BIOC 302 - Ketone Bodies
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
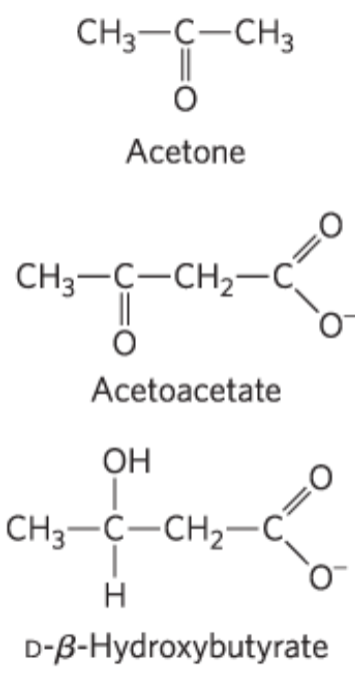
what are the ketone bodies
acetone
acetoacetate
D-beta-hydroxybutyrate
which ketone body is exhaled?
acetone
what happens to acetoacetate and D-beta-hydroxybutyrate?
transported to extrahepatic tissues and converted to acetyl-CoA to be oxidized in the TCA cycle
which ketone form is the predominant one in the body?
D-Beta-hydroxybutyrate
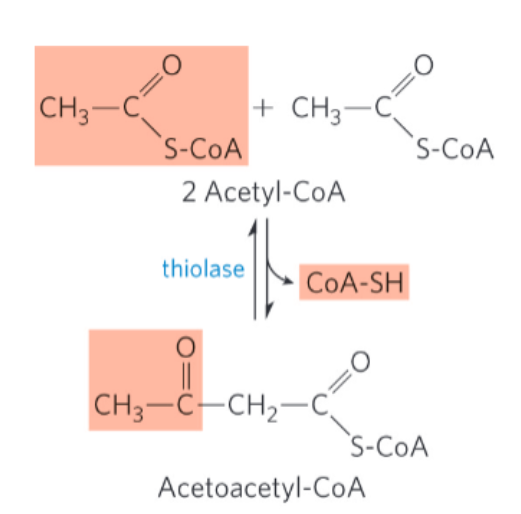
ketone synthesis: step 1
thiolase = catalyzes the enzymatic condensation of two acetyl-CoA molecules to form acetoacetyl-CoA
reversal of the last step of β oxidation
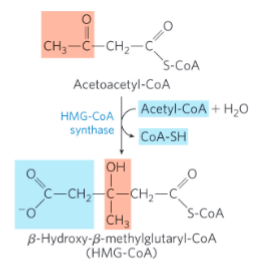
Ketone body synthesis: step 2
HMG-CoA synthase = catalyzes the condensation of acetoacetyl- CoA with acetyl-CoA to form β- hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA)
Ketone body synthesis: step 3
HMG-CoA lyase = catalyzes the cleavage of HMG-CoA to free acetoacetate and acetyl-CoA
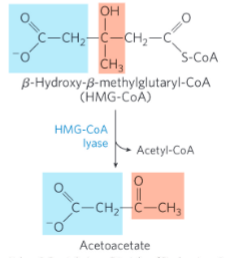
Ketone body synthesis: step 4
acetoacetate decarboxylase = catalyzes the decarboxylation of acetoacetate to acetone OR
D-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase = catalyzes the reversible reduction of acetoacetate to D-β-hydroxybutyrate
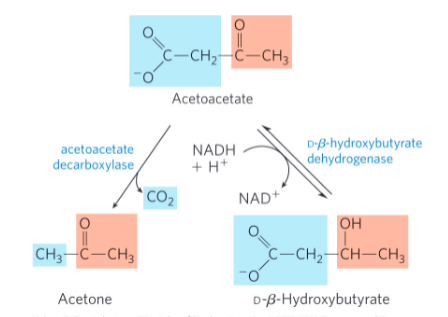
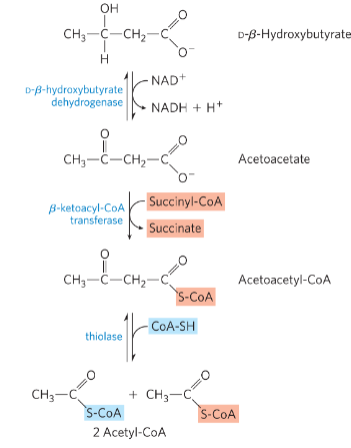
explain + draw the 3 steps of D-beta-hydroxybutyrate breakdown
D-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase = catalyzes the oxidation of D-β- hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate in extrahepatic tissue
β-ketoacyl-CoA transferase = catalyzes the activation of acetoacetate
acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle