Comprehensive Guide to Mobility, Posture, and Nursing Interventions in Healthcare
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Mobility
A nursing goal is to assist in preserving, maintaining, and restoring as much mobility and function as possible.
Assessment of Mobility
The assessment of mobility includes ROM, gait, and exercise.
Range of Motion (ROM)
Includes Active and Passive types.
Activity intolerance
An inadequate amount of physical or physiological energy to undergo or complete a necessary activity.
Activity tolerance
The capacity to successfully complete a necessary activity without distress.
Activities of daily living (ADL)
Basic essential skills that a person does independently every day and are usually related to personal care.
Cardiac Muscle
Only located in the heart and functions involuntarily.
Smooth Muscle
Located in the blood vessels and the visceral organs and functions involuntarily.
Skeletal Muscle
Attached to the skeleton (bones) by tendons and functions voluntarily.
Lordosis
Increased lumbar curvature.
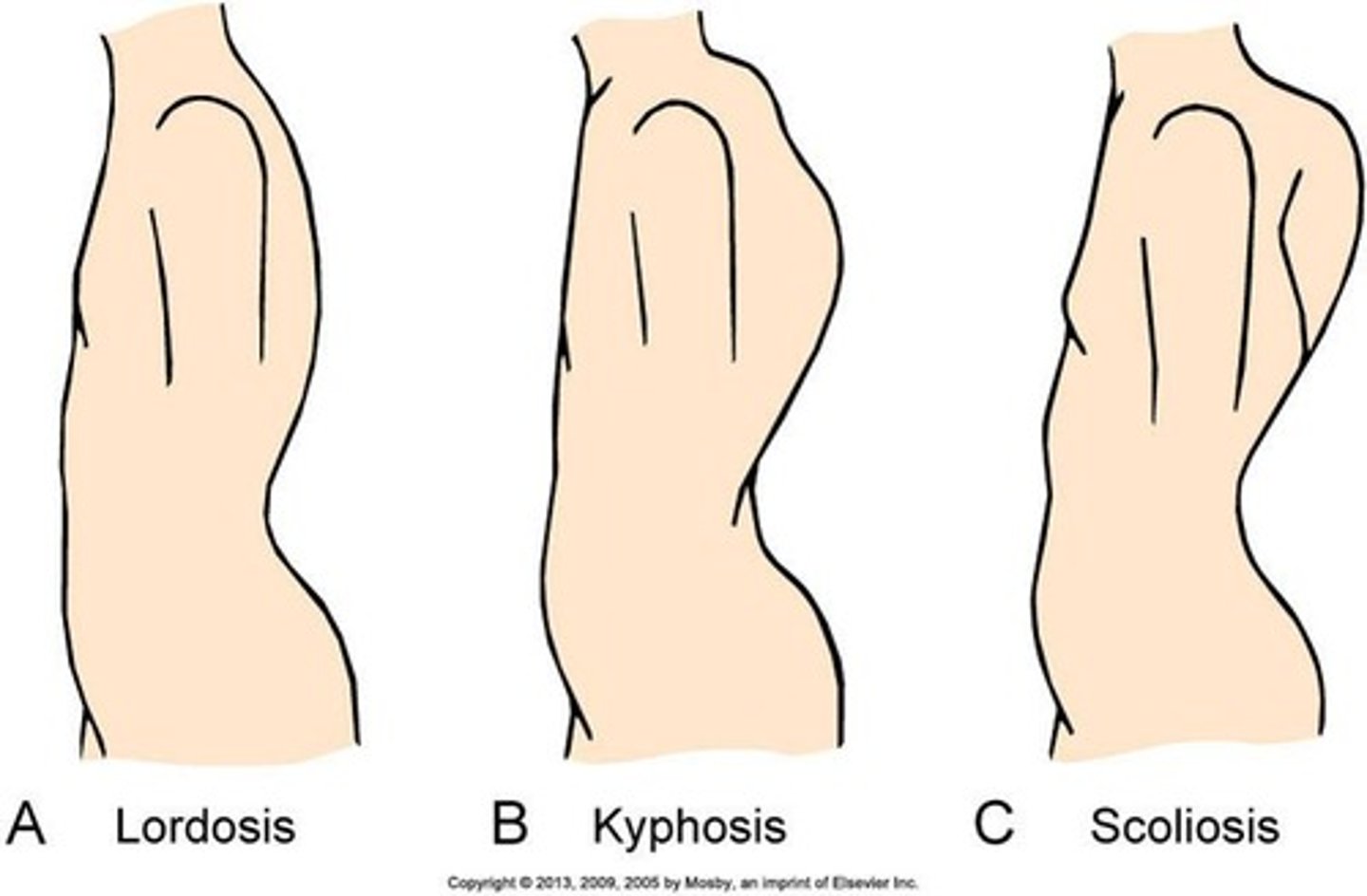
Kyphosis
Increased thoracic curvature.
