Biochem Test 2
1/209
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapters: 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 33, and some 34-35
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
210 Terms
Serine Proteases
synthesized as zymogens in the pancreas then activated by selective proteolysis
selective proteolysis
activates serine proteases
Digestive serine proteases
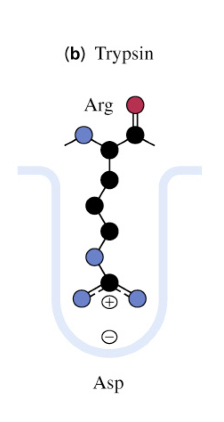
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Elastase
zymogens
inactive enzyme precursers that must be covalently modified to become active
trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, proelastase
zymogens of trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase
enzyme inhibitors
regulates pancreatic zymogens
enzyme cascades
rapid signal amplification
enteropeptidase
activates trypsin
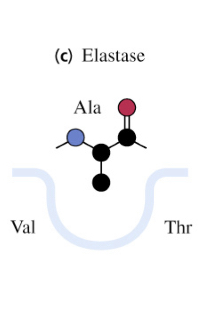
elastase
cleaves on the carbonyl side of AA with small uncharged side chains
structure
dictates function
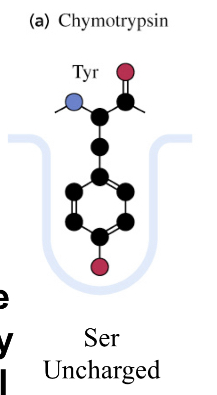
chymotrypsin
active, has a binding pocket
chymotrypsinogen
inactive, AA residues bonded to block the binding pocket, cleavage between residues 13/14, 15/16, and 146/147, opens binding pocket by turning Asp194 outward
Binding site of chymotrypsin
binding site of trypsin
binding site of elastase
binding site
causes substrate specificities due to small structural differences in active site binding cavities
catalytic triad
Asp, His, Ser
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: scissile peptide bond
carbonyl carbon positioned next to the oxygen of Ser-195
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: specificity pocket
binds R1 group holds substrate in place
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: enzyme substrate complex
substrate binding compresses Asp and His
imidazole removes H+ from Ser
nucleophilic O of Ser attacked carbonyl of substrate
first tetrahedral intermediate formed
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: tetrahedral intermediate 1
substrate C-O double bond changes to single bond
negatively charged O moves to oxyanion hole and H-bonds to NH of Gly and Ser
imidazolium of His donates H+ to N of scissile bond yielding cleavage
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: acid-base and covalent catalysis
carbonyl from remaining peptide forms covalent bond with enzyme yielding acyl-enzyme intermediate
peptide product with new amino terminus leave active site
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: hydrolysis
final substrate, H2O enters binding pocket
His abstracts H+ from H2O
Nucleophilic O of OH- reacts with carbonyl of enzyme-acyl intermediate
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: tetrahedral intermediate 2
His imidazolium ion donates H+
formation of second tetrahedral intermediate
stabilized by oxyanion hole
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: product 2
second polypeptide product formed which has new carboxy terminus
a-chymotrypsin mechanism: enzyme and product
final polypeptide product leaves active site
