Chapter 6 Emergency Care and Transportation of the Sick and Injure
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
Physiology
the functions of the body or any of its parts
Pathophysiology
describes how normal physiologic processes are affected by disease
Topographic anatomy
superficial landmarks of the body
*Surface of the body has many definite visible features that serve as guides to the structures that lie beneath them
Anatomic position
position of reference in which the patient stands facing you, arms at the side, with palms of the hands forward
*common starting point for health care providers
*directional terms from patient's perspective
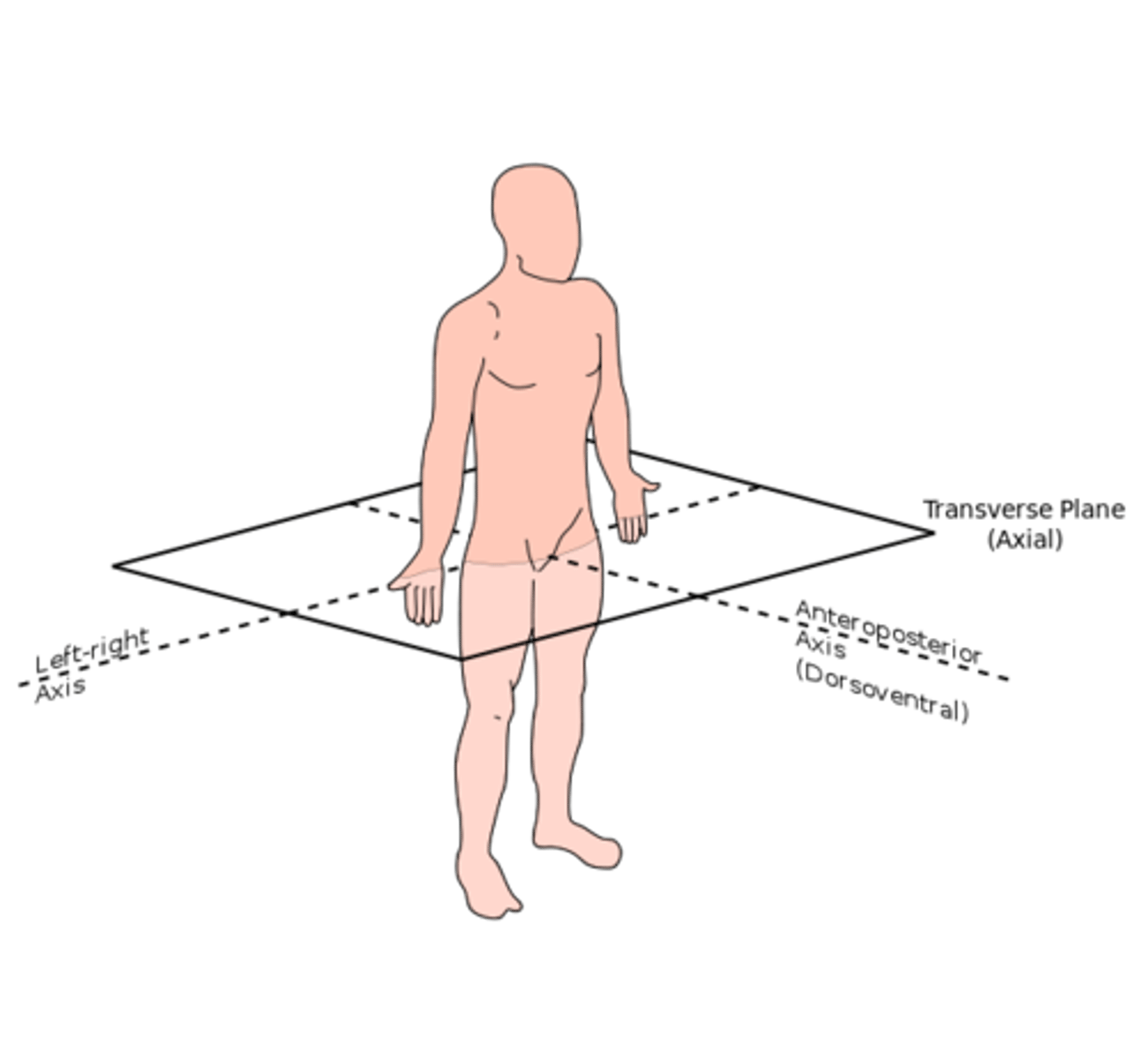
Planes of the body
anatomic planes
3 main axes of body: coronal (frontal), transverse (axial), sagittal (lateral)
planes help you identify the location of internal structures, relationships between and among organs
Coronal plane or frontal
divides the body into a front and back portion
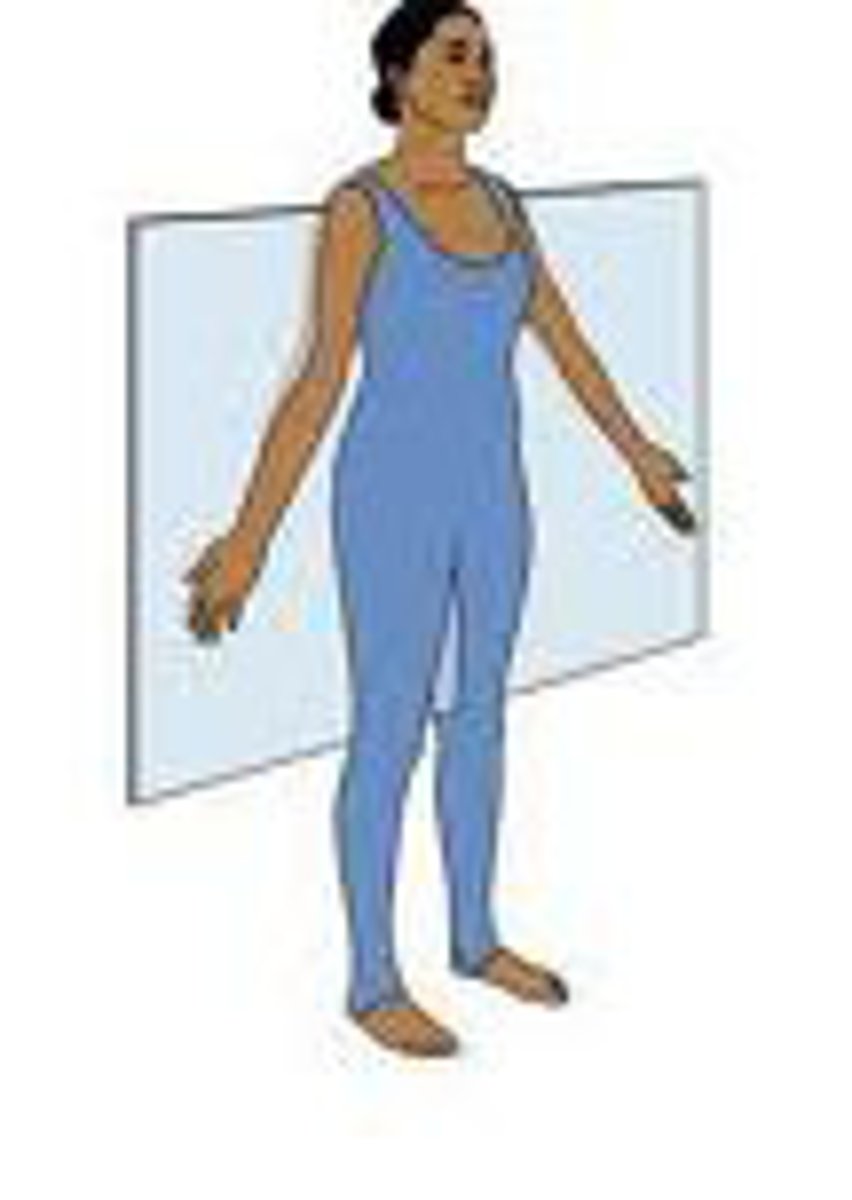

transverse plane or axial
divides the body into a top and bottom portion
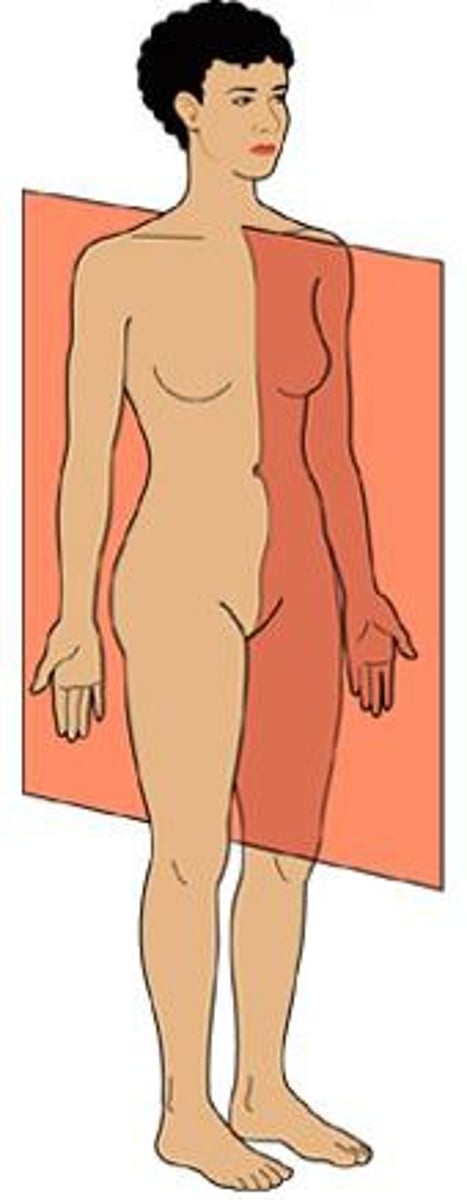
Sagittal Plane or lateral
divides the body in left and right, but not equal portions
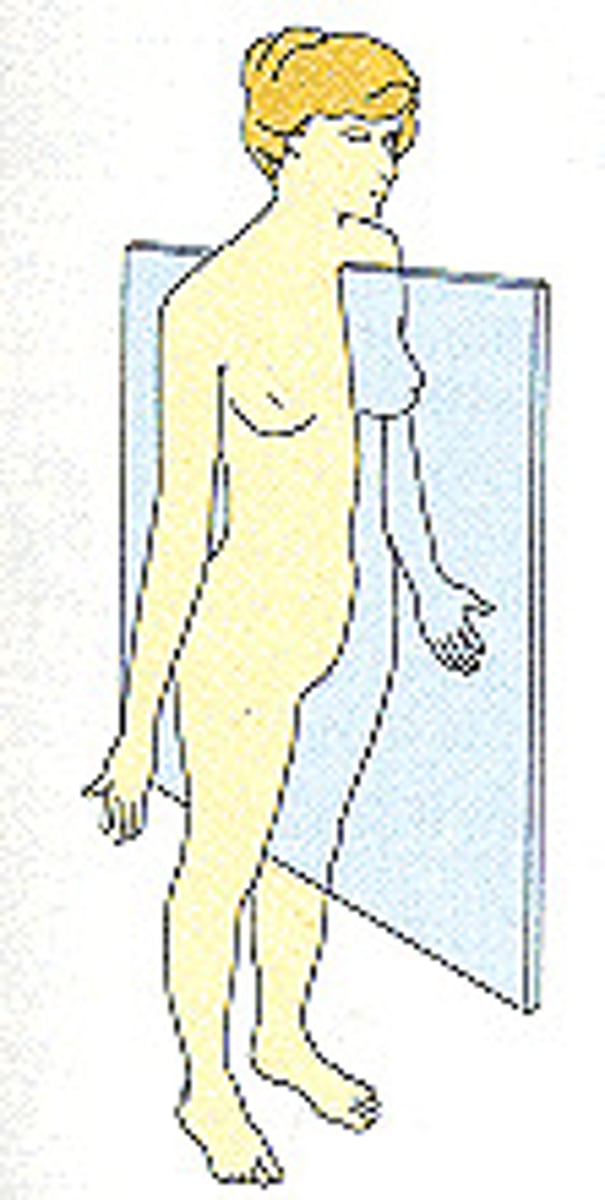
midsagittal plane
Type of Sagittal plane
body is divided into EQUAL left and right
nose and navel found along line midline
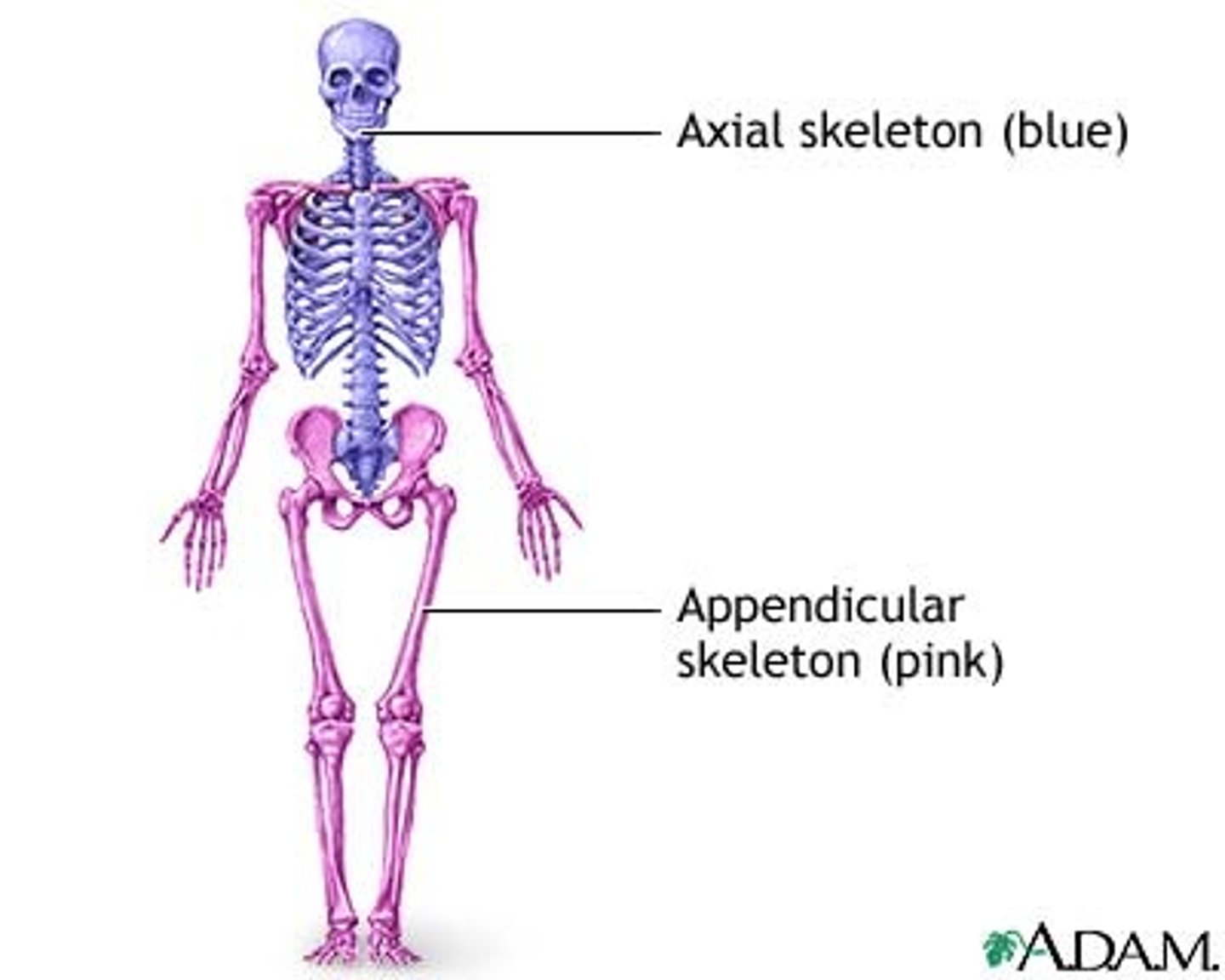
Skeletal System
divided into 2 portions: axial and appendicular
Skeleton
physiology does...
1)Gives the body its recognizable form
2)protects vital organs
3)allows motion of body
4)storage of calcium
5) helps with creation of various type of blood cells
206 bones make up
Ligaments
Tendons
cartilage
connects bone to bone
connects muscle to bone
cushion between bones
Axial Skeleton
Skull, facial bones, thoracic cage (chest or rib cage), vertebral column
*forms foundation to which arms and legs are attached
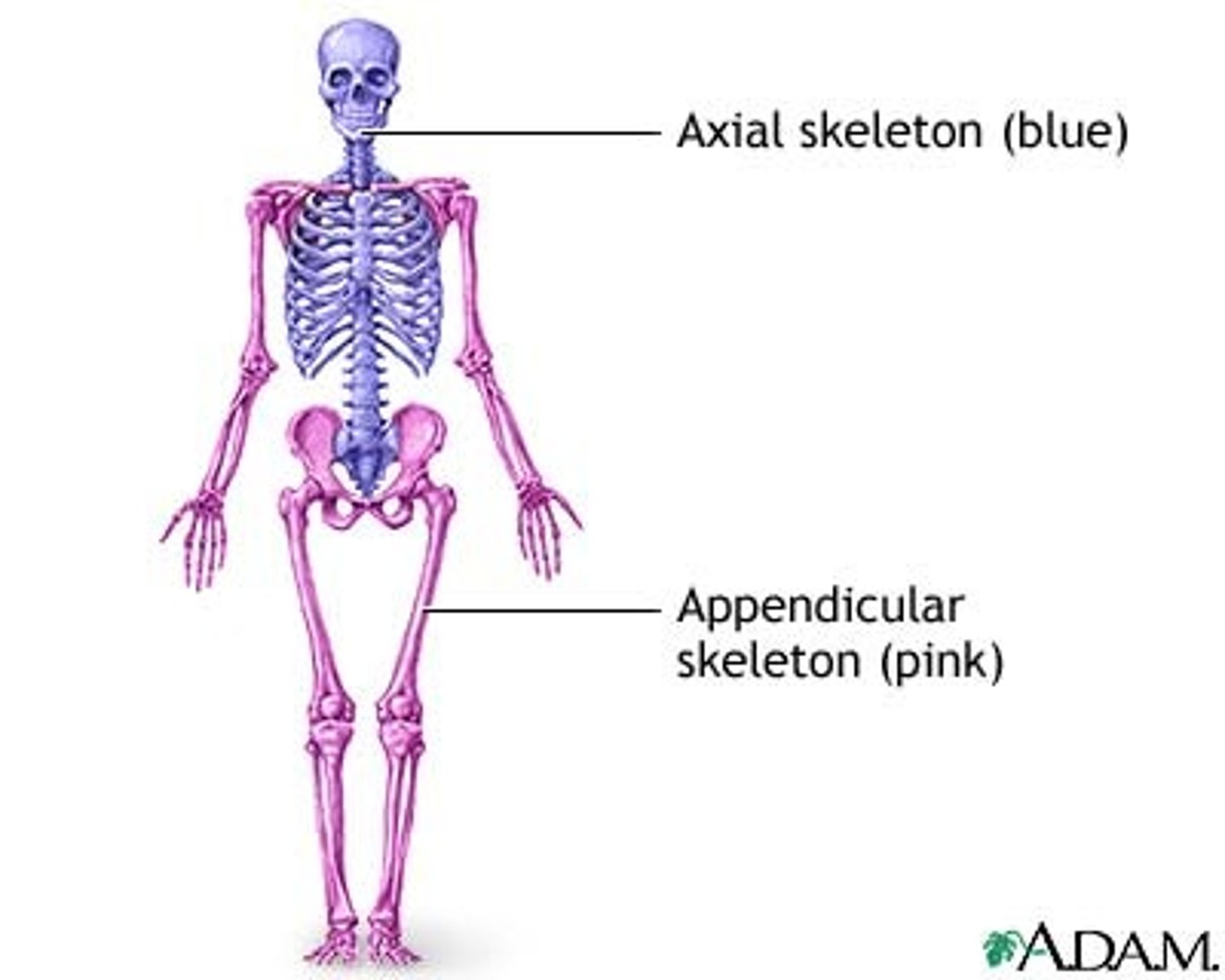
Appendicular skeleton
arms, legs, their connection points, pelvis
Axial Skeleton
SKULL
composed to 2 groups of bones: cranium (4) and facial bones (14)
Axial Skeleton
Cranium bones
composed of a number of thick bones fused together to form a shell above eyes and ears, holds and protect brains
Occiput bones (most posterior portion)
temporal bones (lateral portions)
parietal bones
frontal bone (forehead)
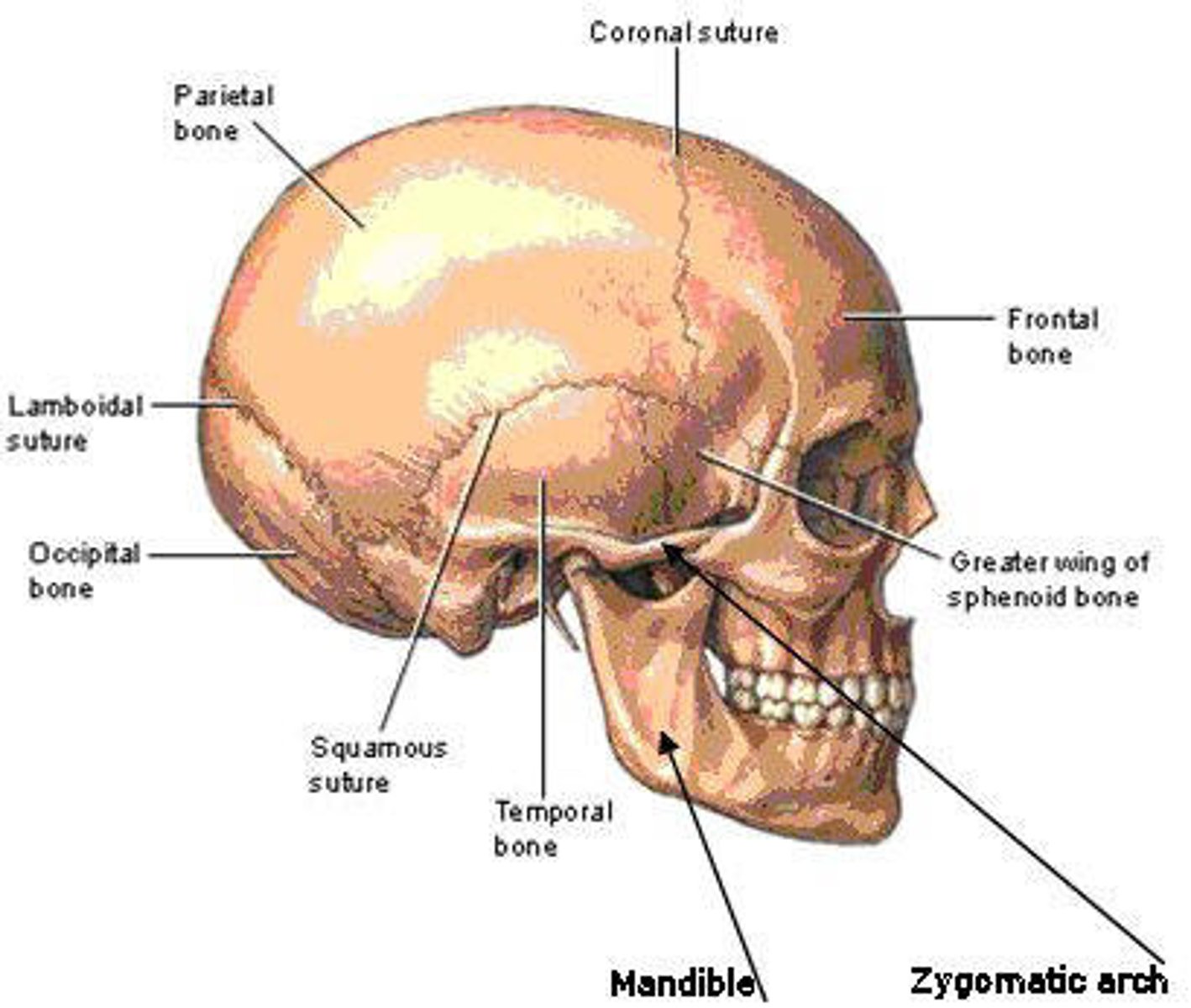
foramen magnum (grand opening)
large opening at the base of skull, how the brain connects to the spinal cord
Axial Skeleton
Facial bones
maxillae - non moveable jawbone
zygomas-cheek bones
mandible-lower moveable portion of jaw
orbit- eye socket, made up of maxilla & zygoma
nose- very short bones, and flexible cartilage
Axial Skeleton
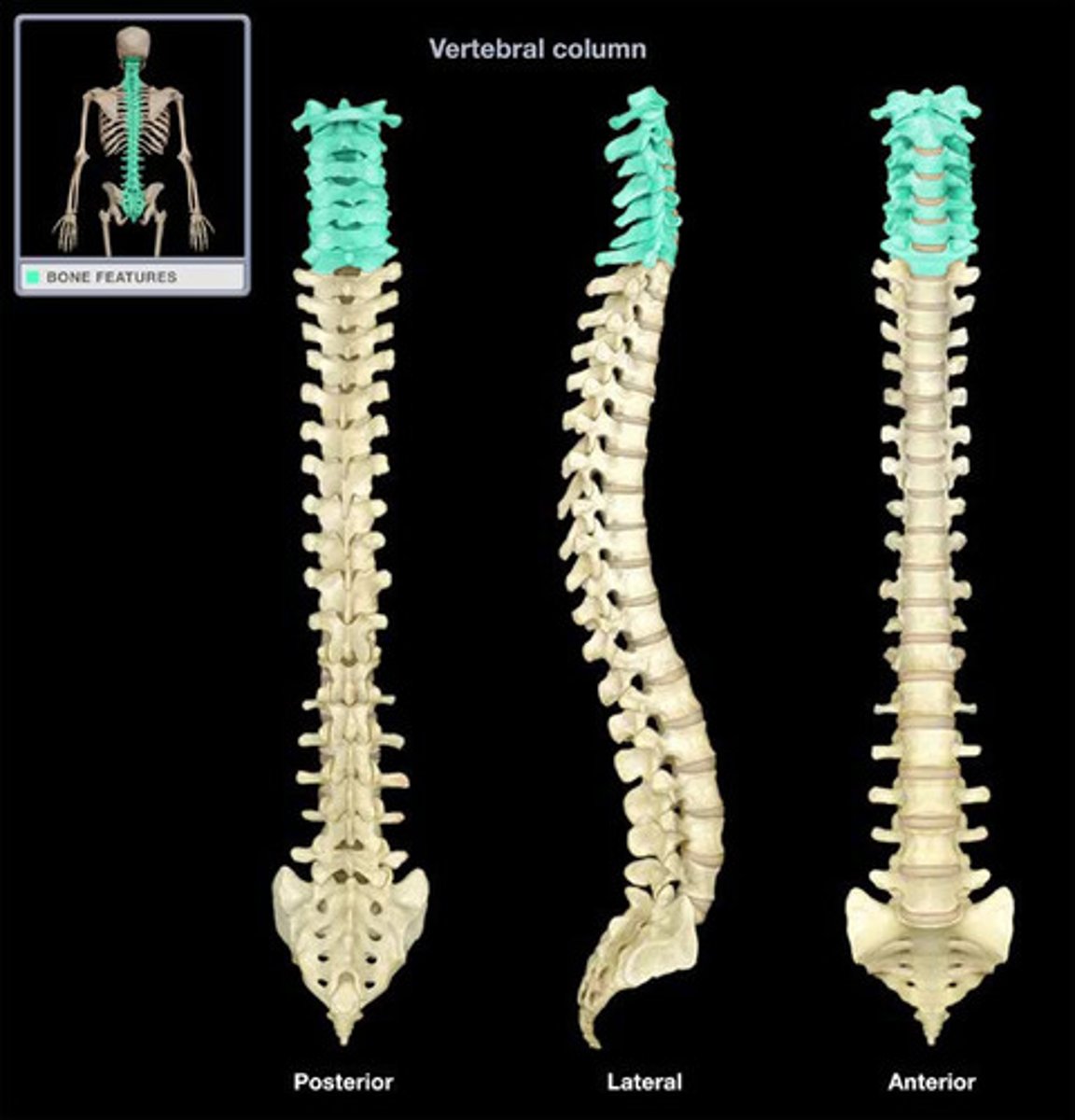
Spinal Column
central supporting structure of body
33 vertebrae (singular- vertebra)
numbered top to bottom
spine divided into five sections
Intervertebral disk
the cushion inbetween vertebrae
trunk forward- FLEX
trunk back-Extend
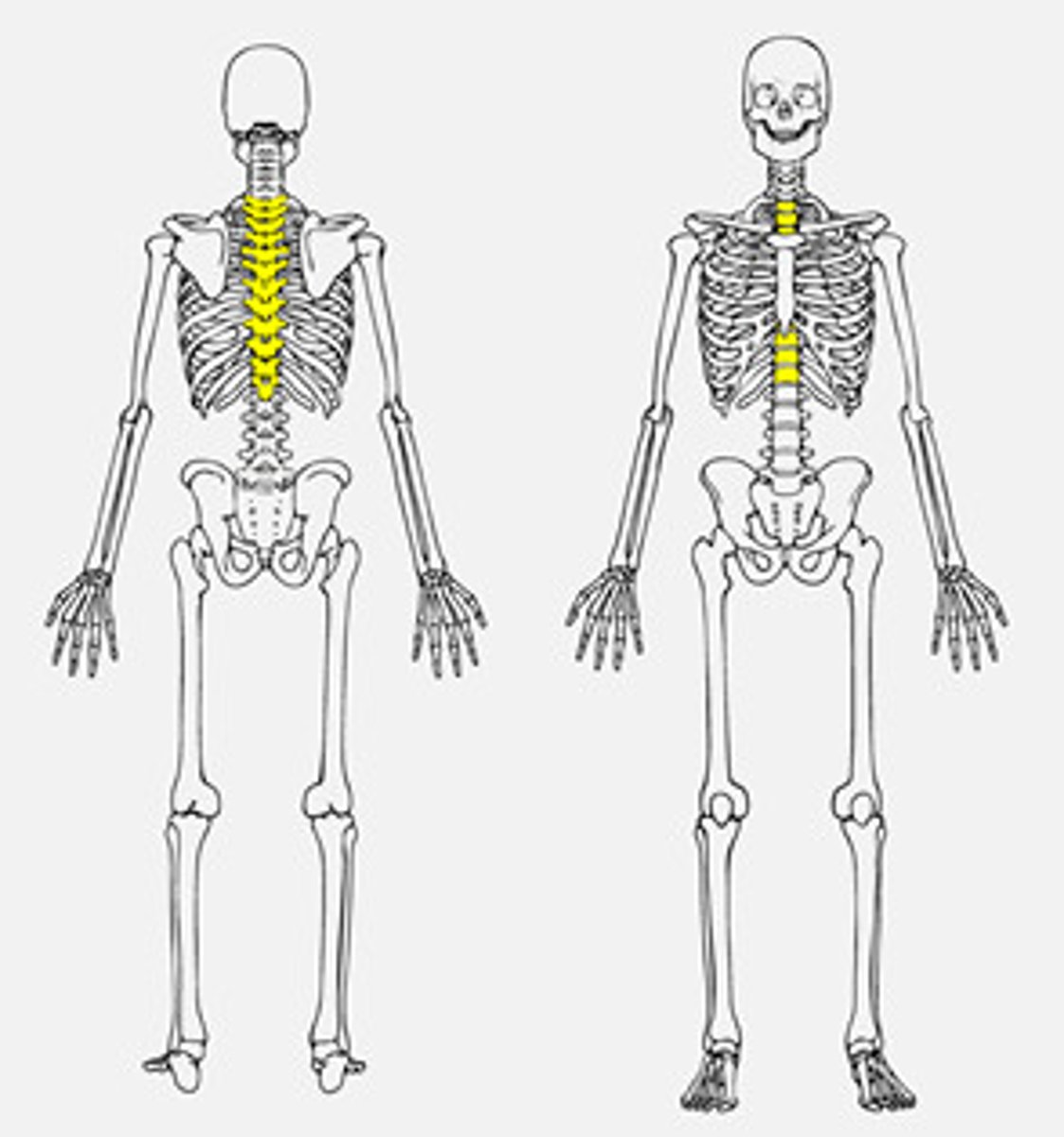
SPINAL COLUMN
Cervical spine (cervical vertebrae 7)
C1-C7 neck form
skull rests on and attaches to both first (atlas) and second vertebra (axix)
move separately, allowing head to turn
SPINAL COLUMN
Thoracic spine (thoracic vertebrae 12)
next 12. one pair of ribs is attached to each of thoracic vertebrae
SPINAL COLUMN
lumbar spine (lumbar vertebrae 5)
next 5 vertebrae
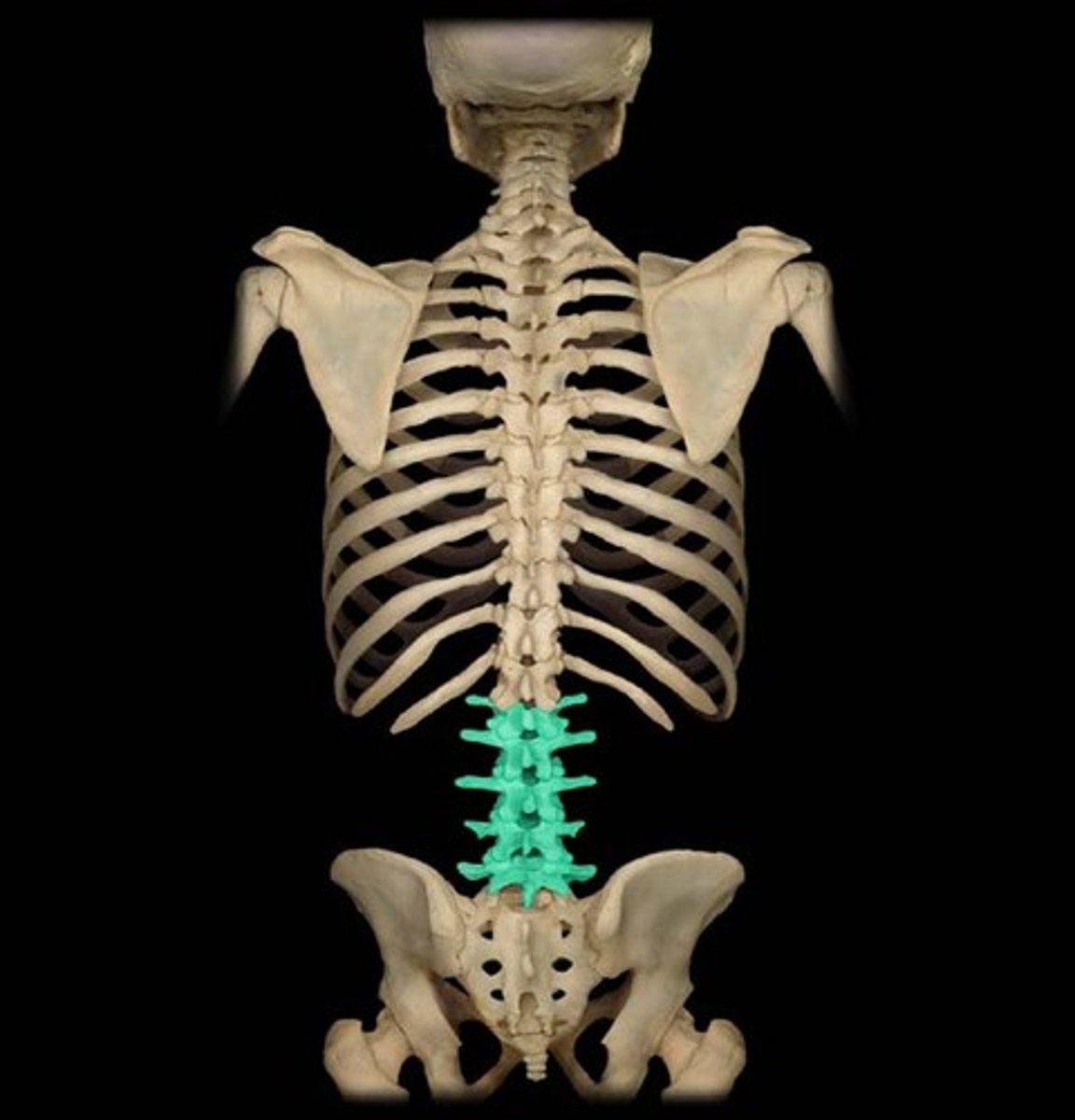
SPINAL COLUMN
sacrum (sacral vertebrae 5)
fused together to form one bone --->Sacrum
joined to pelvis
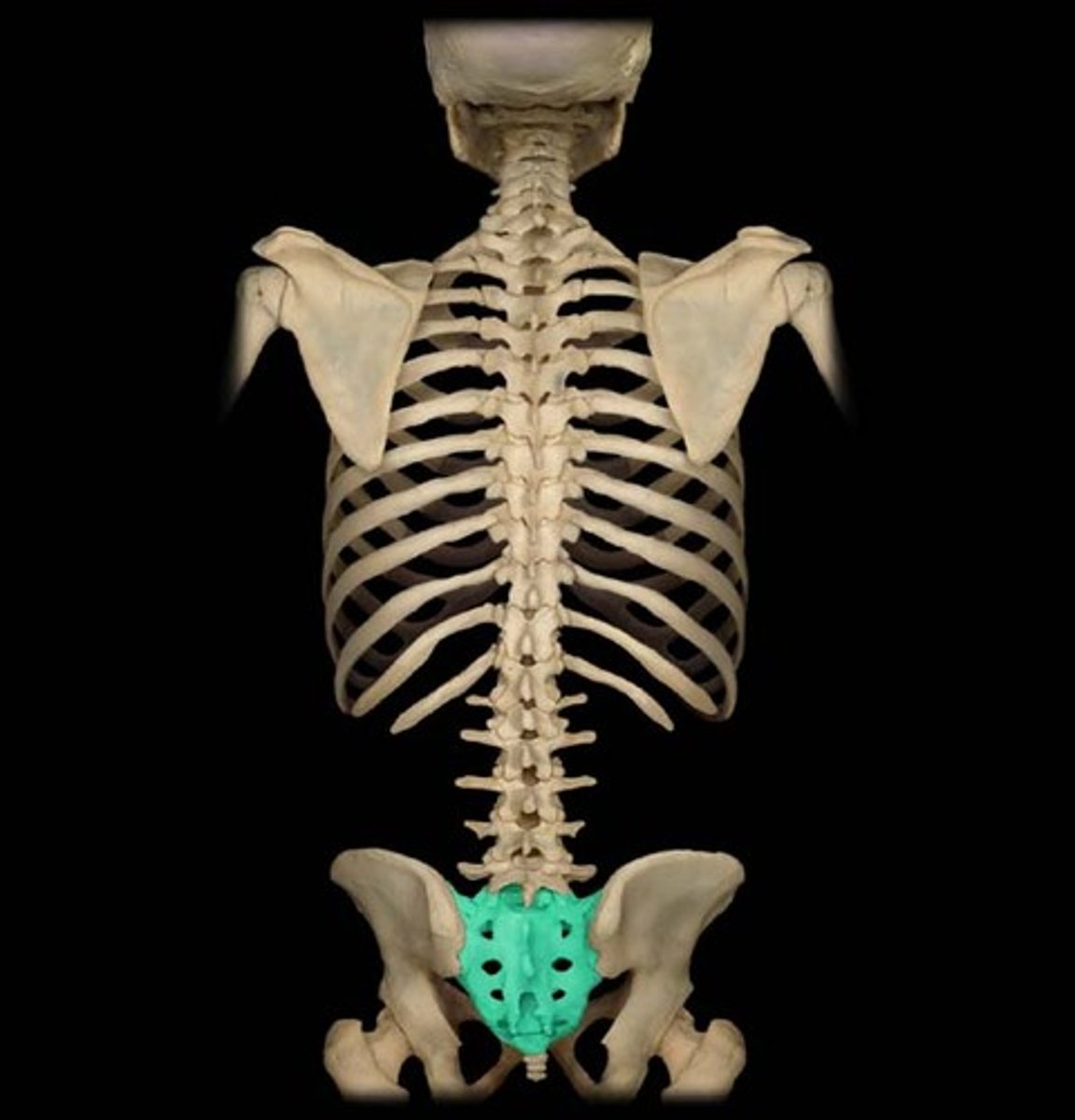
SPINAL COLUMN
coccyx (coccygeal vertebrae 4)
tailbone
last 4 vertebre
fused together
tailbone
Spinal cord EMT note
you must use extreme caution in caring for patients with any spinal injury to prevent further spinal cord injury
Axial Skeleton
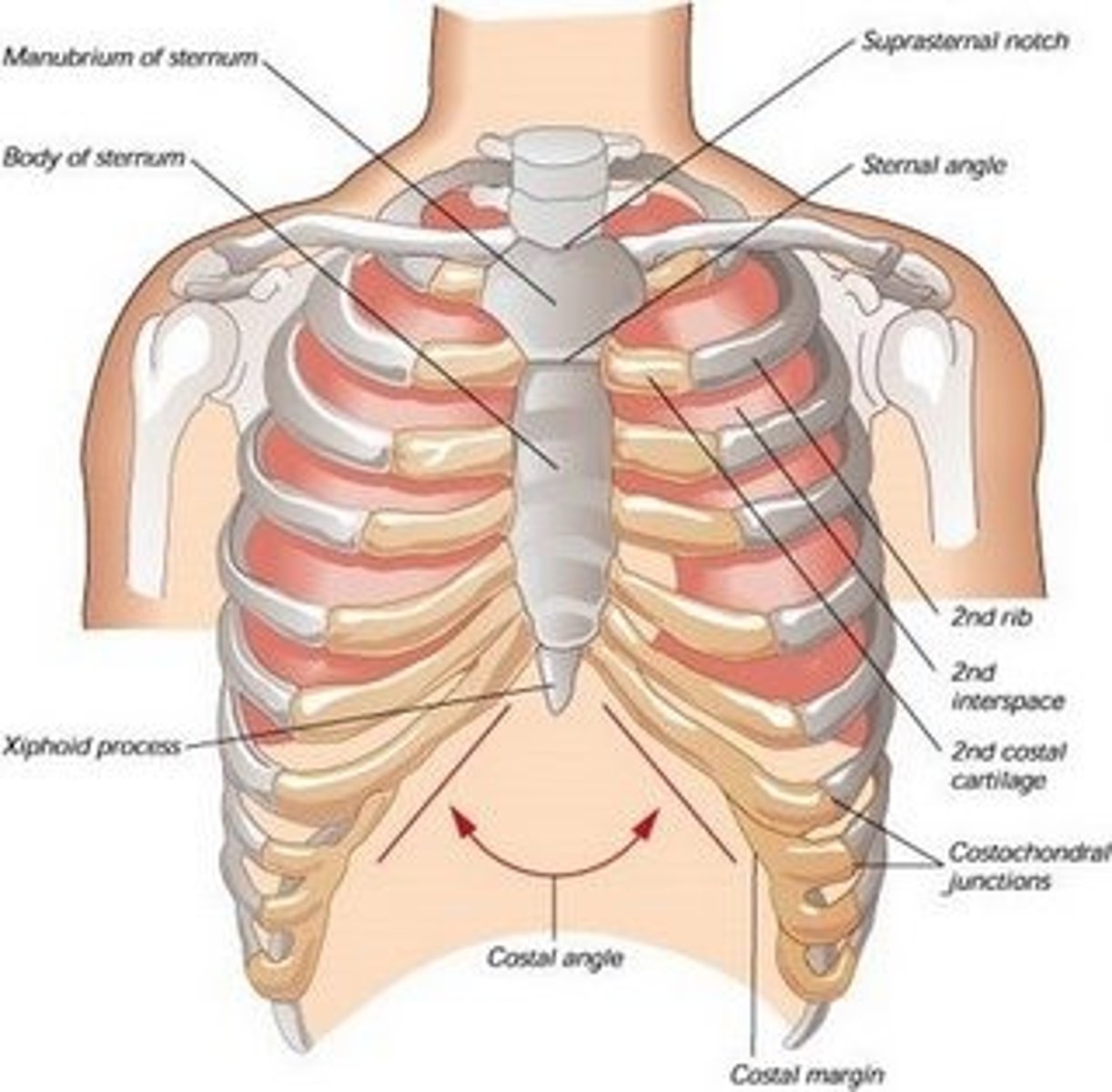
Thorax (chest)
contains heart, lungs, esophagus, great vessels
formed by 12 thoracic vertebrae T1-T12, 12 ribs
midline of chest- sternum
Axial Skeleton
Thorax (chest)
STERNUM
location trachea enters chest
made up: manubrium
body
xiphoid process (narrow, cartilaginous tip)
