chemistry - grade 9
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
1
New cards
particle theory of matter
1. all matter is made up of particles
2. all particles have a little space between them
3. all particles in a substance are identical
4. all particles are in constant motion
5. all particles in the same substance are attracted to each other
2
New cards
4 factors that effect the state of matter
1. energy
2. speed
3. distance
4. attraction
3
New cards
chemistry
the study of matter and the changes it undergoes
4
New cards
pure substance
1 type of particle combined by chemical means
5
New cards
diatomic element
2 of the same atom
6
New cards
what are the diatomic elements?
H, O, F, Br, I, N, Cl
7
New cards
simple element
1 atom
8
New cards
compound
2 or more different atoms that are chemically combined
9
New cards
molecule
a compound/substance with only 1 type of atom
10
New cards
mixture
2 or more particles combined by physical means
11
New cards
homogenous
1 visible phase
12
New cards
solution
when a solute is dissolved in a solvent
13
New cards
alloy
metals melted together
14
New cards
heterogenous
2 visible phases
15
New cards
mechanical mixture
all parts are visible and can be separated
16
New cards
suspension mixture
particles suspended in a gas or liquid
17
New cards
chemical property
characteristic of a substance that happens during a reaction
18
New cards
physical property
described or measurable characteristic of matter
19
New cards
qualitative properties
luster, clarity, brittleness, ductility, viscosity, hardness, malleability
20
New cards
quantitative properties
density, boiling point, freezing point, melting point
21
New cards
density formulae
D=M/V
V=M/D
M=V x D
V=M/D
M=V x D
22
New cards
what is an element?
a name for a type of atom
23
New cards
what do elements contain?
protons (+) electrons (-) neutrons (neutral)
24
New cards
metals
ductile, malleble, lusterous, conductive
25
New cards
non-metals
not conductive
26
New cards
metalloids
found on the staircase and have properties of both metals and non-metals
27
New cards
atomic number
number of protons
28
New cards
atomic mass
mass of protons + neutrons
29
New cards

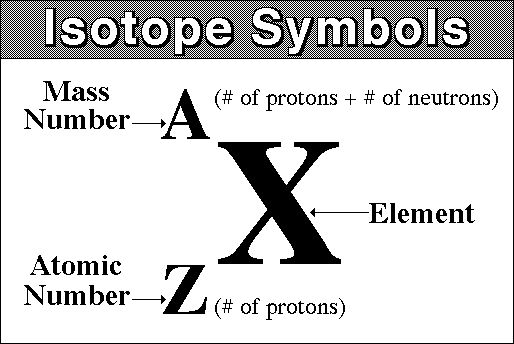
read this standard atomic notation
atomic mass: 9 amu
atomic number: 4
atomic number: 4
30
New cards
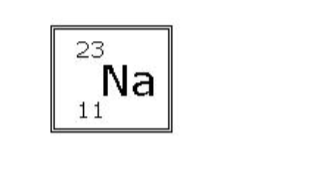
read this standard atomic notation
atomic mass: 23 amu
atomic number: 11
atomic number: 11
31
New cards
isotopes
* type of element
* same number of proton
* different number of neutrons/mass
* same number of proton
* different number of neutrons/mass
32
New cards
carbon dating
looking at the ratio of C-12 to C-14 in a substance to see how many thousands of years an organism has been dead
33
New cards
where does C-14 come from?
Nitrogen. It also takes 5,730 for half of it to turn back into Nitrogen
34
New cards
period number tells us what?
the number of orbitals
35
New cards
group number tells us what?
the number of valence electrons
36
New cards
group 1
* alkali metals
* lustrous, silvery, soft, highly reactive
* lustrous, silvery, soft, highly reactive
37
New cards
group 2
* alkaline earth metals
* burn bright colorful flames
* lustrous, silvery
* not as soft of reactive as group 1
* burn bright colorful flames
* lustrous, silvery
* not as soft of reactive as group 1
38
New cards
group 3-12
* transition metals
* different states of matter
* conductive
* high melting and boiling points
* different states of matter
* conductive
* high melting and boiling points
39
New cards
group 17
* halogens
* highly reactive
* different states of matter
* poisonous in large amounts
* highly reactive
* different states of matter
* poisonous in large amounts
40
New cards
group 18
* noble gases
* colorless, odorless, tasteless
* stable
* glow brightly when electricity passes through
* colorless, odorless, tasteless
* stable
* glow brightly when electricity passes through
41
New cards
why is hydrogen on the metal side if its not a metal?
