human nervous system- CNS,the brain, the eye
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Nervous System
Coordinates body activities through electrical signals.
receptors
Special structures that allow living organisms to sense the stimuli i.e sound receptors in ear
central nervous system
The brain and spinal cord
Transmits & receives messages
sensory neurones
nerve cells that carry messages from cells in the sense organs to the CNS
motor neurones
nerve cells that carry messages from the CNS to effectors
effectors
muscles and glands that respond to nervous impulses
Information Transmission
Signals travel via neurons and synapses.
Reflex Action
Automatic response to stimuli, bypassing brain.
Importance of Reflex Actions
Protects body from harm through quick responses.
i.e if someone shines a bright light in your eye, your pupil automatically gets smaller
so less light gets into the eye
Reflex Arc
Pathway of neurons involved in reflex actions.
reflex arc steps
stimuli→ Receptor → sensory neurone → relay neurone → CNS → motor neurone → effector→ response
example of journey of reflex arc
1. bee stings finger
2.stimulation of pain receptors
3.impulses travel along sensory neurone
4.impulses passed along relay neurone, via synapse
5.impulse travels along motor neurone
6.when impulse reaches muscle, it contracts
Types of Neurons
Sensory, motor and relay
Synapse
connection between two neurones
required practical 7- reaction time with ruler