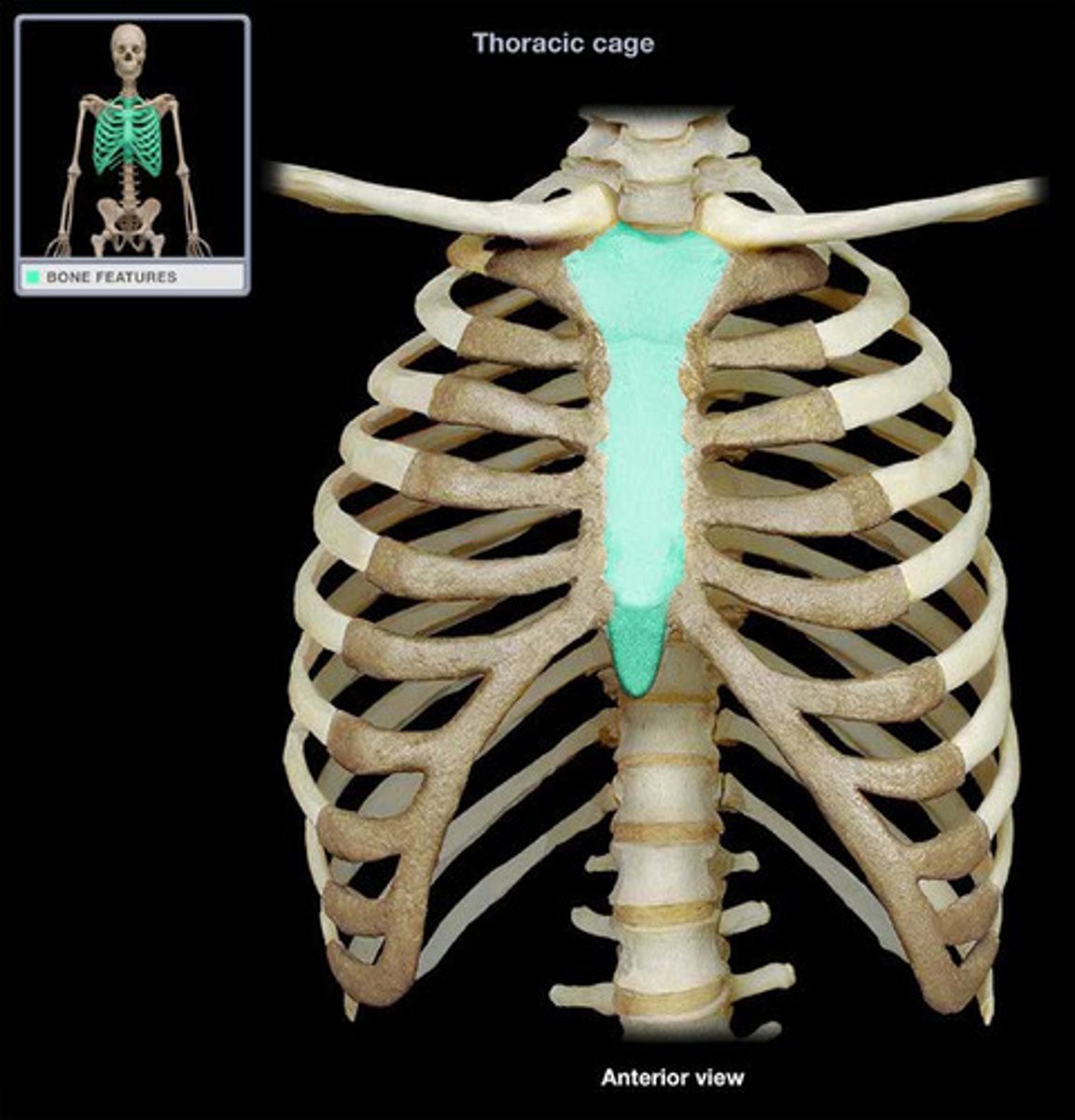
Appendicular Skeleton
Joint (articulation) & joint vocab
*where bones come into contact
*consists: end of bones, fibrous joint capsule, snyovial membrane and ligaments
*degree to which joint can move determined by how the ligaments hold the bone ends an by the configuration of the bones themselves
joint capsule-fibrous sac hold bone ends together
articular cartilage- end of bones in moving joints
synovial fluid-thick lubricant
synovial membrane- inner lining of joint capsule
Joint
Symphysis
joints that that have slight, limited motion in which bone ends are held together by fibrous tissue
Joint
Saroilliac
joint surrounded by tough, thick ligaments, little motion
Joint
ball-and socket-joint
allows rotation and bending
example-shoulder
wrist (modified)
joint
hinge joints
no rotation possible
finger joints, elbow, knee
motion is flexion (bending) and extension (straightening)
EMT note
when a joint is forced beyond its limits, either bones that form will break, or supporting capsule and ligaments will be disrupted
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
extend from the shoulder girdle to fingertips, composed of arm, forearms, hand, and fingers
joints:shoulder, elbow, wrist, fingers
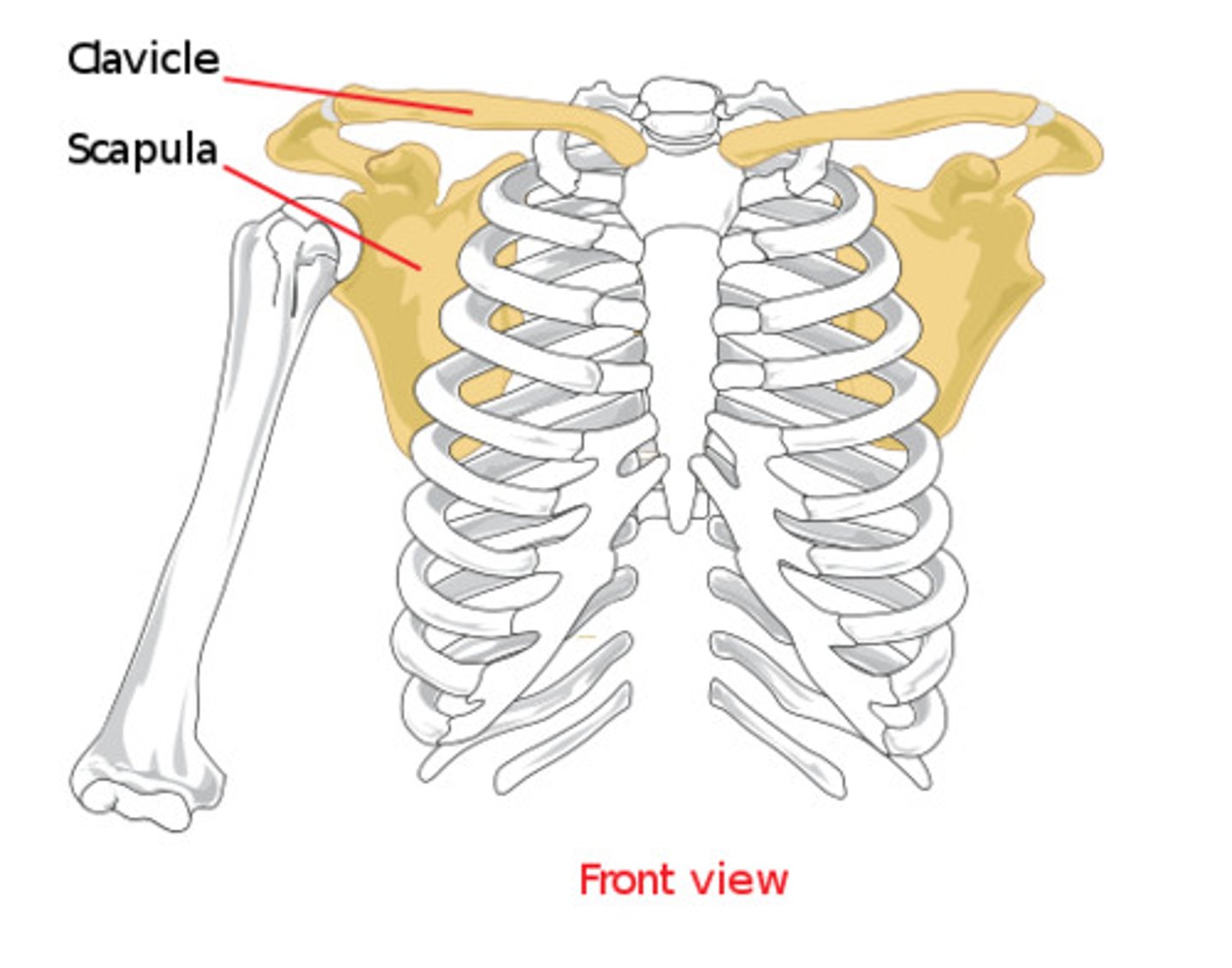
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
Shoulder Girdle
3 bones come together allowing arm to move: clavicle (collar bone), scapula (shoulder glade), and humerus
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
arm p. 184
humerus (supporting bone from shoulder to elbow)
ulna (larger proximal forearm helps to form elbow joint-medial, little finger side)
radius (larger distal forarm, lies on lateral-thumb side
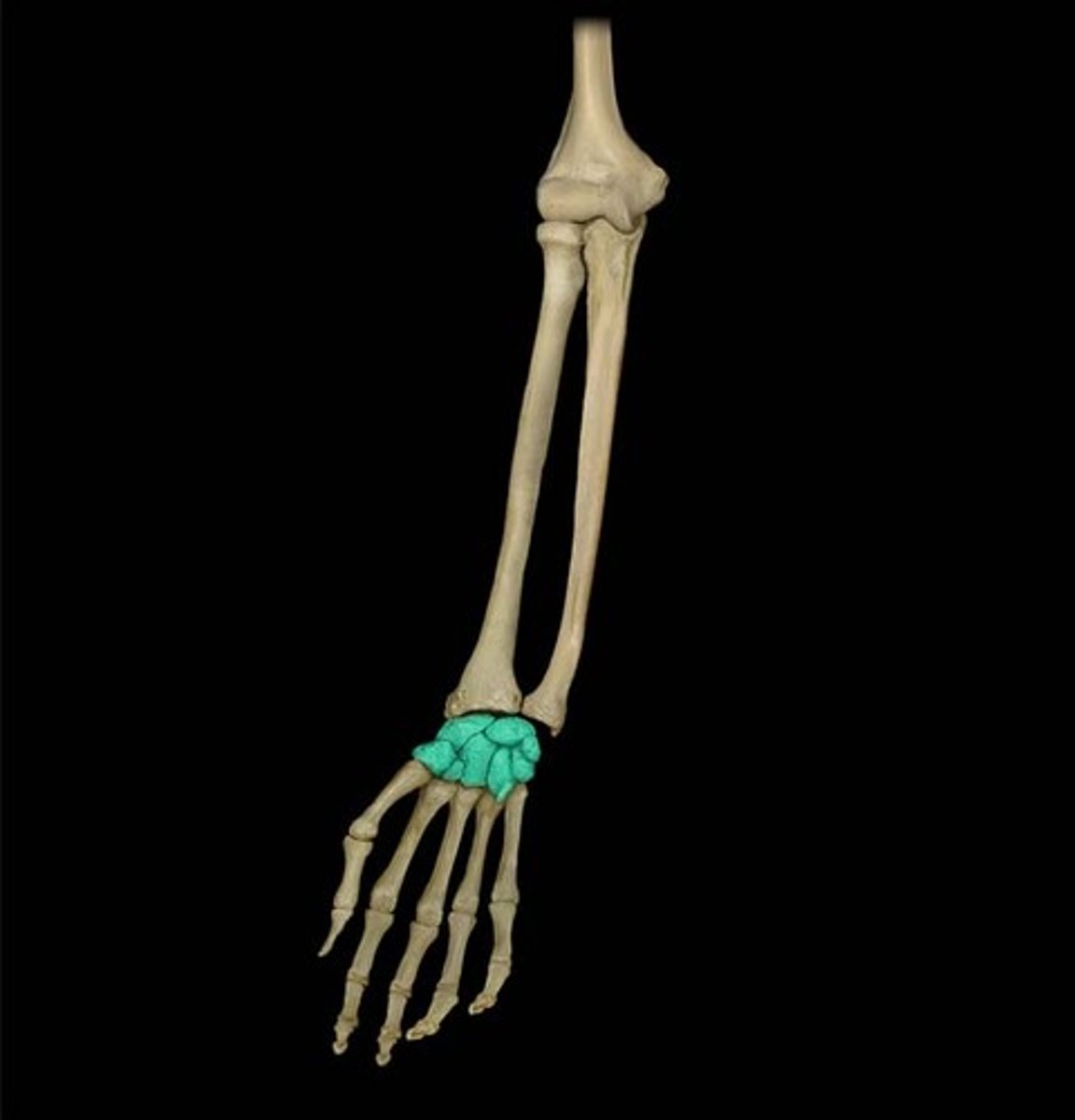
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
Wrist
modified ball and socket joint
formed by ends of the radium and ulna, other small bones
8 bones in wrist called CARPALS
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
Hand
anterior surface- palm
back-dorsal surface
metacarpals (palm)
fingers- phalanges (thumb, 2, four digits, 3)
Appendicular Skeleton
Upper extremities
Pelvis
closed bony ring
consists of:
sacrum
ilium (PICTURED)
ischium
pubis
pubic symphysis (the left and right pubis joined)
acetabelum-where ilium, ishium and public bones met
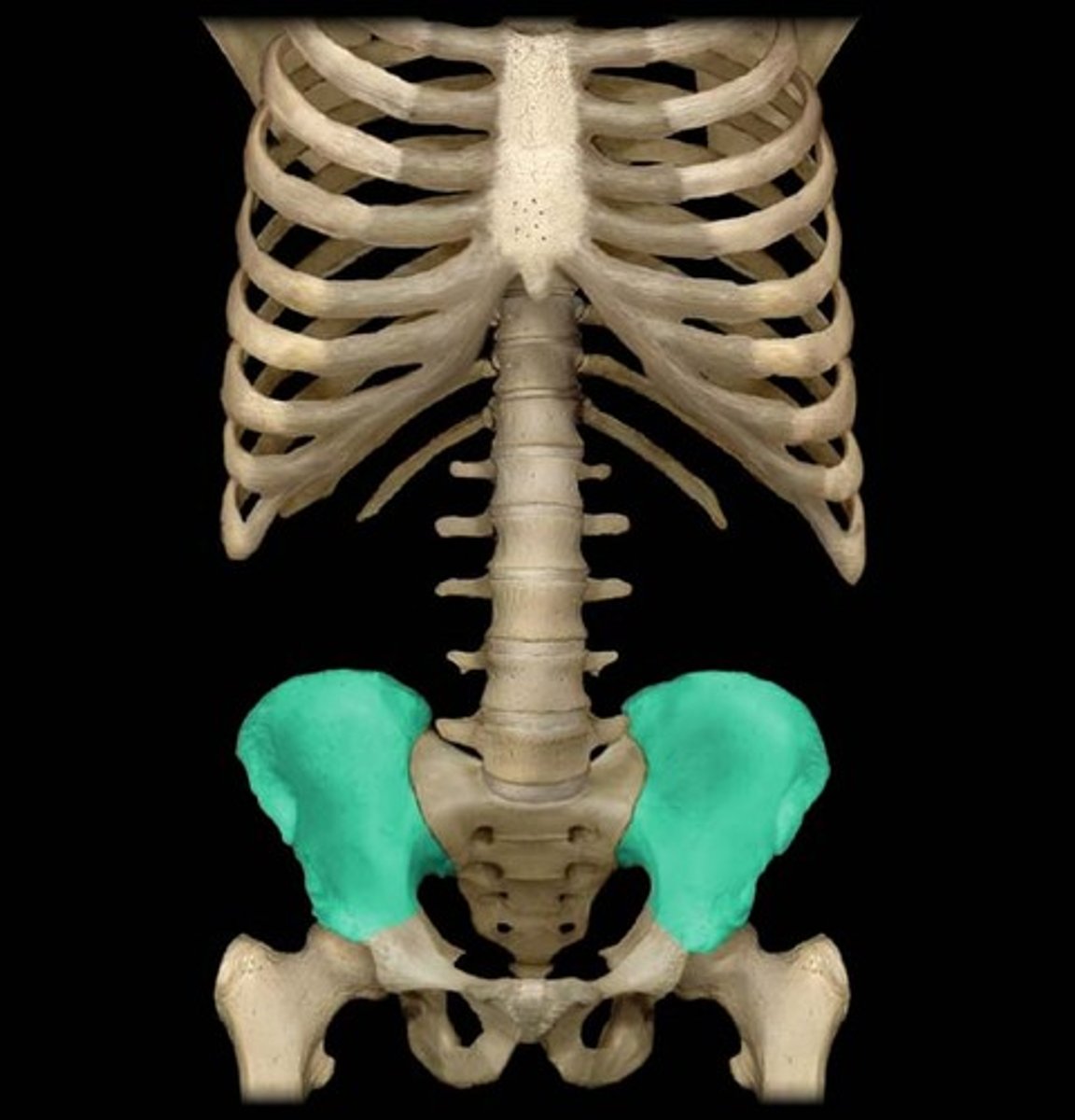
emt note, pelvis
pressure on the pubic symphysis during examination can reveal fractures in pelvis
*these fractures can lead to life threatening bleeding
Appendicular Skeleton
lower extremities
thigh (femur), knee, leg (fibula, tibula)
