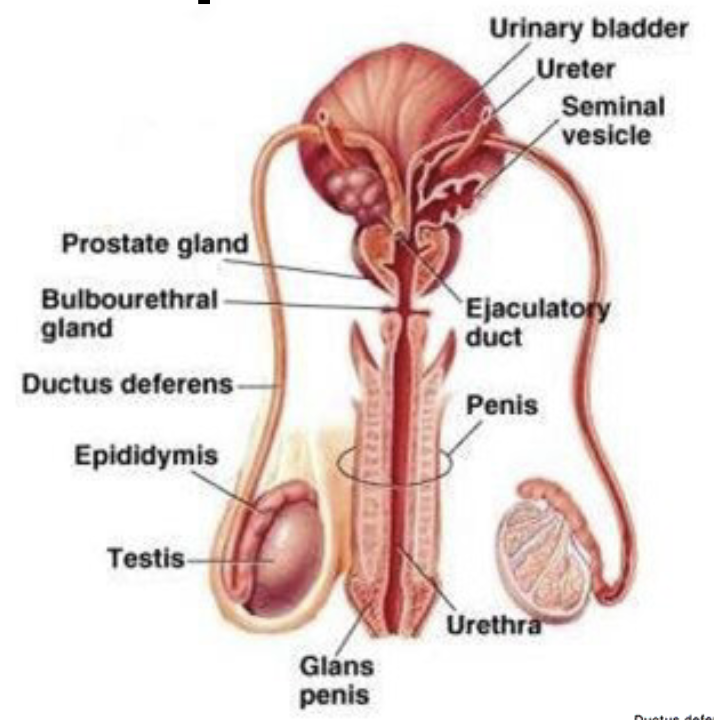
82
New cards
What are the 4 stages of spermatogenesis
* spermatocytogenesis
* spermatidogenesis
* Spermiogenesis
* Spermiation
* spermatidogenesis
* Spermiogenesis
* Spermiation
83
New cards
What is spermatocytogenesis?
from spermatogonium to primary spermatocyte and then secondary spermatocyte
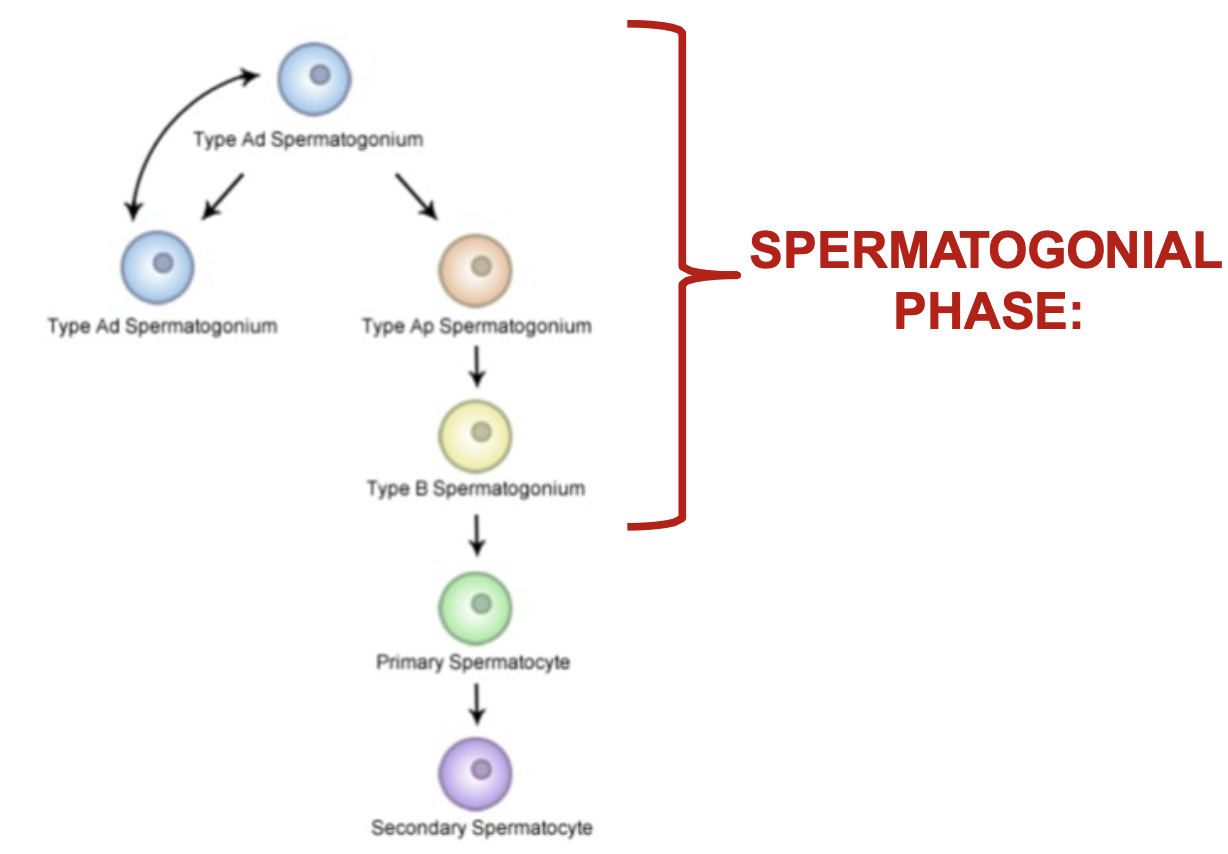
84
New cards
Spermatogonial Phase
* Type A dark (Ad) spermatogonia: stem cells of the seminiferous epithelium
* Type A pale (Ap) spermatogonia: commited to differentiation
* Type B spermatogonia: differentiated from type A
* Type A pale (Ap) spermatogonia: commited to differentiation
* Type B spermatogonia: differentiated from type A
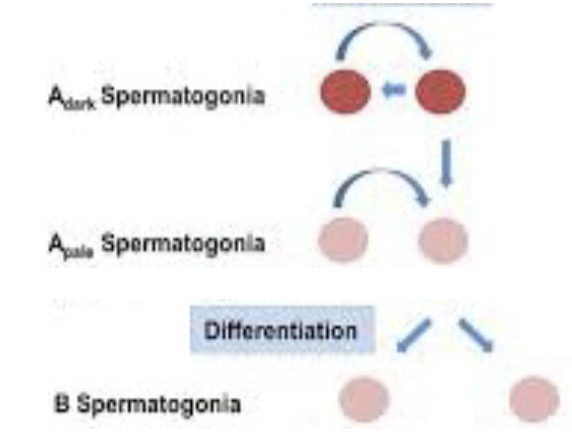
85
New cards
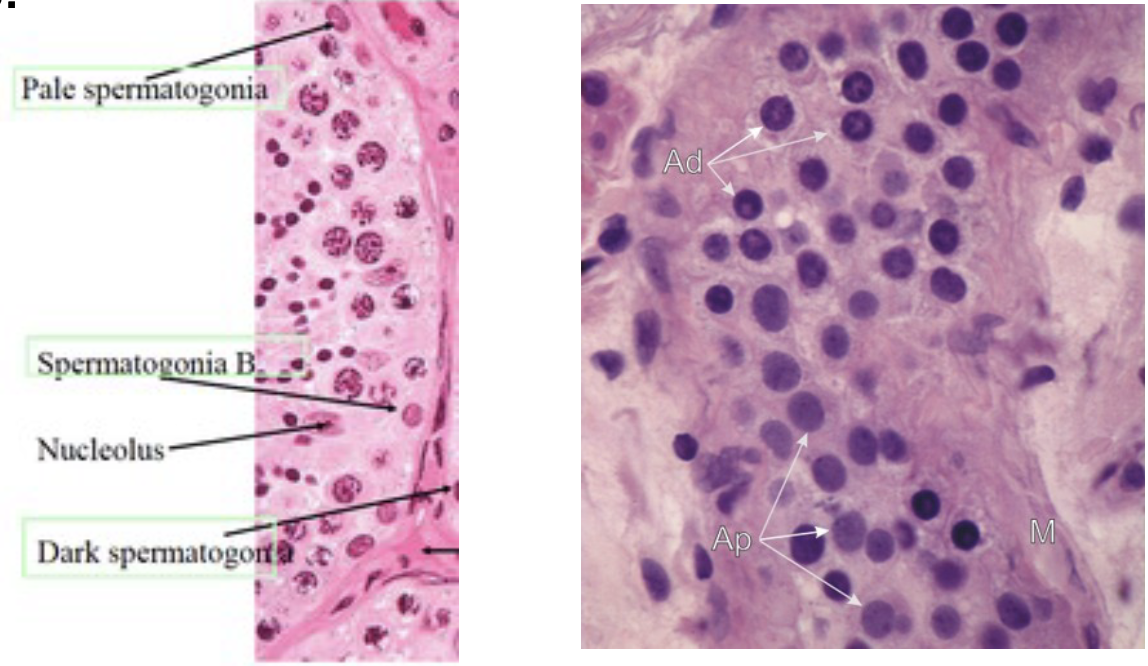
What is the spermatogonial Phase
* Type A(d) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells replicate to \n ensure a constant supply of spermatogonia
* Type A(p) cells, with pale nuclei. These cells divide by mitosis to produce Type B cells.
* Type B cells, which divide to give rise to primary \n spermatocytes.
* Type A(p) cells, with pale nuclei. These cells divide by mitosis to produce Type B cells.
* Type B cells, which divide to give rise to primary \n spermatocytes.
86
New cards
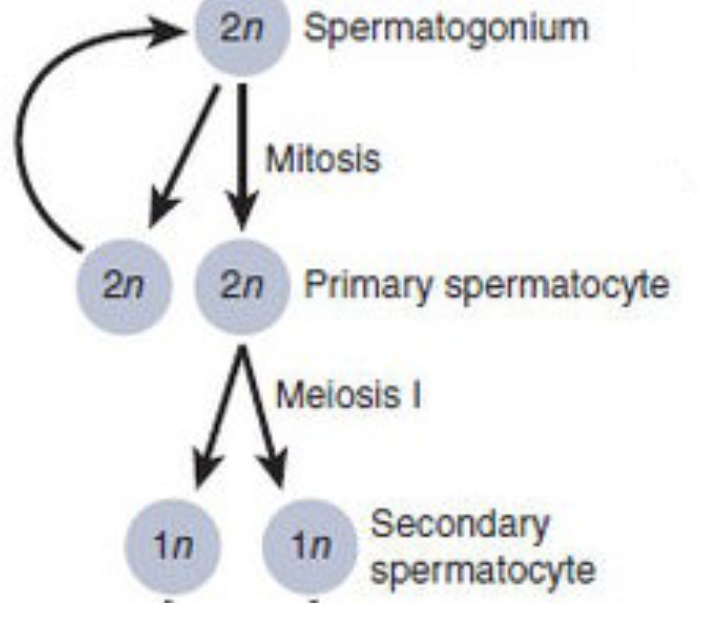
Second Phase of Spermatocytogenesis
* each primary diploid spermatocyte duplicates its DNA and divide in 2 haploid secondary spermatocytes by meiosis 1
87
New cards
What is spermatidogensis?
