Unit Exam - Economics
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Economics
study of how people try to satisfy seemingly unlimited and competing needs and wants through careful use of relatively scarce resources

Need
basic requirement for survival

Want
something we’d like to have but isn’t necessary for survival

Good
useful, tangible item; can be used to satisfy need/want
Value
A worth that can be expressed in dollars and cents
Adam Smith’s Definition of Value
Scarcity + Utility = Value
Paradox of Value
an economic concept that describes the difference in price between essential and non-essential goods. It's based on the idea that water, which is essential for human life, is cheaper than diamonds, which are not essential for human life.
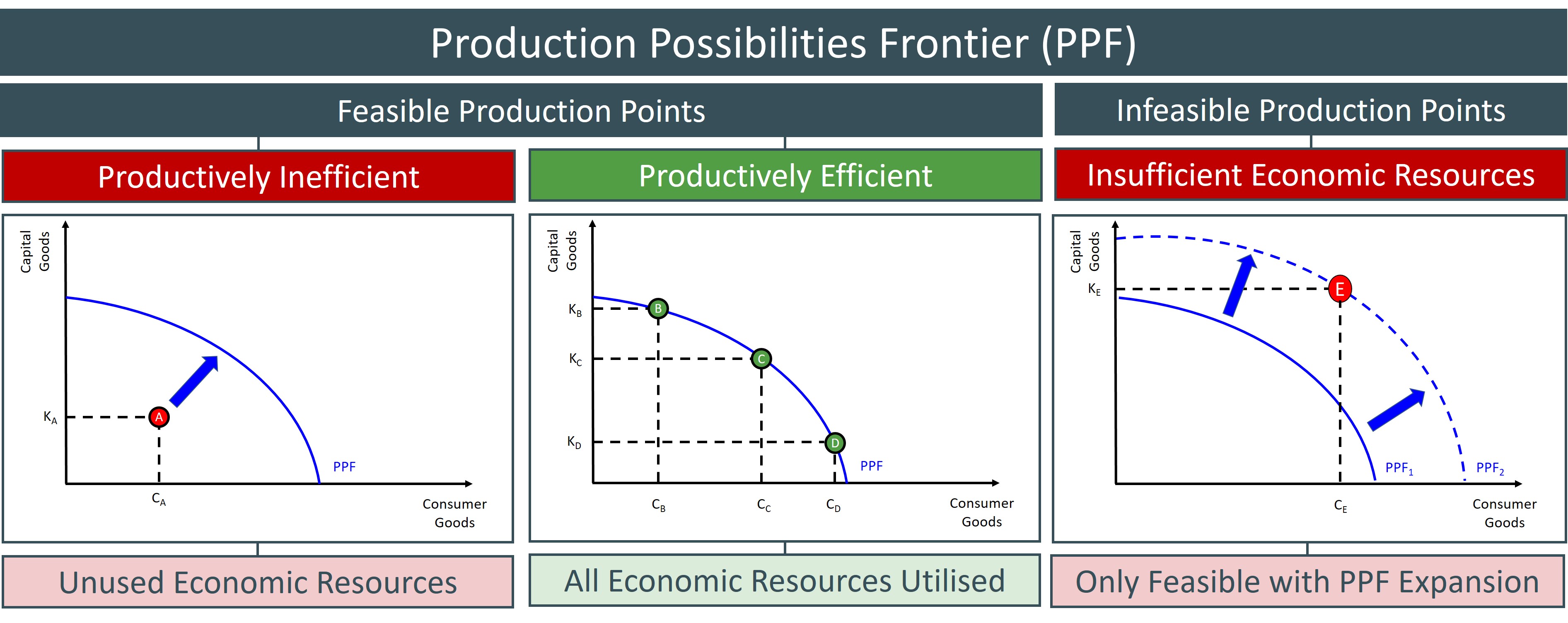
Production Possibility Curve
a graph that shows the maximum amount of two goods that can be produced using a given set of resources and technology
Four Factors of Production
Producing goods and services requires the use of resources, all resources can be classified as one of these factors
Land
All natural resources that are used to produce goods and services. Anything that comes from mother nature (Water, Sun, Plants, Oil, Wood)
Labor
Effort a person devotes to a task for which that a person is paid. (Manual laborers, lawyers, doctors, teachers, etc.)
Physical Capital
A human made resource that is used to create other goods and services (tools, tractors, machinery, buildings, factories, etc.)
Human Capital
Any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experiences (college degrees, vocational training, etc.)
Entrepreneurship
Ambitious leaders that combine factors of production to create goods and services (Henry Ford, Bill Gates, Inventors, Franchise owners, etc.)
Trade-offs
All the alternatives that we give up whenever we choose one course of action over others (Ex. buying a fridge or an airfryer)
Opportunity Cost
The loss of potential gain from other alternatives when one alternative is chosen. (Ex. If you buy an airfryer instead of a fridge you can cook food better, but you lost the opportunity of keeping your food cold.) The value of the option not taken.

Scarcity
When the demand for a good or service is greater than the supply, limiting the choices available to consumers.
This term creates value according to Adam Smith.
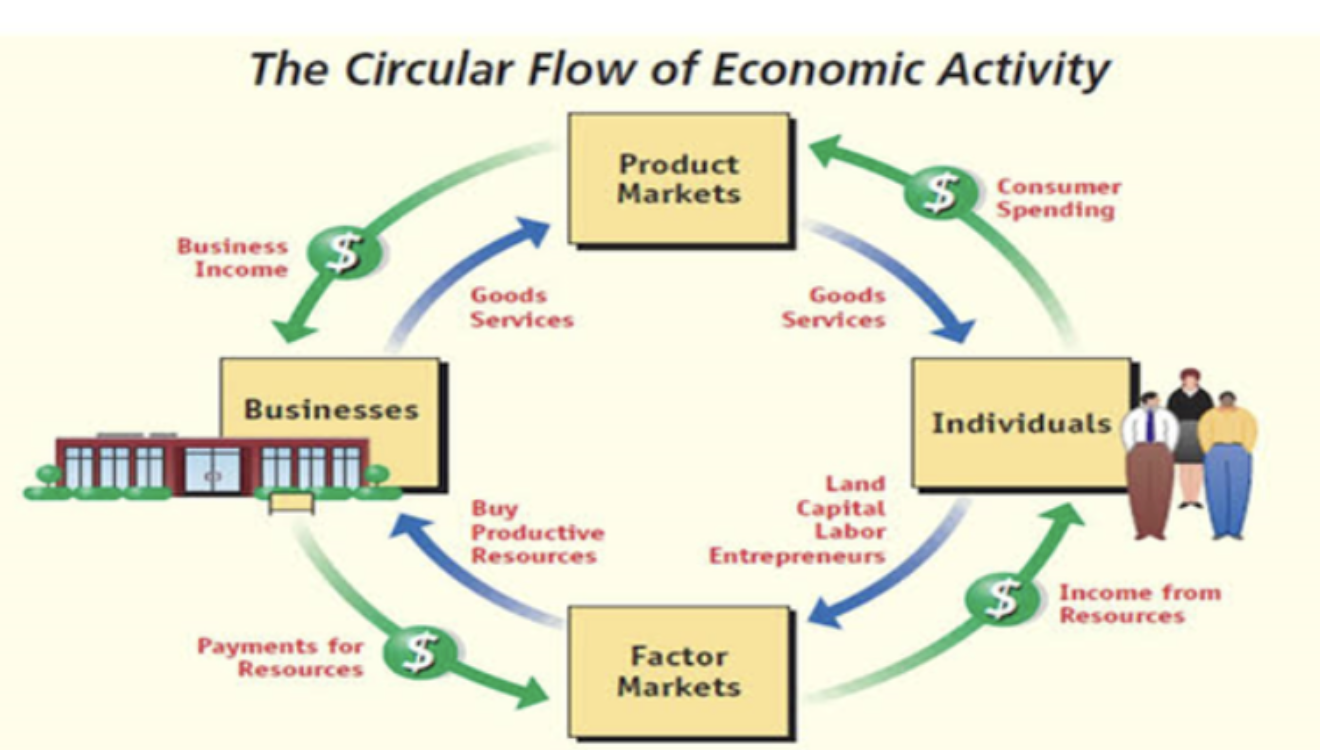
Product Market
The marketplace where households act as buyers, purchasing goods and services produced by businesses, completing the cycle by providing revenue back to the firms which allow them to continue production and pay wages to households in the factor market.
This market acts as the point where goods and services are exchanged for money between consumers and producers.
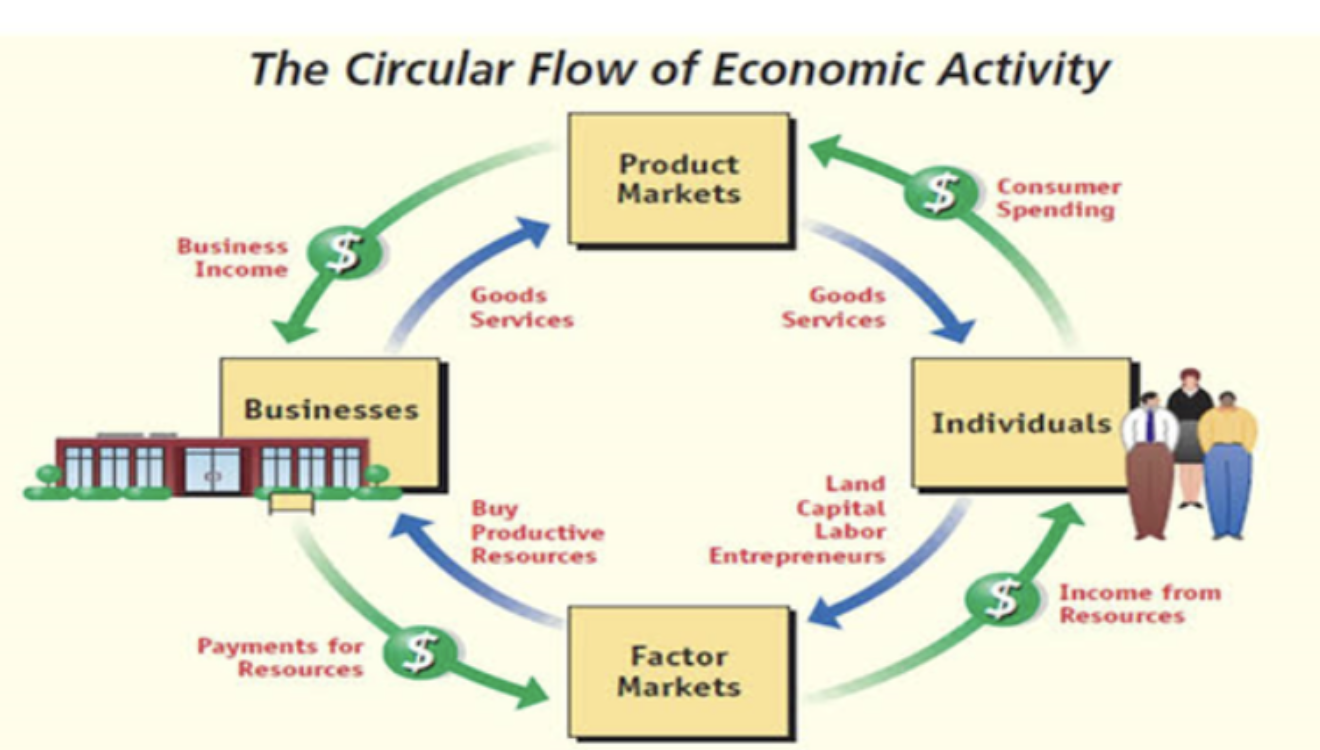
Factor Market
Where households supply factors of production (labor, land, capital) to firms in exchange for income (wages), acting as the platform where businesses acquire the resources needed to produce goods and services. Crucial to the continuous flow of money and goods within the economy.
(PPC) Plotted below curve
Feasible but not efficient
(PPC) Plotted on curve
Feasible and Efficient
(PPC) Plotted above curve
Efficient but not feasible
What does Marx think about Free will?
Karl Marx believed that people have free will and the potential to transform the world, but that modern society limits their ability to do so.
Marxist freedom is Collective and Economic in nature.