femoral head- round structure, connects femor to pelvic girdle by ball-and-sock joint
femer-thigh bone, strongest, longest in body
greater/lesser trochanter
knee- patella (knee cap)-joint connects lower and upper
tibia- lies anterior of leg, larger bone, can palpatate entire surface
fibia- lies on lateral side, palpate head of fibia lateral knee joint
ankle
hinge joint, flexon and extension
foot
contains 7 tarsal bones, five metatarsal
bottom is plantar surface
top is dorsom
toes- formed by 11 phalanges
Musculoskeletal system
refers to the bones and voluntary muscles of the body
protects vital organs
physiology:
1) ability to move
2) able to manipulate environment by contracting and relaxing
3 types of muscles
skeletal (voluntary)l- attaches to the bones of the skeleton
smooth- within blood vessels and intestines (intestines)
cardiac- only within heart
skeletal muscle (p. 187)
voluntary- under direct control of brain
stimulated to contract or relax
striated
principle of antagonistic pairs (bicup and tricep)
bicups
anterior aspect of the humerus
moves the lower part of the arm toward the head
helps slow movement of triceps extending arm
triceps
called three- headed muscles of the arm, three bundles of muscles
homeostasis
a balance of all systems in body
Respiratory System
process of breathing, structures of body that contribute to respiration
*primary purpose is to provide a pathway for air to reach the alveoli
*provide body with O, elimiate CO2
*controls the PH of blood
Respiratory System
*"airway", passage above the larynx (voice box)-dividing line btn upper/lower airway
*located anteriorly and at midline
*consists of:
nose- filter, humidify air
mouth-oral cavity-air enters more directly, less moist
tongue
jaw-mandible
pharyx-composed of nasopharynx, oropharynx,
larynx-voice box-complete arrangement of tiny bones, cartilage, musles, 2 vocal cords. if foreign object --> violent coughing (spasms)
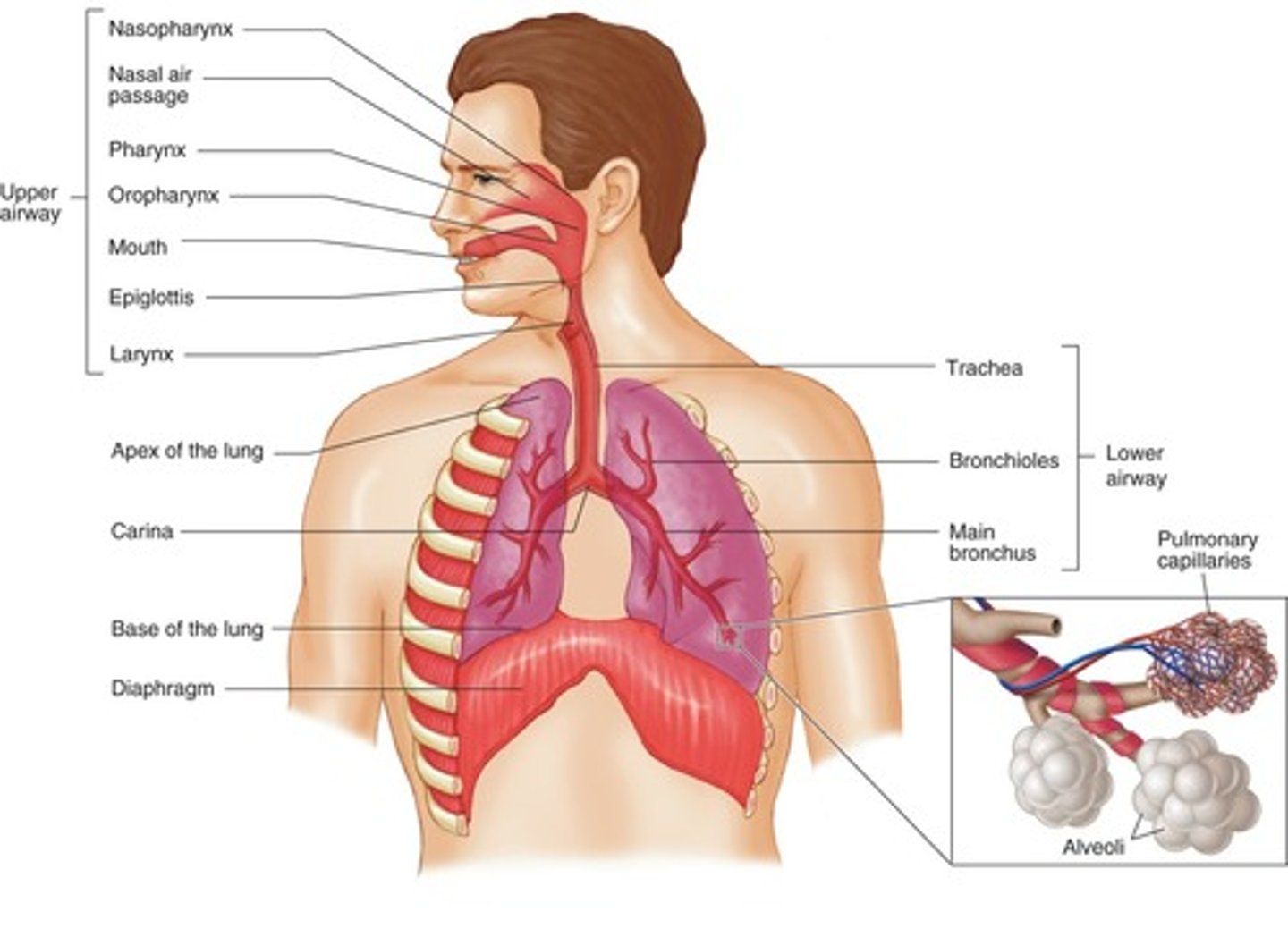
Epiglottis (upper airway)
protects opening of the trachea, thing leaf-shaped flap
Lower Airway
Adams apple- thyroid cartilage, part of the anterior part of the larynx
cricothryoid membrane-felt depression in the midline of the neck inferior to adams apple
Cricoid cartilage-below thyroid cartilage
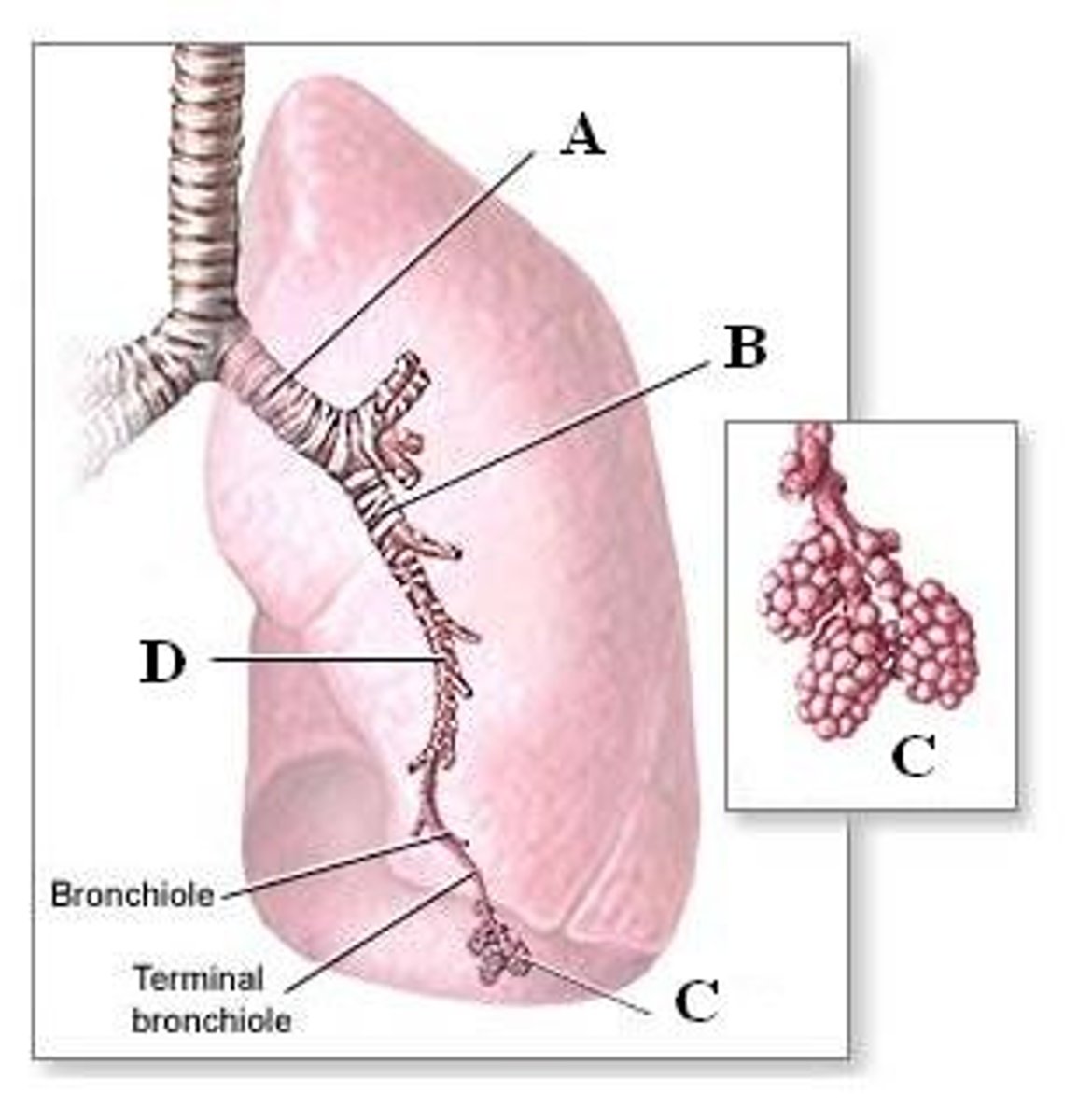
Trachea- (windpipe), rings of cartilage open in back keep from collapsing, ends at the carina and divides into 2 smaller tubes Bronchi
Lower Airway
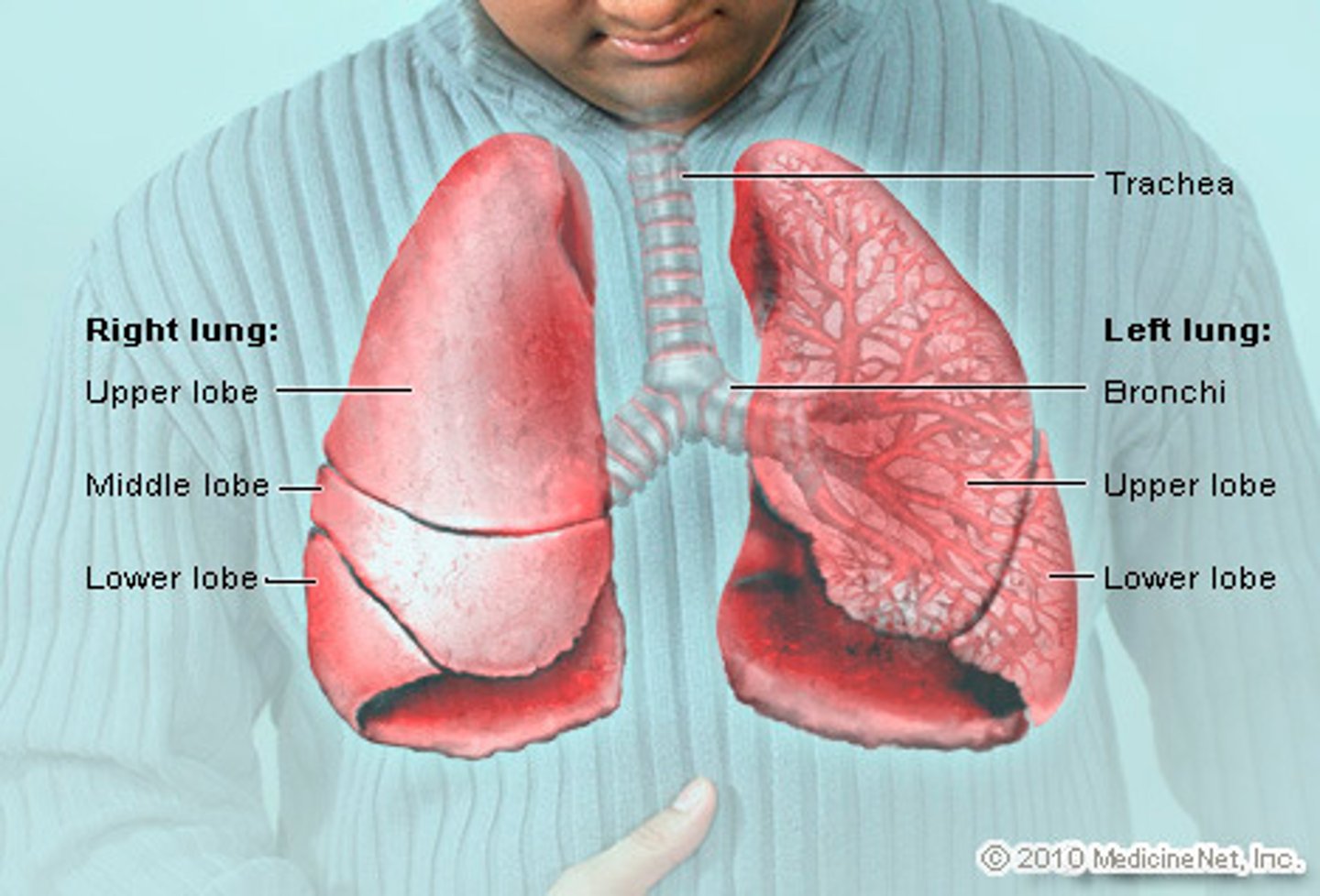
lungs
*held in place by trachea, arteries, veins, pulmonary ligaments
*right lung has 3 lobes
*left has 2 lobes
*have no musle
alveoli
*tiny, grapelike sacs at the end of the bronchioles
*exchange of O and CO2 occurs
*functional units of respiratory system
*walls contain pulonary capillaries that carry CO2 from the body to the lungs and the O from the lungs to the body
pluerua
*covers each lung
*smooth glistening tissue
pleural space
*normal conditions, space does not exist
*when blood or air leaks, surfaces separate
*when chest wall expands, lung is filled with and made to expand by the force exerted thru these closely applied pleural surfaces
Muscles of breaching
*breathing requires little muscle effort
*use accessory muscle groups (abs, pectoral) to assist if resistance in airway
diaphragm
*primary muscle
*voluntary (can hold breath) and involuntary (sleep)
*performs automatic function-concentration of CO2 to high, automatic regulation of breathing continues
*dome-shaped divides thorax from the abdomen
inhalation
diaphragm and intercostal muscles contract
diaphragm moves down, enlarging thoracic cage
intercostal moves ribs up
chest cavity enlarges, air rushes into lungs
*called negative pressure breathing
exhalation
*diaphram and intercostal muscles relax
*thorax decrease
*chest cavity decreases, air is compressed
*pressure is increased and pushed out thru trachea
*called passive
respiration vs ventilation
*respiration is the process of gas exchange
*ventilation is simple movement of air between the lungs and the environment, requiring chest rise and fall
Respiration
as blood travels, it gives O and nutrients to tissues and cells
O passes from the the blood to the capillaries to tissue cells
CO2 and cell wast pas from tissue cells thru capillaries to the blood
brain stem controls breathing
exhaled air contains 16 % O, 3-5 % CO2, rest nitrogen 79%
Diffusion
molecules move from an area with ah higher concentration of molecules (the air) to an area of lower concentration (blood stream)
O and Co2 pass rapidly across these thing tissue layer by diffusion
Ventilation
*medulla oblongata primarily responsible, stimulated by high CO2 levels
Tidal volume
amount of air that is moved into or out of lungs during single breath 500ml in adult
Residual volume
the air that remains in the lungs after maximal expiration
minute volume
measure used to assess amount of air that moves in ad out of the lungs in 1 min
measures the depth
minute volume = respiratory rate x tidal volume
this calc helps determine if a patient is breathing adequately
*min volume to low-- need ventilatory assistance
*evaluate the amount of air being moved with each breath
normal breathing characteristics
normal rate, depth (tidal volume)
regular rhythm or pattern of inhalation/exhalation
clear, audible breath sounds on both sides of chest
reg rise and fall movement both sides
movement of the abdomen
adults 12 to 20 breaths/min
children 12 to 40 breaths/min
inadequate breathing patterns
labored breathing (occurs when air movement is impaired)
agonal gasps: ocassional gasping breaths, cardiac arrests-- need chest compressions & ventilation
muscle retractions able clavicles, btn ribs, below the rib cage
pale or blue skin (cyanotic)
cool, damp,skin
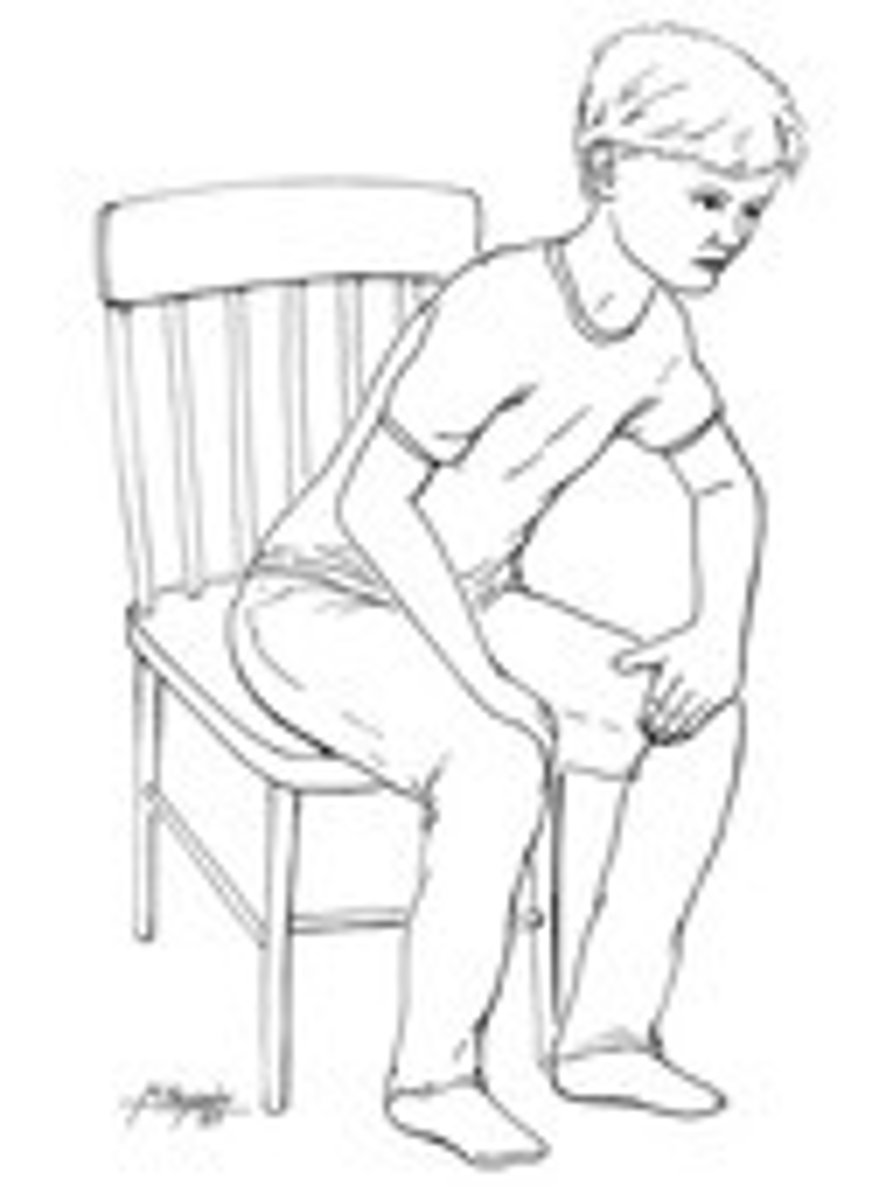
tripod position (leaning forward, leaning into arms)
Circulatory system
cardiovascular system
entirely closed
consists of :
systemic circulation
pulmonary circulation
flow of blood through heart and lungs
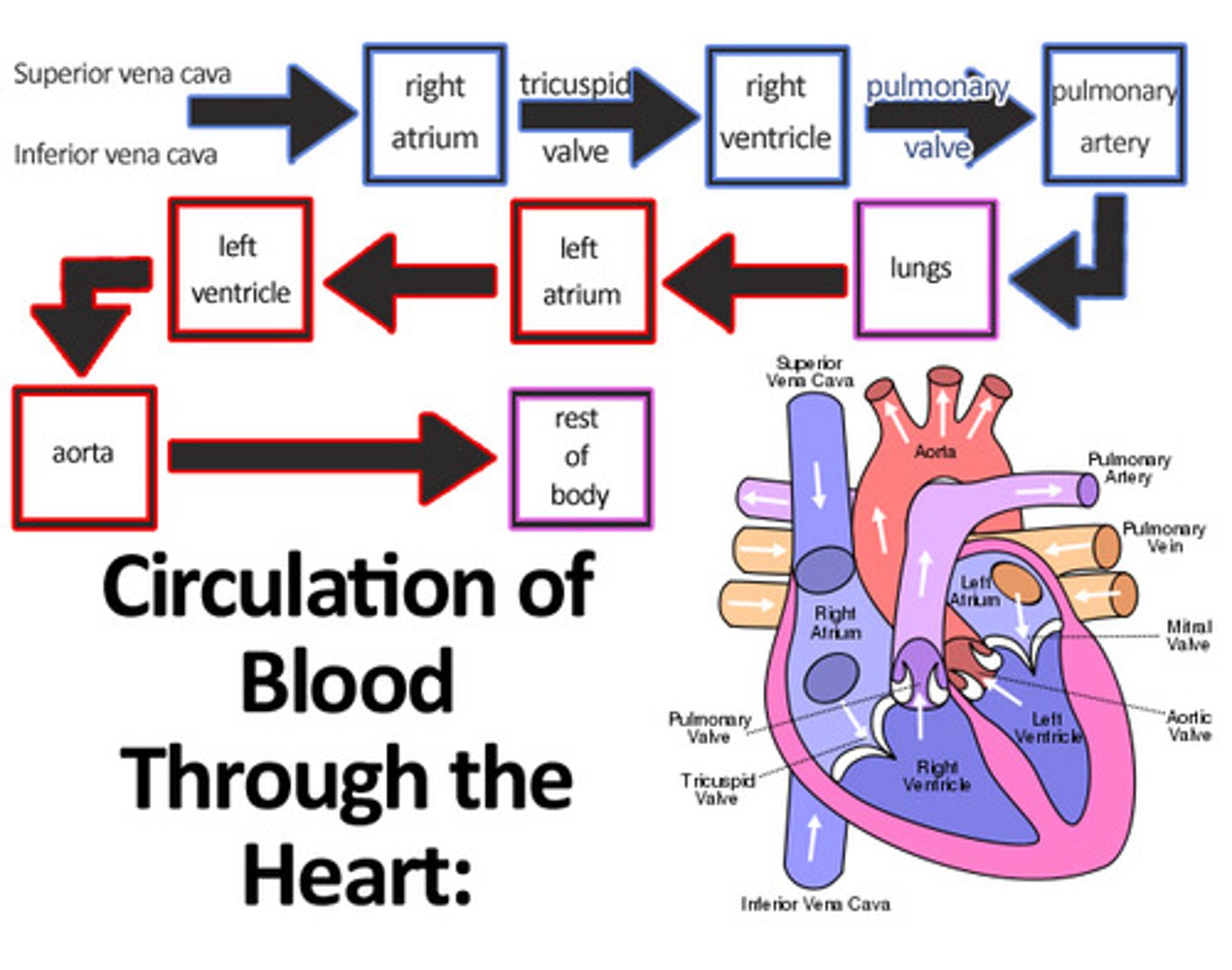
inferior and superior vena cava
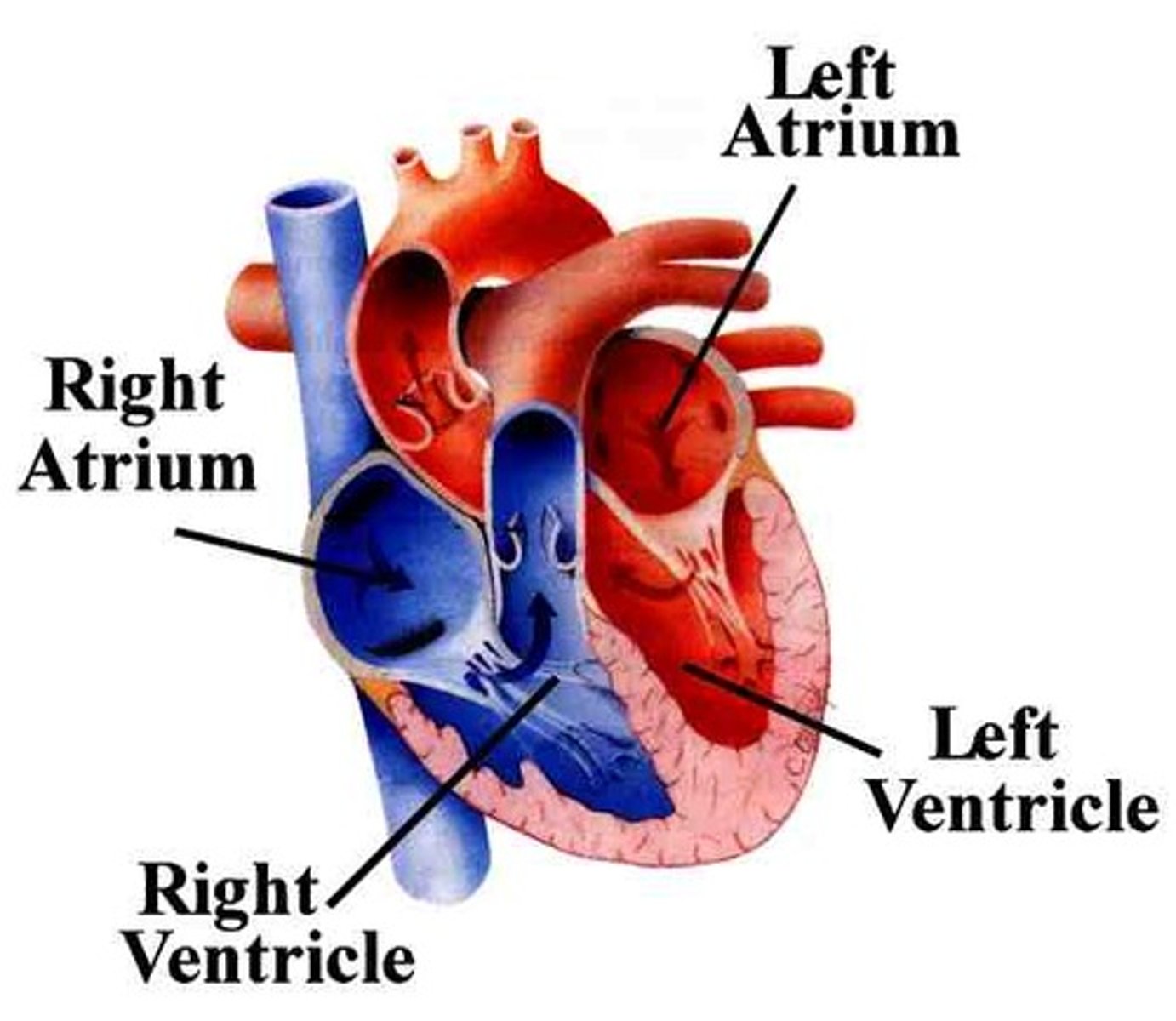
right atrium
right ventricle
pulmonary artery
lungs
pulmonary vein
left atrium
left ventricle
aorta (hearts blood supply)
systemic circulation
portion of circulatory system outside of the heart and lungs
pulmonary circulation
the flow of blood from the right ventricle thru the pumoney arteries and all of their branches and capillaries in the lungs and back to the left atrium thru the venules and pulmonary veins; also called the lesser circulation
heart
*hollow muscle organ appropriately the size of a fist
*myocardium (cardiac muscle)
upper- atrium
lower- ventricle
left side- pumps blood into body, high pressure
right side-supplies blood to the lungs, low-pressure pump
own electrical system
*can tolerate interruption of blood supply for only seconds before heart attack
heart
circulation
blood supply from AORTA-->branches into coronary arteries which supply the heart muscle with oxygenated blood
right side of heart receives blood from the veins of the body
left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs thru the pulmonary veins
*flow of blood thru the four heart chambers is governed by one-way valves
Normal heart rate
resting adult 60-100 beats/min
at each beat- 70 to 80 mL of blood is ejected
in one min- 5 to 6 ml circulated thru all vessels
Heart rate (HR) number heart beats per minute
stroke volume (SV) amount of blood moved in one beat
cardiac output (CO) amount of blood moved in 1 minute
CO= HR x SV
Heart
Electrical conduction system
*contractions produce pumping action
*a network of tissue that conducts an electrical current
*2 processes: deploarization and reploarization
*when injured, heart will not beat properly, low blood pressure, loss of consciousness, cardiac arrest
Arteries
Carry blood from heart to body tissues
aorta is main artery leaving back left of the heart, carries O -rich blood to body
pulmonary artery from heart carries O depleted blood to lungs
arteries brand into smaller arteries ARTERIOLES
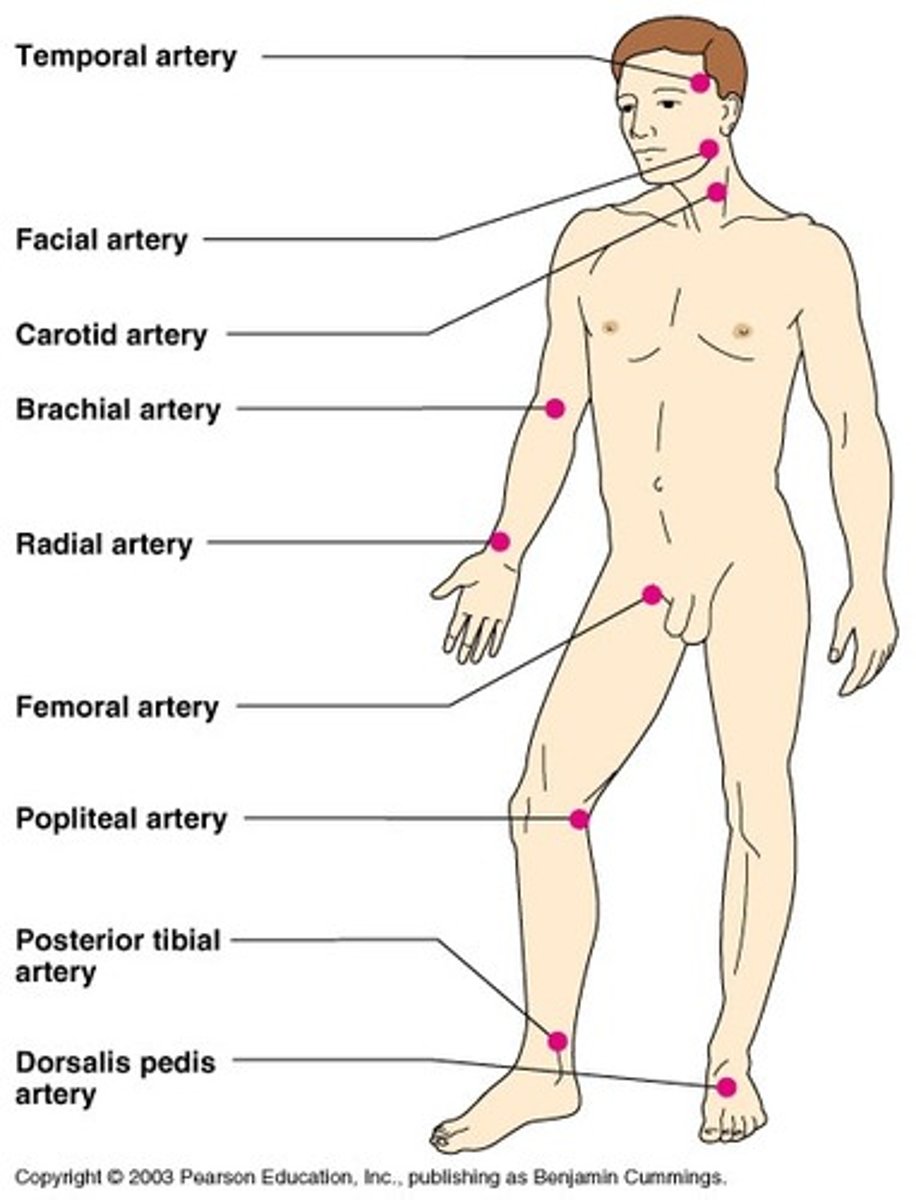
Pulse
*palpated easily at neck, wrist, or groin
*felt most easily where larger arteries near skin can be pushed against a solid structure like a bone or muscle
*forceful pumping of blood out of left ventricle and into major arteries
capillary vessels
fragile divisions of the arterial system that allow contact btn the blood and the cells of the tissues
Veins
*blood returns to heart
*have much thinner walls than arteries and larger in diameter
two major vessels: superior and inferior vanae cavae
Spleen
*all blood passes thru and is filtered
*assists in immune response
*most frequently injured abdominal organ, can lead to several internal bleeding
*blunt trauma -under flexible lower ribs
blood composition
Plasma-yellow fluid carries blood cells and nutrients
red blood cells- contain hemoglobin, color, carries oxygen
white blood cells- bodys immune defense mechanisms again infection
platelets- disc-shaped, initial formation of blood clot (stop bleeding)
(p 204) in body:
adults blood- adults 6L
children 2 to 3L
infants 300 mL
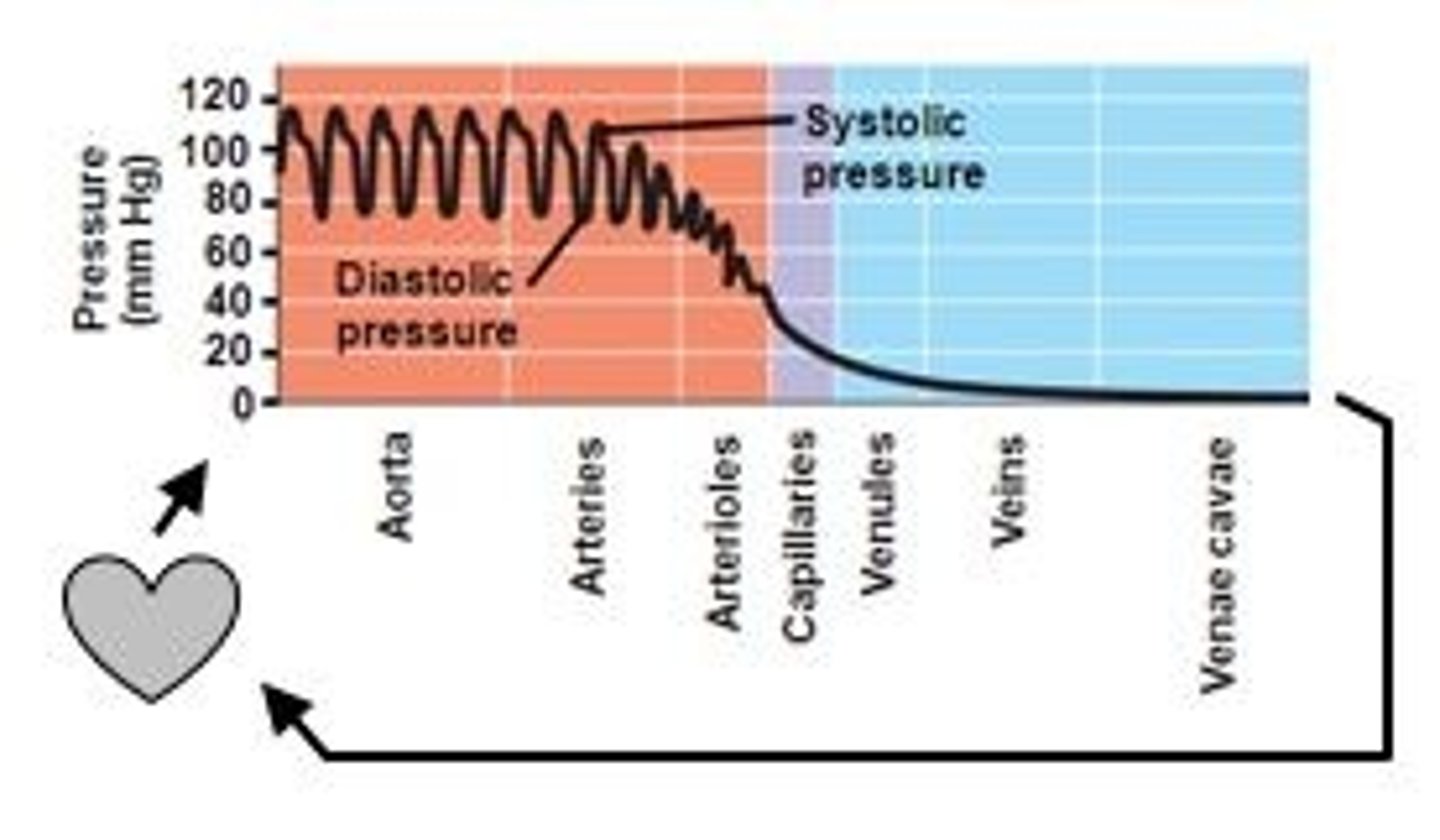
Blood Pressure BP
Cardiovascular pressures (chart pg 204)
pressure the blood exerts against the walls of the arteries
SYSTOLE: left ventricle contracts, high point of pressure wave
DIASTOLE: ventricle relaxes, fills with blood, low point
high and low points of wave measured with sphygmomanometer (blood pressure cuff)
shock
*hypoperfusion
*state of inadequate circulation
*Perfusion- circulation of blood in an organ or tissue in adequate amounts to meet the cells current needs
*loss of blood pressure is an indication that blood is no longer circulating efficiently to every organ
*cells, tissues, organs may die
inadequate circulation
"stroke forumla" as blood pressure fails, pulse increases in an attempt to keep cardiac output costantat 5-6L/min. shock=fails
MAP= CO (HR x SV) x SVR
mean arterial pressure
co cardiac output
SVR systemic vascular resistance
functions of blood
30 percent of blood in heart arteries and capillaries
heart, arteriels= high pressure
veins=low pressure
blood from artery- gush
blood from vein- flows in a steay stream
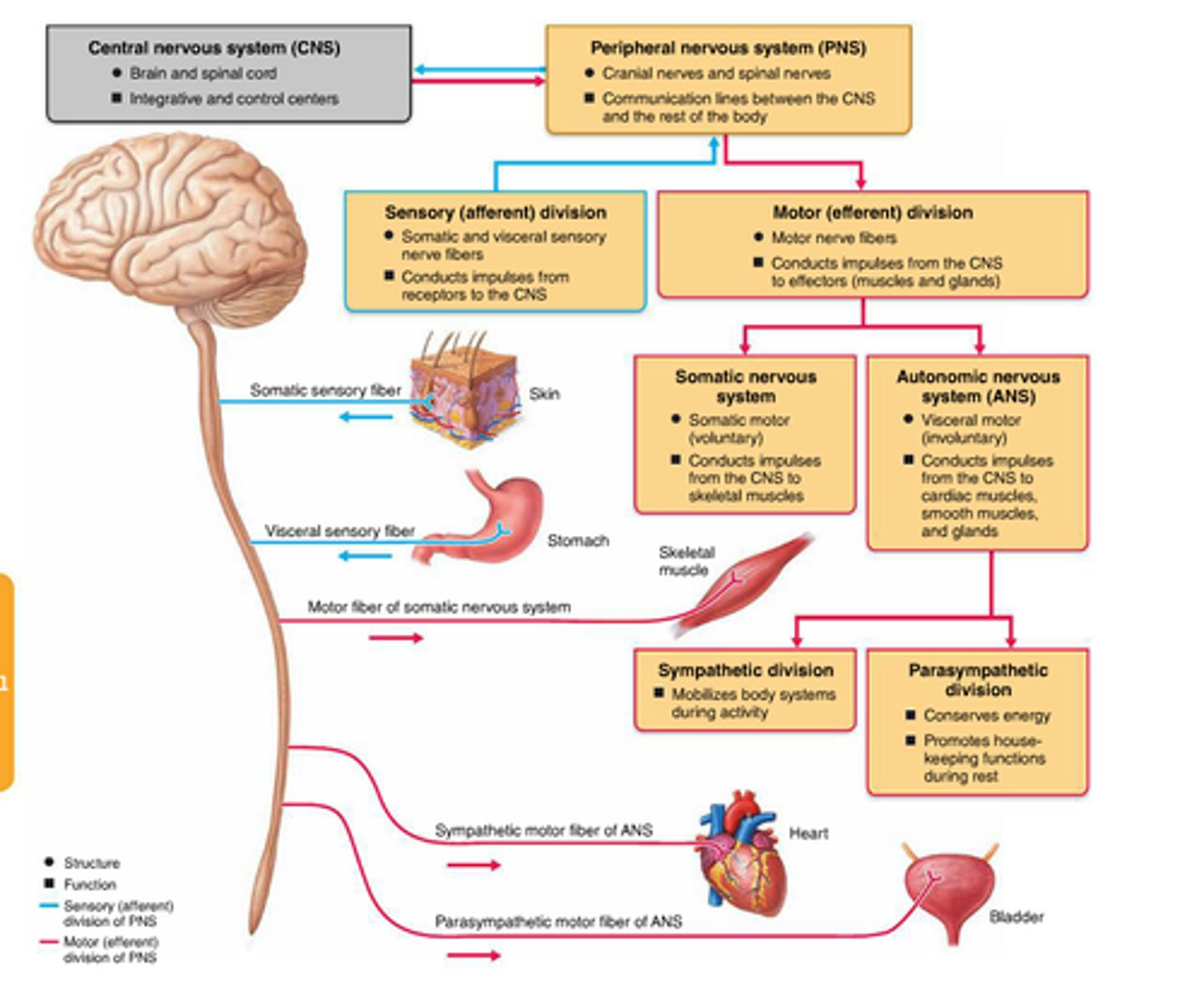
Nervous system
anatomically :
Central NS (brain, spinal cord)
Peripheral NS (nerves outside of above)
functioning
somatic- regulates activites over which there is voluntary control (walking)
autonomic- body systems non-voluntary including digestion
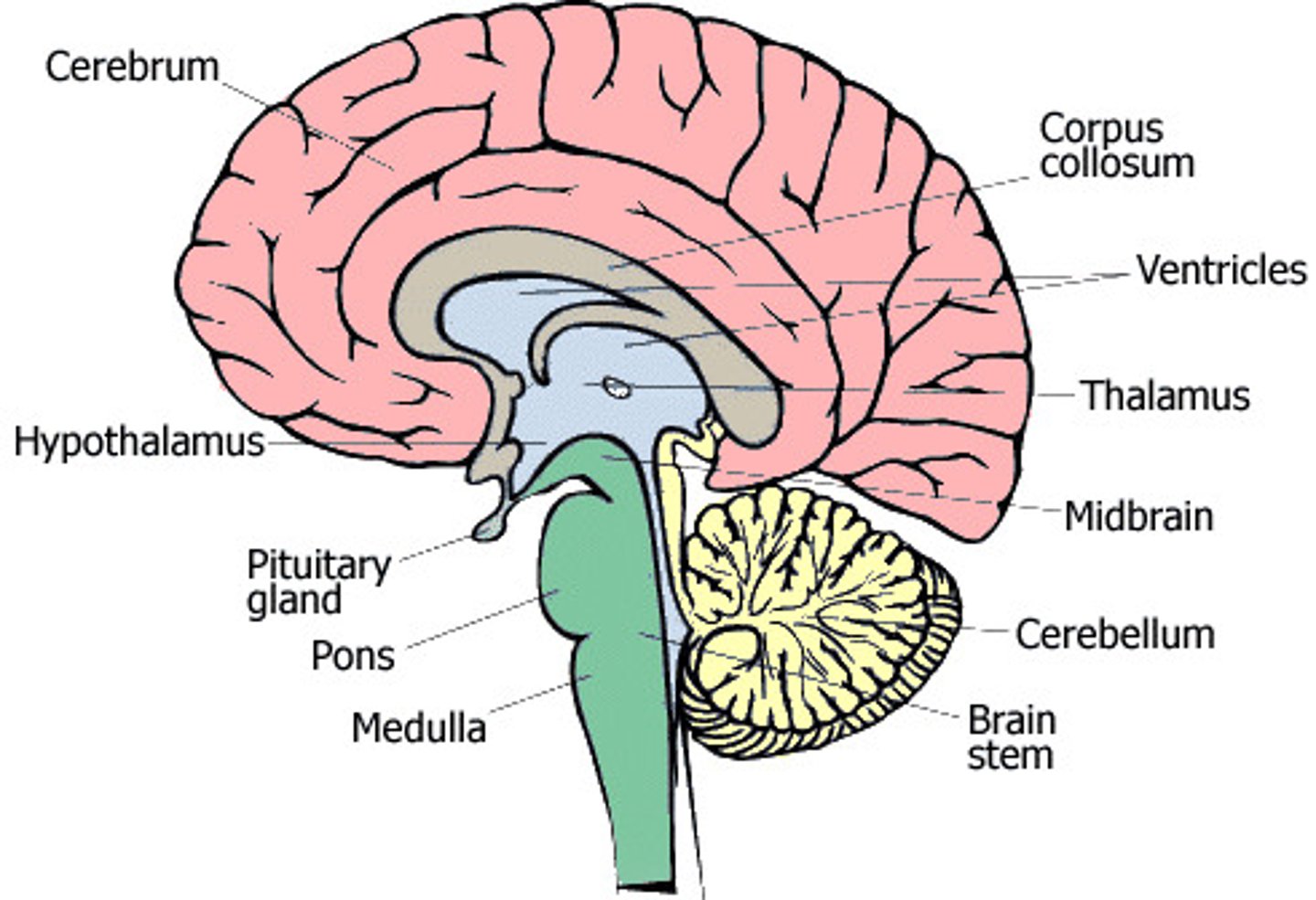
brain CNS
controlling organ of body
cerebrum: largest, gray matter 3/4 volume
cerebellum: little brain, body movements
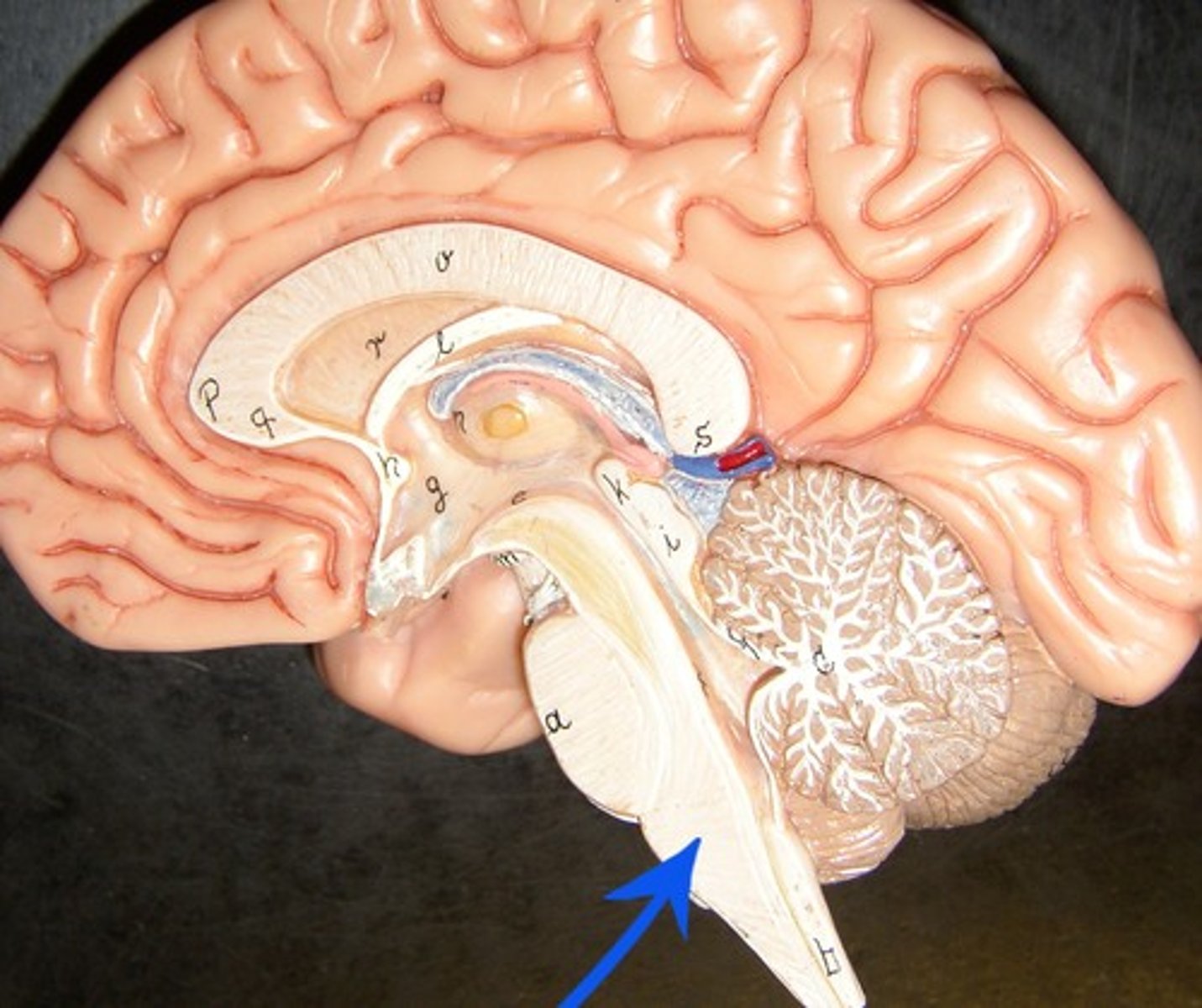
brain stem: controlling center body functions necessary for life (cardiac, consciouness, respiratory
cerebrospinal fluid- if leaking from nose/ears-->skull fracture
spinal cord: an extension from the brain stem, transmit messages btn brain and the body
PNS
Somatic nervous system-
Autononic nervous system-
sympathetic nervous system- emergency functions, fight or flight
parasympathetic -slows down body, non emergency functions
sensory nerves
the nerves that carry sensations such a touch, smell, heat, cold and pain from the body to the central nervous system
*goes to the brain.
motor nerves
carry information FROM the brain to the muscles of the body
*each muscle has its own mtor nerve
integumentary system
in order
epidermis-outermost layer, holds pigment
dermis- special structures- sweat glands, oil glands, hair folicles, blood vessels
subcutaneous tissue-composed largely of fat, helps anchor the skin to muscles below , loss of this layer causes wrinklees
digestive system
abdomen
*disgesting- mouth- anus
2nd major body cavity
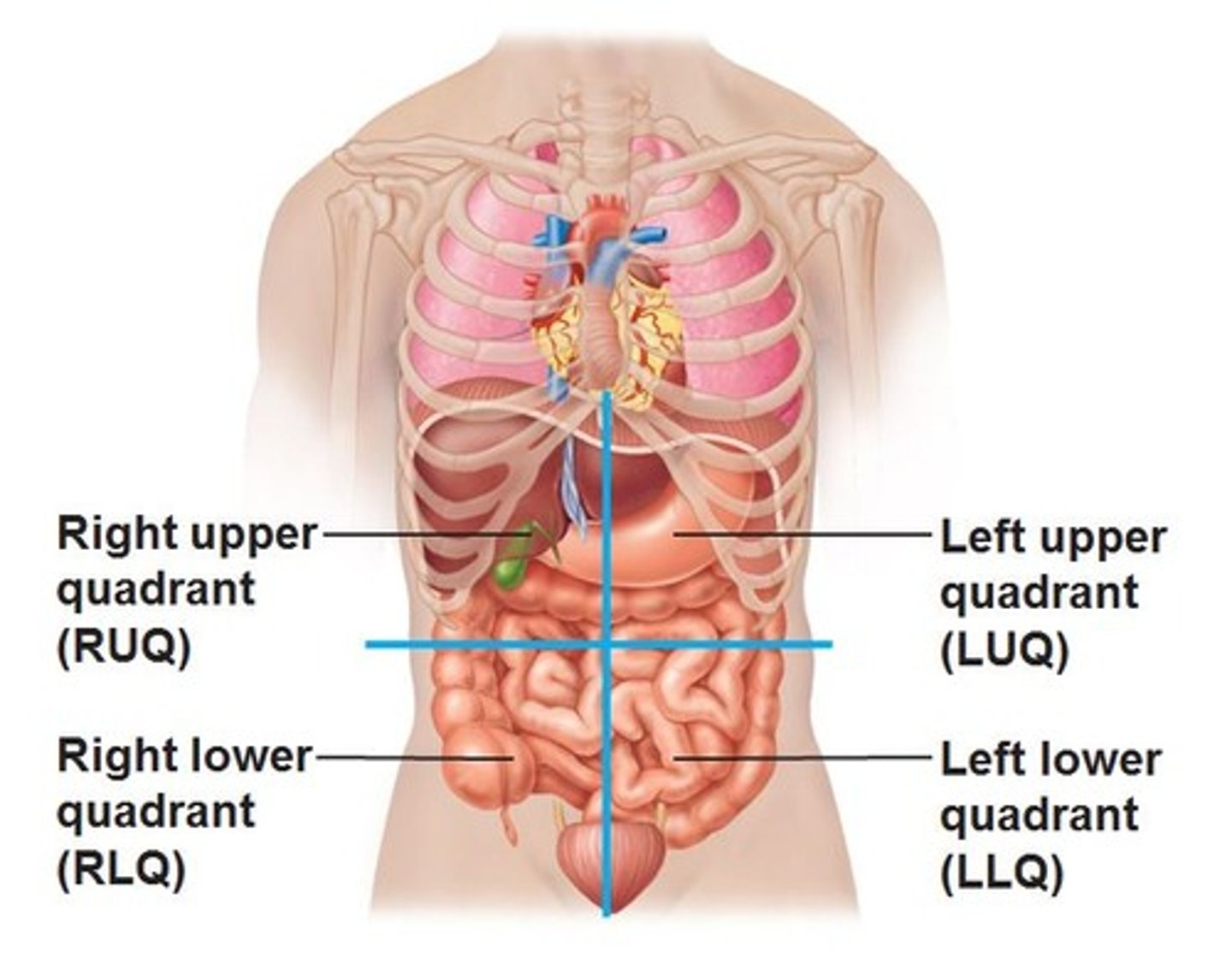
formed by quadrants
LUQ
Somach, portio of colon, spleen
LLQ
sigmoid portions of colon
RUQ
liver, gall bladder, portion of colon
RLQ
appendix, 2 portions of large intestine
pancreas- lies in both top quadrants
bladder- lies in both lower quadrants
small intestines- all four quadrants
digestive path
mouth- mechanically breaks down food
esophagus-moves food from mouth to stomach
stomach-performs chanical and chemical breakdown of food, food in, chyme out
small intestine-major site for cheical creakdown of food
large intestine-water absorptions, formation of feces, bacterial digestion of food
anus-last portion of large intestine, shincter to control release of feces
liver-production of bile, detox blood, primary organ for the storage of sugar or starch for immediate use
pancreas-insulin and glucagon are produced
gallbladder-storage of bile
lymphatic system
spleen, lymph nodes, lymph
supports the circulatory and immune system
relys on movements of body (no pumps)
respiratory compromise
V/Q ventilation/perfusion mismatch
inability of the body to move gas effectivley, which can result in hypoxia, hypercarbia
when ventilation (movement of air btn lungs and environment)- most common is airway blocked by tongue, or contraction of muscles during asthma attack
respiratory (gas exchange) is impaired by atmosphere, high altitudes, in pneumonia
affects of respiration compromise
O levels fall, CO2 rises
body increases respiratory rate
blood becomes acidic