Genetics
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science sem 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
Genetics is the…
study of heredity
Heredity is the….
study of biological inheritance
What is biological inheritance?
The passing down of biological traits
What are genes?
genes instruct cells to build proteins that determine how we look and function.
what are codones?
codones code for a piece of protein called amino acid
What is meosis?
when cells divide to form sex cells (sperm/egg cells)
the copies made are not identical to the orginal cells.
cell division process that results in new cells with half the number of chromosomes of the original cell
how many individual chromosomes are left after meosis
23 individual chromosomes are left
What is mitosis?
this is when one body cell divides to make 2 identical copies of itself
cell division process that results in new genetically identical cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell
Mitosis is needed ______ for ____ and _______.
mitosis is needed everyday for repair and growth.
What are chromosomes?
DNA that is wrapped around proteins to form a bundle
packed tightly so long strands of DNA can fit into a nucleus
How many chromosomes do humans typically have?
46 chromosomes per body cell.
What are somatic cells?
body cells
what are germline cells?
cells that divide into sperm and egg cells during meiosis
what are somatic mutations?
mutations in body cells that are not passed offspring.
what is an example of a somatic mutation?
mutations in skin cells can cause skin cancer but are not passed on.
what is klinefelter disease?
when a male is born with an extra X chromosome.
occurs as random genetic error
what are chromosomal mutations?
involves changes in the structure and number of chromosomes.
What is a karyotype?
the complete set of chromosomes in an individual
How are karyotypes organised?
grouped in pairs of homologous chromosomes
arranged in length, banding pattern, centromere position, satellite endings
What are homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes inherited from each parent
what are sex chromosomes
the pair of chromosomes which will determine the gender of a baby
determine what gender a baby will be with the sex chromosomes XX
female
determine what gender a baby will be with the sex chromosomes XY
male
What are autosomes?
chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes
What is nondisjunction?
when chromosomes do not seperate evenly
what is trisomy?
having an extra copy of a chromosome.
What is monosomy
term for having only one copy of a chromosome
what is an example of monosomy?
Turner syndrome (XO)
What is a genotype?
the genetic makeup of an organsim
written in letters
e.g: Hh
What is phenotype
the appearance of an organism
what it physically looks like
written in words.
what is an allele
one form of a gene that has 2 or more alternative genes
Give 2 examples of alleles
skin colour, hair colour
What does heterozygous
Genotype with 2 different alleles
hetero = different
E.g: Hh
Homozygous what is it?
genotype has 2 identical alleles
What is a dominant gene?
dominant a trait (phenotype)
that requires only one allele to
be present for its expression in a
heterozygote
what is a recessive gene?
a trait (phenotype)
that will only be expressed in
the absence of the allele for the
dominant trait
What are diploid cells?
cells that are genetically identical
results from mitosis
What is chromatid?
one identical half of a replicated chromosome
what is a centromere?
the section of chromosome that holds together two sister chromosomes
What are daughter cells?
what is a zygote?
zygote a cell formed by the fusion of male and female reproductive cells
diploid
the possession of two copies of each chromosome in a cell
(appear as 23 pairs in each cell-typically with pair)
what are daughter cells?
cells that are formed after cell division
What are gametes?
reproductive or sex cells.
what are nucleotides?
chemical units that contain specific bases that form DNA code.
Building blocks of DNA
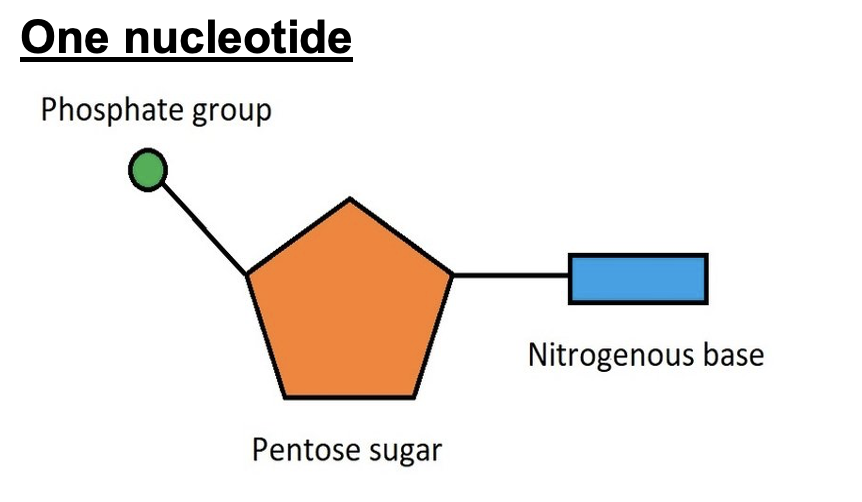
what are nucleotides made up of?
within a nucleotide there is a: Phosphate group
Pentose sugar
Nitrogenous base
What is the rule of complementary pairing?
A → T
G → C
What does A, T, G, C stand for?
Adenine
Thymine
Guanine
Cytosine
what does DNA provide for and organisim?
DNA provides chemical instructions about how to build an organsim.
What are the codones
A,T,G,C bases
What are the different types of mutations?
Deletion
Addition/Insertion
Substitution
Point mutations
What is deletion mutations?
one or more codon bases are deleted
What is addition mutations
an additional codon is added in to a gene
what is substitution mutations
Occurs when one nucleotide swaps for another
what is an amino acid
an organic compound that forms the building blocks of proteins
what is a silent mutation?
when the change in DNA code is actually the smae amino acid.
what is an example of a silent mutation?
sickle cell anaemia.
what are point mutations
when there is a change to one of the nitrogenous bases (A,T,G,C)
where are nucleotides found?
Make up the DNA
a sugar, base phosphate make up…
one nucleotide.
protein, amino acid, DNA, nucleotides,
Differnce between gametes and sex chromosomes
gametes = sperm and egg
sex chromosomes = 23 pair that determine gender of person
Difference between genes and chromosomes
difference between gene and DNA
what is klinefelter’s?
a chromosomal disorder that is where there is an extra X chromosome in a male
What are the letters of of mitosis?
PMAT
what are the names for the phases of mitosis?
prophases
Metaphase (middle)
Anaphases (away)
telophase (begin to seperate)
what is the function of a punnet square?
Used to predict outcome of a genetic cross.
Shows which allele for a certain trait are present in the gametes of each parent.
Then shows possible ways these can be combined.
List the 4 types of domiance
Complete dominance
Incomplete/partial dominance
Codominance
Sex-linked
what is complete dominance?
only dominant allele shows phenotype
What is incomplete/partial domiance?
both dominant alleles are able to be express themselves (partially)
Red flower + White flower = PINK flower
what is co-domiance?
both dominant alleles express themselves equally
Human blood groups= AB, Cow hair colour.
What are sex linked dominance?
trait is due to allele on X chromosome.
more in males than females,
females can be carriers
What are the 4 inheritance pattererns.
Autosomal dominant
autosomal recessive
x-linked dominant
X-linked recessive
Each affected person Has an affected parent: occurs in every generation
Autosomal dominant
Both parents of an affected person are carries; not typically in every generation
Autosomal recessive
Female more frequently affected as all daughter & no sons of an affected man will be affected
can have affected male & females in same generation
X linked dominant
Males more frequently affected
Affected males often present in each generation
X-linked recessive
X-linked recessive
Both parents of an affected person are carries; not typically in every generation
Autosomal dominant
Each affected person Has an affected parent: occurs in every generation
X-linked recessive
Males more frequently affected
Affected male often present in each g
X linked
What are DNA triplets
DNA triplets code for a particular amino acid