Clinical Dentistry 3- Traumatic Injuries to Permanent Teeth
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
max incisors
which teeth are most commonly injured
pulp test
you should .... following trauma to a tooth as a baseline, however its not always immediately accurate
3
pulp testing is considered accurate ... months following trauma
modality of choice
CBCT is the imaging ..... for most dental diagnosis including trauma
75
crown fractures make up ....% of tooth fractures
complicated
a crown fracture that includes the pulp is considered to be ...
uncomplicated
a crown fracture that does not include the pulp is considered to be ...
pulp chamber; root development
in the PA to diagnosis an uncomplicated crown fracture it is important to evaluate the size of the ... and stage of the ....
no
will an uncomplicated or complicated crown fracture be sensitive to percussion
no
is an NS-RCT needed to treat an uncomplicated crown fracture
24; PDL
you should pulp cap a complicated crown fracture when:
- Short exposure period after trauma (<.... h)
- Small exposure
- Not associated with .... injury
Ca(OH)2; MTA
to pulp cap after a complicated crown fracture, cover the pulp with ..... or .... and restore the tooth
cementum
a crown root fracture involves the enamel, dentin, and ....
2
in diagnosis of a crown root fracture you need ....+ PA radiographs
immature
when treating a crown root fracture pulp capping or pulpotomy is acceptable for an .... tooth
pulp
a root fracture involves dentin, cementum, and ....
no
is the apical segment usually displaced in a root fracture
apical 1/3
in what segment of the tooth root is the prognosis of a root fracture the best
cervical 1/3
in what segment of the tooth root is the prognosis of a root fracture the worst
angles
diagnosis of a root fracture requires 2+ PA radiographs taken at different ...
3-4; 4
a root fracture can be treated with a splint for .... weeks (apical or middle 1/3) or up to ..... months (coronal third)
pulp necrosis
a root fracture can be treated with NS-RCT if .... occurs
25
...% of root fractures will develop pulp necrosis
alveolar fracture