* the creation of spermatids from secondary \n spermatocytes. Secondary spermatocytes \n produced earlier rapidly enter meiosis II and divide \n to produce haploid spermatids.
88
New cards
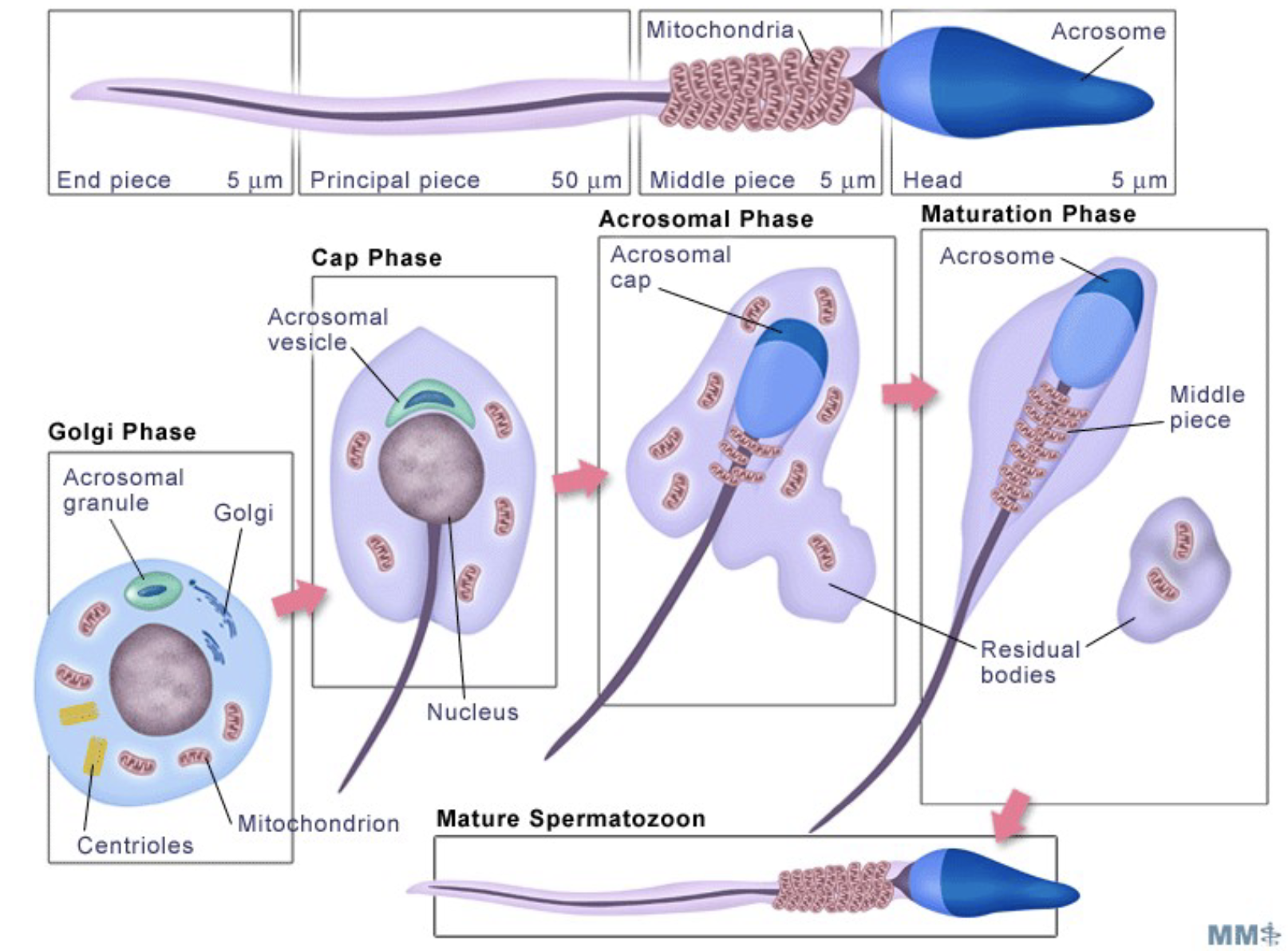
What is spermiogenesis?
* spermatids form a tail by growing microtubules on one of the centrioles (basal body)
* microtubules = axoneme.
* anterior part of the tail (called midpiece) thickens because mitochondria are arranged around → energy supply.
* DNA undergoes packaging → highly condensed.
* tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive.
* Golgi apparatus surrounds the condensed nucleus → \n acrosome.
* testosterone removes the remaining extra \n (residual bodies) and organelles.
* residual bodies are phagocytosed by Sertoli cells. \n cytoplasm \n MATURE SPERMATOZOA, but NOT MOTILE
* microtubules = axoneme.
* anterior part of the tail (called midpiece) thickens because mitochondria are arranged around → energy supply.
* DNA undergoes packaging → highly condensed.
* tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive.
* Golgi apparatus surrounds the condensed nucleus → \n acrosome.
