Unit 2 Test 1 on Organelles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Organelle
Special structures within the cell that works together to help the cell function
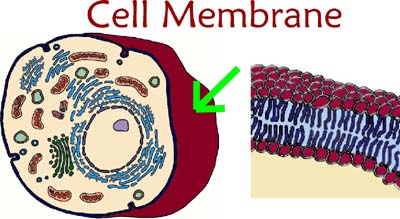
Cell (plasma) membrane
Controls what goes in & out of a cell and is critical for communication and maintaining a stable internal environment(homeostasis). And is made of 2 players of phospholipids (phospholipid bilayer)
Cytoskeleton
gives the cell shape , moves organelles around, and provides structual support for animal cells(who don’t have a cell wall) and is made of proteins
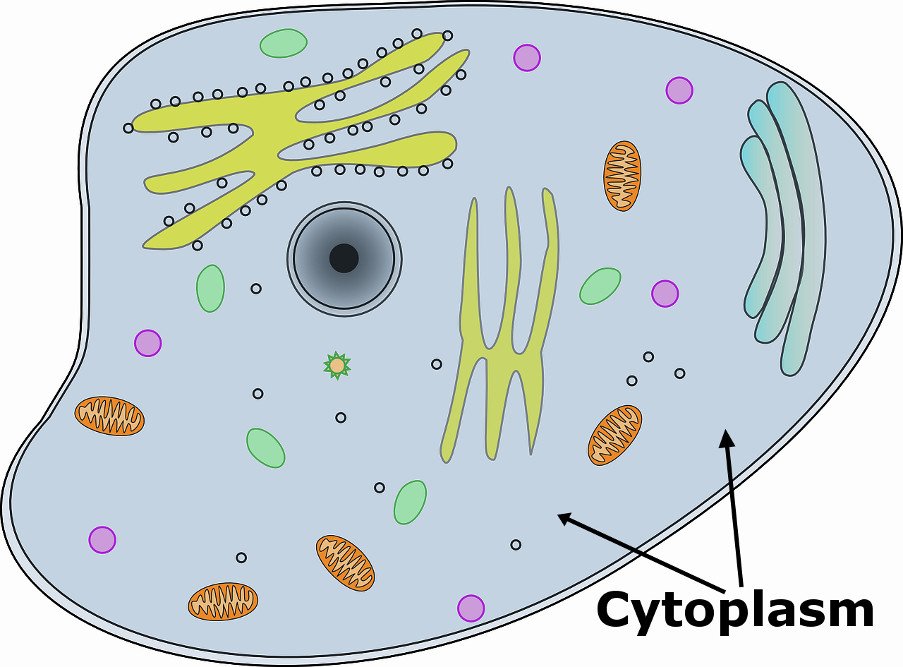
Cytoplasm
Holds everything in place, provides a solution for chemical reactions to take place in
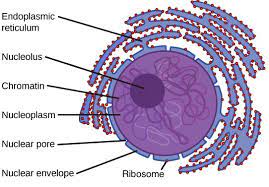
Nucleus
Protects DNA that controls the activities of the cell
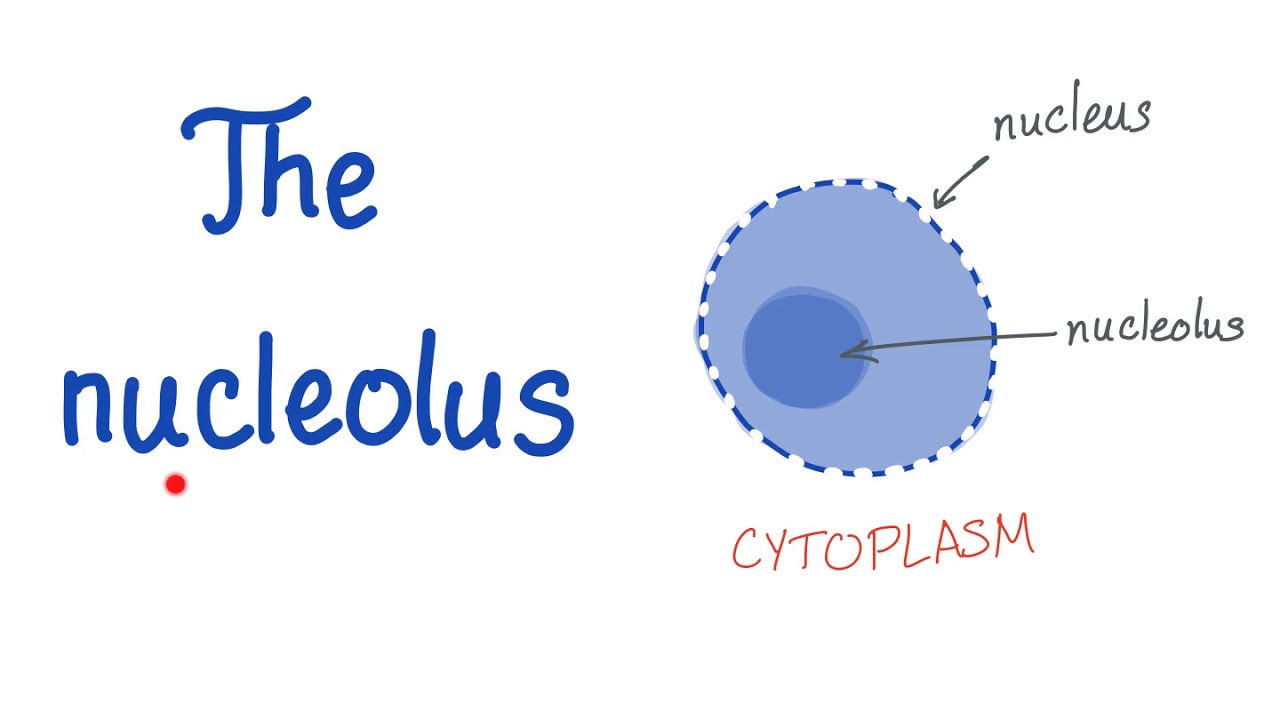