if when the mobility of one tooth is tested and several move, this is associated with an ...
4
to treat an alveolar fracture reposition and then splint involved teeth with a flexible splint for ... weeks
concussion
which type of traumatic luxation injury:
- No displacement
- No mobility
- Usually sensitive to percussion and/or
tender to touch
Treatment:
- Flexible splint is optional - can be
used for the comfort of the patient for 7-10 days
subluxation
which type of traumatic luxation injury:
- Tooth is tender to touch and mobile,
but not displaced
- Hemorrhage from gingival sulcus
possible
Diagnosis:
- 2+ PA radiographs
- No radiographic abnormalities
Treatment:
- Flexible splint is optional
- splint for 2 weeks using a flexible splint up to .4mm
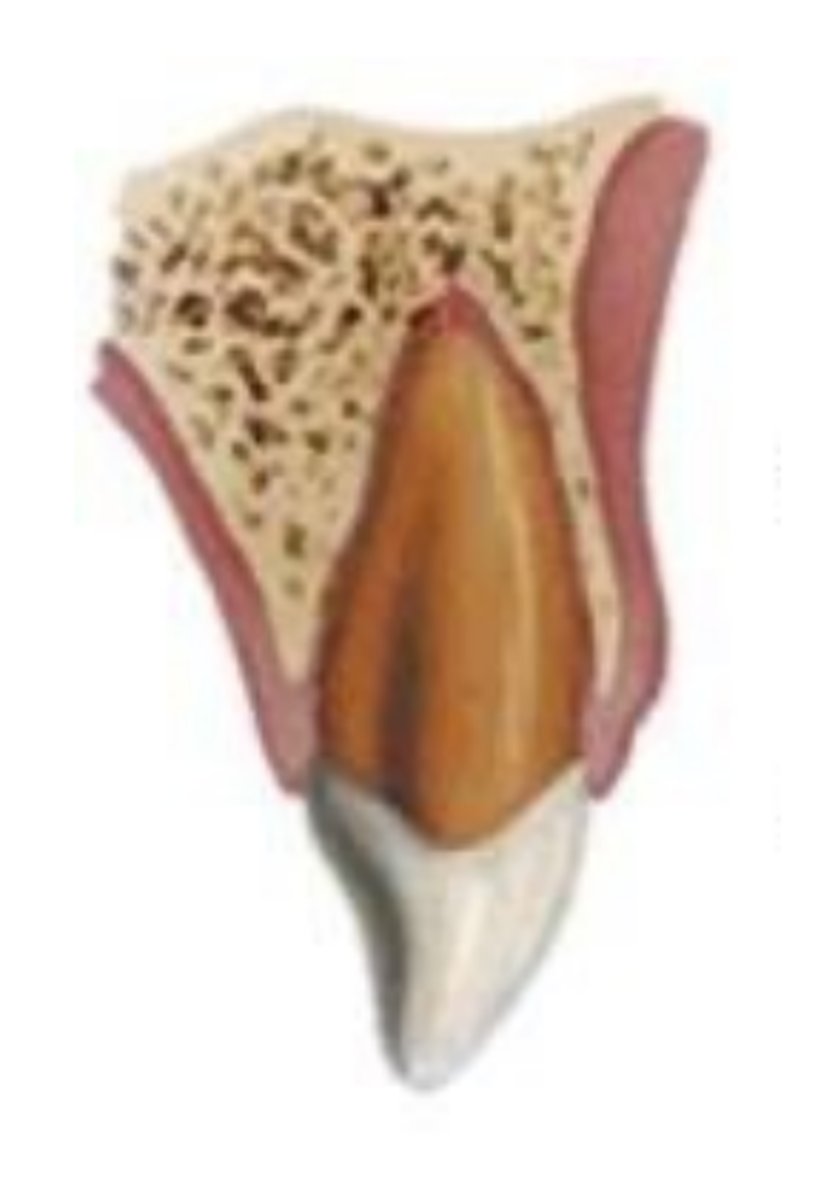
extrusion
which type of traumatic luxation injury:
- Elongated, mobile tooth
- Partial displacement of the tooth out
of socket.
- Angulated radiograph: increased PDL space apically
Treatment:
- Reposition
- Stabilize tooth with flexible splint for
1-2 weeks
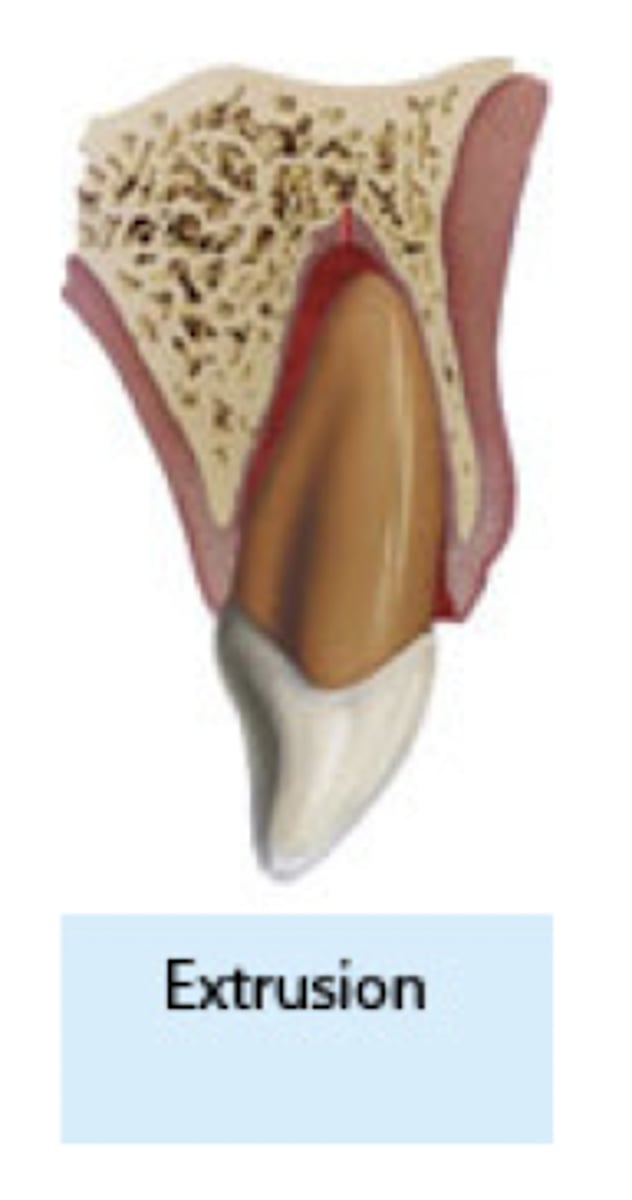
2
you should splint an extrusion for .... weeks
lateral luxation
which type of traumatic luxation injury:
- Displacement of a tooth buccally or lingually
- Usually accompanied by fracture of socket
- Usually locked into bone
- Not tender to touch, not mobile
Diagnosis:
- 2+ angulated PA radiographs
Treatment:
- Reposition the tooth into normal
position
- Confirm with radiograph
- Stabilize tooth with a flexible splint for 1-2 weeks
- Follow up
- Necrotic? → NS-RCT
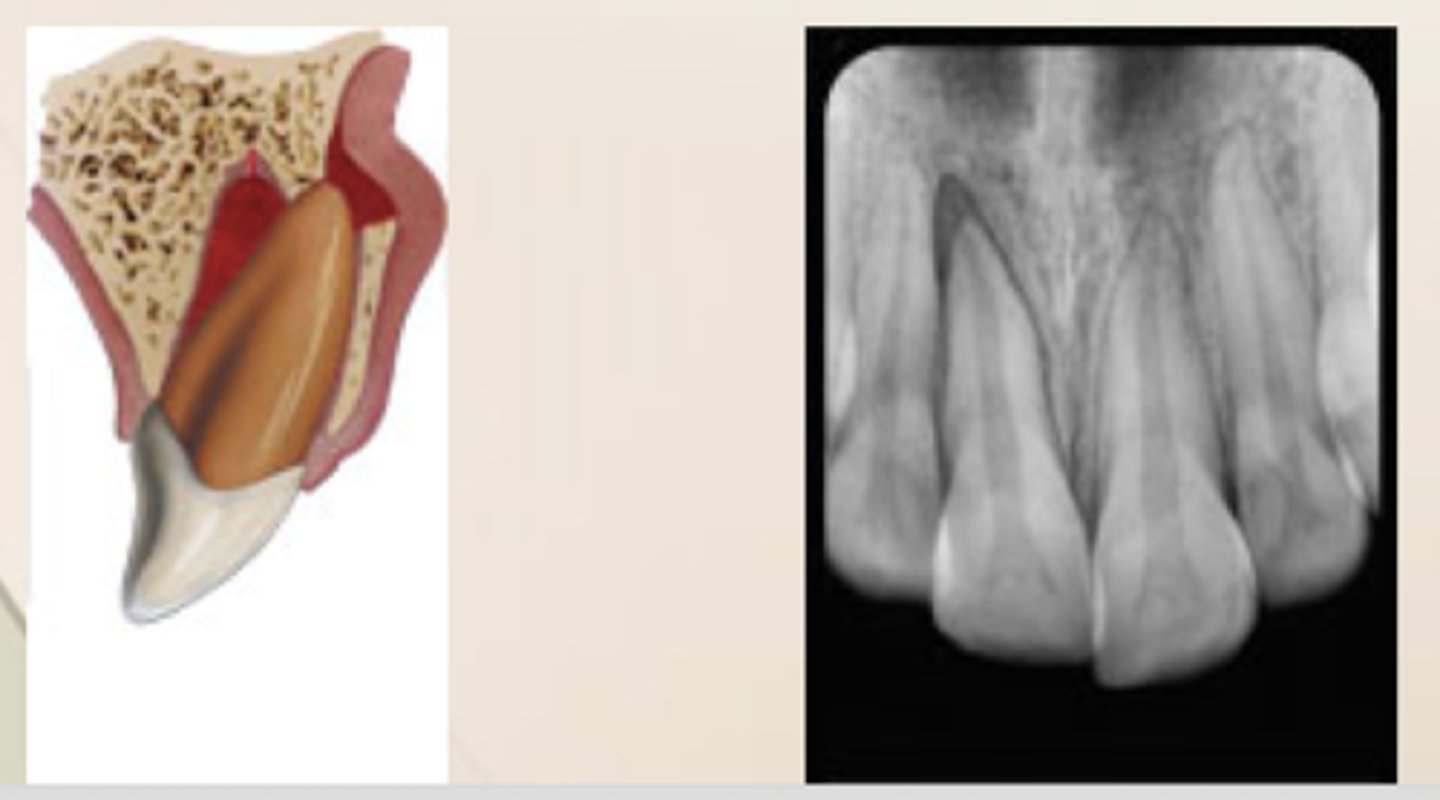
2
you should splint an lateral luxation for .... weeks
intrusion
which type of traumatic luxation injury:
- Apical displacement of tooth into the alveolar bone
- Tooth is driven into the socket, compressing the PDL
- Tooth appear to be shortened or missing
- Severe type of luxation injury
Treatment:
- Reposition the tooth with orthodontic or surgical extrusion
- Prognosis is poor
- High rate of Pulp Necrosis (96%)
and Root Resorption
- Initiate endodontic treatment at 2 weeks
- Recommend Ca(OH)2 for up to 4
weeks
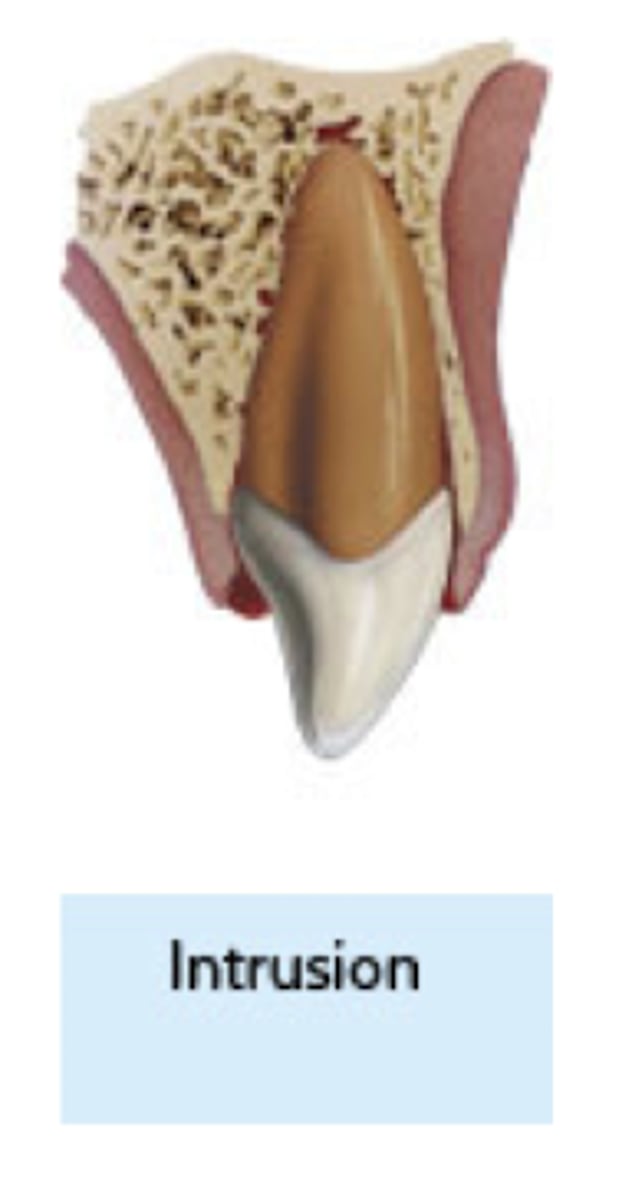
poor
the prognosis of an intruded tooth is ...
2; 4
on an intruded tooth initiate endodontic treatment at ... weeks and use Ca(OH)2 for up to .... weeks
4
you should splint an intrusion for .... weeks
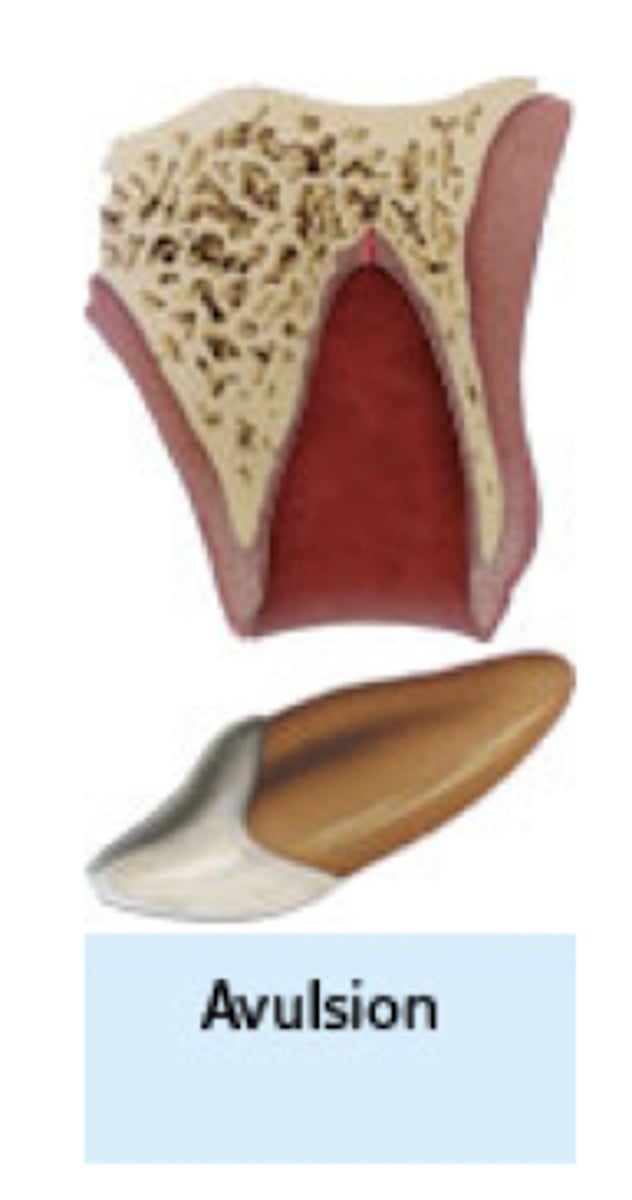
avulsion
what type of traumatic injury:
- The tooth is separated from socket
completely
- PDL torn
extra alveolar time
.... in the most critical factor in avulsion injury healing
ankylosis
extra alveolar time causes the PDL cell to dry out and causes an inflammatory response to the tooth and .....
propolis
what is the best storage media for an avulsed tooth
milk
what is the best most readily available storage medium for an avulsed tooth
crown
if an tooth is avulsed, the patient should handle the tooth by the .... only
dirty
the patient should rinse an avulsed tooth only if its ... without scrubbing or scraping
no
should you curette the socket of an avulsed tooth
revascularization
an avulsed tooth with <60 minutes extraoral time and an open apex:
- the main goal is .... of the pulp
1-2
an avulsed tooth with <60 minutes extraoral time and an open apex:
- after replanting the tooth, splint for ... weeks with a flexible wire with a diameter up to 4 mm
pulp necrosis
an avulsed tooth with <60 minutes extraoral time and an open apex:
- only perform NS-RCT if there is ...
NS-RCT; Ca(OH)2
an avulsed tooth with <60 minutes extraoral time and an closed apex:
- always begin ..... within 7-10 days
- this perform in 2 visits with ..... placed inbetween
1-2
an avulsed tooth with <60 minutes extraoral time and an closed apex:
- splint for .... weeks
nsrct; closed
- the main difference between management of an avulsed tooth with an extra-alveolar time <60 minutes with an open vs closed apex is ... is always required for a .... apex.
- replantation, splinting, and antibiotics are otherwise the same
60
an avulsed tooth with an extraoral time >.... minutes will have a poor long term prognosis
ankylosis; resporption
an avulsed tooth with an extraoral time >60 minutes has an expected outcome of .... related root ....
esthetics; function
the treatment of an avulsed tooth with an extraoral time >60 minutes has the main goal of restoring ... and ....
1-2
an avulsed tooth with >60 minutes extraoral time and an open apex:
- splint for ... weeks
- administer antibiotics for 7 days
4-6
an avulsed tooth with >60 minutes extraoral time and an closed apex:
- splint for .... weeks with a flexible wire with a diameter up to 4 mm
- always begin NS-RCT within 7-10 days
- this perform in 2 visits with Ca(OH)2 placed inbetween
doxycycline; penacillin
an avulsed tooth may include adjunct medication of:
- .... 2x/day for 7 days at appropriate dose for patient age and weight
- ..... VK 500 mg q6h for 7 days
nylon fishing line (.13-.25 mm)
what is an alternative to flexible wire in splinting a tooth
1-2
obturation of an avulsed tooth should have Ca(OH)2 in place for .... months
30
<.... minutes extraoral time for an avulsed tooth has the best prognosis
transport conditions
what is the 2nd most important factor in the prognosis of an avulsed tooth
time before endo treatment
what is the 3rd most important factor in the prognosis of an avulsed tooth
7-10
when an avulsed tooth requires RCT, it should be initiated within .... days
splinting technique
what is the 4th most important factor in the prognosis of an avulsed tooth
stage root development
what is the 5th most important factor in the prognosis of an avulsed tooth
root surface treatment
what is the 6th most important factor in the prognosis of an avulsed tooth
intrusion with closed apex
what luxation injury has the worst prognosis (about 0%)
yellow
.... discoloration is common in teeth with pulp obliteration
asymptomatic
>2/3 of teeth with pulpal obliteration are ....
1-27
The incidence of pulp necrosis following PCO is variable ranging from .....%, but is generally considered low
periapical
RCT is indicated for PCO when there are clinical symptoms and/or definite
radiographic findings suggestive of ..... disease
nonvital bleaching
If RCT is required after pulp canal obliteration and there are aesthetic concerns, a ..... technique can be considered
surface
what type of external root resorption:
- Localized injury to cementum (Concussion, Subluxation)
- Local inflammatory response
- Periodontal healing and root surface
repair will occur within 14 days
- May or may not be radiographically
visible
- No treatment is required
concussion; subluxation
what 2 injuries are associated with surface resorption
inflammatory
what type of external root resorption:
- Damage of the periodontium
- Bacteria within tubules
- 2-visit NS-RCT with Ca(OH)2 can
arrest resorptive process and
promote healing
replacement
what type of external root resorption:
- Severe damage to the periodontium (Intrusion, Avulsion)
- “Fusion” of the tooth root with the
adjacent alveolar bone
Diagnosis:
- Tooth is immobile
- High percussive tone
- No visible PDL space
Treatment:
- Cannot be arrested or repaired
- Survive for a number of years
intrusion; avulsion
what 2 injuries are associated with replacement resorption