* testosterone removes the remaining extra \n (residual bodies) and organelles.
* residual bodies are phagocytosed by Sertoli cells. \n cytoplasm \n MATURE SPERMATOZOA, but NOT MOTILE
89
New cards
Spermiation
* The release of the mature spermatozoa from the sertoli cells into the lumen of the seminiferous tubule
90
New cards
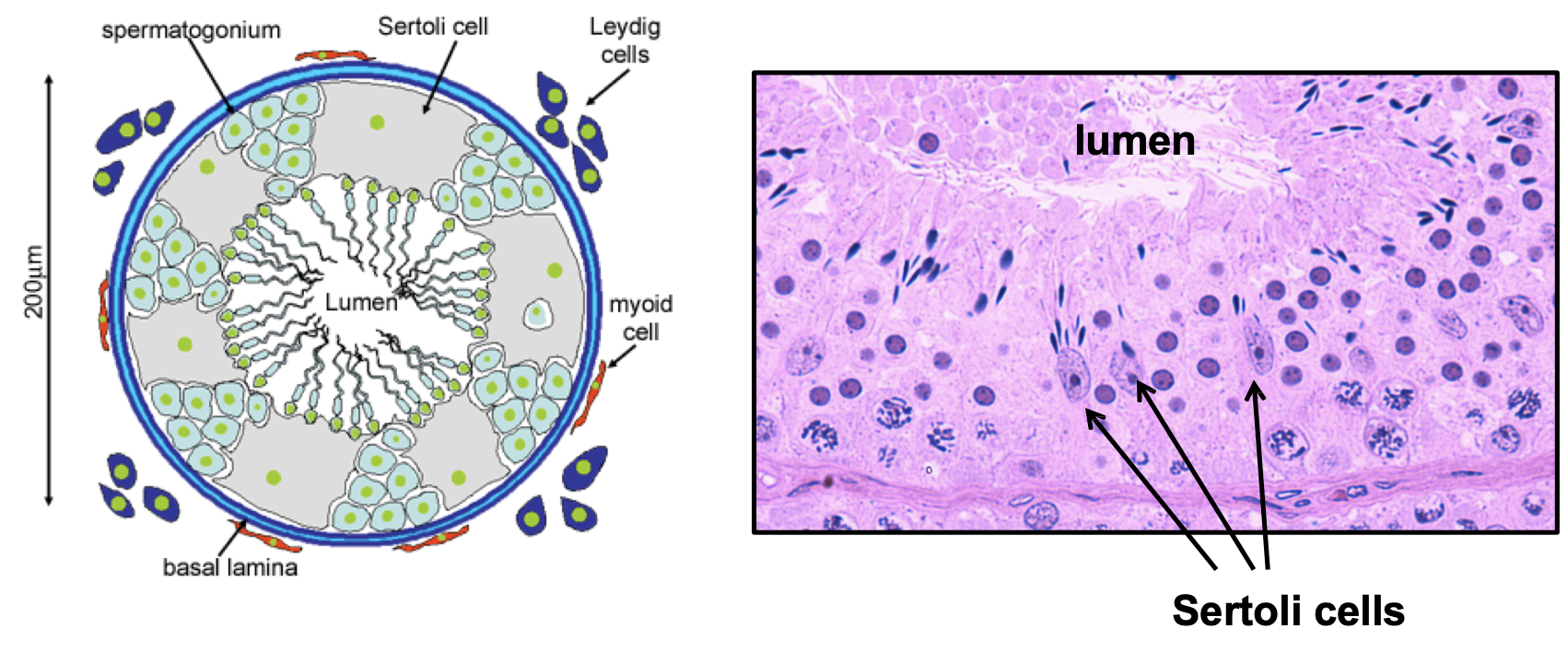
Sertoli cells
* Provide structural and metabolic support to the developing sperm cells
* A single Sertoli cell extends from the basement membrane to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule
* A single Sertoli cell extends from the basement membrane to the lumen of the seminiferous tubule
91
New cards
Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
* spermatogenesis occurs at puberty due to the interaction of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland and Leydig cells.
* FSH stimulates both the production of ABP by Sertoli \n cells, and the formation of the blood-testis barrier.
* inhibin acts to decrease the levels of FSH.
* The Sertoli cells themselves mediate parts of spermatogenesis producing the hormones estradiol and \n inhibin.
* FSH stimulates both the production of ABP by Sertoli \n cells, and the formation of the blood-testis barrier.
* inhibin acts to decrease the levels of FSH.
* The Sertoli cells themselves mediate parts of spermatogenesis producing the hormones estradiol and \n inhibin.
