physics - forces & their effects (9.1 - 9.10)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
9.1 why do some objects interact at distance without contact?
some forces act at distance with no contact due to a field
force field
space around an object where it can affect other objects
9.1 how objects interact - at distance without contact: gravitational fields
gravity occurs between 2 objects with mass
moon & earth affect each other - moon in earth’s gravitational field & vice versa
9.1 how objects interact - at distance without contact: electrostatic fields
object charged with static electricity has electric/electrostatic field around it - affects objects in it
2 close same charge objects produce pair of forces - same size, act in opposite directions
9.1 how objects interact - at distance without contact: magnetic fields
magnetic field = space around magnet where it affects other materials
magnet attracts objects made from magnetic materials
magnet can attract/repel another magnet
9.1 why do some objects interact by contact?
objects touching = contact forces between them
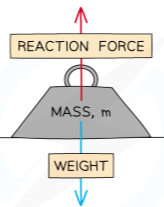
9.1 how objects interact - by contact: normal contact force
e.g. standing on floor:
upwards force from floor on you = normal contact force
9.1 how objects interact - by contact: friction
e.g. boat on water:
needs engine to keep moving - water resistance (form of friction) slows it down
force from engine & water resistance = contact forces
9.1 how objects interact - producing pairs of forces
e.g. gravitational forces between 2 objects with mass:
can be represented as vectors (arrows showing direction & magnitude)
these 2 forces = action-reaction forces
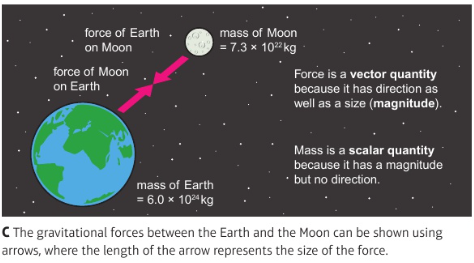
action-reaction forces
pairs of forces acting on diff. objects in opposite directions
9.2 vector vs scalar quantities
vector: magnitude & direction - e.g. weight, displacement
scalar: magnitude - e.g. mass, distance
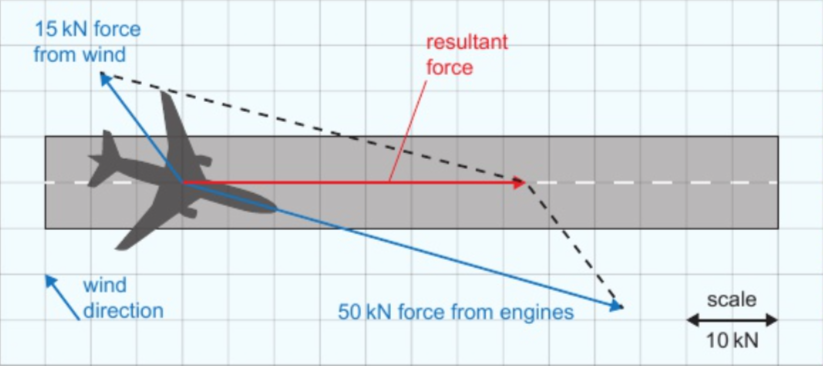
9.3 vector diagrams - finding resultant force
draw force arrows to scale at correct angles
draw lines to make parallelogram
resultant force = diagonal of parallelogram - measure arrow to find size of resultant force
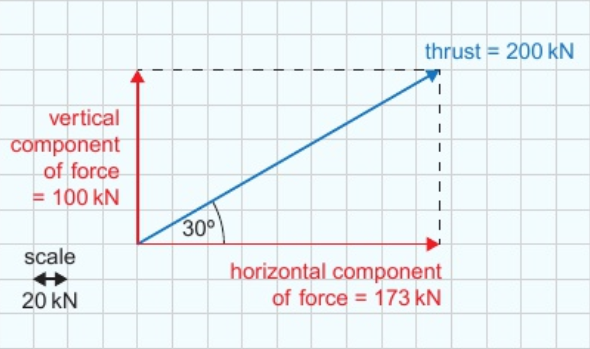
9.3 vector diagrams - resolving forces
draw force arrow to scale at correct angle
draw rectangle with sides in directions needed (e.g. horizontal & vertical)
sides of rectangle = resolved forces - measure arrows to find size of forces
9.4 free body force diagrams
direction of arrow = direction of force
length of arrow = size of force
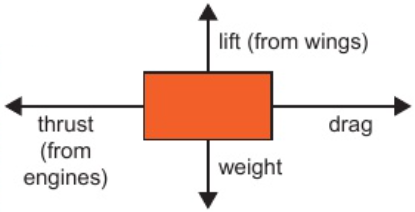
9.5 forces acting on isolated solid object/system
several forces lead to resultant force on object
9.5 balanced forces
forces equal in size & opposite in direction:
resultant force = 0
forces on object balanced
moment definition
turning force
what does moment of force depend on?
size of force
where force applied
9.6 situations where forces can cause rotation
e.g. pivot:
fixed point object rotates around
9.7 moment of a force equation
moment of a force (N m) = force (N) x distance normal to direction of force (m)
M = fd
9.8 principle of moments - rotational forces in equilibrium
sum of clockwise moments = sum of anti-clockwise moments
9.9 how do levers transmit rotational effects of forces?
bar that pivots about a point
transfers force
9.9 how do gears transmit rotational effects of forces?
rotation passed from one gear → next by interlocking teeth
9.10 ways of reducing unwanted energy transfer - lubrication
reduces friction between moving parts - less heat lost