it shares similar properties like 1 valence electron and reactivity
42
New cards
Democritus
came up with the idea of small indivible particles called atoms
43
New cards
Aristotle
rejected the idea of atoms, thought everything is elemental
44
New cards
Dalton
billiard ball model, all atoms of a specific are the same
45
New cards
Thomson
chocolate chip cookie model, electrons being evenly disturbed inside positive space
46
New cards
Rutherford
discovered protons + nucleus, predicted the discovery of neutrons. Together these subatomic particles make up the mass of atoms. Also stated that electrons surrounded the nucleus in a cloud
47
New cards
Bohr
said electrons orbit nucleus in shells like planets (bohr-rutherford planetary model)
48
New cards
Chadwick
discovered neutral subatomic particles called neutrons. Said that neutrons and protons make up the mass of atoms
49
New cards
law
a universally accepted fact, the foundation of science
50
New cards
hypothesis
an educated guess, can be disproven or proven with just one experiment
51
New cards
theory
explanation for a set of observations, based upon verified hypothesis. NOT a fact
52
New cards
physical change
change in state/arraignment, no new substance formed (ex: freezing)
53
New cards
chemical change
2 substances react to form new subsance
54
New cards
5 evidence of chemical change
* new color
* new odor
* precipitate (solid made from 2 liquids)
* hard to reverse
* gas formation
* new odor
* precipitate (solid made from 2 liquids)
* hard to reverse
* gas formation
55
New cards
ion
charged atom
56
New cards
cation
looses electrons to become a positively charged atom. Looses electrons if it has less than 4 electrons
57
New cards
anion
gains electrons to become a negatively charged atom. gains electrons if it has more than 4 electrons
58
New cards
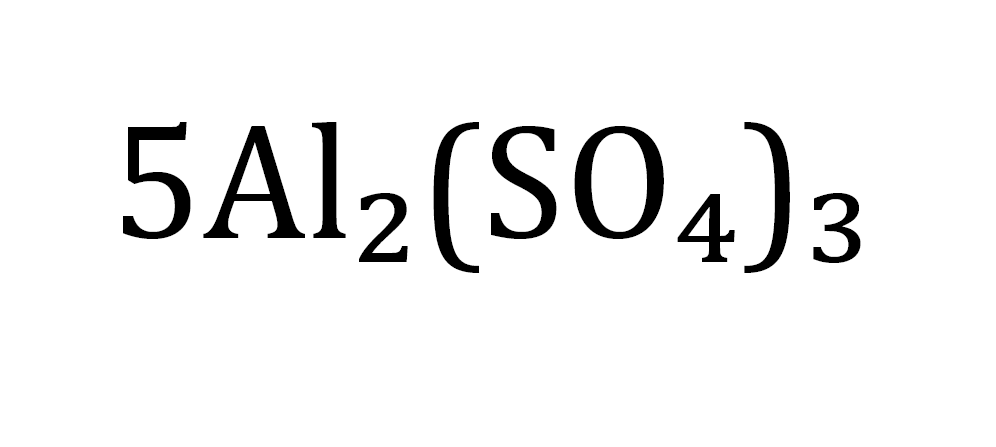
count this atom
5 molecules
10 Al
15 S
60 0
10 Al
15 S
60 0
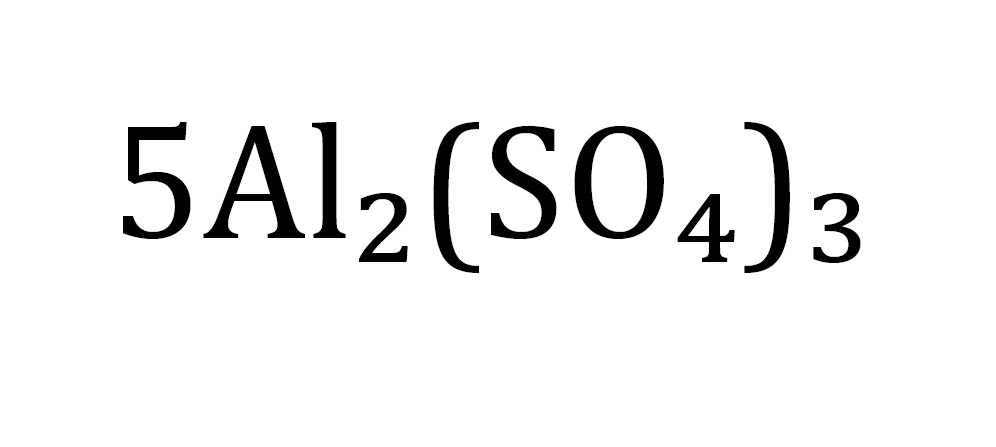
59
New cards
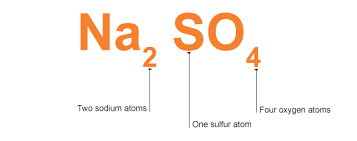
count this atom:
Na2SO4
Na2SO4
2 Na
1 S
4 O
1 S
4 O