Nucleolus
Makes rRNA which make up ribosomes. (pretty much makes ribosomes)
c
Makes proteins
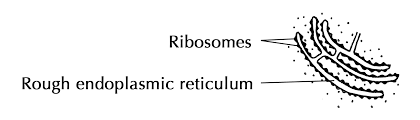
Rough ER
Makes proteins and packages them for secretion and covered with ribosomes

Smooth ER
Makes lipids (membrane)

Golgi Apparatus
Gets vesicles of protein from the ER and processes, sorts, and ships proteins to where needed
Vesicles
Mini-carts that transfer protein around the cell
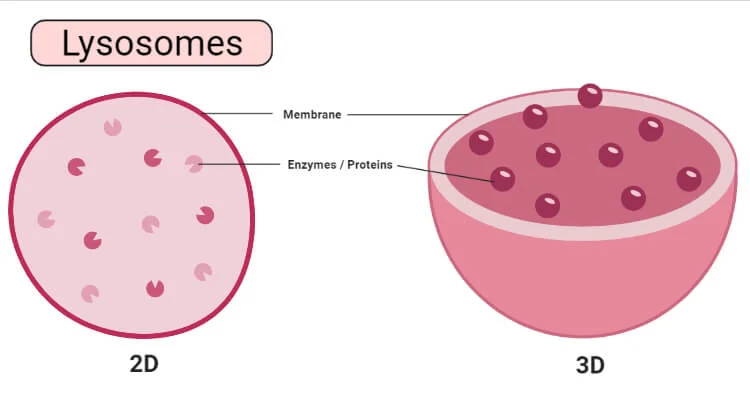
Lysosomes
Only in animal cells, Break down dead stuff like food, bacteria, and old parts of the cell. Is able to perform cell death (apoptosis)
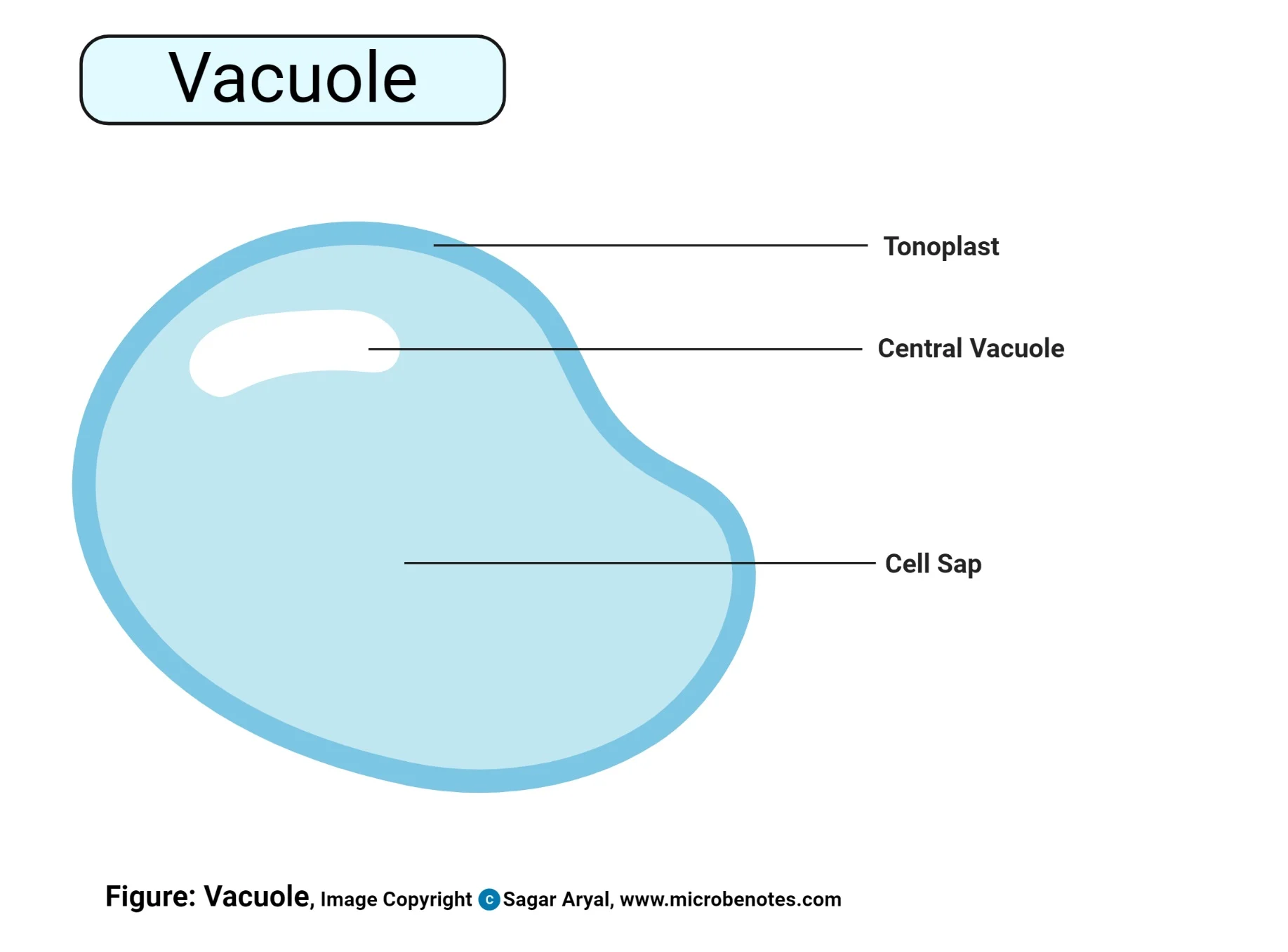
Vacuole
Storage (water, nutrients, waste, etc)
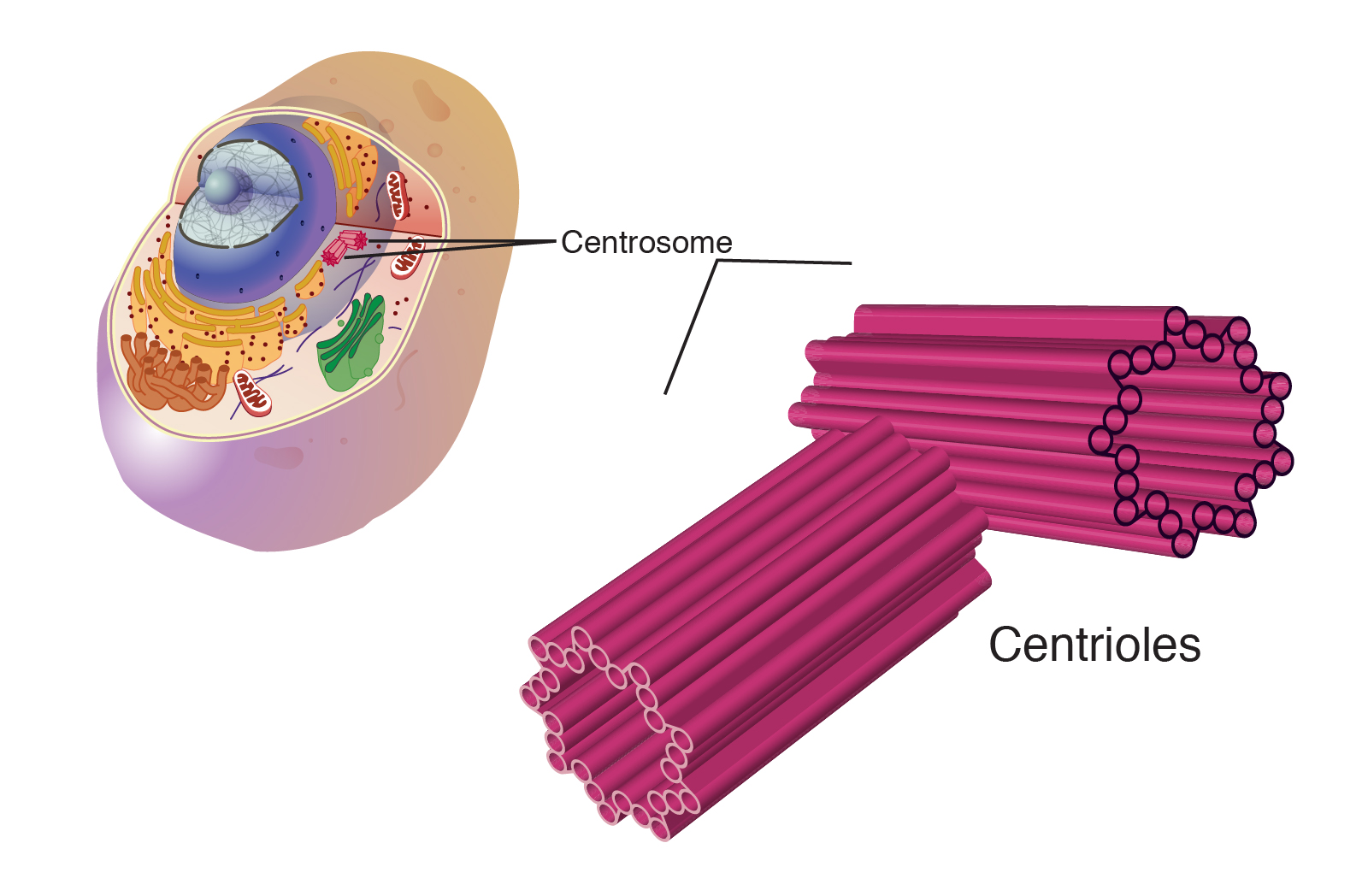
Centrioles
Also called centrosomes and is only found in animal cells. Appear during cell division and help cells divide by pulling chromosomes apart.