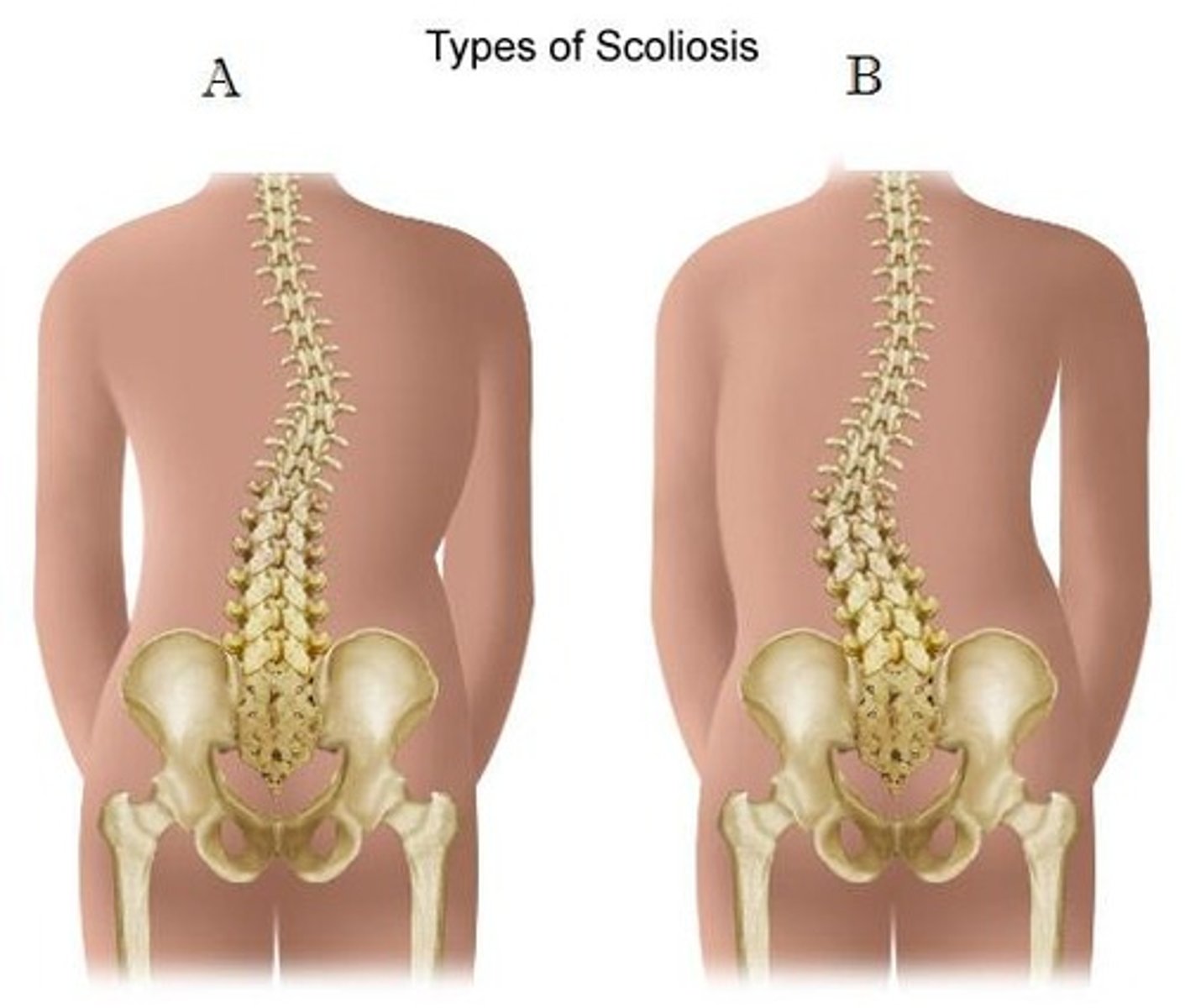
Scoliosis
Lateral curvature that can be thoracic, lumbar, or both - rarely cervical.
