Arrhenius and Drug Degradation (Final)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
10%
No more than _________ decrease in the active content should take place within the shelf life at the recommended storage temperature
accelerated stability testing
Drug product is exposed to (stress conditions) extremes of temperature, humidity, and light in order to predict the shelf life
k increases
In the Arrhenius equation if A is increased what happens to k?
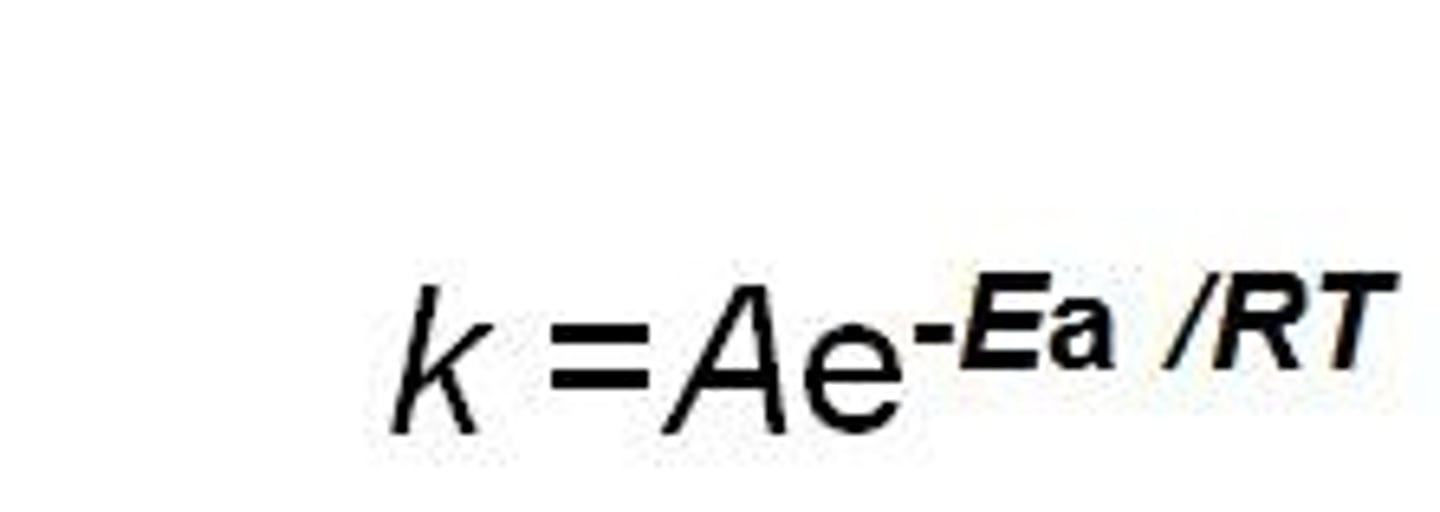
k decreases
In the Arrhenius equation if Ea is increased what happens to k?
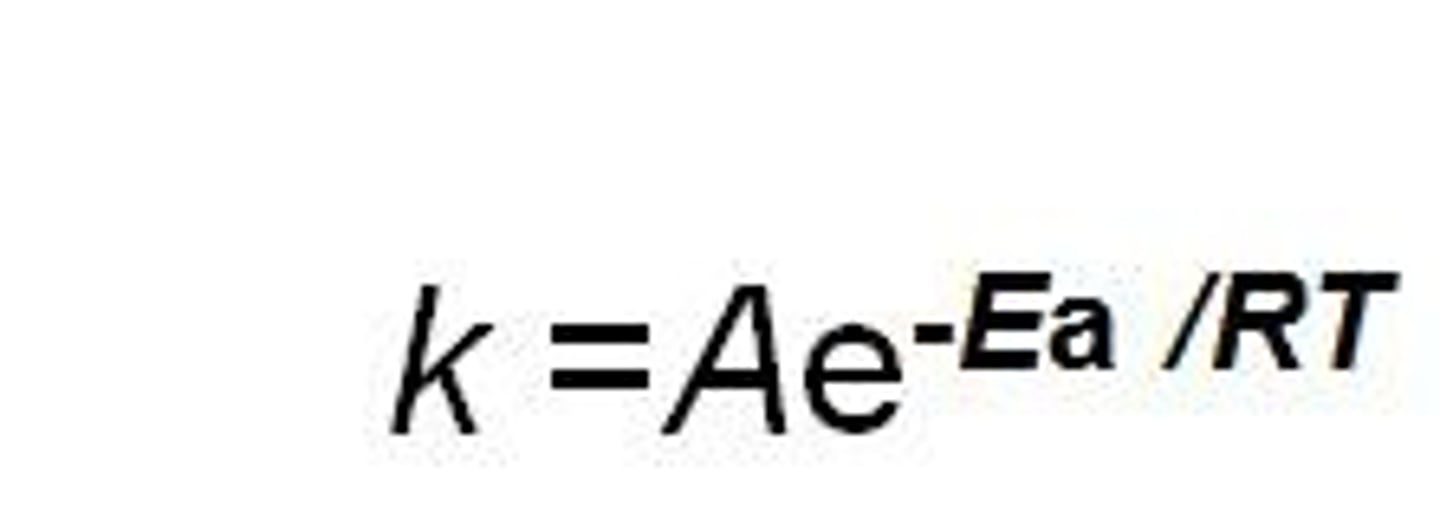
it increases
In the Arrhenius equation if temperature increases then what happens to k?