1)arm resting on edge of table
2)hold at zero end and drop
3)measure where caught to determine reaction time
4)repeat
required practical 7- reaction time computer
simple computer games i.e clicking the mouse
Brain Function
Controls thoughts, movements, and homeostasis.
labelled brain
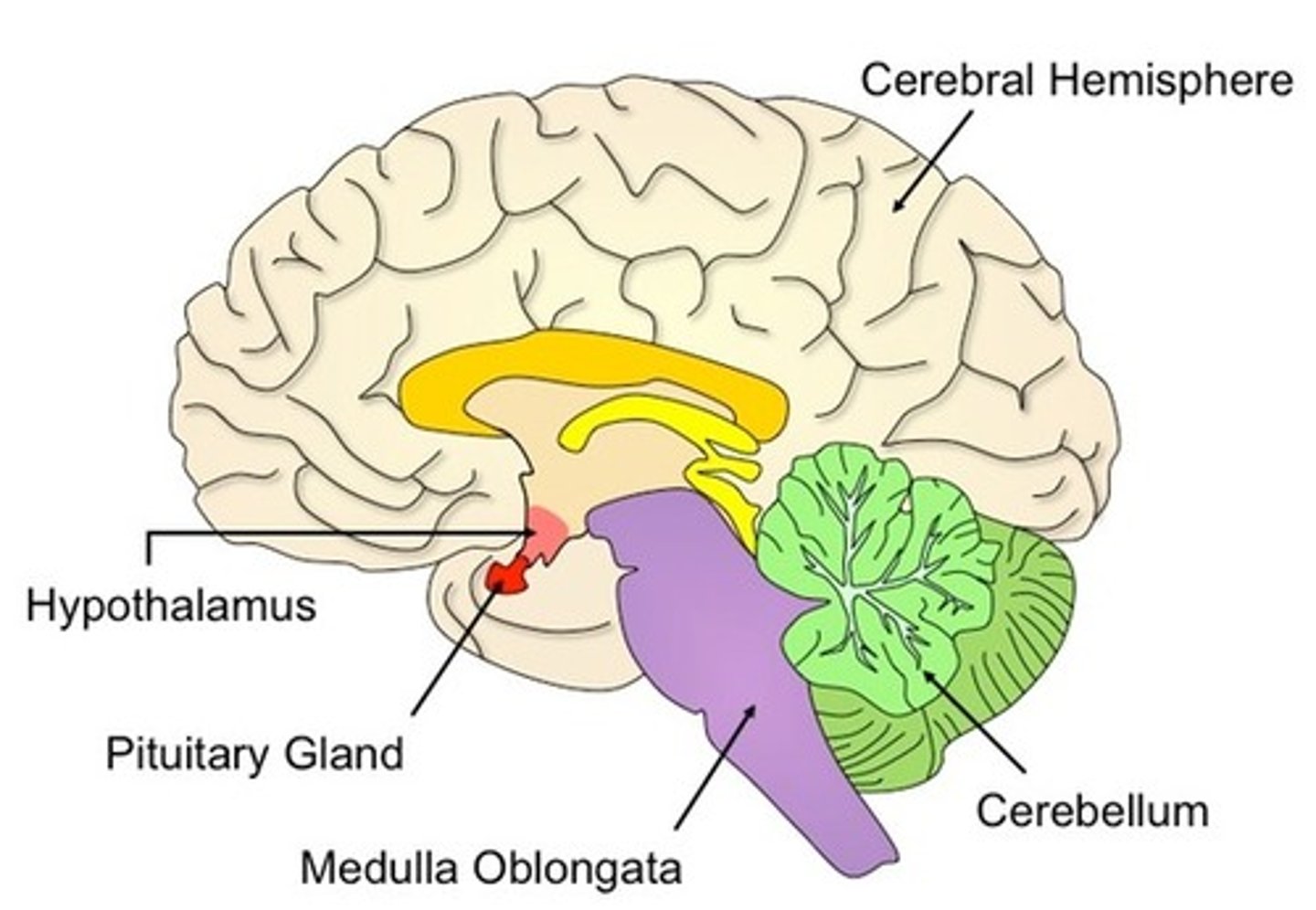
Cerebral Cortex
wrinkly bit
Responsible for consciousness, intelligence and memory
Cerebellum
at the back, star like
Coordinates muscle movement
Medulla
controls unconsciousness activities like breathing and heart rate.
Hypothalamus
regulating body functions
pituary gland
releases hormones that control body actions
how do scientists study the brain
1) Studying patients with brain damage
