Nucleic Acids - chemistry
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the primary functions and the location of DNA and RNA?
DNA’s main function is to store genetic information and acts as the blueprint for life
DNA is found in the nucleus
RNA’s main function is to transfer the information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis
RNA is found within all parts of the cell
What are the structural composition of a nucleotide and nucleoside?
Nucleoside has a nitrogen-containing base (a purine and pyrimidine molecule) and a five carbon sugar that is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA that is linked together by a glycosidic bond
Nucleotide has a nitrogen-containing base (a purine and pyrimidine molecule) and a five carbon sugar that is deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA with an additional phosphate group that is covalently attached to the 5’ carbon of the sugar
What is the classification of the heterocyclic bases found in nucleic acids as either pyrimidine or purine?
Purine - adenine and guanine
Pyrimidines - cytosine, thymine, and uracil
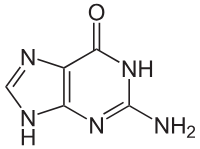
What kind of molecule is this? It is purine or pyrimidine
Guanine
purine
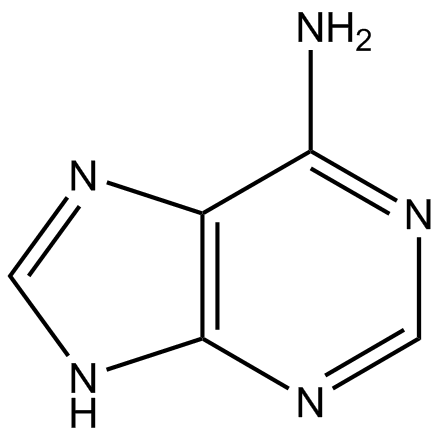
What kind of molecule is this? It is purine or pyrimidine
Adenine
purine
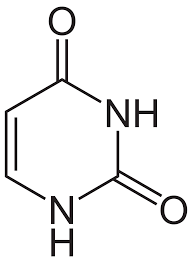
What kind of molecule is this? It is purine or pyrimidine
Uracil
pyrimidine
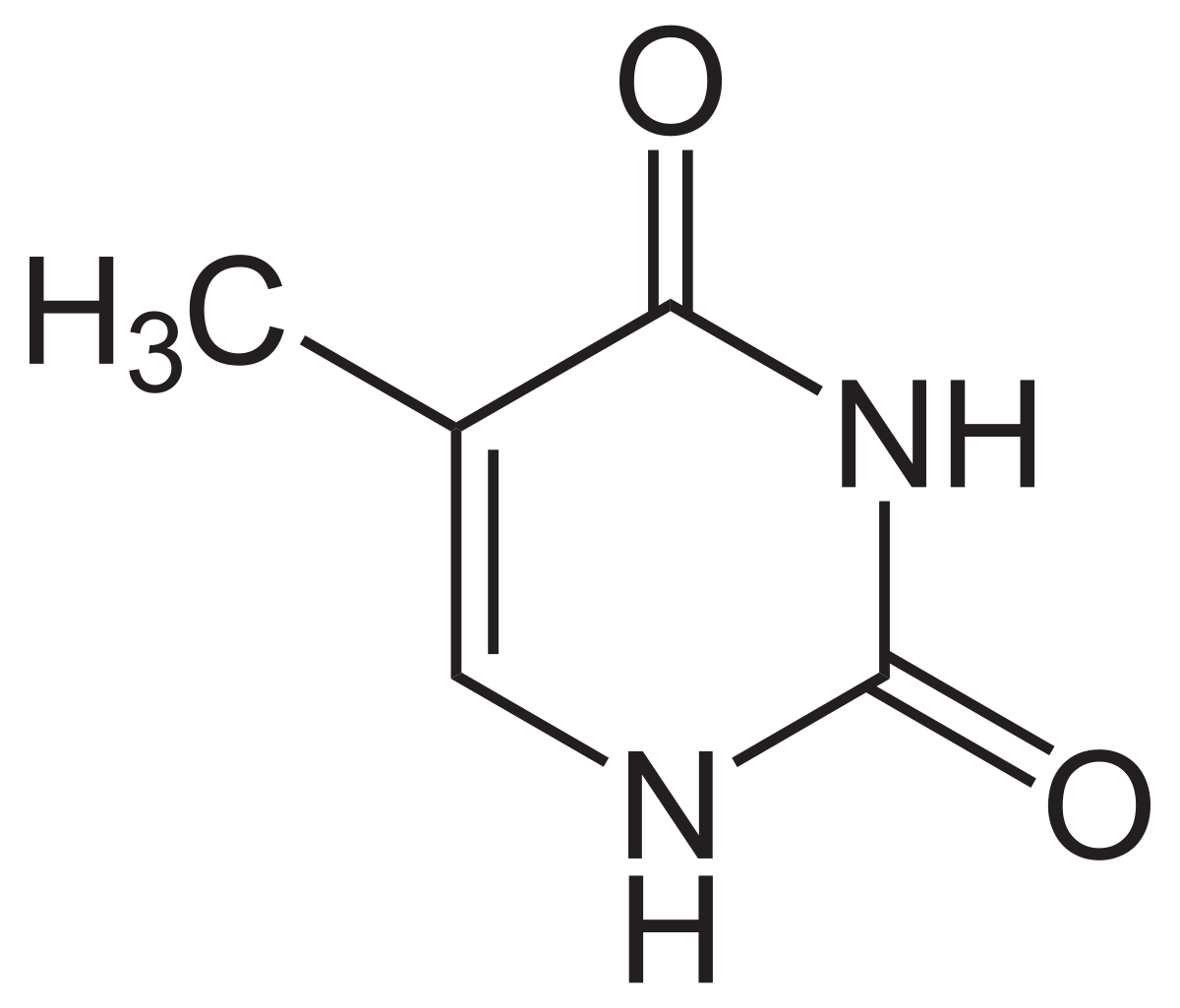
What kind of molecule is this? It is purine or pyrimidine
Thymine
pyrimidine
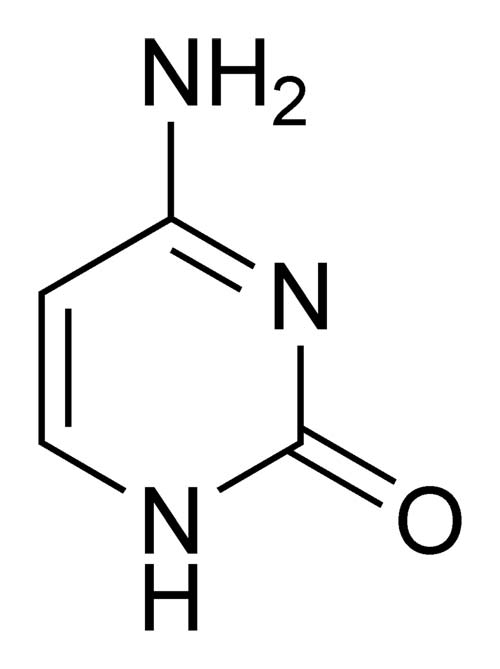
What kind of molecule is this? It is purine or pyrimidine
Cytosine
pyrimidine
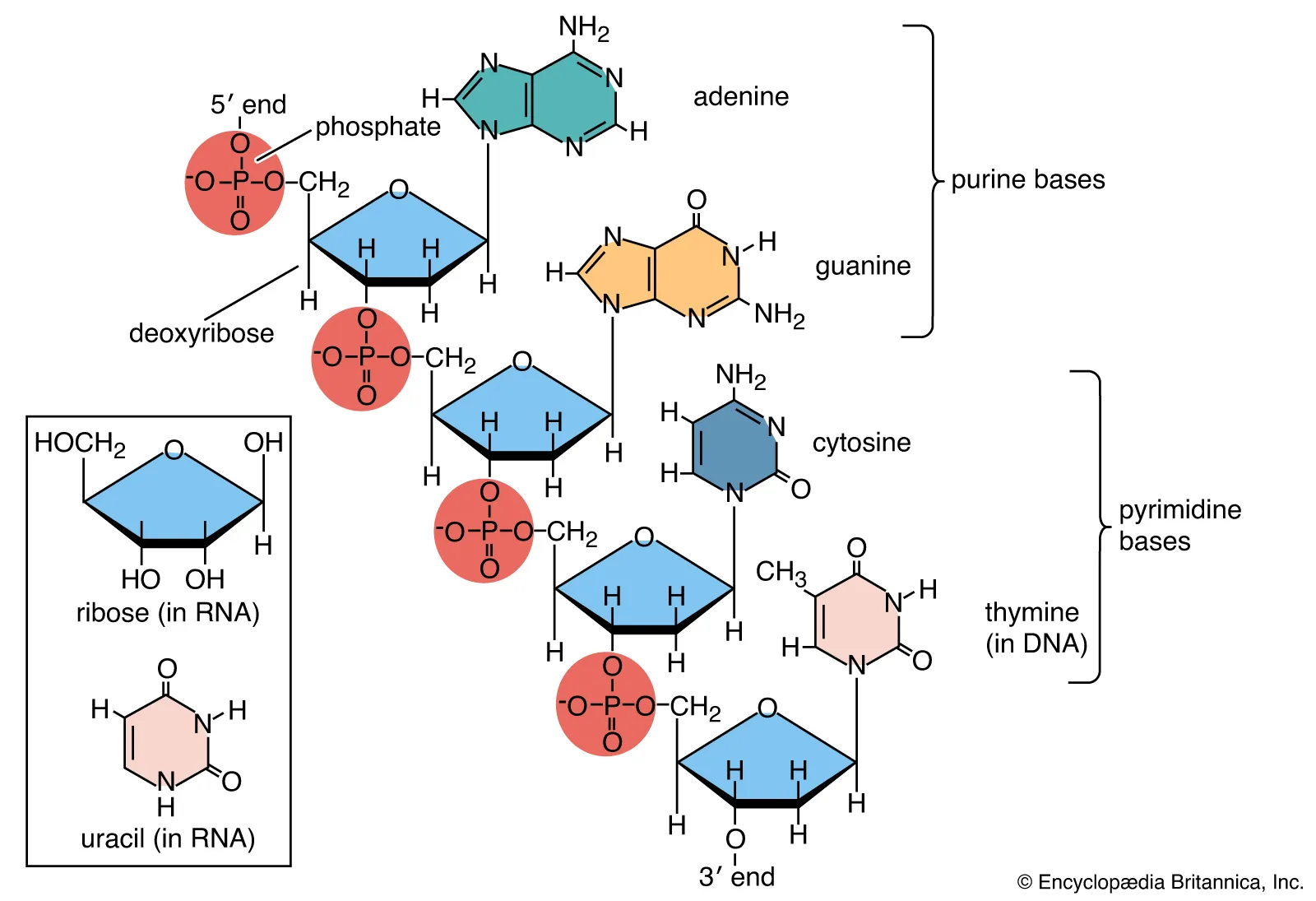
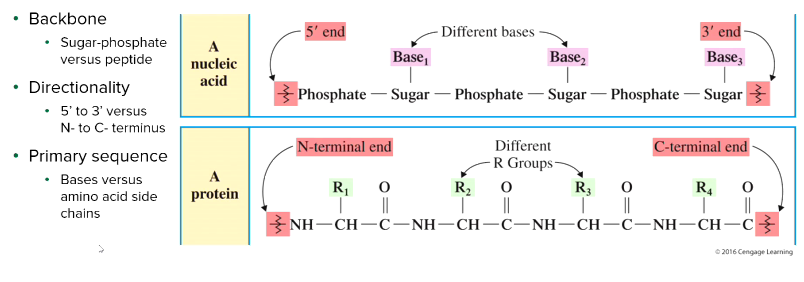
What is the primary nucleic acid structure of DNA?
the order in which the bases are stacked together
Made up of a deoxyribose sugar and a phosphate backbone
Has nitrogen-containing bases that are connected via hydrogen bonds
Contains guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine
Read from the beginning of carbon 5 to the end of carbon 3
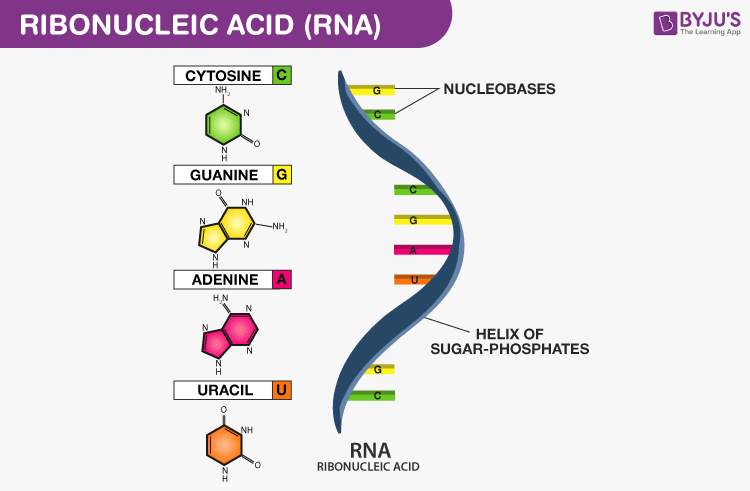
What is the primary nucleic acid structure of RNA?
The way bases are stacked together
Linked together via phosphodiester bonds
Has a sugar (ribose) phosphate backbone
Includes guanine, cytosine, or uracil
Read from the beginning of carbon 5 to the end of carbon 3
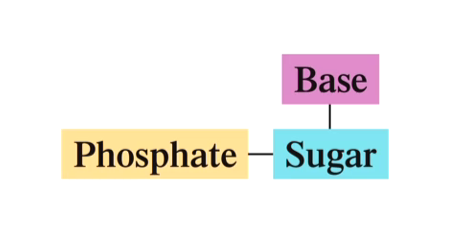
Define nucleic acid.
Unbranched polymers made up of nucleotide monomers
What is a nucleotide?
A molecule with three subunits: sugar that is bonded to both a phosphate group and a heterocyclic base
What base is found in ONLY DNA?
Thymine
What base is found in ONLY RNA?
Uracil
What bases are found in BOTH RNA and DNA?
adenine
cytosine
guanine
What are nucleosides?
A molecule that only has a sugar and a base that are bonded together
The base is always attached to carbon 1 on the sugar
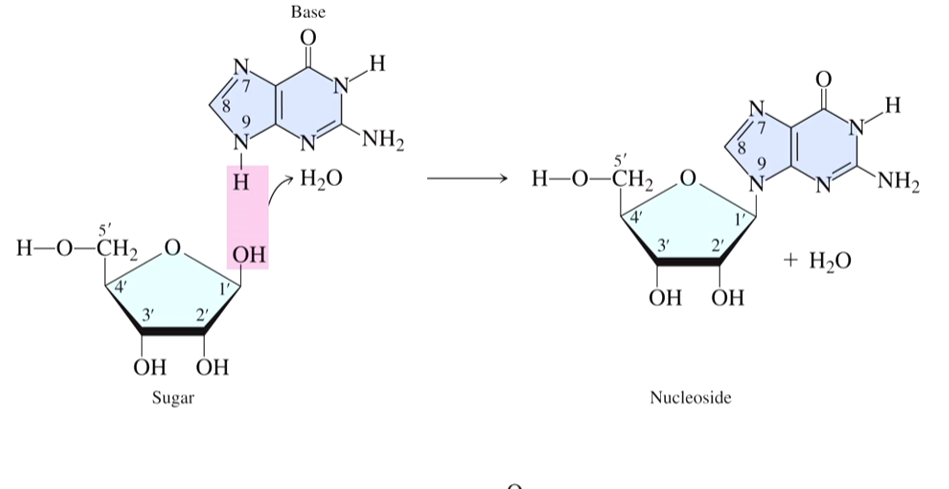
How are nucleotides formed?