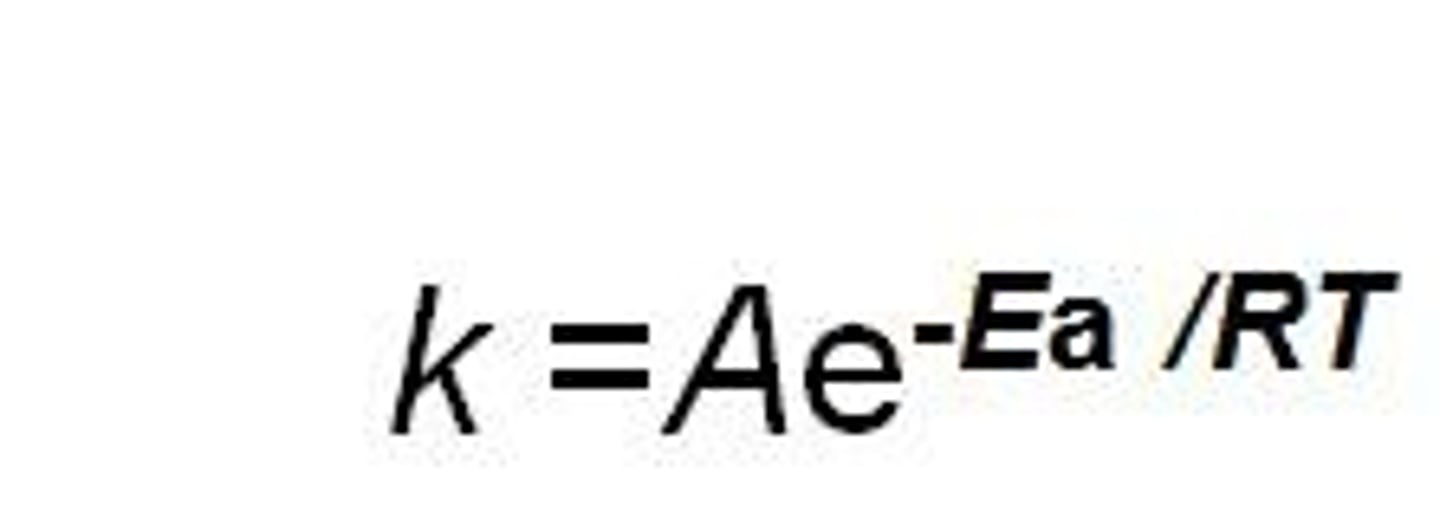
k
specific reaction rate constant at temperature T
A
-arrhenius factor or frequency factor
-indicates how many collisions have the correct orientation for product formation
Ea
energy of activation (cal. mol ^-1)
R
gas constant (1.987)
T
temperature (degree K)
Arrhenius equation
is based on the collision theory which supposes that particles must collide with both the correct orientation and with sufficient kinetic energy if the reactants are to be converted into products
they lower Ea
What effect do catalysts have on Ea?
Activation energy (Ea)
is the minimum kinetic energy a molecule must possess in order to undergo a reaction
increase
Lowering Ea will lead to an ________ in the k or rate of the reaction.
Increases
__________ in T leads to an increase in k. Roughly, rate of reaction doubles with every 10 degrees C rise in temperature.
Arrhenius plot
used to determine activation energy
Q10 approach
-is based on Ea but independent of reaction order
-method that can estimate shelf-life
Q10
the ration of 2 different reaction rate constants
12.2
A Q value of 2 corresponds to an Ea value of what?
19.4
A Q value of 3 corresponds to an Ea value of what?
24.5
A Q value of 4 corresponds to an Ea value of what?
T90 (T2)
estimated shelf life
T90 (T1)
the given shelf like at a given temperature
Delta T
the difference in the temperature between T1 and T2
1. Hydrolysis
2. Oxidation
3. stabilization against photolysis
4. thermal degradation
5. racemization
What are the mechanisms of drug degradation?
-specific acid catalyzed hydrolysis
-specific base catalyzed hydrolysis
-solvent catalyzed hydrolysis
-general acid base catalyzed hydrolysis
Drug moiety could be susceptible to what?
ways to stabilize against hydrolysis
•Select pH of optimum stability
•Select buffers that do not catalyze hydrolysis
•Complexation - Only uncomplexed drug will undergo hydrolysis
•Decrease solubility - formulate as suspensions
•Use of surfactants - Micellar entrapment
•Use of co-solvents
•Decrease drug in solution
•Formulate as solid dosage forms
•Lyophilized products
reaction rates
If you alter activity coefficients what is directly affected?
change in pKa and viscocity
What indirectly affects the reaction rate?
polar
More polar solvents will favor reaction proceeding in a direction that produces ________ products.
nonpolar
non polar solvents will favor reaction proceeding in a direction that produces ___________ products.
yes
Does dielectric constants effect the co-solvents on reaction rates?
oxidation
-removal of electrons
-involves free radical chain reactions
-influenced by heat and light
-antioxidants
-chelating agents
-optimum pH
-avoid light
-store at low temps
How can you stabilize a molecule against oxidation?
oxygen scavengers
antioxidants: sulfites, ascorbic acid, mono thioglycerol
chain reaction terminators
preferentially become stable radical which can be combined with other radicals to terminate chain reactions
ex: BHA or BHT
reducing agents
reducing oxidized drugs
ex: ascorbic acid
chelating agents
removes metal catalysts, EDTA
displace oxygen with nitrogen or other inert gases
How can you protect a molecule from dissolved oxygen?
-amber colored bottles
-aluminum foils
What are different things we use to protect a drug from photolysis/light?
Furosemide
What is an example of a drug that must be stabilized against photolysis?
Covid-19 vaccines
What is an example of a drug that must have thermal degradation?
racemization
tetracycline by epimerization