2) Electrically stimulating the brain
3) MRI scans
1) Studying patients with brain damage
if small part of brain is damaged, the effect on patient tells you the role of the area damaged
2) Electrically stimulating the brain
brain can be stimulated electrically to observe what different parts of the brain does
3) MRI scans
produces very detailed picture of the brain structure
used to find out which areas are active when people are doing normal things like listening to music
Eye Function
Receives light and enables vision.
Labelled eye diagram:
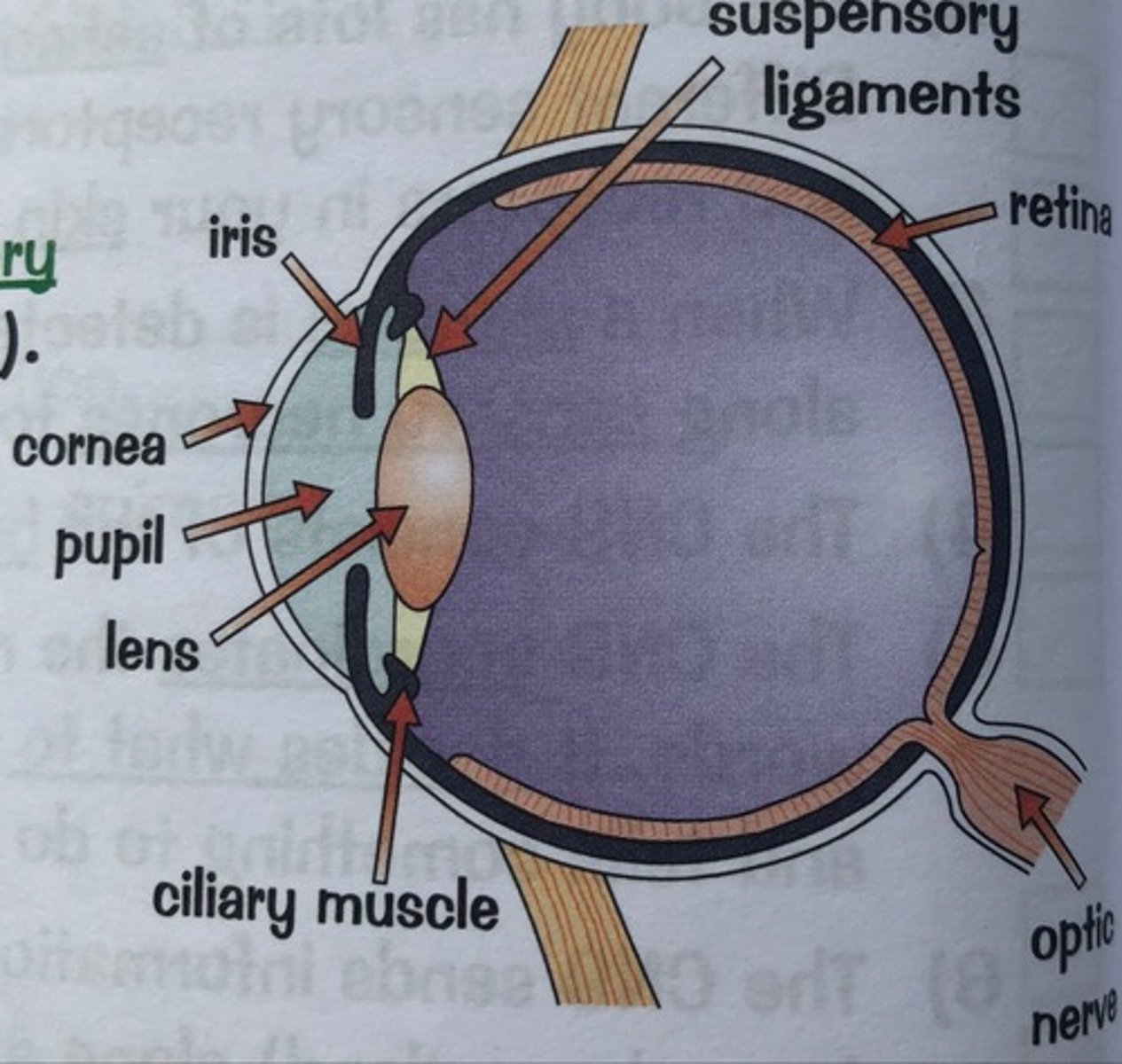
Sclera
white of the eye
supports wall of eye
cornea
The clear tissue that covers the front of the eye
refracts light into the eye