Nucleoside reacts with the phosphate group
The base is always attached to the carbon 5 on the sugar
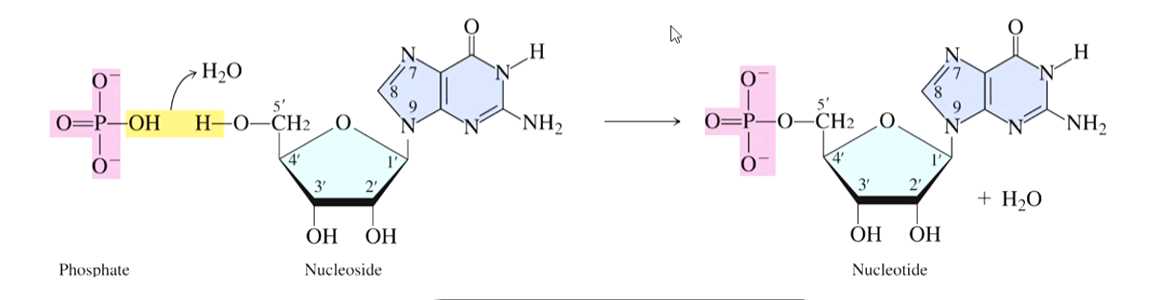
What are the bonds of the sugar molecules called?
Phosphodiester bonds
What is the importance of the negative charge on the phosphate group?
It gives the nucleic acids its acidic property
How do we read the sequence of DNA and RNA?
Read sequence from the 5' carbon end to the 3' carbon end.
List the forces that stabilize DNA.
hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
base stacking interactions (including van der Waals forces)
hydrophobic interactions
electrostatic interactions with the surrounding solvent
Identify a complementary DNA sequence for a given sequence
double helix that contains two DNA strands that around each other
Describe the steps involved in DNA replication
1.) Separation of the template strand is achieved through the DNA helicase that unzips the DNA
2.) Nucleotides are added to the template strands that are held together by hydrogen bonds
3.) creation of a continuous strand that is made by DNA polymerase, which can only work from 5’ to 3'. It leads to a strand that can grow continuously, and the lagging strand grows in segments
4.) Okazaki fragments are joined together by DNA ligase
Match the enzymes involved in DNA replication to their function.
DNA helicase - unwinds the DNA strand
DNA polymerase - causes the continuous growth of the DNA strand
DNA ligase - binds Okazaki fragments together
What are the possible pairs of complementary bases, and how many hydrogen bonds do they form?
Adenine and thymine w/ creates 2 hydrogen bonds
cytosine and guanine w/ creates 3 hydrogen bonds
True or false: complementary bases are found in equal amounts of DNA.
True
What is base stacking in DNA?
Helps stabilize the double helix that lies in the same plane
can interact with the base above and below it by Van der Waals forces (a type of London dispersions forces)
What is the secondary structure of RNA?
Single strand molecule that is normally shorter than DNA
contains adenine, guanine,, cytosine, and uracil
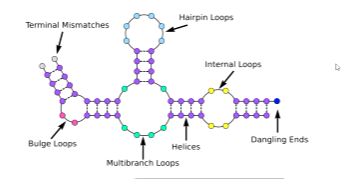
What are Okazaki fragments?
Fragments that are created through the lagging of the continuous growth of s strand