How is Inheritance explained?
1/27
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosome pairs in a cell which carry the same genes at the same gene loci, however the alleles may differ.
Nucleic acid monomer (draw a diagram)
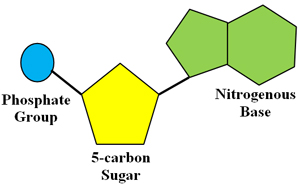
Gene
A section of DNA that codes for protein
Chromosomes
A molecule of DNA, coiled and recoiled around histones.
Genome
The complete set of DNA contained within the haploid set of an organism’s chromosomes
Karyotype
A photograph of a person’s chromosomes lined up in order of size
Alleles
Different forms of the same gene
Genotype
The combination of alleles at a given gene locus
Phenotype
the physical expression of a trait, based on that genotype and environmental influences
Chiasma
A point at which chromosomes cross over
Dominant
The dominant trait will be expressed in the organism if the allele is present
Recessive
A trait will only be expressed when two copies of the allele for this trait are present
Heterozygous
An organism with 2 different alleles (eg. Aa)
Homozygous
An organism with 2 copies of the same allele (eg. AA or aa)
Gregor Mendel
An Austrian monk who bred many pea plants and studied their traits
Punnett square
A grid used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of two parents’ offspring.
Incomplete Dominance
Occurs when neither trait is completely dominant over the other. The heterozygote will have an intermediate phenotype.
Codominance
Occurs when both traits are dominant. The heterozygote will display both traits as both alleles are expressed.
Test Crosses
A test performed to deduce the genotype of an organism that displays the dominant phenotype. This is done by crossing the ‘unknown’ genotype organism with an organism with a known phenotype and looking at the phenotypes in the offspring.
Linked Genes
Tend to be inherited together. Reduces the genetic variation in the offspring.
Recombination
Exchange of alleles between homologous chromosomes due to crossing over. Increases genetic variation in the offspring.
Epigenetics
The study of changes in organisms caused by modifying gene expression. Determined by DNA packaging.
DNA methylation
Addition of a methyl group (CH3) to a cytosine (C) nucleotide.
Histone Acetylation
Addition of acetyl groups to histone proteins.
X Inactivation in female (mammals)
In each somatic cell, one of the X chromosomes is randomly inactivated and condenses into a barr-body.
Monohybrid cross
A cross between two organisms which are heterozygous in respect to one specific gene.
Epigenetic factors
Biological mechanisms that can modify gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequence.
Structure of DNA
A double helix made up of many repeating nucleotides.