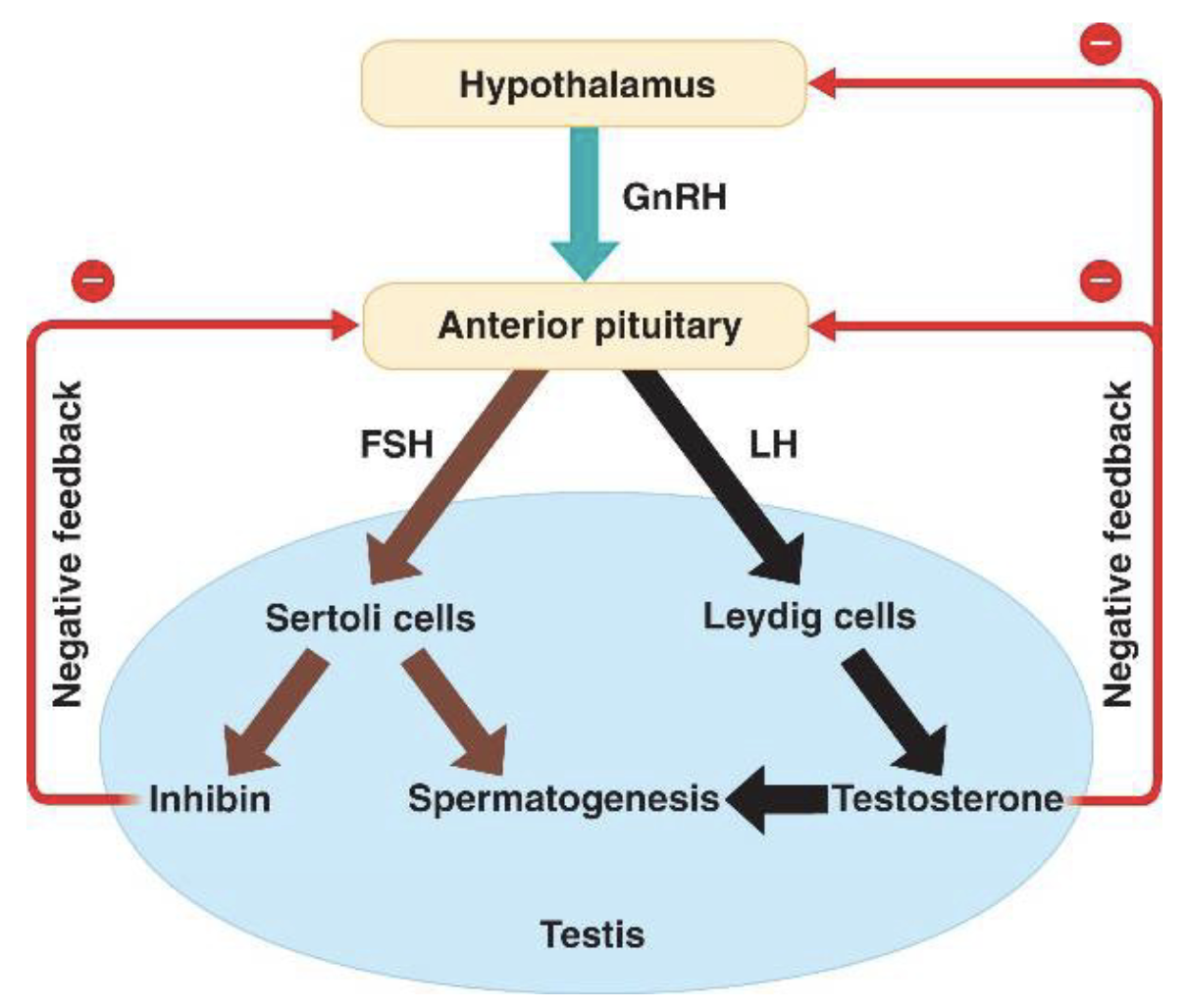
92
New cards
How does sperm transport in the male?
* transported by testicular fluid from the seminiferous tubules to the head(capus) of the epididymis
* 4-12 days in the epididymal duct → biochemical maturation
* On ejaculation, the spermatozoa pass through ductus \n deferens and mix with secretion from the **seminal vesicles** (fructose and prostaglandins) and **prostate glands** (citric acid, acid phosphatase, zinc and magnesium ions