iris
contains muscle that allows it to control the diameter of the pupil and therefore how much light enters
lens
Focuses light onto retina
retina
Contains sensory receptors that process visual information and sends it to the brain
focusing on near object
Ciliary muscles contract
suspensory ligaments loosen
lens is thicker and refracts light rays strongly
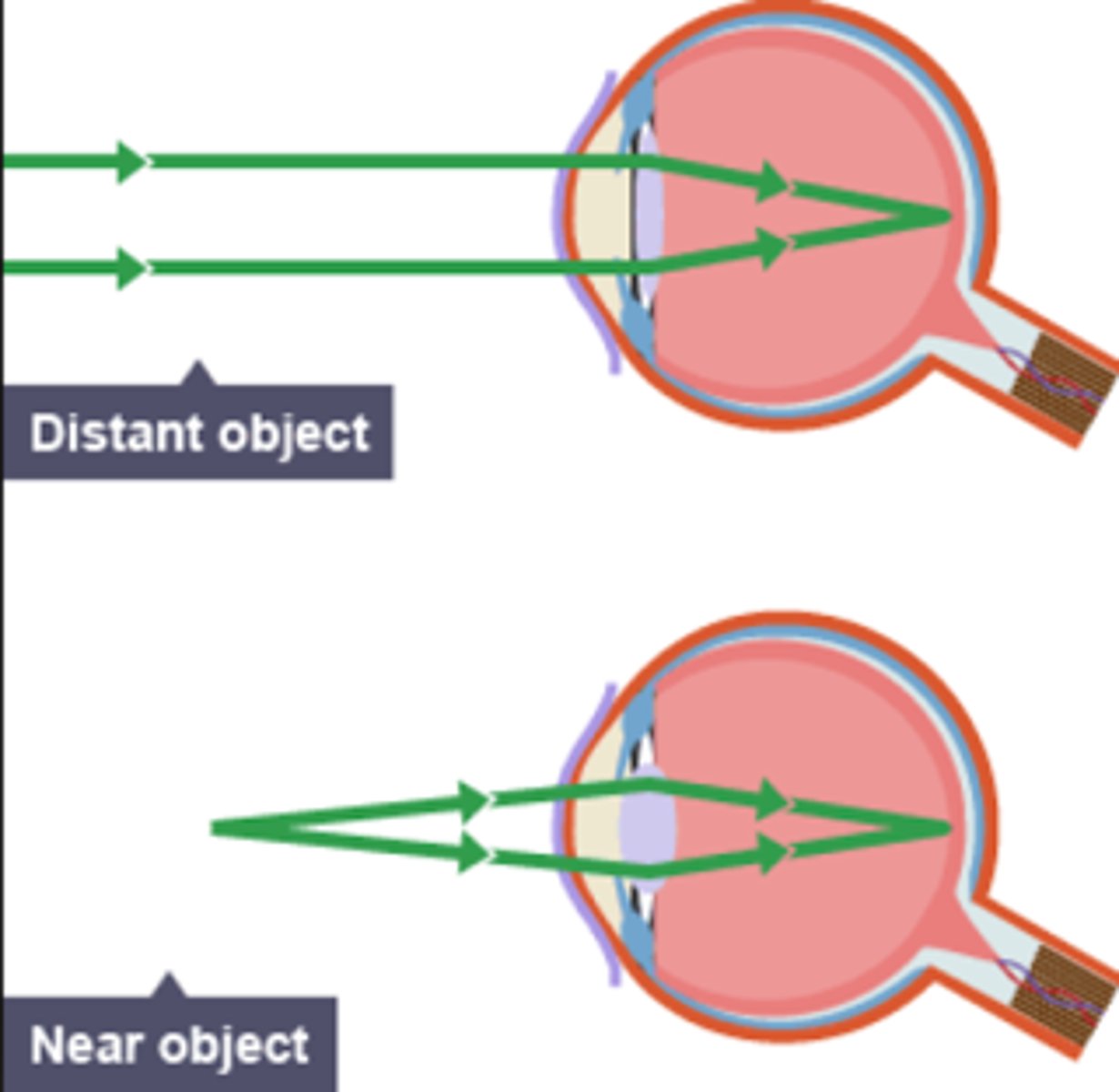
focusing on far object
ciliary muscles relax
suspensory ligaments tightened
lens flattens
slightly refracts light
bright light
Circular muscles contract
Radial muscles relax
Pupil constricts
dim light
Circular muscles relax
Radial muscles contract
Pupil dilates
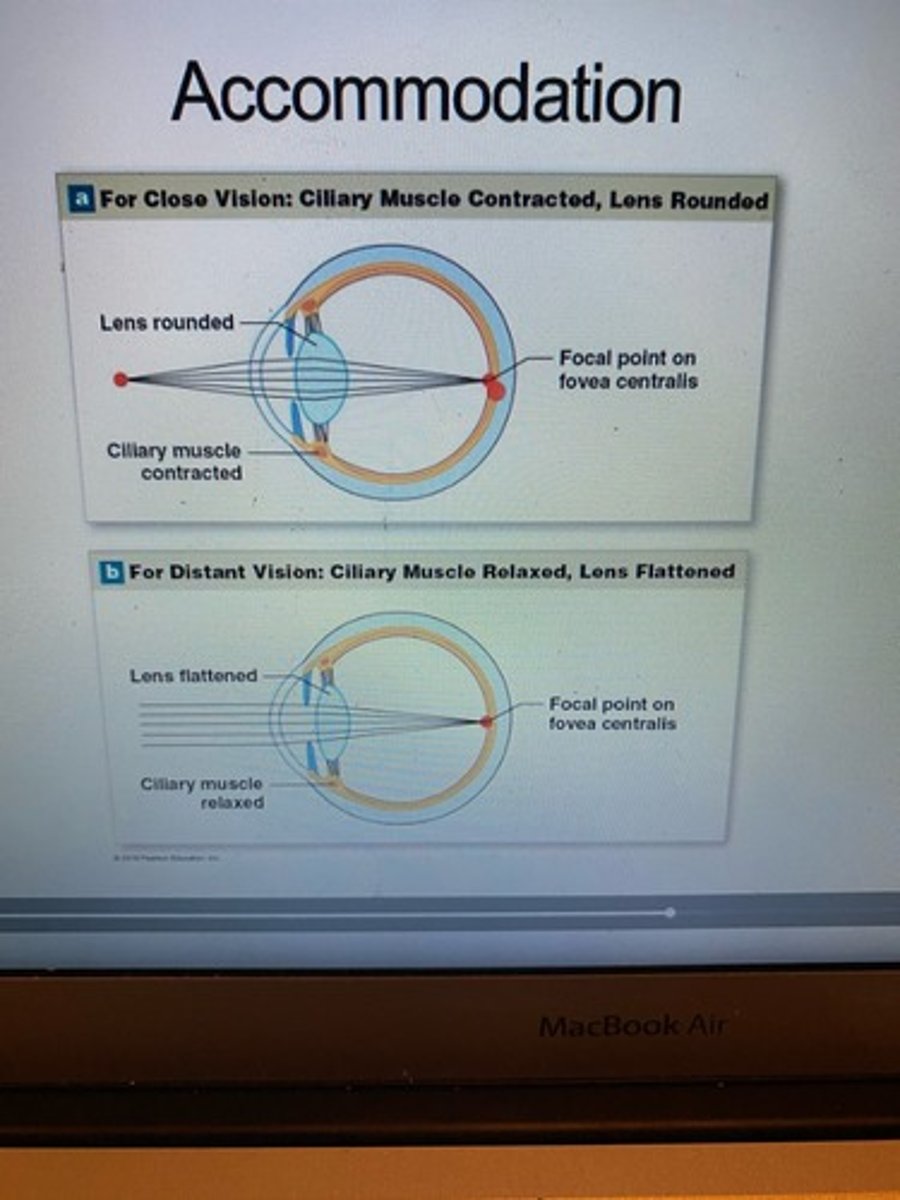
Accommodation
