GENETICS FINAL
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Which of the following events occurs during meiosis but not mitosis?
A) Segregation of sister chromatids
B) Pairing of homologous chromosomes
C) Replication of the DNA strand
D) Alignment of chromosomes on the metaphase plate
E) none of the abov
B
In humans and other mammals, males and females generally have the same level
of expression of X-linked genes. This is because...
A) in females, one X chromosome is inactivated in every somatic cell.
B) in males, the one X chromosome is hyperactivated in every somatic cell.
C) in males, one X chromosome is inactivated in every somatic cell.
D) none of the abov
A
which of the following elements are not transcribed:
A) coding region
B) exon of gene
C) ribosome binding site
D) intron
E) promoter
E
A eukaryotic chromosome is composed of:
A) one long DNA double helix packaged into units called the polysome
B) one long DNA double helix packaged into units called the nucleosome
C) two long DNA double helix molecules that meet at the centromere
D) one long RNA molecule
E) none of the above
B
The enzyme that replicates the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes is known as
A) RNA polymerase
B) Telomerase
C) Reverse transcriptase
D) Ribosome
B
f a trait is controlled by two codominant alleles of one gene, what phenotypic ratio
is expected in the offspring of a mating of two heterozygotes?
A) 2:1
B) 3:1
C) 1:2:1
D) 1:1
E) 4:1
C
Mitosis results in ________ chromosome number, whereas meiosis results in
________ chromosome number.
A) a doubling of; no change in
B) no change in; no change in
C) a reduction by half in; no change in
D) no change in; a doubling of
E) no change in; a reduction by half in
E
Which type of chromosomal rearrangement is most likely to result in lethality?
A) inversion
B) duplication
C) deletion
D) translocation
C
Nonsense suppressors result from mutations in...
A) a gene with a deletion in three consecutive base pairs
B) the anti-codon loop of a tRNA gene
C) the start codon of a transcribed gene
D) the intron region of a transcribed gene
E) None of the abo
B
Sickle cell anemia is a recessive trait in humans. In a cross between a father who
has sickle cell anemia and a mother who is heterozygous for the sickle cell allele, what is the
probability that all of their first three children will be unaffected?
A) 1/4
B) 1/2
C) none
D) 1/8
E) 1/16
D
Suppose that in plants, smooth seeds (S) is dominant to wrinkled seeds (s), and
tall plants (T) is dominant to short plants (t). Homozygous plants that were tall/smooth and
short/wrinkled were crossed. The resulting F1 progeny were crossed to short/wrinkled plant.
What proportion of the F2 progeny is homozygous for short and wrinkled alleles?
A) 1/2
B) 1/4
C) 1/8
D) 1/16
E) 0
B
In four o’clock plants, the allele for red flowers is incompletely dominant over the
allele for white flowers so that the heterozygotes are pink. What percentage of flower colors
would you expect among the offspring if pink flowers are crossed to red flowers?
A) 100% pink
B) 25% pink, 75% red
C) 50% pink, 50% red
D) 75% pink, 25% red
C
In the common daisy, genes A and B control flower color. Both genes have a
dominant allele (A or B) and a recessive allele (a or b). At least one copy of each dominant
allele is required for flowers to be colorful instead of white. Predict the genotype and
phenotype of the progeny of a cross between two white-flowered plants, one homozygous for
the recessive allele of A and the other homozygous for the recessive allele of B.
A) A/A; b/b, white
B) a/a; B/B, white
C) A/a; B/b, colorful
D) A/a; B/b, white
E) a/a; b/b, colorful
C
f the template DNA strand has a sequence 5’-TTACCCGGGCAT-3’ then the
RNA transcript would have the following sequence:
A) 5’- TTACCCGGGCAT -3’
B) 5’-AUGCCCGGGUAA -3’
C) 5’-ATGCCCGGGTAA-3’
D) 5’-UUACCCGGGCAU-3’
E) none of the above
B
An E. Coli strain possesses the following genotype: F(O^c )/I+ P+ O+ Z+ Y+
O^c is a mutation in the operator that prevents repressor binding. The structural genes (Lac Z
and Lac Y)...