Torticollis
A postural abnormality affecting the neck.
Congenital hip dysplasia
A postural abnormality affecting the hip.
Knock-knee
A postural abnormality where knees go inward.
Bowlegs
A postural abnormality where legs curve outward.
Club foot
A postural abnormality affecting the foot.
Foot drop
A postural abnormality where the foot drags.
Immobility
A state of being unable to move, which can be due to bed rest or other factors.
Disuse atrophy
Muscular deconditioning due to lack of use.
Systemic Effects of Immobility
Includes metabolic changes, decreased appetite, electrolyte imbalances, and increased risk of bone fracture.
Gastrointestinal (GI) system functions
Can be affected by immobility, leading to constipation risk and pseudodiarrhea.
Respiratory changes
Includes atelectasis and hypostatic pneumonia as effects of immobility.
Nursing Interventions for Metabolic Changes
Includes high-protein, high-calorie diet, with Vitamin B and C, and may require enteral feedings.
TCDB
A nursing intervention that stands for Turn, Cough, Deep Breathe, used to prevent atelectasis and pneumonia.
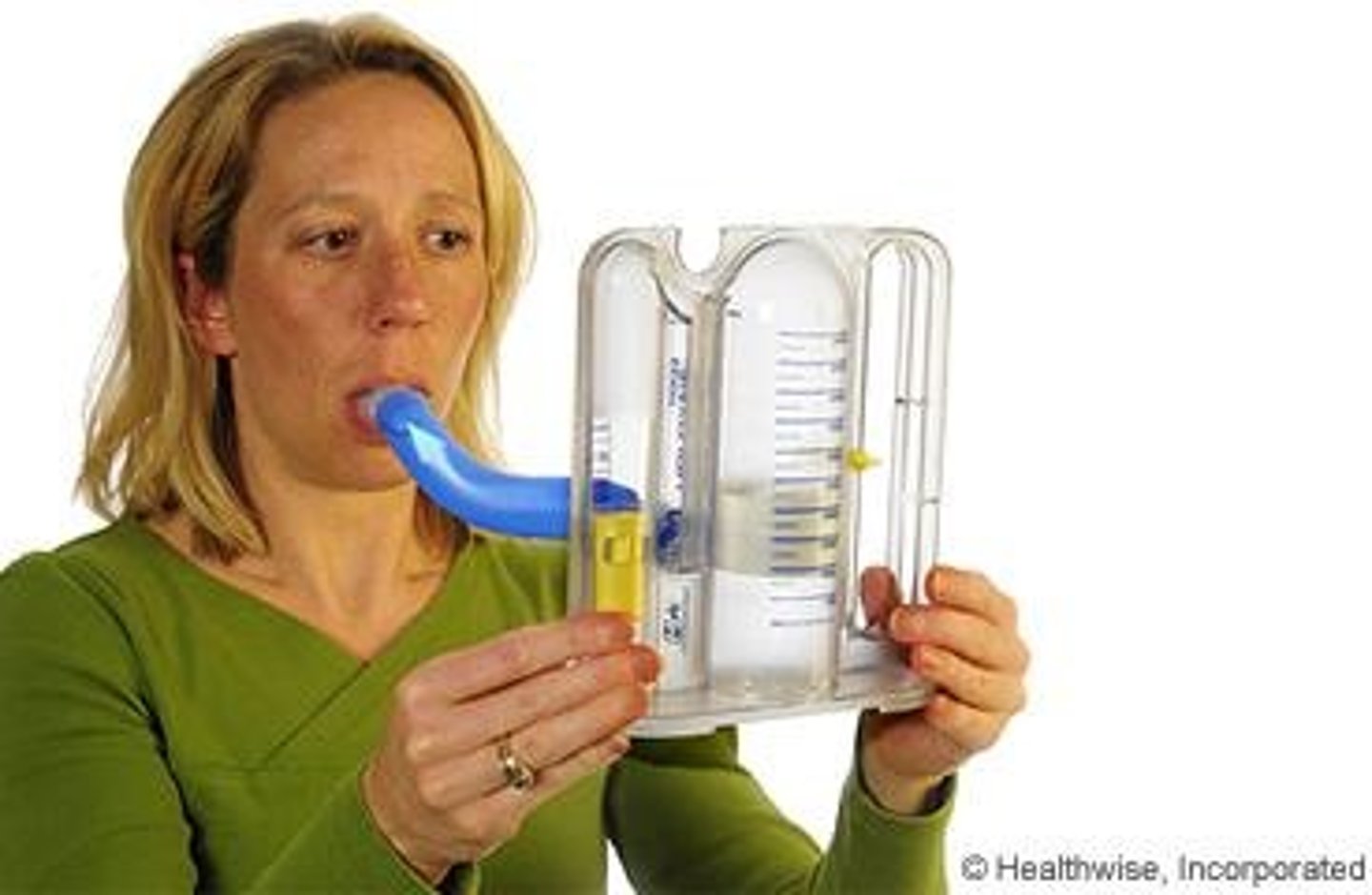
Incentive spirometer
A device used to encourage deep breathing and lung expansion.
PO hydration
Oral hydration that helps keep skin moist and prevents breakdown.
TEDS
Compression stockings used to prevent blood clots.
SCDS
Sequential Compression Devices used to promote venous return and prevent blood clots.
Dangle legs prior to standing
A method to prevent orthostatic hypotension before standing.
Heparin
An anticoagulant medication used to prevent blood clots.
Lovenox
A low molecular weight heparin used to prevent blood clots.
ROM exercises
Range of Motion exercises to maintain joint flexibility and prevent atrophy.
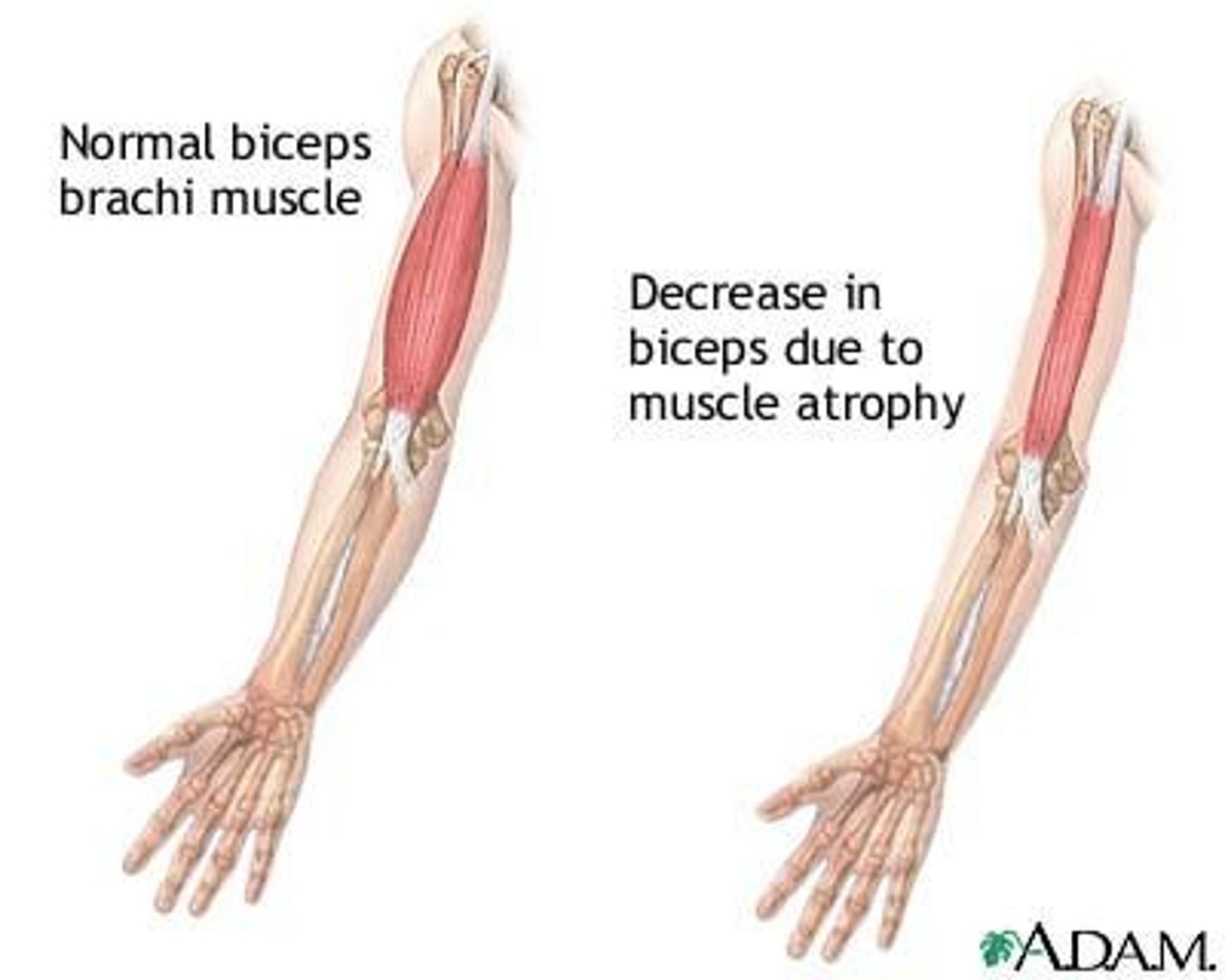
Muscle atrophy recovery
It takes approximately 4 weeks to recover from atrophy due to immobility.
Skin assessment
Involves palpating for induration and assessing for color changes.
Abnormal reactive hyperemia characteristics
1) An area that does not blanch; 2) A reddened area that remains red for longer than 1 hour.
Proper Positioning
The process of intentionally placing the body in a specific way to promote comfort and prevent injury.
Common Patient Positions
Positions such as Trendelenburg and Reverse Trendelenburg used for patient care.