Eye's adjustment for focusing on objects.
Myopia
Nearsightedness- can see close objects in clear focus
light is focused at front of retina
lens too curvy
eyeball is too long
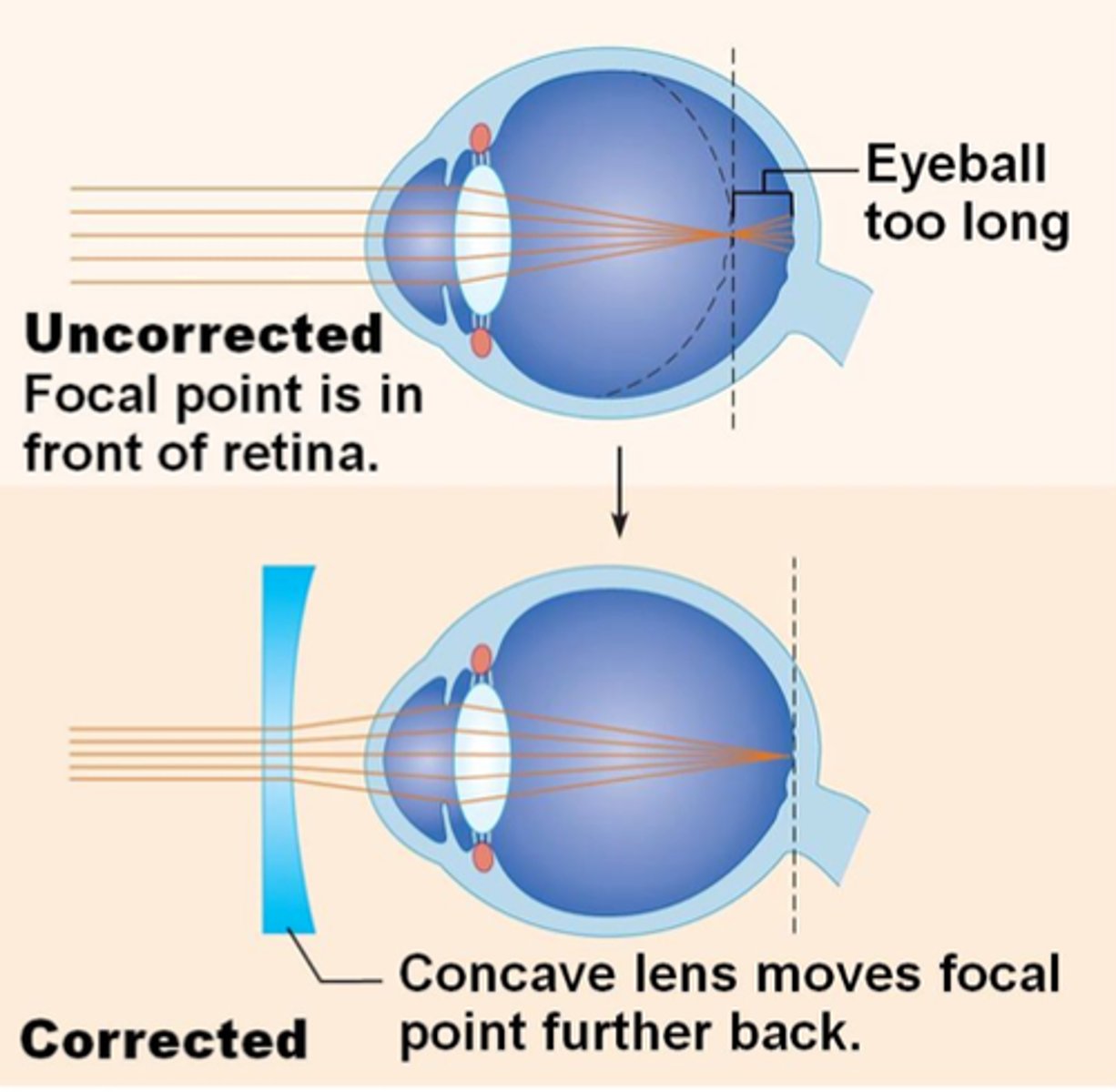
Short sighted treatment
glasses with concave lens (curves inwards) so light can focus on the retina
Hyperopia
Farsightedness- an focus clearly on far objects
light focused behind retina
lens too flat
eyeball too short
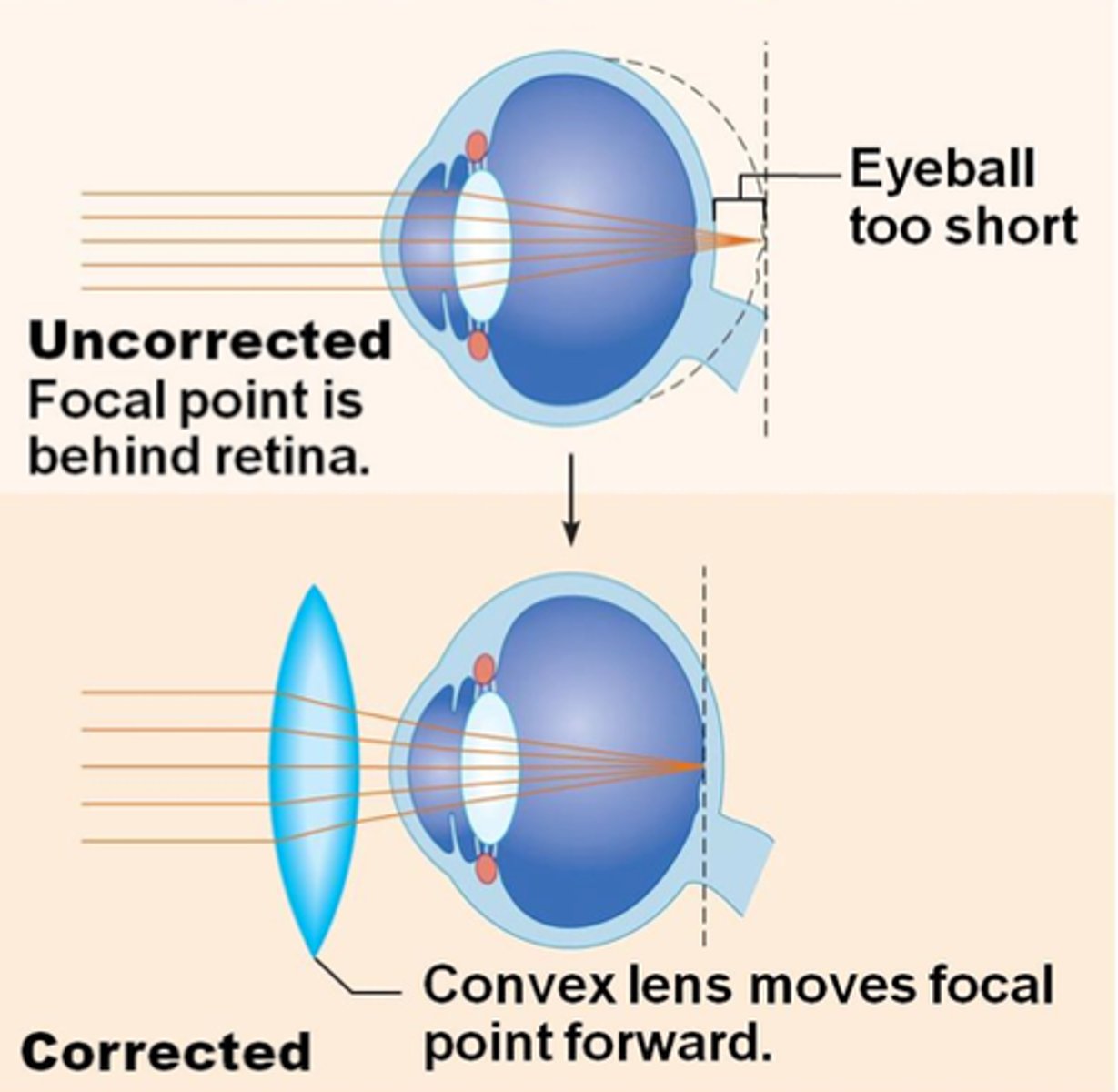
long sighted treatment
glasses with convex lens (curves outwards) so light can focus on the retina
Temperature Regulation
thermoregulatory centre in brain which contains receptors that are sensitive to temp of blood flowing through brain
how body temp is regulated via negative feedback
too high- thermoregulatory centre receives info from temp receptors and triggers effectors i.e sweat glands to counteract change
too low-thermoregulatory centre receives info from temp receptors and triggers effectors i.e muscles to produce a response
too hot
1)hair lies flat
2)sweat is produced via glands and evaporates into skin. this transfers energy to environment
3)blood vessels dilate so more blood flows close to surface of skin-vasodilation
too cold
1)hairs stand up to trap insulating layer of air
2)no sweat produced
3)blood vessels constrict to close off skins blood supply- vasconstriction
4)when cold, you shiver too which need respiration that transfers energy to warm up body