A) will be transcribed both in the presence and absence of lactose
B) will not be transcribed under any conditions
C) will be transcribed only if lactose is present
D) will be transcribed only if lactose is absent
E) will be transcribed but not translated
C
An E. Coli strain possesses the following genotypes: F(O+ )/Is P+ Oc Z+ Y+
Is is a mutation in the repressor that eliminates lactose binding and Oc prevents repressor
binding. The structural genes (Lac Z and Lac Y)...
A) will be transcribed both in the presence and absence of lactose
B) will not be transcribed under any conditions
C) will be transcribed only when lactose is present
D) will be transcribed only when lactose is absent
E) will be transcribed but not translated
A
An E. Coli strain possesses the following genotype: F(I- P- O+ Z+ Y+ )/I+ P- O+ Z+ Y+
I- eliminates the ability of the repressor to bind the operator and P- eliminates the ability of RNA
polymerase to bind the promoter. The structural genes (Lac Z and Lac Y)...
A) Will not be transcribed under any conditions
B) Will be transcribed both in the presence and absence of lactose
C)Will be transcribed only if lactose is present
D)Will be transcribed only if lactose is absent
E) will be transcribed but not translated
A
A researcher identifies a recessive mutation in rats he calls "zigzag" that causes
the development of a bent tail in rats. A second recessive mutation is identified by another
researcher that she calls "crooked" that also causes a bent tail in rats. A true-
breeding "zigzag" rat is crossed with a true breeding "crooked" rat. All their progeny have bent
tails. This indicates that...
A) the "zigzag" and "crooked" mutations are complementary.
B) the "zigzag" and "crooked" mutations are not complementary.
C) the "zigzag" and "crooked" mutations are alleles of the same gene.
D) A and C
E) B and C
E
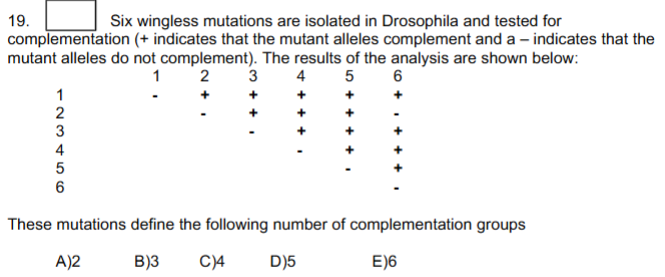
B and
D
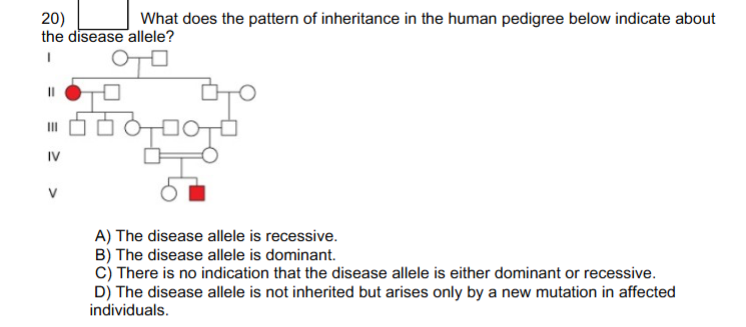
A
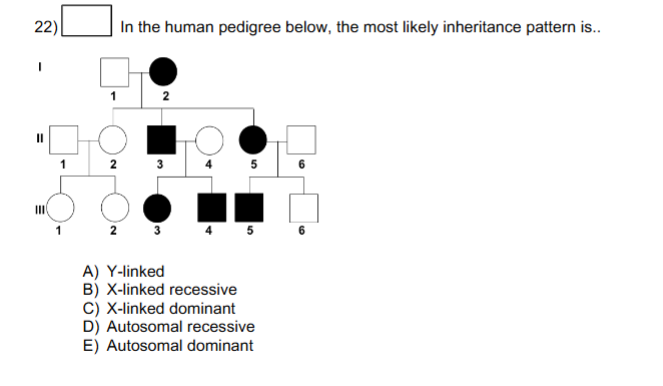
E
The yellow mutation is an X-linked recessive mutation in Drosophila, causing
yellow body color. A yellow-bodied female is crossed to a male with wild type body color. Male
progeny from this cross..
A) all will be yellow body color.
B) all will be normal body color.
C) 1/2 will be yellow body color.
D) 1/4 will be yellow body color
A