Comp Sci
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Abacus (2500 BCE)
It was invented in 2500 BCE in Mesopotamia and is the oldest recognized computing device. It was a hand-operated calculator that efficiently added and subtracted large numbers.
Analytical Engine (1800s)
invented by Charles Babbage, it was the first design for a general purpose computer. It was unfortunately never completed, but it pioneered the idea of a computer that could perform multiple functions.
Ada Lovelace (1800s)
Writer of hypothetical programs for the Analytical Engine, recognizing her as the world's first programmer.
Hollerith’s Tabulating Machine (1890)
Created by Herman Hollerith for the U.S. Census, this electromechanical device used punch cards to significantly speed up data processing. It completed the census in 2.5 years, saving time and money, and eventually led to the foundation of IBM.
Computer “Bug”
On September 9th 1947, Grace Hopper was working on a Mark II Aiken calculator computer, when a moth got trapped between relay contacts. Ever since then, a computer bug is used to describe an error or glitch in a system.
vacuum tubes
used to upgrade calculation computers resulting in faster computations. The first computer to use vacuum tubes was the Colossus Mark I used by the Nazis. The Colossus Mark I is considered the first programmable electronic computer.
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) (1946)
It was made at UPenn and designed by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckhart. It was the first general purpose, programmable, and electronic computer. It is believed to have done more arithmetic than the human race in its 10 years of operation. It was made up of 17468 vacuum tubes, occupied about 1800 sqft, and weighed about 30 tons.
transistor
upgraded the vacuum tubes. It was able to switch on and off 10,000 times per second. Transistors are 50 nanometers or less in size, and are very fast and long lasting since there are no moving parts.
IBM 608 Transistor Calculator (1957)
was the first IBM product to use transistor circuits without any vacuum tubes and is believed to be the world's first all-transistorized calculator to be manufactured for the commercial market.
Mechanical Relay (1940s)
This was an electrically-controlled mechanical switch, which acted similarly to a water faucet in transporting electrons. However, it had many limitations, such as lack of speed, wear and tear, and insect attraction when used in bigger machines.
CPU
Central Processing Unit
ALU
Arithmetic Logic Unit
what are the 4 parts of the cpu
Register
ALU
Control Unit
Cache
Clock of a CPU
It regulates and synchronizes how fast operations are executed by the CPU
three main phases of operation within the CPU
Fetch - Decode - Execute
How do I know if a bit is 0 or 1?
If the bit’s value can be subtracted from the number without going negative, write 1 and subtract it. Otherwise, write 0. For example, in this picture the bit equal 48 and 48 - 128 is negative so it get a 0 but 48-32 and 16 is positive so it gets a 1
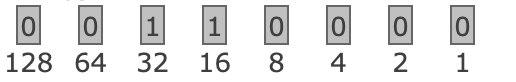
What is the ASCII Value of 0?
48
The ASCII value of a and A
a=97, A=65
Boolean Logic for XOR
XOR is TRUE if the inputs are different.
XOR is FALSE if the inputs are the same.
if they’re opposites its True but if theyre they same its false
Boolean Logic for AND
If it is 1(true) and 1(true), then the whole thing is true, but if it is 1(true) and 0(false) then the whole thing is false
If its AND they both have to be true for it to be true; and false and false is false
Boolean Logic for OR
Same rules as XOR, but TRUE AND TRUE equal true or 1 and 1 equal 1
Only 1 on them have to be true for it to be true
How to convert Binary to Decimal
Step 1:List out powers of 2 up until the number of digits given, from right to left
Step 2:Add all powers of 2 that have binary value of 1
16 8 4 2 1
1 0 0 1 1
1+2+16=19
Adding Binary Numbers
1+1=10, 1+1+1=11
How to convert decimal to binary
Start with your decimal number.
Look at the largest power of two that is not bigger than your number.
If that value fits, write a 1 and subtract it from your number.
If it doesn’t fit, write a 0 and don’t subtract anything.
Move to the next smaller power of two and repeat.
Keep going until you reach 1.
The sequence of 0s and 1s you wrote is the binary number.
Boolean Logic Shapes for AND / OR

Registers
really fast memory storing data internally for the CPU
ALU
Where all the calculation happens
Control unit
the command center that coordinates everything
Cache
small memory to store extra data to speed things up
Multiplier Logic Unit (MLU)
Where all the multiplication happens
BUS
moves data between parts of the computer so it connects CPU, RAM, storage, and devices
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Stores programs and data while the computer is running
Command (CMD)
tells the CPU what to do
head unit
The part that starts operations
Primary Memory
The volatile memory that the CPU can access directly and quickly. It includes both the RAM and ROM.
Second Memory
Non-volatile Memory that is not immediately accessible by a computer and is used for long term. It includes the Hard Drive and SSD.
Read Only Memory(ROM)
Non-volatile memory that permanently stores essential instructions and data, like firmware, needed to start a device
SSD
Fast and durable storage device that uses integrated circuits (flash memory) to store data electronically
Hard Drive
a computer's primary, non-volatile storage device.
Input Devices
Hardware used to send data, commands, or signals to a computer, translating human actions into electronic signals the machine can process, enabling user interaction. Ex: microphone and mouse
Output Devices
Hardware that converts processed digital data into a human-perceptible form. Ex: Speaker and Printer
Operating System (OS)
System software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provide common services for computer programs (other application software).
Main Tasks of an OS
Process Management
Memory Management
File Management
Device Management
Network Management
Security Management
Provide an User Interface (UI)
Process Management
Became essential with introduction of multi-processes. Manage how the CPU is used by different processes
Memory Management
It Uses Virtual Memory. Two Main Uses:
Memory protection - memory for different processes are kept protected from each other
Memory utilization - allocating and deallocating
File Management
Three main Uses:
Read/Write Files
Security (read/write/execute access)
Organization (directories/folders)
Device Management
Allow all applications not to have to worry about how to connect to different models of devices (printer, display… etc)
Control Program/Monitor (CP/M)
The dominant OS before DOS from the 70s to mid 80s
Later Control Program for Microcomputers
Lose popularity to DOS because IBM could not close a deal with CP/M and went with Microsoft instead
Many of the features in MSDOS were borrowed from CP/M
Disc Operating System(DOS)
Each computer brand had its own DOS
Microsoft DOS became the most popular DOS because IBM decided to license it
No Graphical User Interface (GUI)
Command Line Interface (CLI)
Single user and Single process
Uniplexed Information and Computing Service(UNIX)
It replaced the Multics (MULTiplexed Information and Computing Service)
Multi-users and Multi-processes (Multi-tasks)
Memory protection
Base of most modern OS (iOS and Android)
LINUX - Free UNIX like OS created by Linus Torvalds
BSD - Berkeley Software Distribution (MacOS based off this)
Microsoft Windows
Early versions of windows (pre-95) was still mostly running on DOS with a GUI
Crash often because of lack of memory protection
Becomes the most dominant OS in the world
Window NT (for New Technologies) was an enterprise version with all the new features and stability
Windows XP in the 2000s was built on NT and therefore solved most of the problems and make Windows even more popular
Mac OS
Introduced with the Macintosh in 1984
Apple, or Steve Jobs, did NOT invented the GUI. They have aligitly visited the Xerox PARC (Palo Alto Research Center) and “stole” the idea.
The first successful commercially available GUI
NOT true multitasking
MacOS became UNIX like since 2001 (When Steve Jobs returned to Apple)
non-volatile
(of a computer's memory) retaining data even if there is a break in the power supply and turns off.
Random Access Memory(RAM)
Serves as a computer's fast, short-term memory that temporarily holds data for active applications, allowing the CPU to access it quickly
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
Modern standard defining the software interface between a computer's operating system and its platform firmware (BIOS replacement), enabling faster booting, support for large drives, better security
Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
Essential firmware on your computer's motherboard that starts up hardware, runs diagnostics, and loads the operating system, but is being replaced by UEFI
Version of Windows OS from the earliest to the latest
Windows 95→Windows XP→Windows Vista→Windows 7
Multiplexed Information and Computing Service(Multics)
influential time-sharing mainframe operating system. Introduced key concepts like virtual memory, and robust security, and serving as a direct inspiration for the development of Unix.