enzyme can now cleave a new polypeptide
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
ionic reaction where both electrons stay with one atom→ ionic intermediate + leaving group
contain a nucleophile and an electrophile
Direct displacement
two molecules react to form a 5 group transition state
formation of tetrahedra intermediate
type of nucleophilic substitution
cleavage reactions (both electrons)
most common, both electrons stay with one atom
ex: formation of carbanion or carbocation
cleavage reactions (one electron)
less common, one electron remains with each product
formation of free radicals
Carbanion
made from cleavage reactions
carbon retains both electrons
carbocation
made from cleavage reactions
carbon looses both electrons
oxidation reduction reactions
addition of O, removal of H, removal of electrons
electrons transferred between two species
oxidizing agent
gains electron (is reduced)
reducing agent
donates electron (is oxidized)
enzymes
lower activation energy of reactions
substrate binding
enzymes position substrates for reaction, formation of transition state more frequent and lowers activation energy
transition state binding
transition state bound more tightly than substrates, lowers activation energy
Binding modes of enzymes
proximity effect and transition state stabilization, increase reaction rate 10,000 to 100,000 fold
proximity effect
collects and positions substrates into active site
reduces their degrees of freedom
results in a large loss of entropy
enhanced concentration of substrates predicts rate acceleration
transition stat stabilization
transition state binds more tightly than substrates
reactions of carboxylates with phenyl esters
increased rates are seen when the reactants are held more rigidly in proximity
thermodynamic pit
formed due to excessive enzyme substrate complex stabilization, little or no catalysis
Km
substrate dissociation constant, indicate weak binding to enzymes
Serine protases active site
Asp-102, His-57, Ser-195 are arrayed in a hydrogen bonded network
cofactors
required by some enzymes for activity
essential ions
type of cofactor, mostly metal ions
coenzymes
type of cofactor, organic compounds, act as group (ex H/ electrons) transfer reagents
Apoenzyme + cofactor → holoenzyme
inactive protein only → activated
metal ions
participate in catalysis, tightly bound, participate in binding of substrate at the active site
metabolic coenzymes
can be synthesized within the body
vitamin derived coenzymes
cannot be synthesized within the body
activator ions
type of essential ion, loosely bound
includes: Ca++, K+, Mg++, Mn++
metal ions of metalloenzymes
type of essential ion, tightly bound
includes: Fe-5 center, zinc, copper, cobalt
cosubstrates
type of coenzyme, loosely bound
includes: ATP, SAM, UDP-sugar, NAD+/NADP+, tetrahydrofolate, CoA, ubiquinone, protien coenzymes
altered during reaction and regenerated by another enzyme
prosthetic groups
type of coenzyme, tightly bound
includes: FMN/FAD, TPP, PLP, biotin, adenosyl / methyl cobalamin, lipoic acid / lipoamide