* 4-12 days in the epididymal duct → biochemical maturation
* On ejaculation, the spermatozoa pass through ductus \n deferens and mix with secretion from the **seminal vesicles** (fructose and prostaglandins) and **prostate glands** (citric acid, acid phosphatase, zinc and magnesium ions
93
New cards
What is hypospermia
* production of not enough sperm
94
New cards
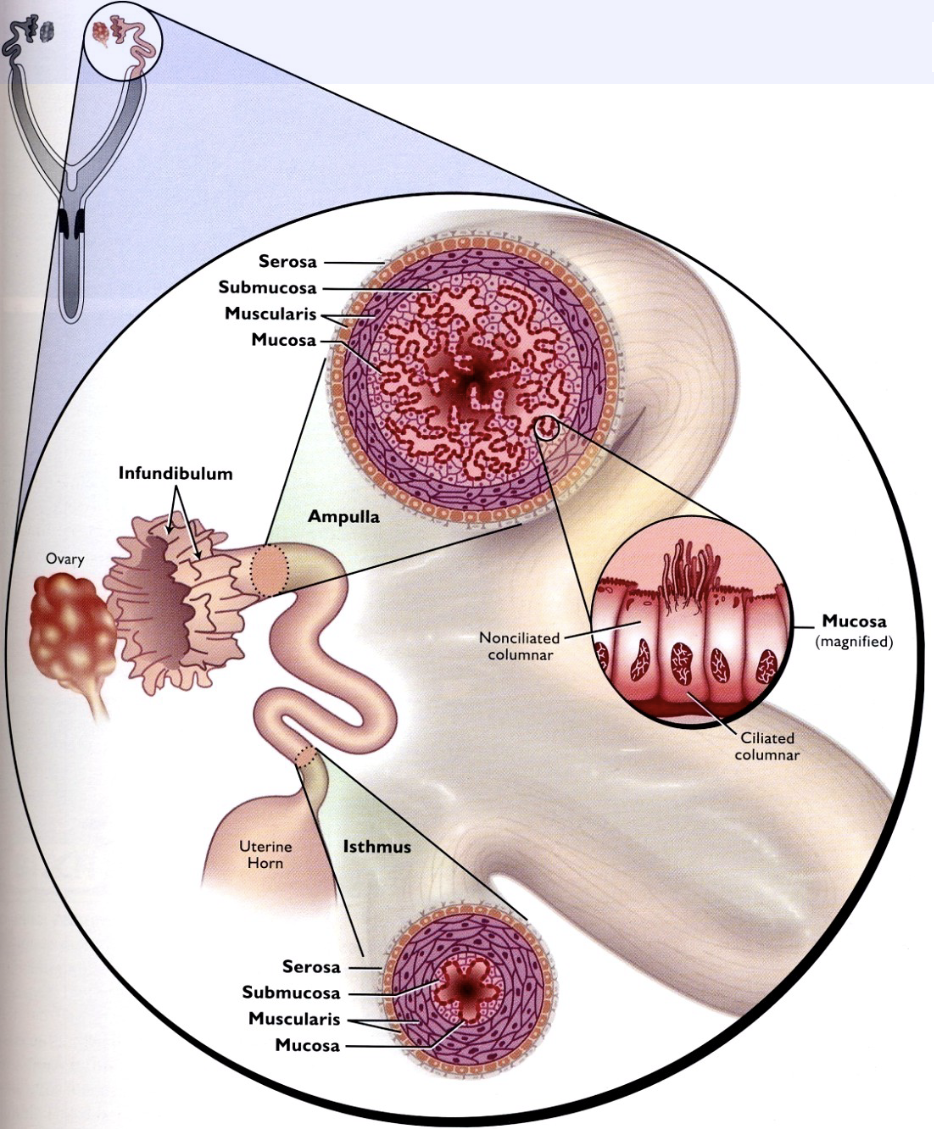
Follicular rupture into peritoneal cavity near…?
Frimbriae (Infundibulum) of the oviduct
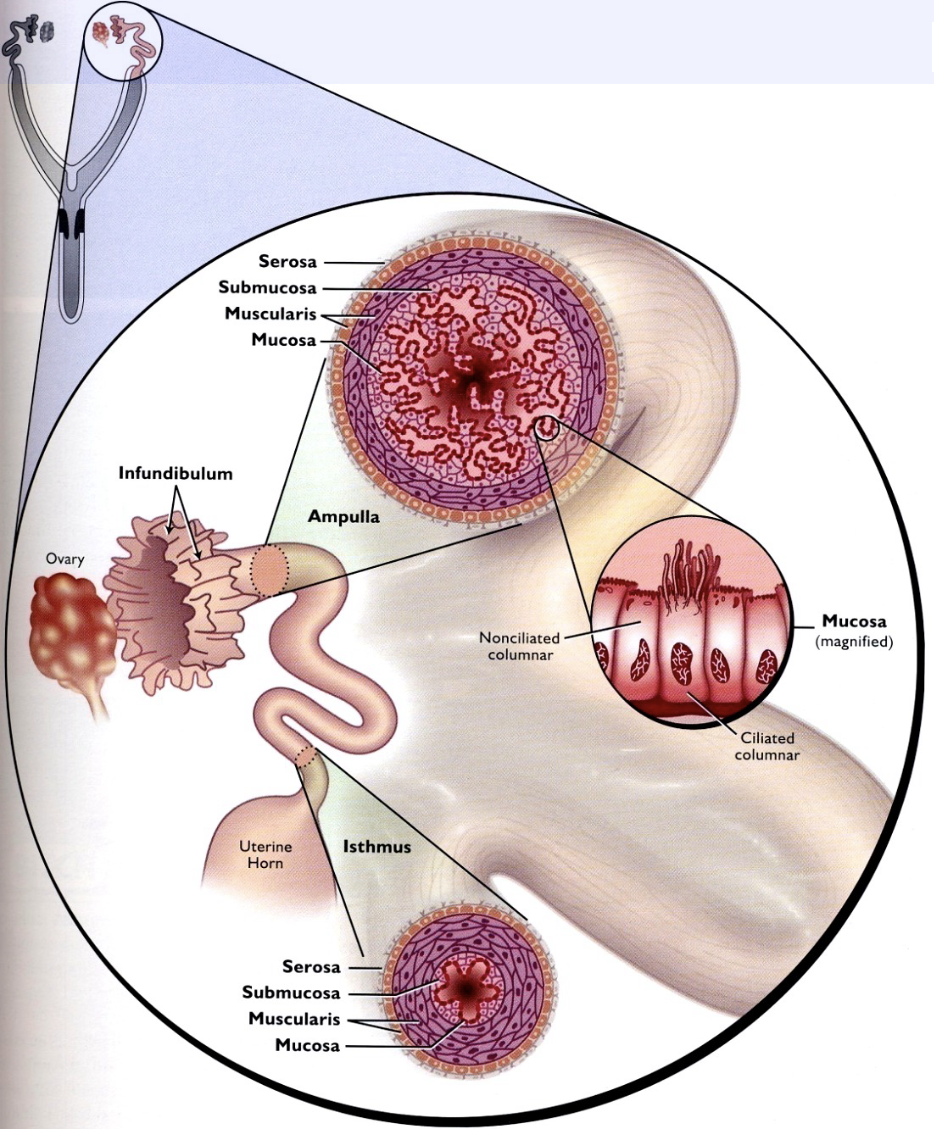
95
New cards
Ciliated epithelial cells and \n the activity of the smooth \n muscle of the oviduct actively \n funnel the ovum into the \n oviduct to the region of
ampulla
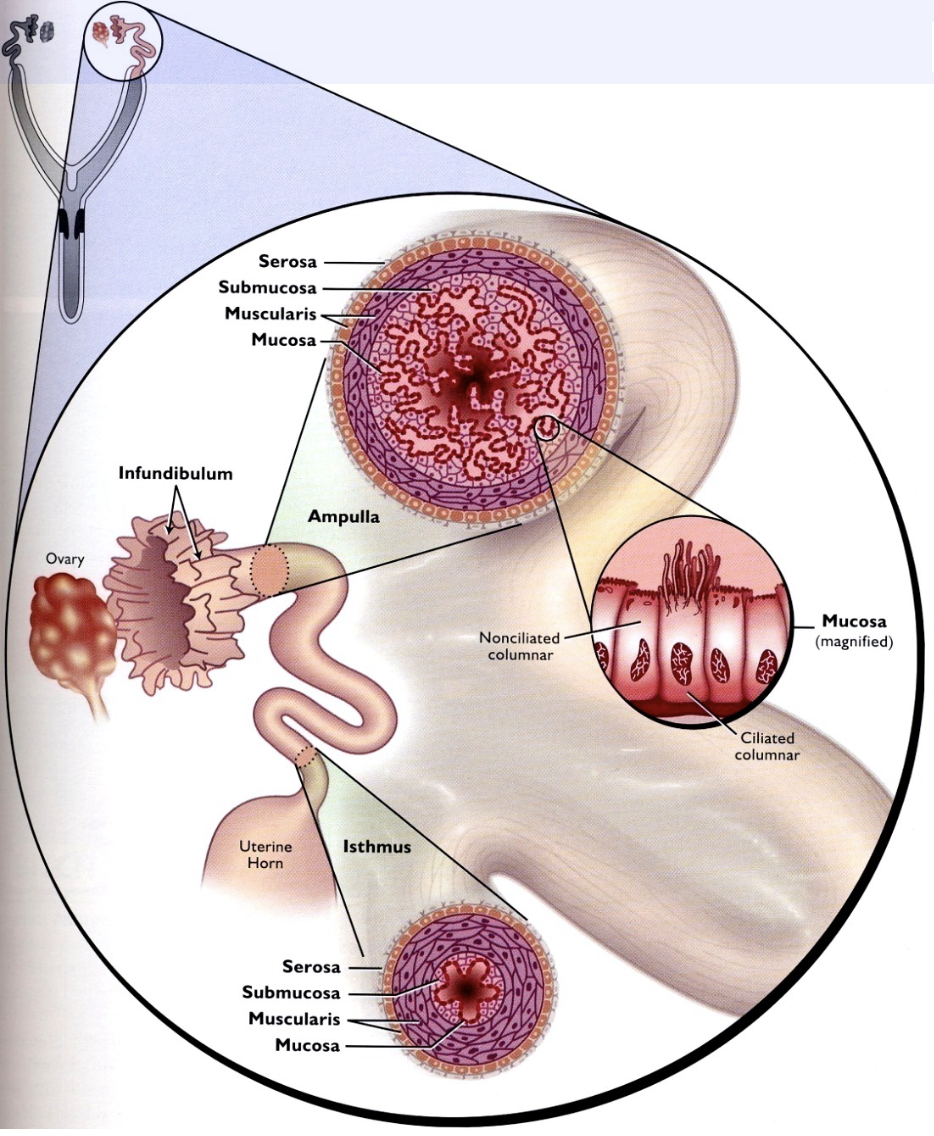
96
New cards
Fertilization occurs at
ampulla or ampulla/isthmus junction
97
New cards
How long does tubal transport in humans take
* 3-4 days
98
New cards
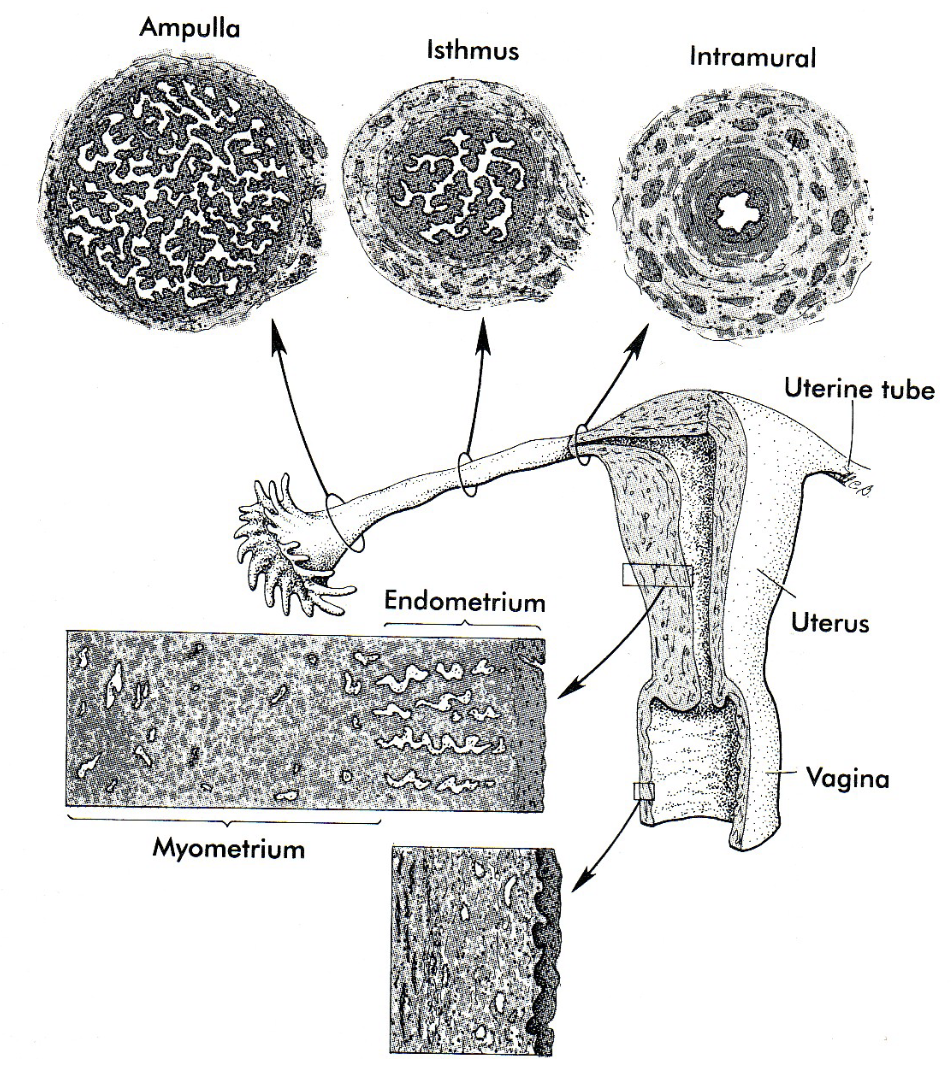
How long does slow transport take in the ampulla
approx. 72hrs
99
New cards
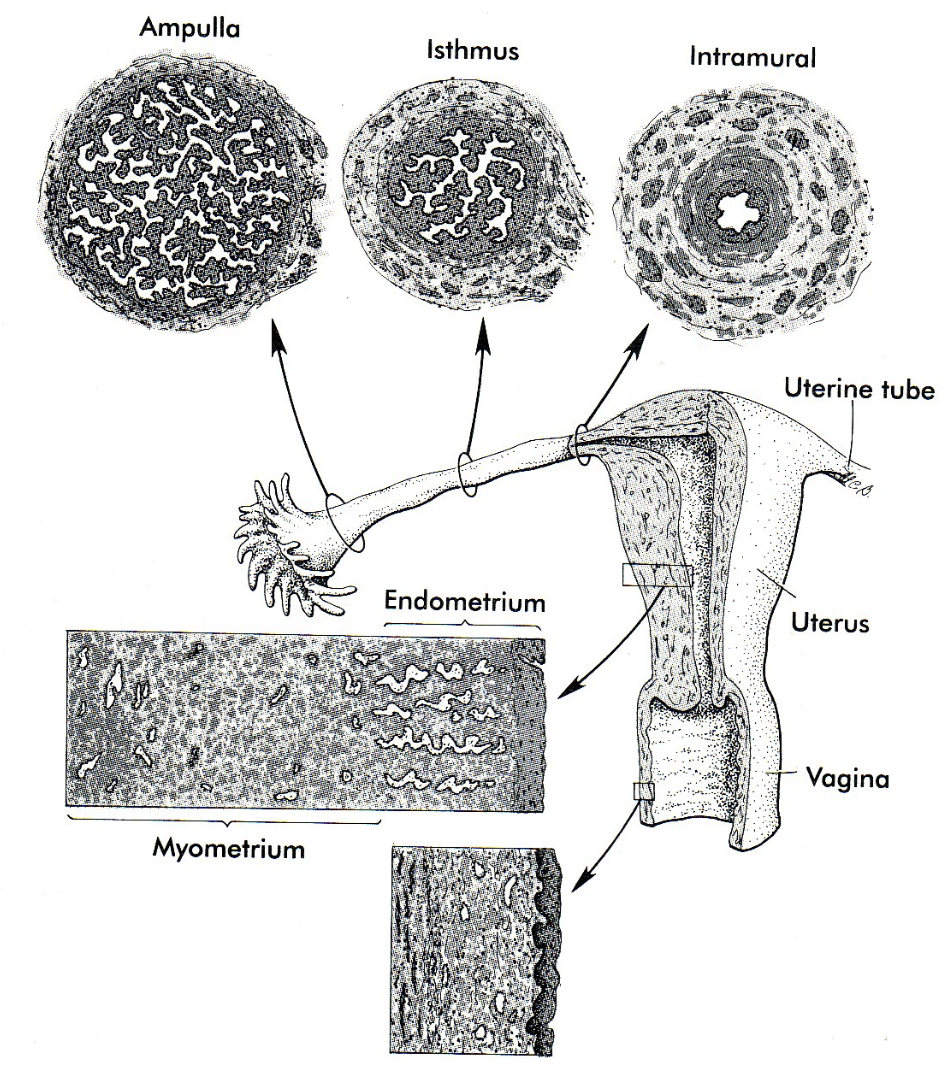
How long does rapid phase through the isthmus and into the uterus
approx. 8hrs
100
New cards
What hormone is necessary for egg to pass the uterotubal junction
* progesterone