W4L5: Electrophilic addition reactions: tricks
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Carbocation rearrangements
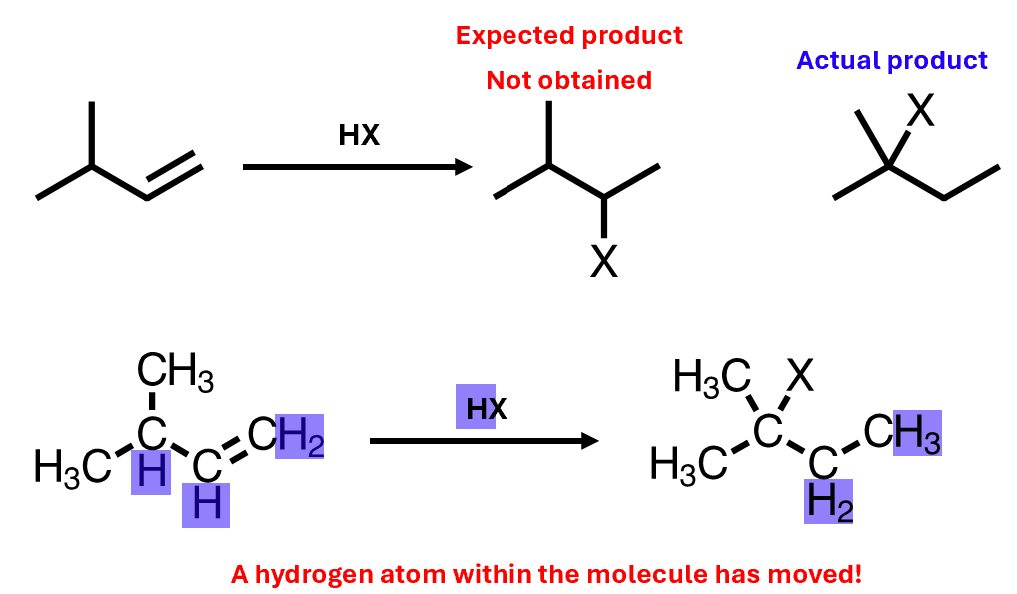
Carbocation rearrangements can lead to initially unexpected products
Hydrogen atom within the molecule has moved
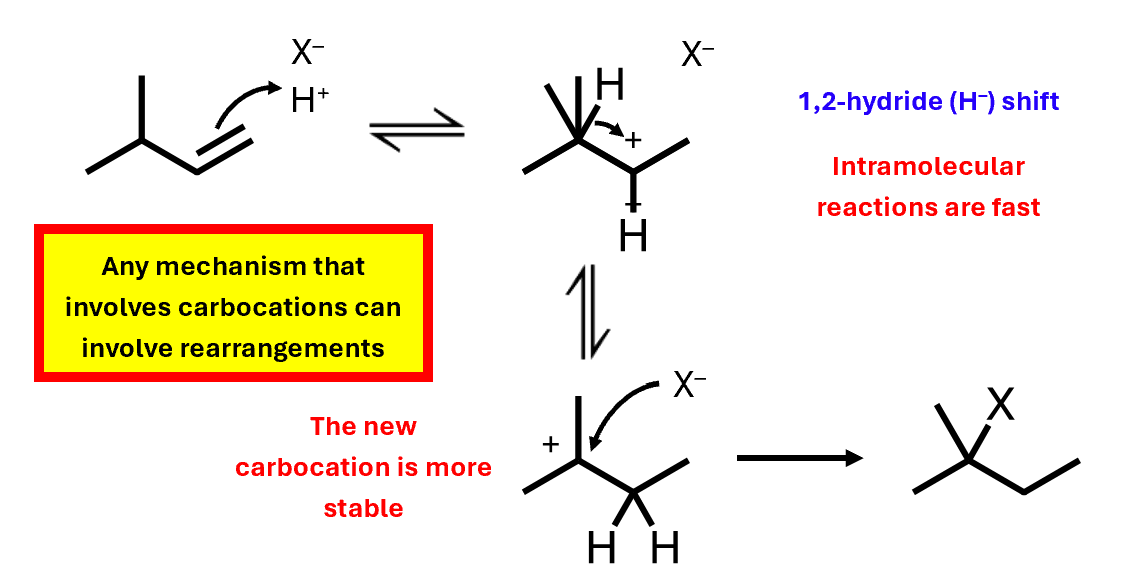
Carbocation rearrangement increasing stability
Rearrangement occurs when it can increase the carbocation stability
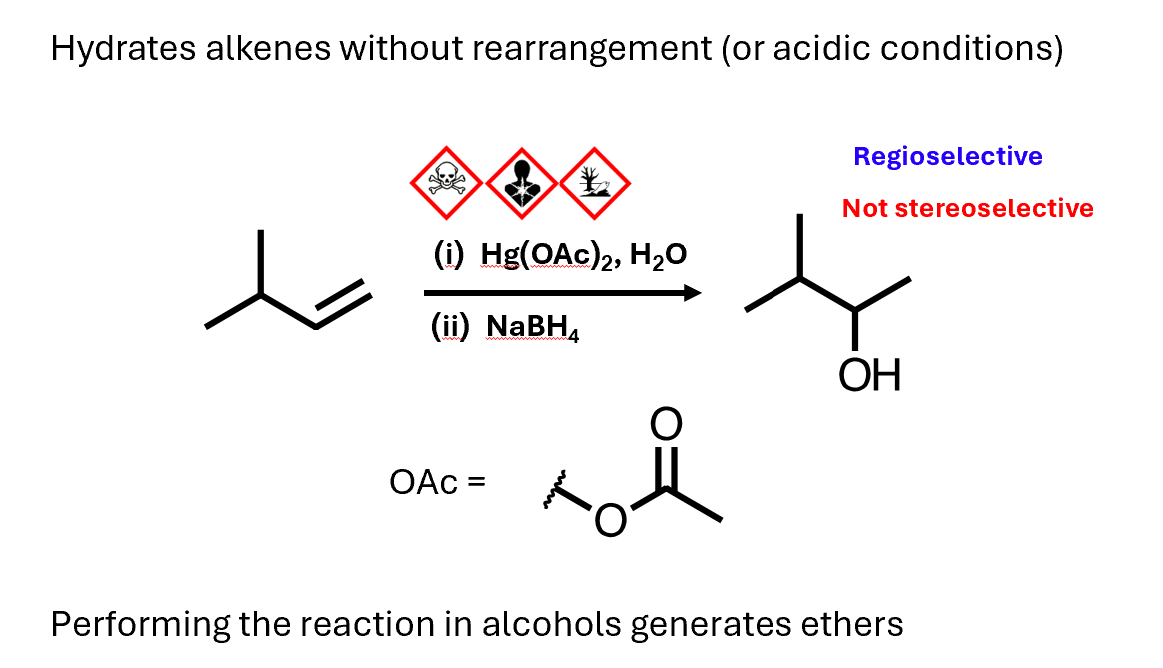
Oxymercuration-reduction
Hydrated alkenes without rearrangement (or acidic conditions)
Uses mercury acetate and water to install the alcohol, followed by reduction with sodium borohydride to remove the mercury
It's regioselective installing the oxygen on the more substituted position of the double bond
Like the normal hydration reaction, though, it's not stereoselective as the oxygen can add from either side of the double bond
You can also use it to make ethers, if you use an alcohol as the solvent instead of water
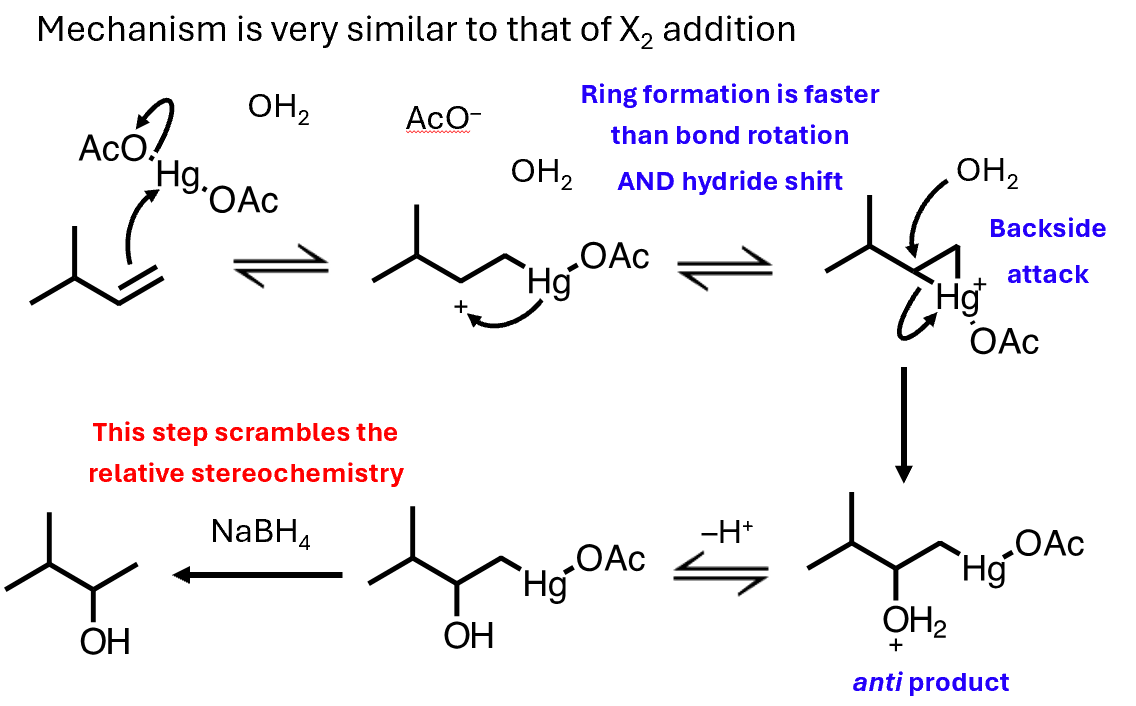
Oxymercuration-reduction mechanism
The first step (oxymercuration) is stereospecific (anti) and regioselective (Markovnikov) due to the mercurinium ion intermediate.
The second step (demercuration) destroys stereochemistry, so the final alcohol is not stereospecific, even though the mechanism initially was.
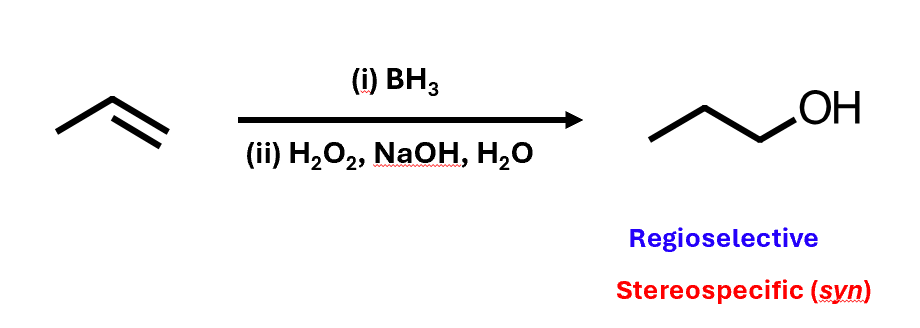
Hydroboration-oxidation
Hydrates at the less substituted end of an alkene
Referred to as “anti-Markovnikoff” addition
Markovnikoff’s Rule: “the hydrogen atom is added to the carbon with the greatest number of hydrogen atoms”
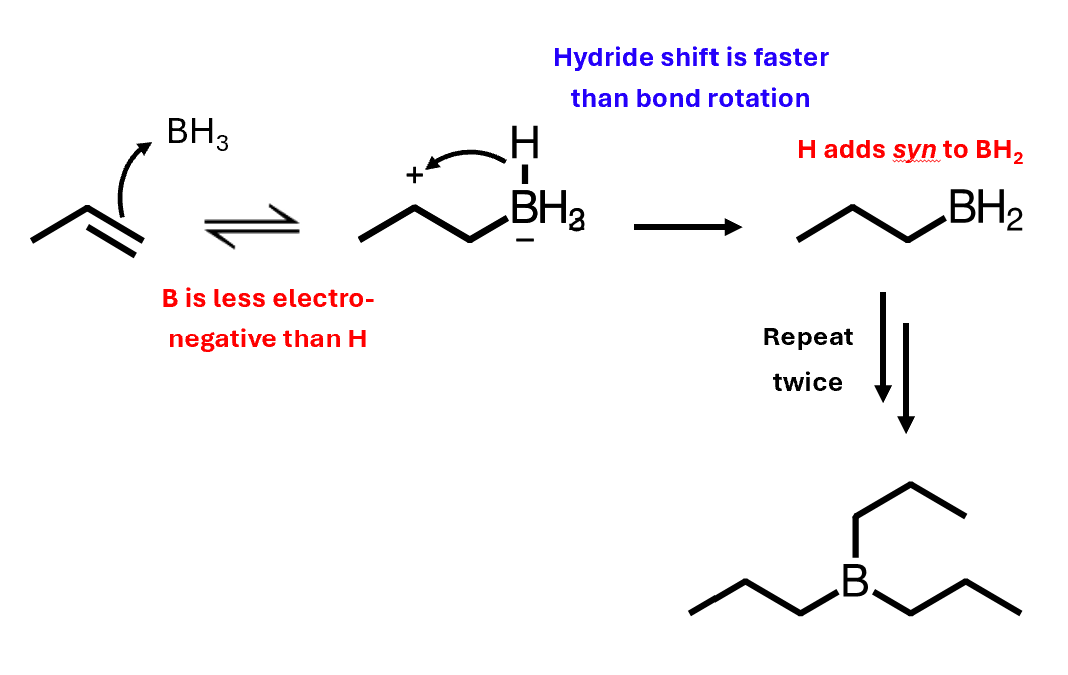
Hydroboration mechanism
Alkene is the nucleophile, borane is the electrophile
Boron is less electronegative than hydrogen, so boron gets attacked first
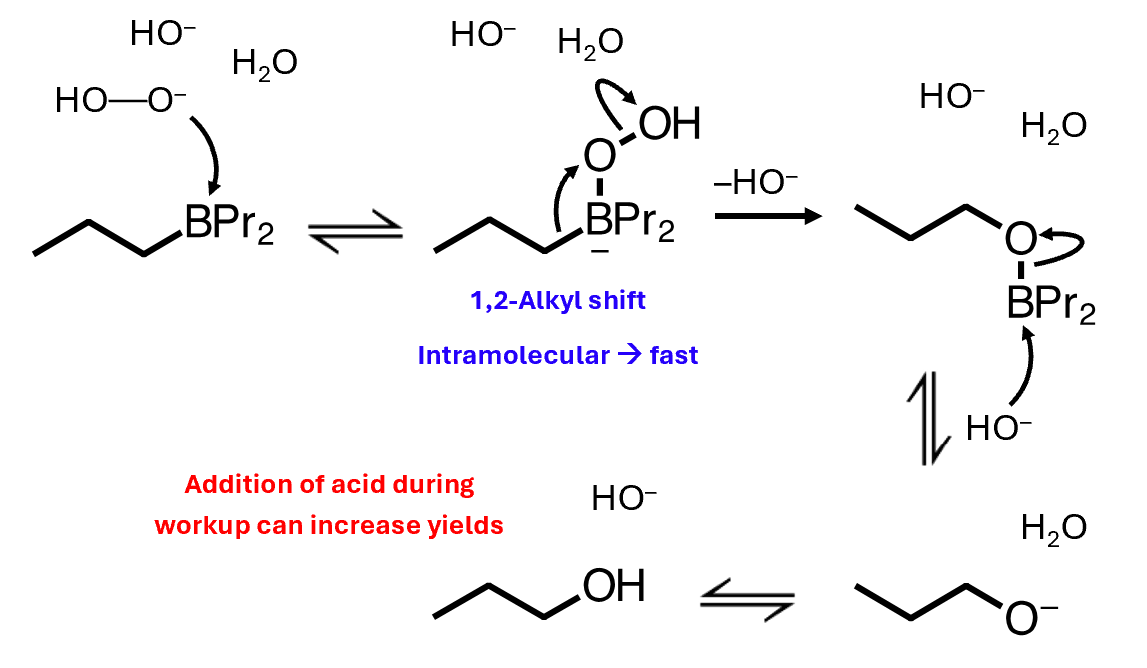
Oxidation mechanism
The oxidation step converts the C–B bonds in the organoborane into C–O bonds through nucleophilic attack by peroxide, an intramolecular 1,2-alkyl shift, and final hydrolysis — giving anti-Markovnikov alcohols efficiently and without rearrangement.