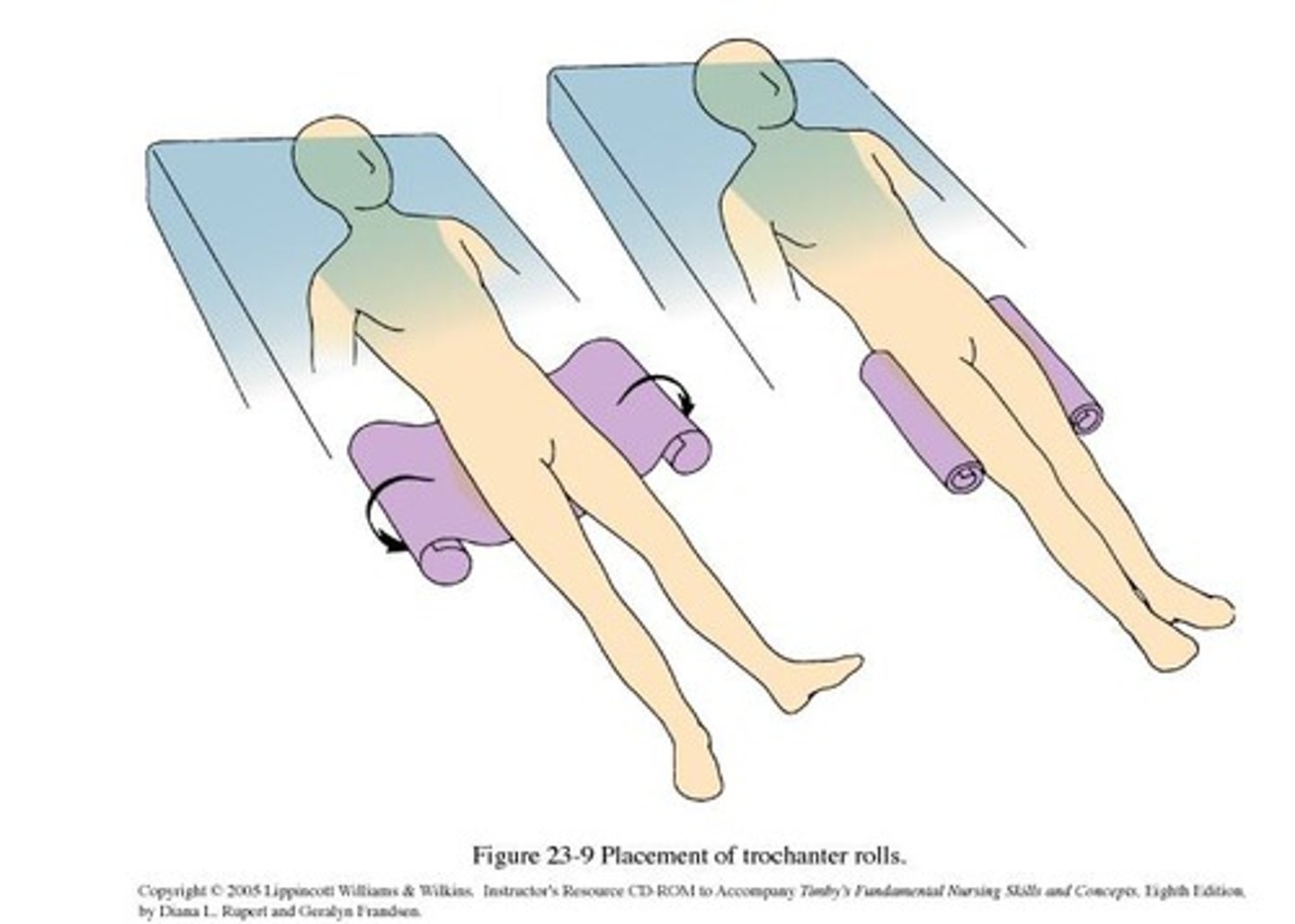
Devices Used For Positioning
Includes pillows, footboards, trochanter rolls, and wedge pillows.
Crutch Walking
Involves techniques like 2-point gait, 3-point gait, and 4-point gait.
Walker Walking
Sizing the walker while the patient is standing erect, with elbows flexed 15-30 degrees.