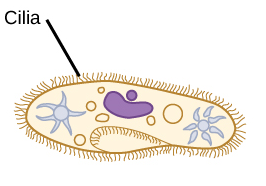
Cilia
Short and numerous and move fluid across cells surface
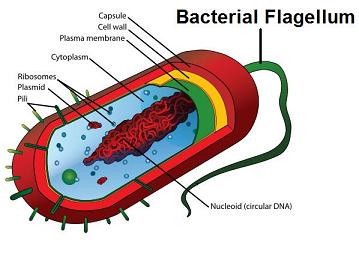
Flagella
Longer and Fewer and moves entire cell through extra cellular fluid
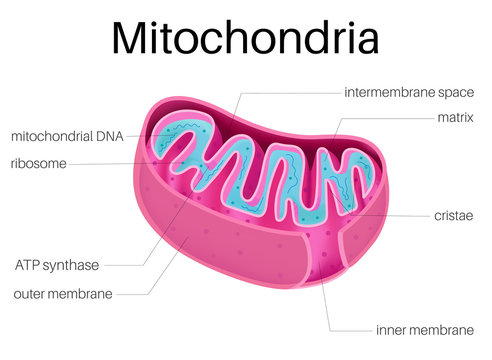
Mitochondria
Break down food to release ATP energy and powerhouse of the cell
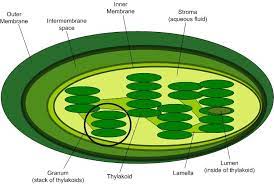
Chloroplast
Plant cells only and is where photosynthesis happens and converts energy from sun to energy in sugar (glucose)

Cell Wall
Plant cells only and protect and maintain the shape of the plant cell and is made of cellulose in plants
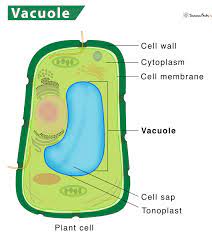
Central Vacuole
Plant cells only and is a large storage center
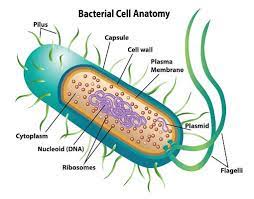
Prokaryotic
Bacteria and Archea cells and don’t have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles

Eukaryotic
Animals, Plants, Fungi, and protists cells and have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
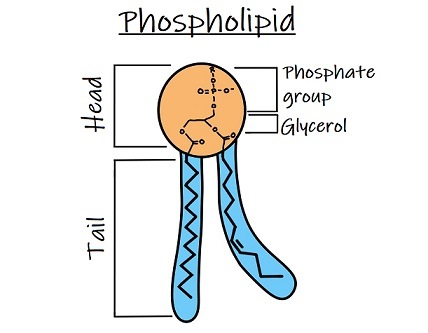
Lipids for Phospholipids
There are two layers of fats that make up the phospholipid bilayer. The fats are phospholipids. The phospholipids have hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
Proteins for Phospholipids
Proteins are embedded for transportation.
Carbohydrates for Phospholipids
Carbohydrates are embedded for structure. Phospholipids have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails. (2 fatty acids+1 phosphate) When they are put together in water the heads face the water and the tails face each other on the inside of the heads. This makes the membrane selectively permeable.
Why Ribosomes are essential
Ribosomes make proteins in a process called translation. Ribosomes on the rough ER make proteins to export out of the cell. Ribosomes floating within the cytoplasm make proteins to use within the cell.
Proteins don't have a main function, because they pretty much just run your body. Proteins help make up enzymes, hormones, bones muscles, and antibodies. They also aid in transportation, movement, receptors, and are also an energy source. Without proteins, we wouldn't be able to survive, and ribosomes make proteins.
There are many other organelles that support the ribosome because their mission is so important. The nucleolus makes rRNA, which makes up ribosomes. The Golgi apparatus gets vesicles of proteins from the ER (which contains ribosomes) to process, sort, and ship the proteins to where they are needed. The rough endoplasmic reticulum and the cytoplasm houses the ribosomes.
Unicellular
Consisting of a single cell
Multicellular
composed of many cells that may organize into tissues-organs-organ systems