remain bound to the enzyme during the reaction and may be covalently / tightly bound to enzyme
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
requires 5 coenzymes, in eukaryotes has 102 subunits
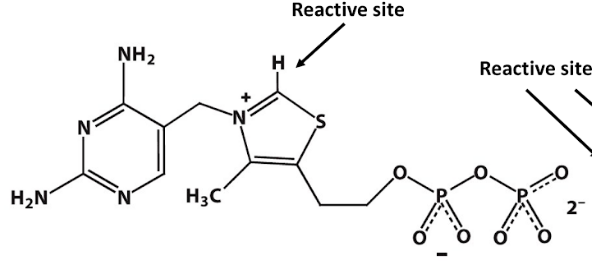
coenzyme: thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Enzyme: pyruvate dehydrogenase
coenzyme: flavin adenine nucleotide (FAD)
Enzyme: mono amine oxidase
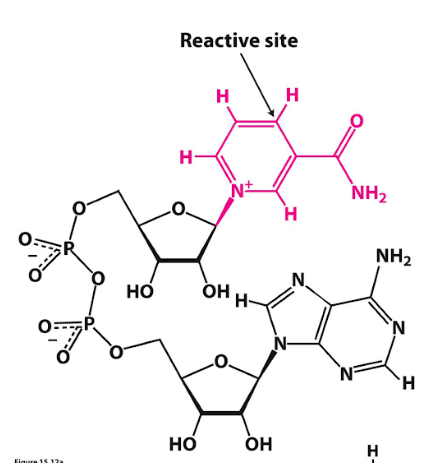
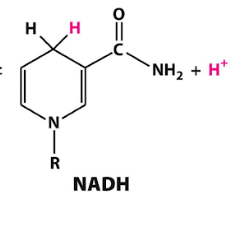
coenzyme: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
Enzyme: lactate dehydrogenase
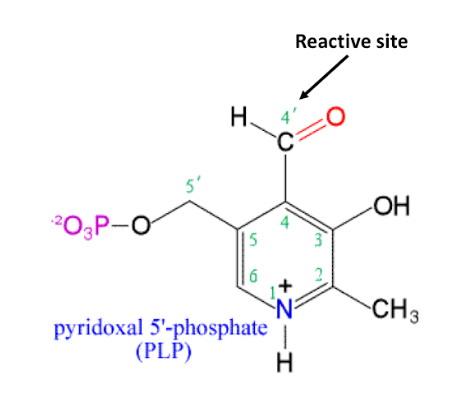
coenzyme: pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
Enzyme: glycogen phosphorylase
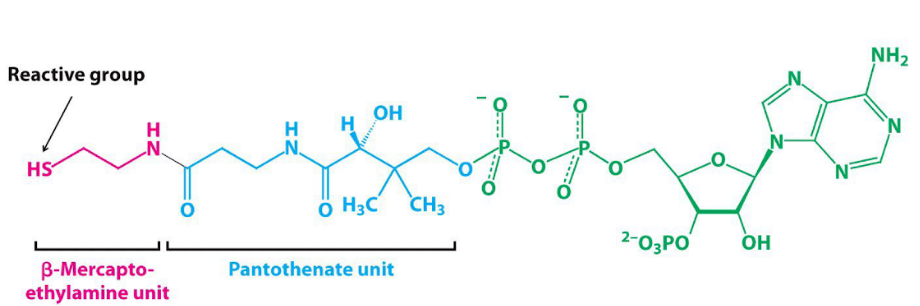
coenzyme: coenzyme A (CoA)
Enzyme: acetyl CoA carboxylase
coenzyme: biotin
Enzyme: pyruvate carboxylase
coenzyme: 6’-deoxyadenosyl cobalamin
Enzyme: methyl malonyl mutase
coenzyme: tetrahydrofolate
Enzyme: thymidylate synthase
metal: Zn2+
Enzyme: carbonic anhydrase
metal: Mg2+
Enzyme: EcoRV
metal: Ni2+
Enzyme: urease
metal: Mo
Enzyme: nitrogenase
metal: Se
Enzyme: glutathione peroxidase
metal: Mn2+/3+
Enzyme: superoxide dismutase
metal: K+
Enzyme: acetoacyl CoA thiolase
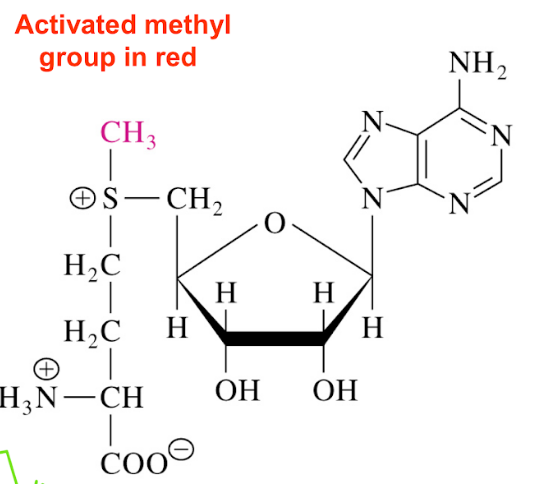
SAM (s-adenosylmethionine)
donor of methyl groups for most biosynthetic reactions (ex synthesis of hormone epinephrine from norepinephrine)
Vitamins
organic substance required in trace amounts for a number of essential biochemical reactions
cannot be made by an organism instead obtained from nutrients
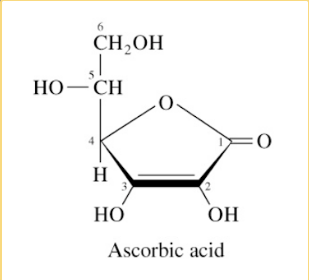
vitamin: ascorbate (C)
disease: scurvy
vitamin: nicotinic acid (B3)
disease: pellagra
vitamin: riboflavin (B2)
disease: growth retardation
vitamin: pantothenate (B5)
disease: dermatitis in chickens
vitamin: thiamine (B1)
disease: beriberi
vitamin: pyridoxal (B6)
disease: dermatitis in rats
vitamin: biotin
disease: dermatitis in humans
vitamin: folate
disease: anemia, spina bifida
vitamin: cobalamin (B12)
disease: pernicious anemia
vitamin c
not coenzyme, reducing reagent for hydroxylation of collagen
thiamine (B1)
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
typical reaction type: aldehyde transfer
riboflavin (B2)
flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
typical reaction type: oxidation-reduction
pyridoxine (B6)
pyridoxal phosphate
typical reaction type: group transfer to or from amino acids
nicotinic acid (niacin B3)
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
typical reaction type: oxidation-reduction
pantothenic acid (B5)
coenzyme A
typical reaction type: acyl-group transfer
biotin (B7)
biotin-lysine adducts (biocytin)
typical reaction type: ATP-dependent carboxylation and carboxyl-group transfer
Folic acid (B9)
tetrahydrofolate
typical reaction type: transfer of one-carbon components; thymine synthesis
cobalamin (B12)
5’-deoxyadenosyl cobalamin
typical reaction type: transfer of methyl groups; intramolecular rearrangements
NAD+
NADH
FAD
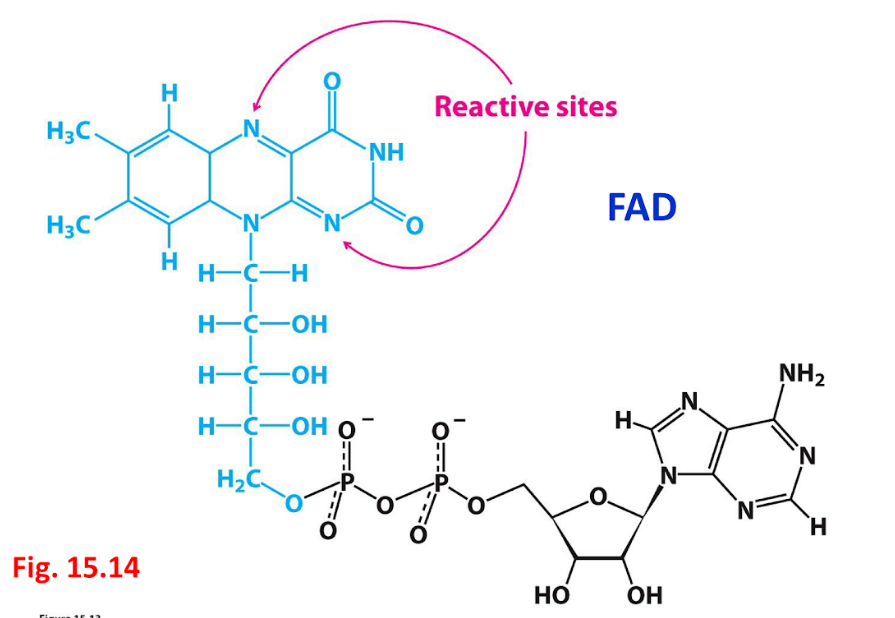
FADH2
CoA
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
pyridoxal phosphate