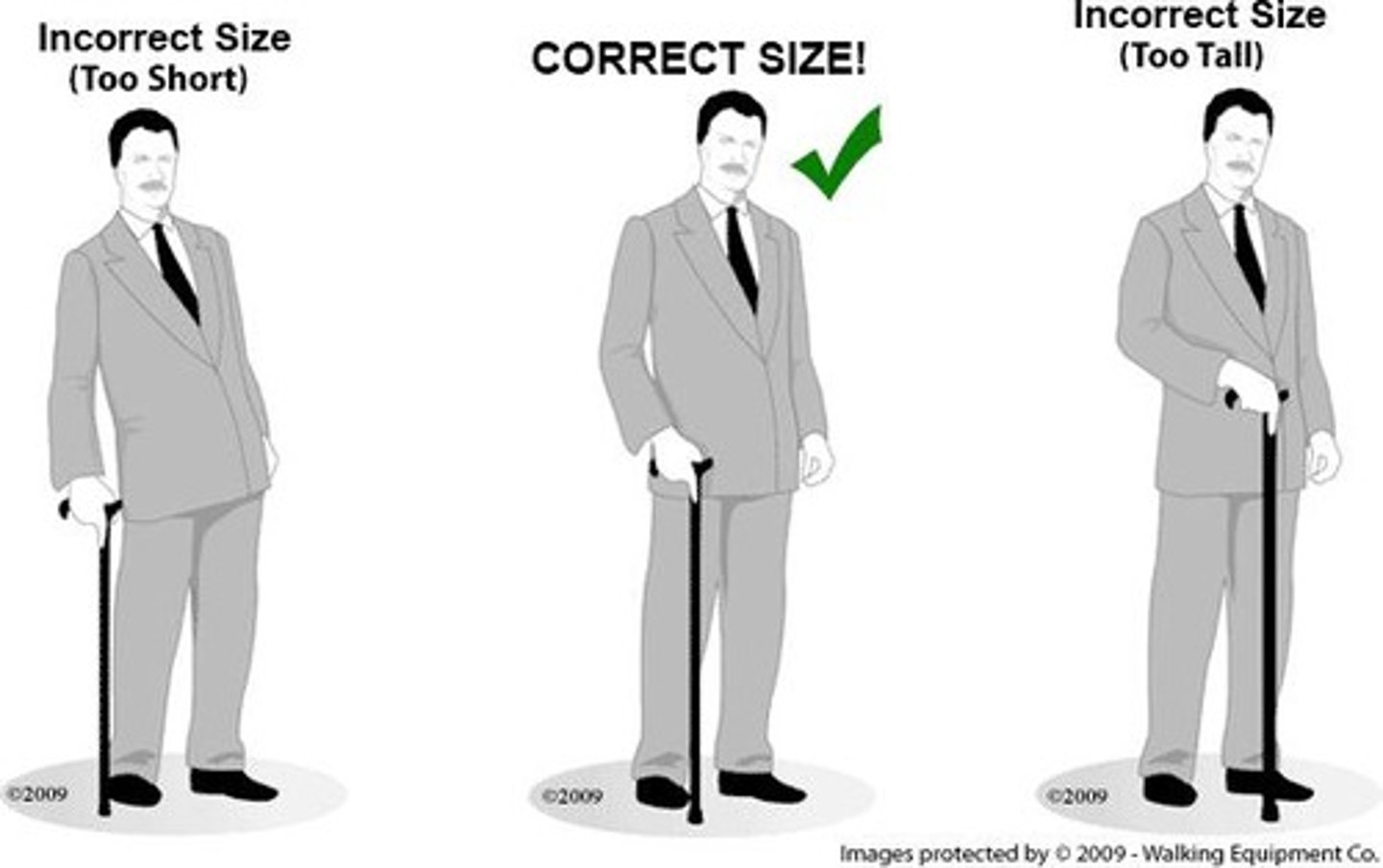
Cane Use
Should be used on the strong side, with specific measurements for placement and height.
Nursing Diagnosis Examples
Includes Risk for Disuse Syndrome, Impaired mobility, and Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity.